Speckle noise reduction in swept-source optical coherence tomography by retinal image registration
-
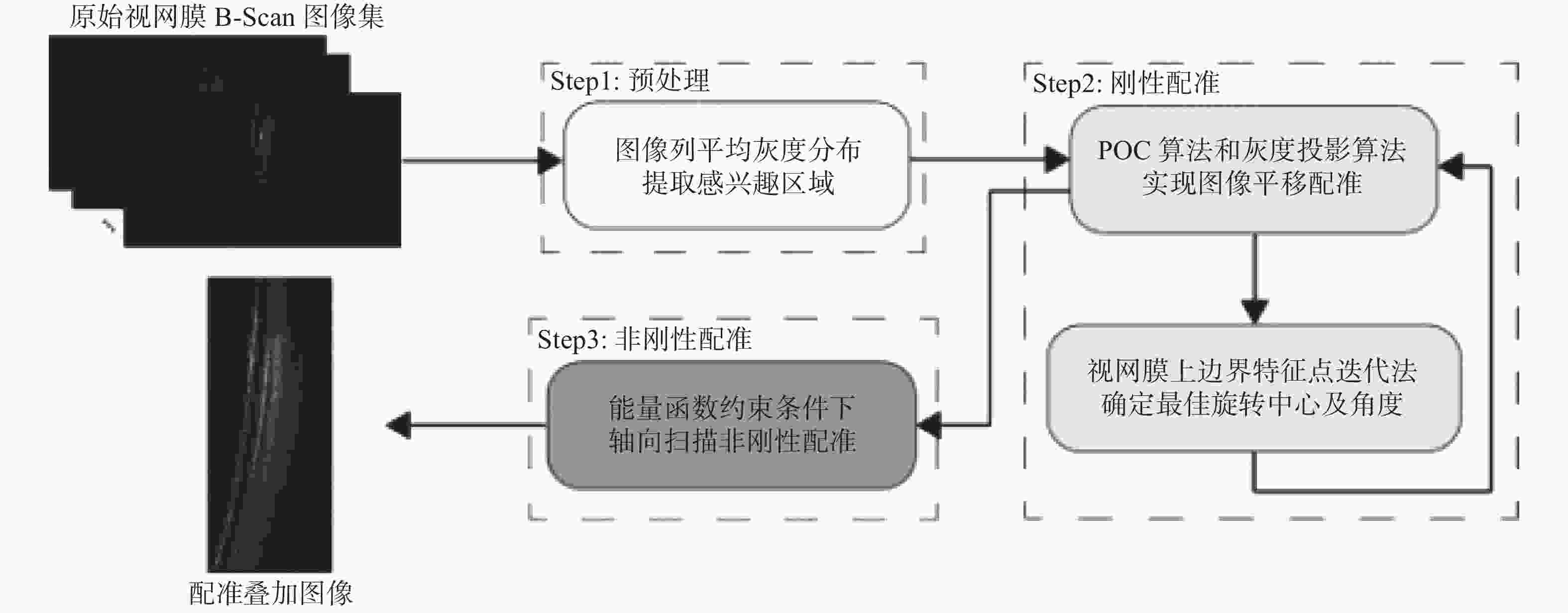
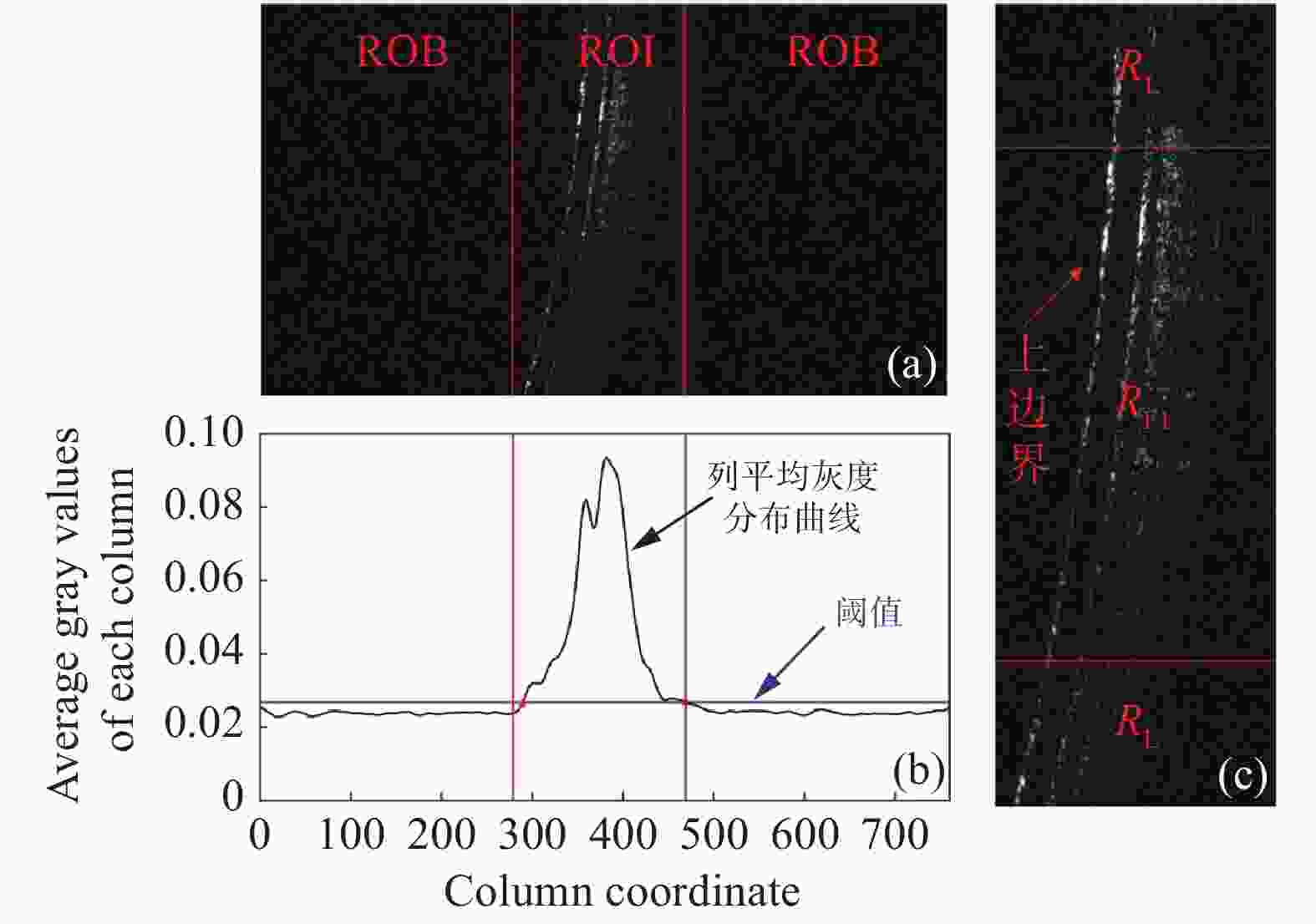
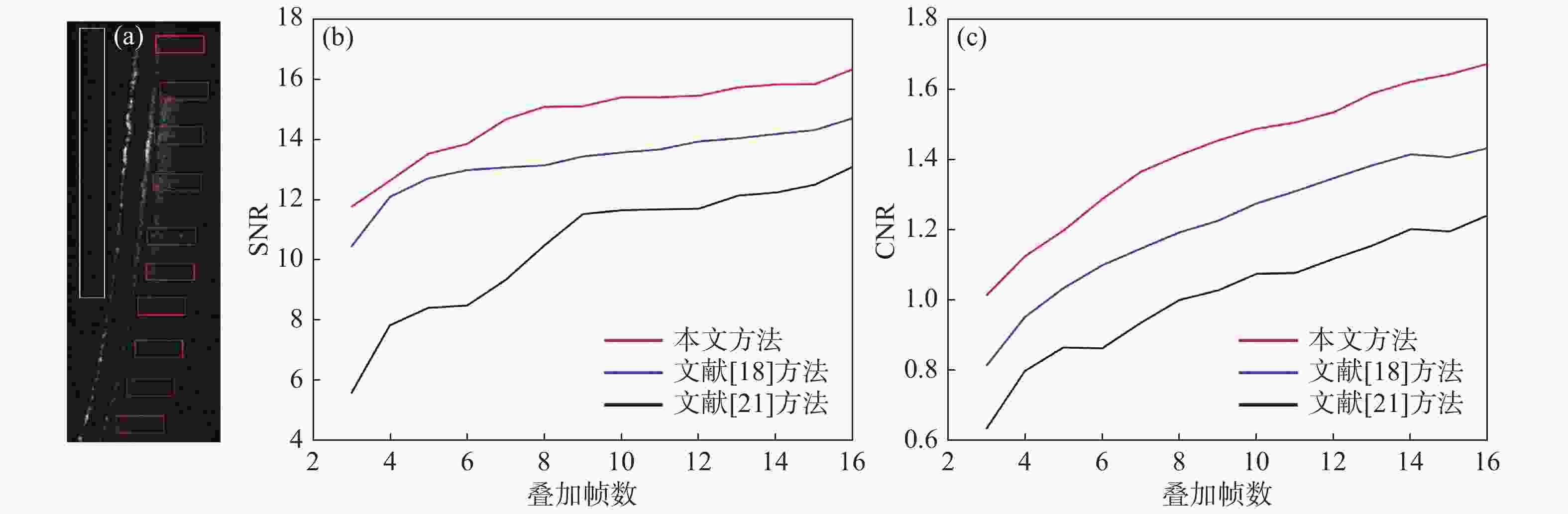
摘要: 多帧叠加平均处理是去除扫频光学相干层析系统散斑噪声、获得较为清晰结构信息的有效方法,但眼睛的震颤、漂移、微眼跳等生理特性和系统光路特性会使图像之间存在错位,导致叠加效果不佳、结构稳定性差,为此本文提出一种基于灰度分布信息和目标几何信息相结合的配准算法。该方法根据图像平均灰度分布提取包含目标信息的感兴趣区域,通过相位相关算法和基于分段拟合的灰度投影算法的双重作用校正图像的平移变换;通过拟合视网膜上边界作为特征点迭代确定最佳旋转参数,并再次重新估计平移参数,实现图像的刚性配准;最后通过轴向扫描一对一映射法以能量函数为约束条件实现图像的非刚性配准。对活体兔眼进行实验,结果表明,本文算法配准后的叠加图像边界清晰,结构信息增强,信噪比和对比度平均有效提高一倍多。本算法适用于强噪声视网膜B-Scans图像的配准,能满足多种类型OCT系统的叠加成像需要,具有较高的鲁棒性和图像配准精度。Abstract: The averaging of multiple B-Scans is an effective method of reducing speckle noise in Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography (SS-OCT) and obtaining clear structural information. However, physiological characteristics such as eye tremor, drift, micro-saccade, and the optical structure of an SS-OCT system cause geometric transformation between images, resulting in poor multi-frame averaging. In this paper, we propose a registration algorithm based on the combination of gray distribution information and target geometric information. This method extracts the region of interest containing target information using the average gray distribution of an image, and corrects the transformation of the image with the collective effect of the phase correlation algorithm and the gray projection algorithm based on the fitting of the curve of its segments. Then, the process is repeated with the upper boundary of the retinal image fitted as the feature points to determine the optimal rotation parameters. The translation parameters are re-estimated again to achieve the rigid registration of the image. Finally, a one-to-one mapping method of axial scanning is used to achieve the non-rigid registration of the image with the energy function as the constraint. Experiments on live rabbit eyes show that the averaged image has clear boundaries, enhanced structural information, and its signal-to-noise and contrast-to-noise ratios are more than doubled their previous values on average. The algorithm is suitable for the registration of B-Scan images with strong speckle noise and can meet the averaging needs of many types of OCT systems. It has high robustness and image registration accuracy.
-
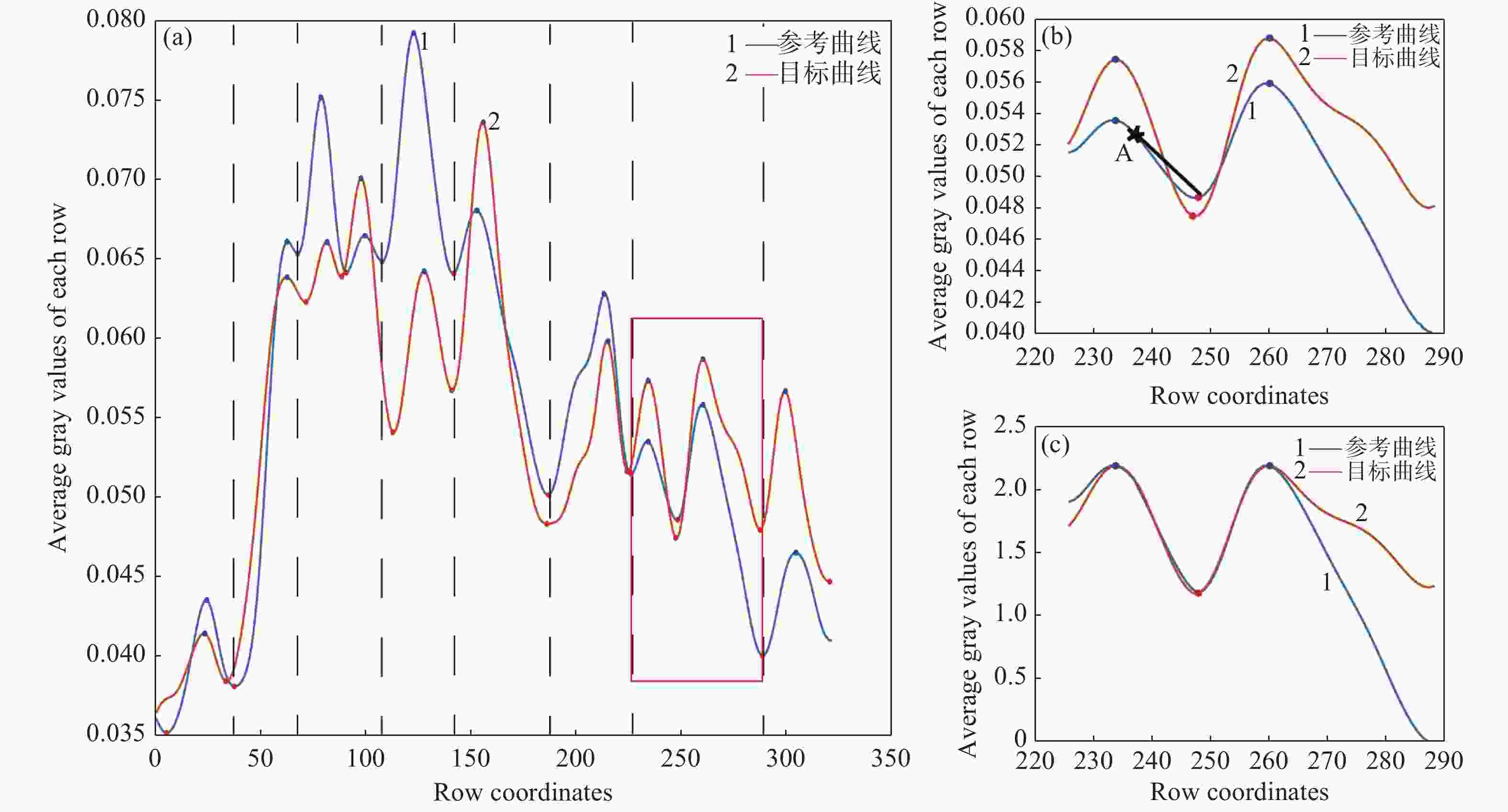
图 4 分段拟合处理过程。(a)曲线分割结果(黑色虚线为分割线);(b)原始曲线段(最佳连接点A、黑色直线为包络线);(c)处理后的曲线段
Figure 4. Fitting process of curve segments. (a) Results of curve segmentation (the dotted black line is the segmentation line); (b) original curve segment results (optimal connection point A, the straight black line is the envelope); (c) curve segment after processing
图 5 刚性配准结果。(a)上边界提取过程;(b)平移配准后的叠加图;(c)旋转配准后的叠加图(绿色为参考图像,紫色为目标图像)
Figure 5. Results of rigid registration. (a) Upper boundary extraction process; (b) averaging image after translation registration; (c) averaging image after rotation registration. (Green is the reference image, purple is the target image)
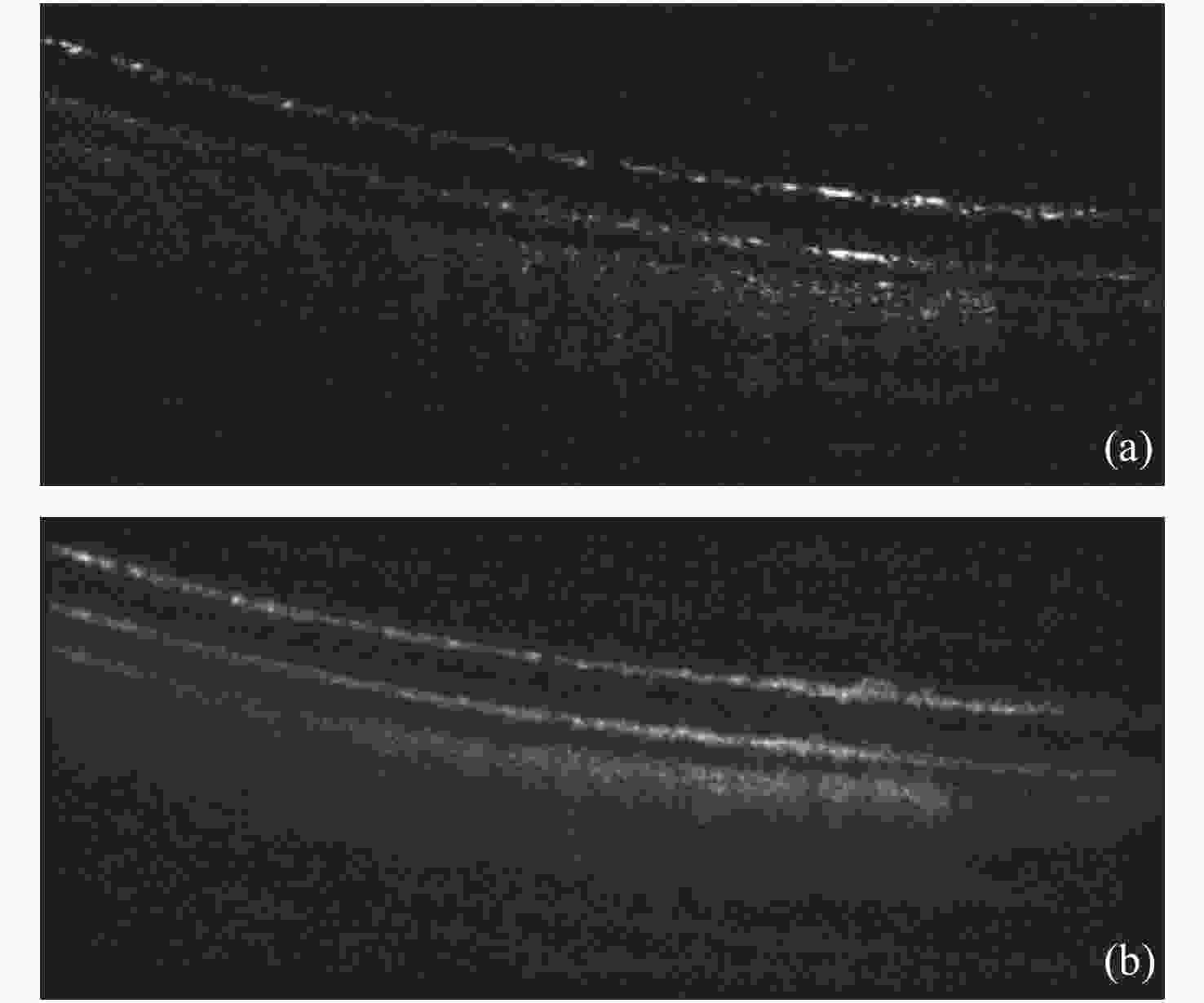
图 6 非刚性配准结果。(a)刚性配准后的叠加图及局部放大图;(b)非刚性配准后的叠加图及局部放大图(绿色为参考图像,紫色为目标图像)
Figure 6. Results of non-rigid registration. (a) Average image obtained after rigid registration; (b) average image obtained after non-rigid registration (The red dashed box represents an enlarged partial view; Green is the reference image, and purple is the target image)
表 1 本文配准算法较对比算法的提升效果
Table 1. Improvement performance of proposed algorithm comparing with other algorithms
-
[1] SAHYOUN C C, SUBHASH H M, PERU D, et al. An experimental review of optical coherence tomography systems for noninvasive assessment of hard dental tissues[J]. Caries Research, 2019, 54(1): 43-54. [2] PASAOGLU I, SATANA B, ALTAN C, et al. Lamina cribrosa surface position in idiopathic intracranial hypertension with swept-source optical coherence tomography[J]. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology, 2019, 67(7): 1085-1088. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1736_18 [3] PARK J H, YOO C, JUNG J H, et al. The association between prelaminar tissue thickness and peripapillary choroidal thickness in untreated normal-tension glaucoma patients[J]. Medicine, 2019, 98(1): e14044. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014044 [4] 汪毅, 刘珊珊, 张玮茜, 等. 扫频光学相干层析角膜图像轮廓自动提取算法[J]. 物理学报,2019,68(20):204201. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20190731WANG Y, LIU SH SH, ZHANG W Q, et al. Automatic contour extraction algorithm for swept-source optical coherence tomography cornea image[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(20): 204201. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20190731 [5] VIRA J, MARCHESE A, SINGH R B, et al. Swept-source optical coherence tomography imaging of the retinochoroid and beyond[J]. Expert Review of Medical Devices, 2020, 17(5): 413-426. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2020.1755256 [6] LOU SH L, CHEN X D, HAN X Y, et al. Fast retinal segmentation based on the wave algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 53678-53686. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2981206 [7] SCHMITT J M, XIANG S H, YUNG K M, et al. Speckle in optical coherence tomography[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 1999, 4(1): 95-105. doi: 10.1117/1.429925 [8] 蔡怀宇, 张玮茜, 陈晓冬, 等. 眼科光学相干层析成像的图像处理方法[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(4):731-740. doi: 10.3788/co.20191204.0731CAI H Y, ZHANG W Q, CHEN X D, et al. Image processing method for ophthalmic optical coherence tomography[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(4): 731-740. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191204.0731 [9] JORGENSEN T M, THOMADSEN J, CHRISTENSEN U, et al. Enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio in ophthalmic optical coherence tomography by image registration—method and clinical examples[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2007, 12(4): 041208. doi: 10.1117/1.2772879 [10] SZKULMOWSKI M, WOJTKOWSKI M. Averaging techniques for OCT imaging[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(8): 9757-9773. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.009757 [11] MARTINEZ-CONDE S, MACKNIK S L, HUBEL D H. The role of Fixational eye movements in visual perception[J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2004, 5(3): 229-240. doi: 10.1038/nrn1348 [12] KLEIN T, HUBER R. High-speed OCT light sources and systems [Invited][J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2017, 8(2): 828-859. doi: 10.1364/BOE.8.000828 [13] 余轮, 魏丽芳. 眼底图像配准技术研究进展[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志,2011,28(5):1043-1047.YU L, WEI L F. Progress of research in retinal image registration[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 28(5): 1043-1047. (in Chinese) [14] NIEMEIJER M, GARVIN M K, LEE K, et al. Registration of 3D spectral OCT volumes using 3D SIFT feature point matching[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2009, 7259: 72591I. [15] NIEMEIJER M, LEE K, GARVIN M K, et al. Registration of 3D spectral OCT volumes combining ICP with a graph-based approach[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8314: 83141A. [16] CHEN M, LANG A, YING H S, et al. Analysis of macular OCT images using deformable registration[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2014, 5(7): 2196-2214. doi: 10.1364/BOE.5.002196 [17] KHANSARI M M, ZHANG J, QIAO Y CH, et al. Automated deformation-based analysis of 3D optical coherence tomography in diabetic retinopathy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(1): 236-245. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2924452 [18] CHENG J, DUAN L X, WONG D W K, et al.. Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by image registration and matrix completion[C]. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Springer, 2014: 162-169. [19] LEE S, LEBED E, SARUNIC M V, et al. Exact surface registration of retinal surfaces from 3-D optical coherence tomography images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2015, 62(2): 609-617. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2014.2361778 [20] LEZAMA J, MUKHERJEE D, MCNABB R P, et al. Segmentation guided registration of wide field-of-view retinal optical coherence tomography volumes[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2016, 7(12): 4827-4846. doi: 10.1364/BOE.7.004827 [21] DU X Y, GONG L, SHI F, et al.. Non-rigid Registration of Retinal OCT Images Using Conditional Correlation Ratio[M]. CARDOSO M J, ARBEL T, MELBOURNE A, et al.. Fetal, Infant and Ophthalmic Medical Image Analysis. Cham: Springer, 2017: 159-167. [22] OJANSIVU V, HEIKKILA J. Image registration using blur-invariant phase correlation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2007, 14(7): 449-452. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2006.891338 [23] 孙辉, 马天玮. 基于相位相关的目标图像亚像元运动参数估计[J]. 液晶与显示,2011,26(6):858-862. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20112606.0858SUN H, MA T W. Sub-pixel motion estimation based on phase-only correlation[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2011, 26(6): 858-862. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20112606.0858 [24] 万钇良, 王建立, 张楠, 等. 一种基于相位相关与子图像的偏振图像配准方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(5):530-536. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193405.0530WAN Y L, WANG J L, ZHANG N, et al. Polarized image registration method based on phase correlation and sub-graph[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(5): 530-536. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193405.0530 [25] PERONA P, MALIK J. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1990, 12(7): 629-639. doi: 10.1109/34.56205 [26] 王亚强, 陈波. 一种改进的各向异性扩散超声图像去噪算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2015,30(2):310-316. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153002.0310WANG Y Q, CHEN B. Improved anisotropic diffusion ultrasound image denoising algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2015, 30(2): 310-316. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153002.0310 [27] PUVANATHASAN P, BIZHEVA K. Interval type-II fuzzy anisotropic diffusion algorithm for speckle noise reduction in optical coherence tomography images[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(2): 733-746. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.000733 -






 下载:
下载: