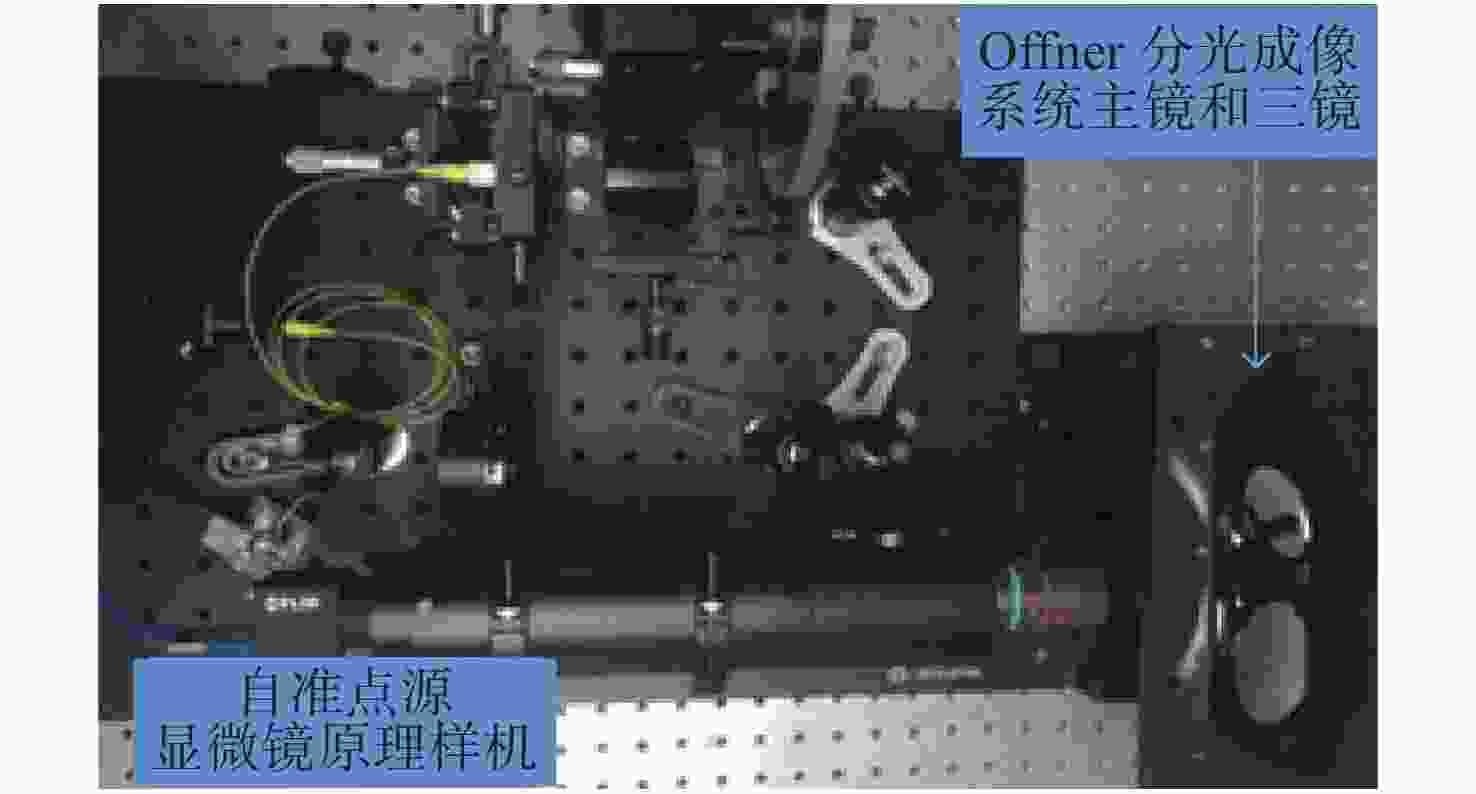
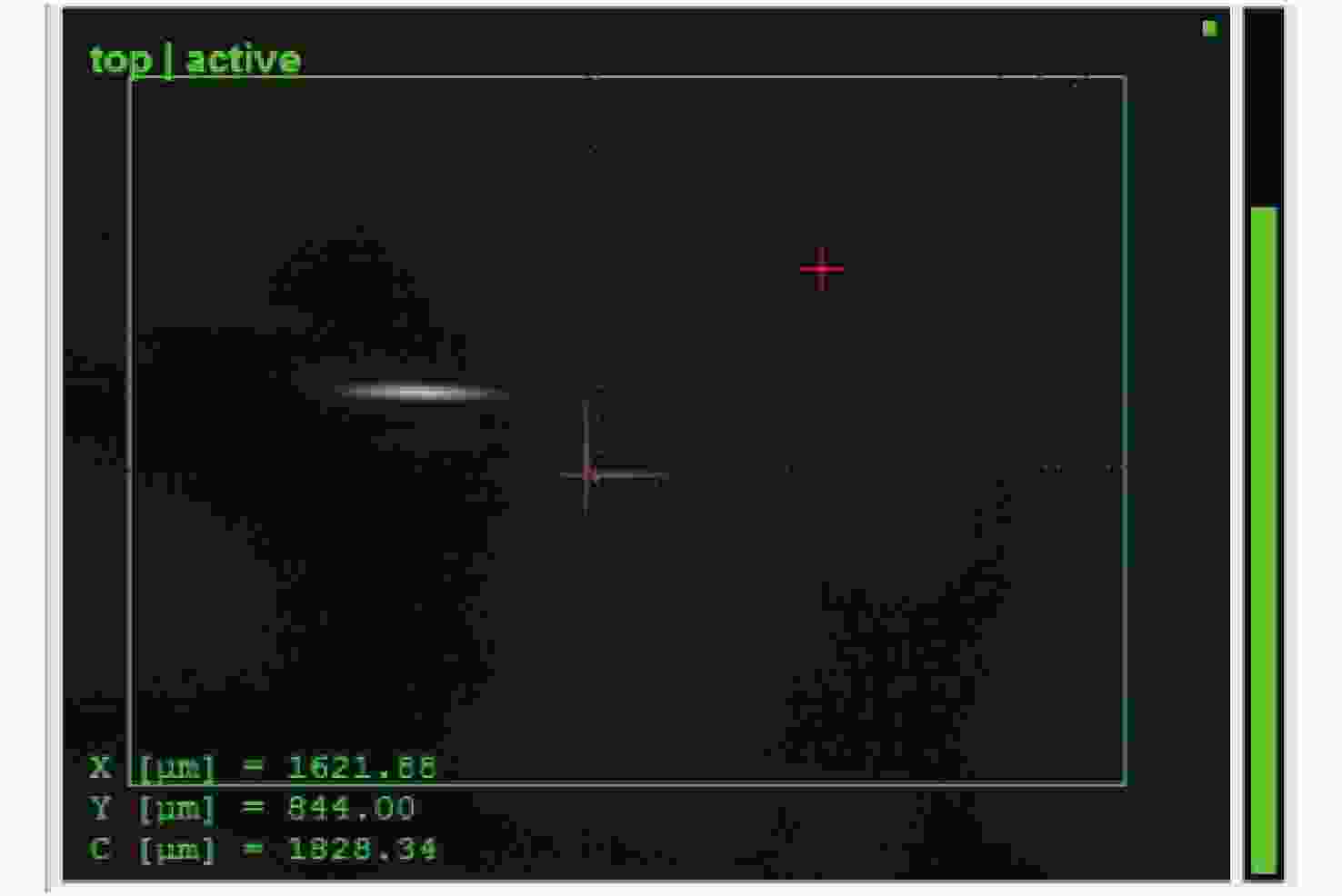
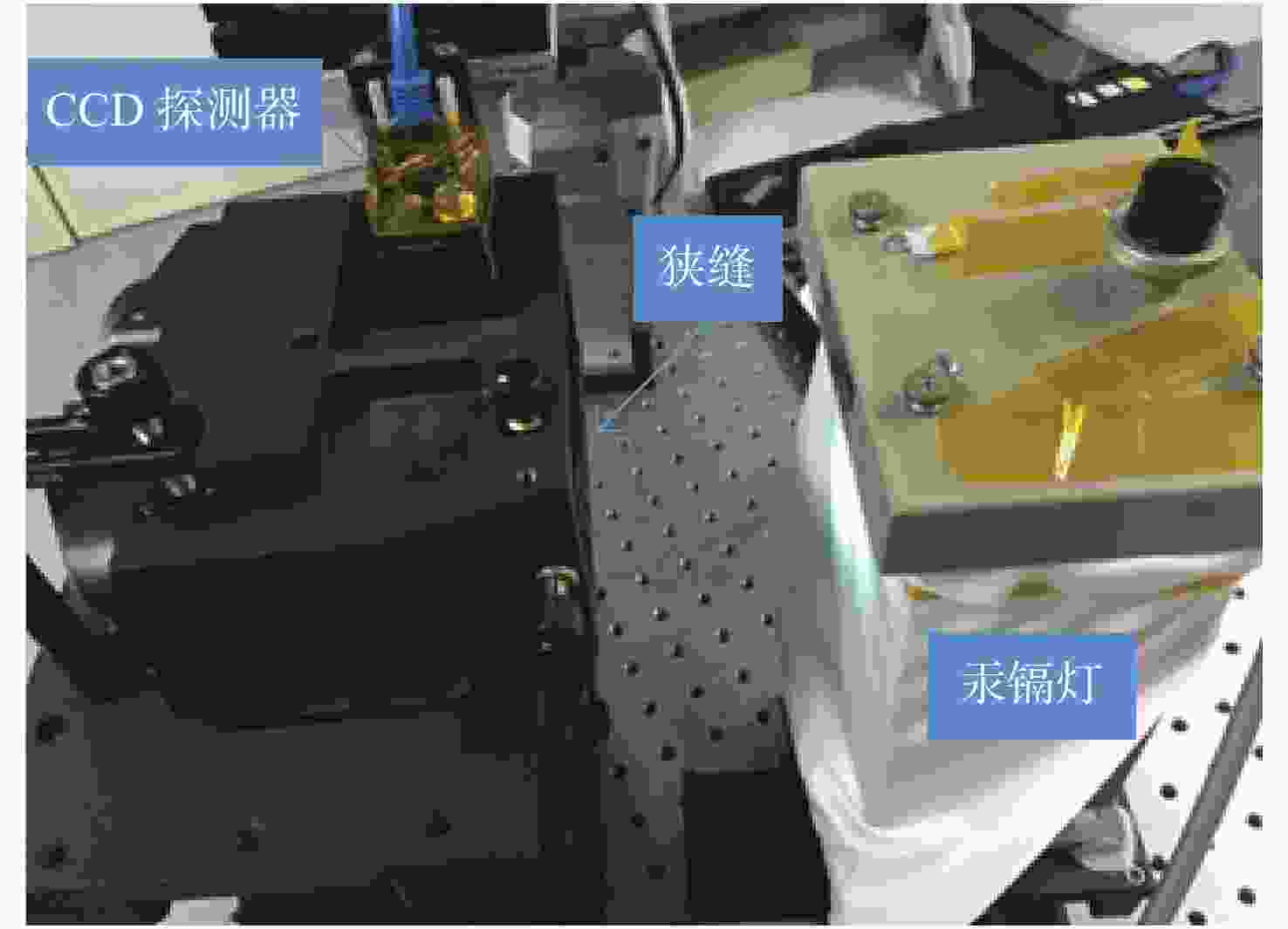
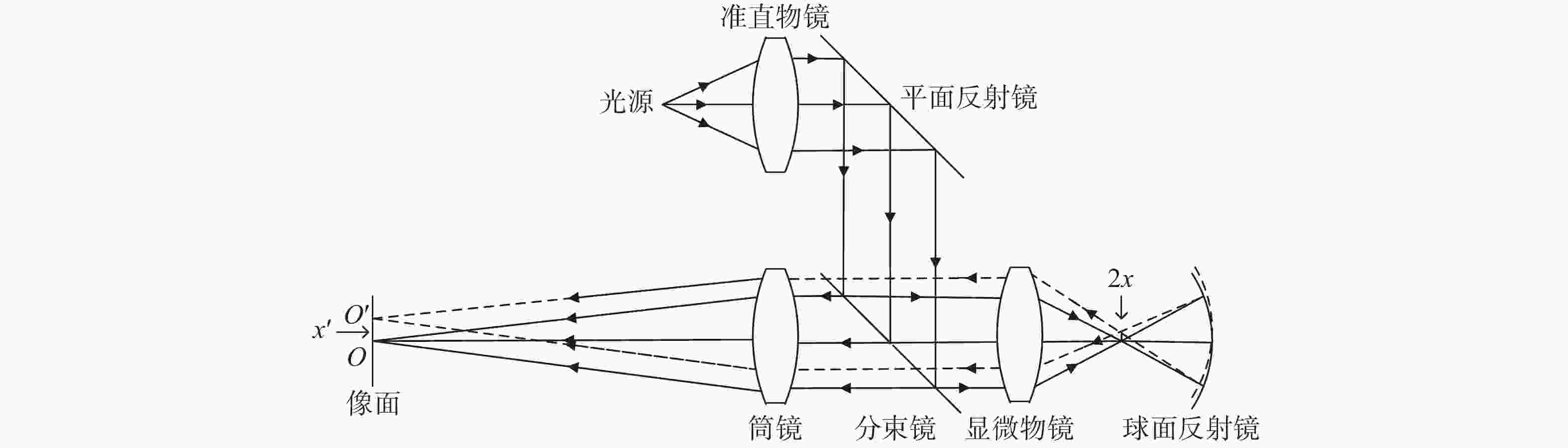
Fast alignment of an offner imaging spectrometer using a spherical autostigmatic method
-
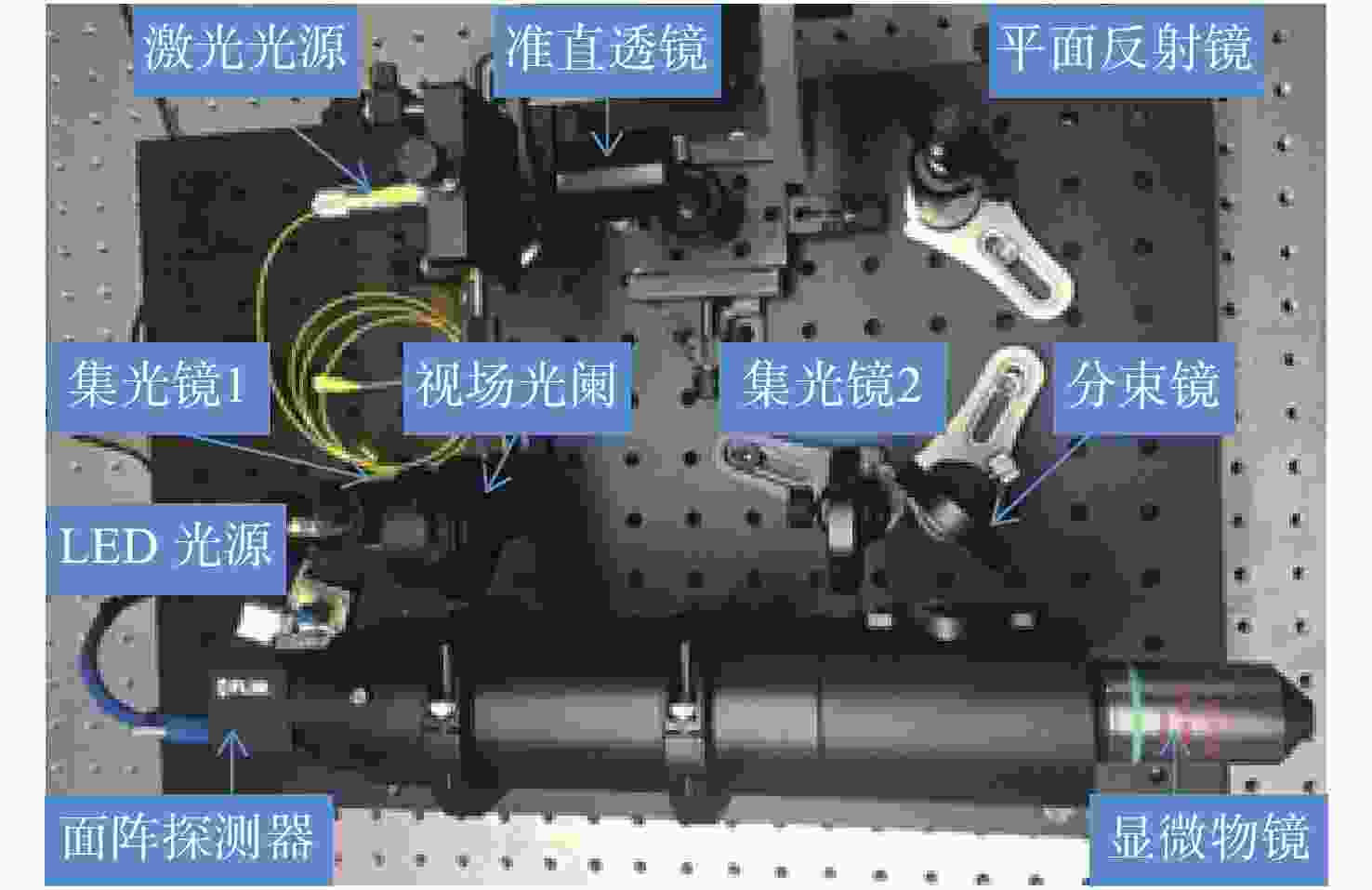
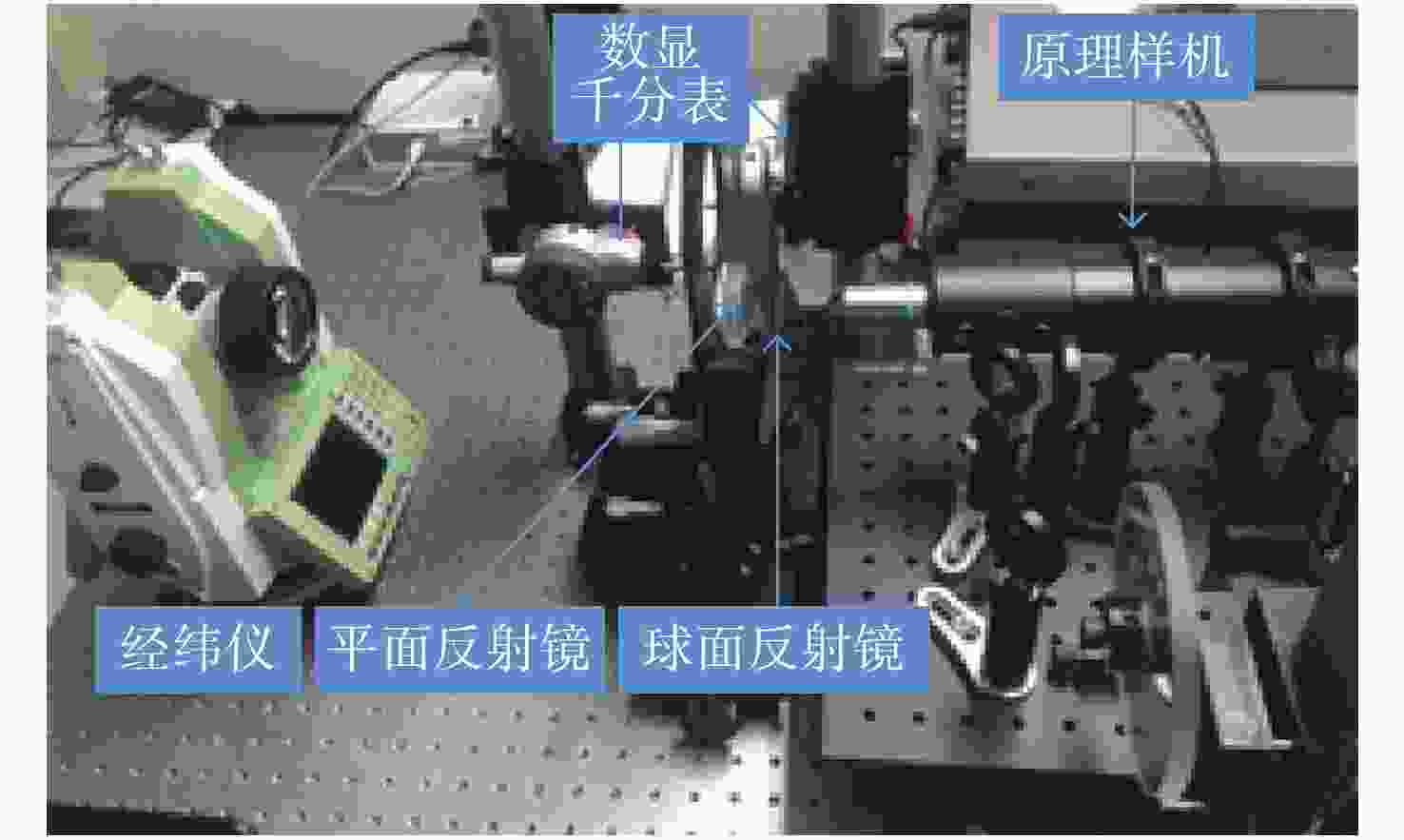
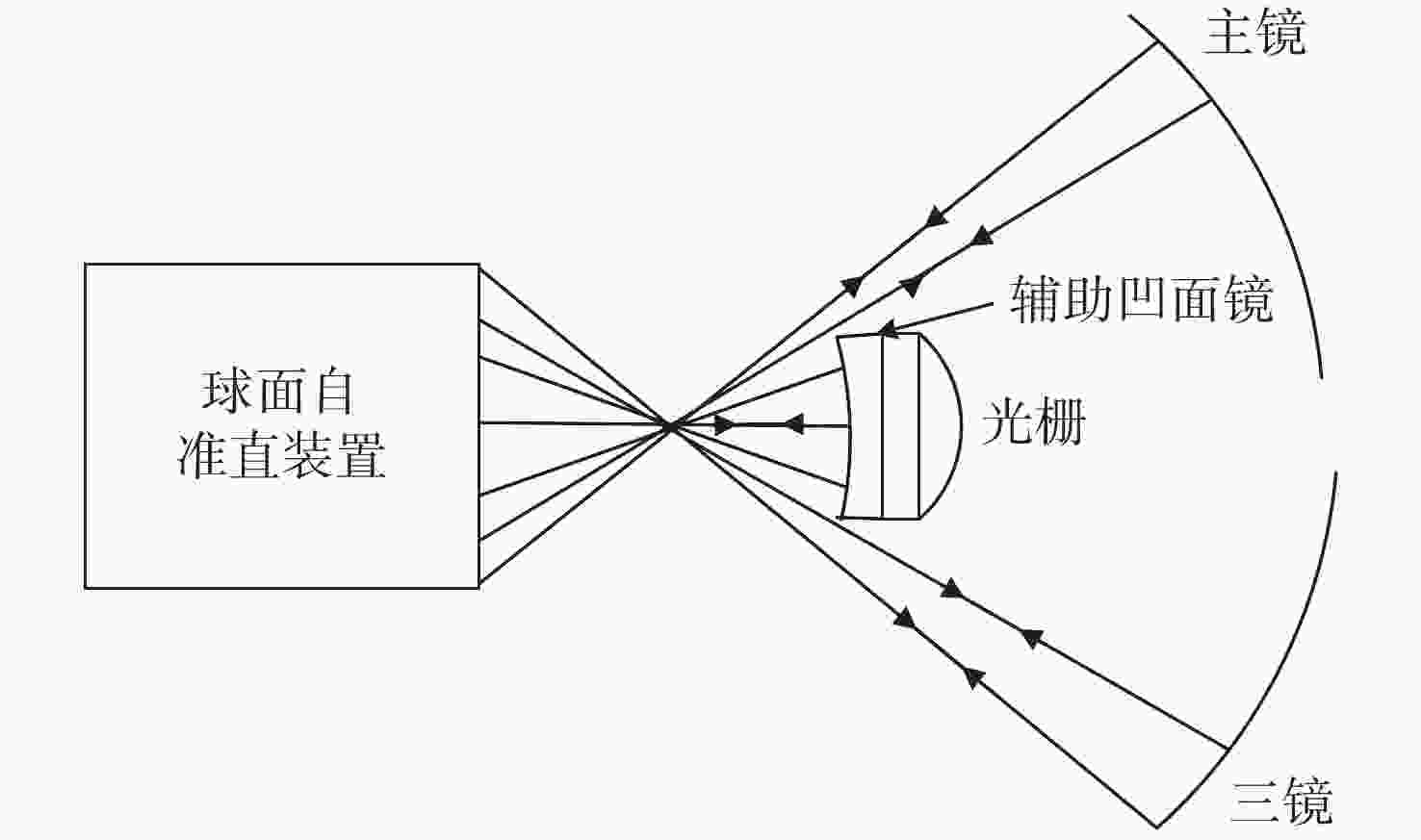
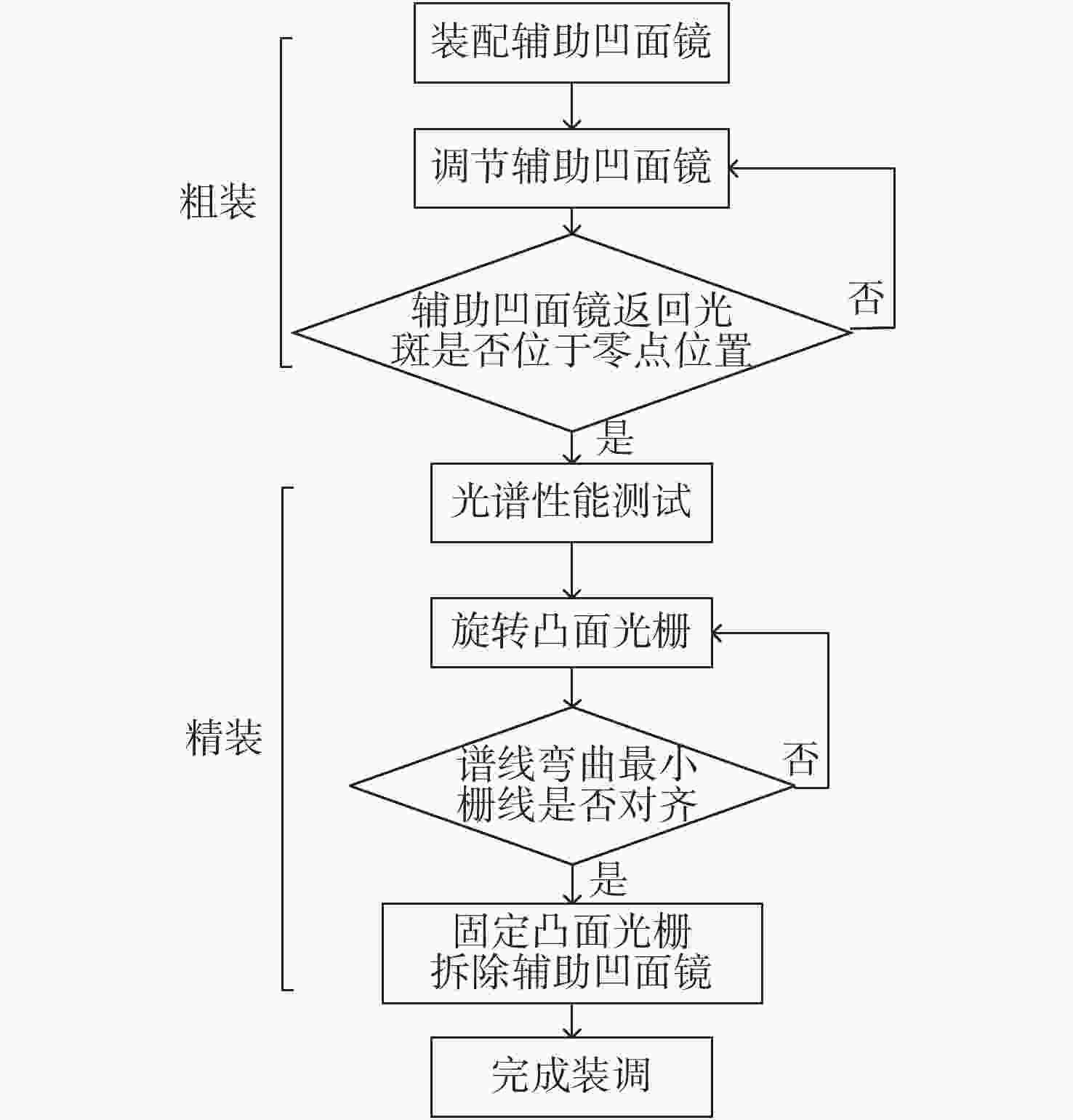
摘要: Offner分光成像系统由凸面光栅和两个凹面反射镜组成。光学结构上同心的特点使其具有相对孔径大、畸变小、结构紧凑等优点。为了降低Offner分光成像系统的装调难度,提高装调效率,本文基于同心特点和球面自准直原理,研究了Offner分光成像系统的快速装调方法。首先搭建球面自准直装置,当该装置生成的点光源位于球面反射镜曲率中心处时,其反射像点和点光源重合。通过检测反射像点和点光源之间的位置偏差,可判定球面反射镜曲率中心位置的偏离程度。利用该装置定位主镜、凸面光栅和三镜的曲率中心位置,完成Offner分光成像系统的装调。实验结果表明,两块离轴凹面反射镜的曲率中心间距误差可控制在10 μm以内,装调完成的分光成像系统成像性能较好,满足指标要求。与现有装调方法相比,该方法具有易于对准、装调速度快、所需设备成本低等优点。
-
关键词:
- Offner分光成像系统 /
- 同心特性 /
- 球面自准直 /
- 快速装调
Abstract: Offner imaging spectrometers consist of a convex grating and two concave mirrors. The concentric characteristics of the optical structure allow it to have a large relative aperture, small distortion and a compact structure. In order to reduce the difficulty of aligning an Offner imaging spectrometer and improve its efficiency, this paper presents a fast alignment method for Offner imaging spectrometers based on the concentric characteristic and spherical autostigmatic method. Firstly, a spherical autostigmatic device is built, which can generate a point source. When the point source is located at the spherical mirror’s center of curvature (CoC), its reflection image point and the point source coincide. By measuring the distance between the reflection image point and the point source, the positional deviation of the spherical mirror’s CoC can be determined. The Offner imaging spectrometer is completed by locating the CoC of its primary mirror, convex grating and tertiary mirror. The results show that the location error of the two off-axis concave mirrors’ CoC can be controlled within 10 μm, and our imaging performance requirements for the imaging spectral system are satisfied. Compared with pre-existing methods, this method is easier to operate, lower in cost and has faster alignment capabilities. -
表 1 对心分辨率测量数据
Table 1. Alignment resolution measurement data
$x$/μm ${x_i}$ $x'$/μm $\delta $/μm 0 926.497 0.0 0.0 12 792.524 11.6 −0.4 21 682.097 21.1 0.1 31 568.828 30.8 −0.2 40 457.068 40.5 0.5 52 322.229 52.1 0.1 60 220.331 60.9 0.9 最大误差0.9 μm 标准差0.4 μm 表 2 Offner分光成像系统指标要求
Table 2. System specifications of Offner imaging spectrometer
指标 要求 色散范围 6.6 mm 光谱分辨率 2 nm 谱线弯曲 <2%像元 色畸变 <2%像元 MTF ≥0.73 表 3 Offner分光成像系统装调公差分配结果
Table 3. Assembly adjustment tolerance distribution results of Offner imaging spectroscopy system
公差类型 狭缝 主镜 光栅 三镜 窗口 装调公差 倾斜/arc min X 1 基准 1 0.3 1 Y 1 基准 1 0.3 1 Z 1 基准 — — — 偏心/mm X 0.02 基准 0.02 0.01 — Y 0.02 基准 0.02 0.01 — 轴向位置/mm 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.155 表 4 Offner分光成像系统性能测试结果
Table 4. Performance test results of Offner imaging spectrometer system
测试次数 平均光谱分辨率/nm 谱线弯曲/pixel 色畸变/pixel 1 1.86 0.60% ±0.92% 2 1.91 1.25% ±1.82% 3 1.90 1.38% ±0.81% 平均 1.89 1.08% ±1.18% -
[1] OFFNER A. New concepts in projection mask aligners[J]. Optical Engineering, 1975, 14(2): 142130. [2] MERTZ L. Concentric spectrographs[J]. Applied Optics, 1977, 16(12): 3122-3124. doi: 10.1364/AO.16.003122 [3] KWO D, LAWRENCE G, CHRISP M. Design of a grating spectrometer from a 1:1 Offner mirror system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1987, 818: 275-279. doi: 10.1117/12.978898 [4] REININGER F M, DAMI M, PAOLINETTI R, et al. Visible infrared mapping spectrometer-visible channel (VIMS-V)[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1994, 2198: 239-250. doi: 10.1117/12.176753 [5] PEARLMAN J, CARMAN S, SEGAL C, et al. . Overview of the hyperion imaging spectrometer for the NASA EO-1 mission[C]. Proceedings of IGARSS 2001. Scanning the Present and Resolving the Future. Proceedings. IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IEEE, 2001: 3036-3038. . [6] MURCHIE S, ARVIDSON R, BEISSER K, et al. Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112(E5): E05S03. [7] 刘玉娟. 基于同心光学系统的新型成像光谱仪研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院研究生院(长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2012.LIU Y J. The study on newly imaging spectrometers based on concentric optics[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2012. (in Chinese). [8] 赵美红, 李文昊, 巴音贺希格, 等. Offner成像光谱仪的消像差技术[J]. 光学 精密工程,2017,25(12):3001-3011. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172512.3001ZHAO M H, LI W H, BAYANHESHIG, et al. Aberration correction technique of Offner imaging spectrometer[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(12): 3001-3011. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172512.3001 [9] 张浩, 方伟, 叶新, 等. 中/长波红外双衍射级次共路Offner成像光谱仪[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(4):965-974. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152304.0965ZHANG H, FANG W, YE X, et al. Dual-order overlapped Offner imaging spectrometer in middle-and long-wave infrared regions[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(4): 965-974. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152304.0965 [10] 刘玉娟, 崔继承, 巴音贺希格, 等. 凸面光栅成像光谱仪的研制与应用[J]. 光学 精密工程,2012,20(1):52-57. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20122001.0052LI Y J, CUI J CH, BAYANHESHIG, et al. Design and application of imaging spectrometer with convex grating[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2012, 20(1): 52-57. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20122001.0052 [11] ZHU J CH, SHEN W M. Analytical design of athermal ultra-compact concentric catadioptric imaging spectrometer[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(21): 31094-31109. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.031094 [12] MOUROULIS P, GREEN R O. Review of high fidelity imaging spectrometer design for remote sensing[J]. Optical Engineering, 2018, 57(4): 040901. [13] MOUROULIS P Z, MCKERNS M M. Pushbroom imaging spectrometer with high spectroscopic data fidelity: experimental demonstration[J]. Optical Engineering, 2000, 39(3): 808. doi: 10.1117/1.602431 [14] 刘玉娟, 巴音贺希格, 崔继承, 等. 凸面光栅成像光谱仪的干涉法装调[J]. 光学 精密工程,2011,19(8):1736-1742. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20111908.1736LI Y J, BAYANHESHIG, CUI J CH, et al. Interferometric alignment of imaging spectrometers with convex gratings[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2011, 19(8): 1736-1742. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20111908.1736 [15] STEEL W H. The autostigmatic microscope[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 1983, 4(4): 217-227. doi: 10.1016/0143-8166(83)90015-5 [16] PARKS R E. Autostigmatic microscope and how it works[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(6): 1436-1438. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.001436 [17] PARKS R E, KUHN W P. Optical alignment using the point source microscope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5877: 102-116. -





 下载:
下载: