A fast blind denoising method for grating image
-
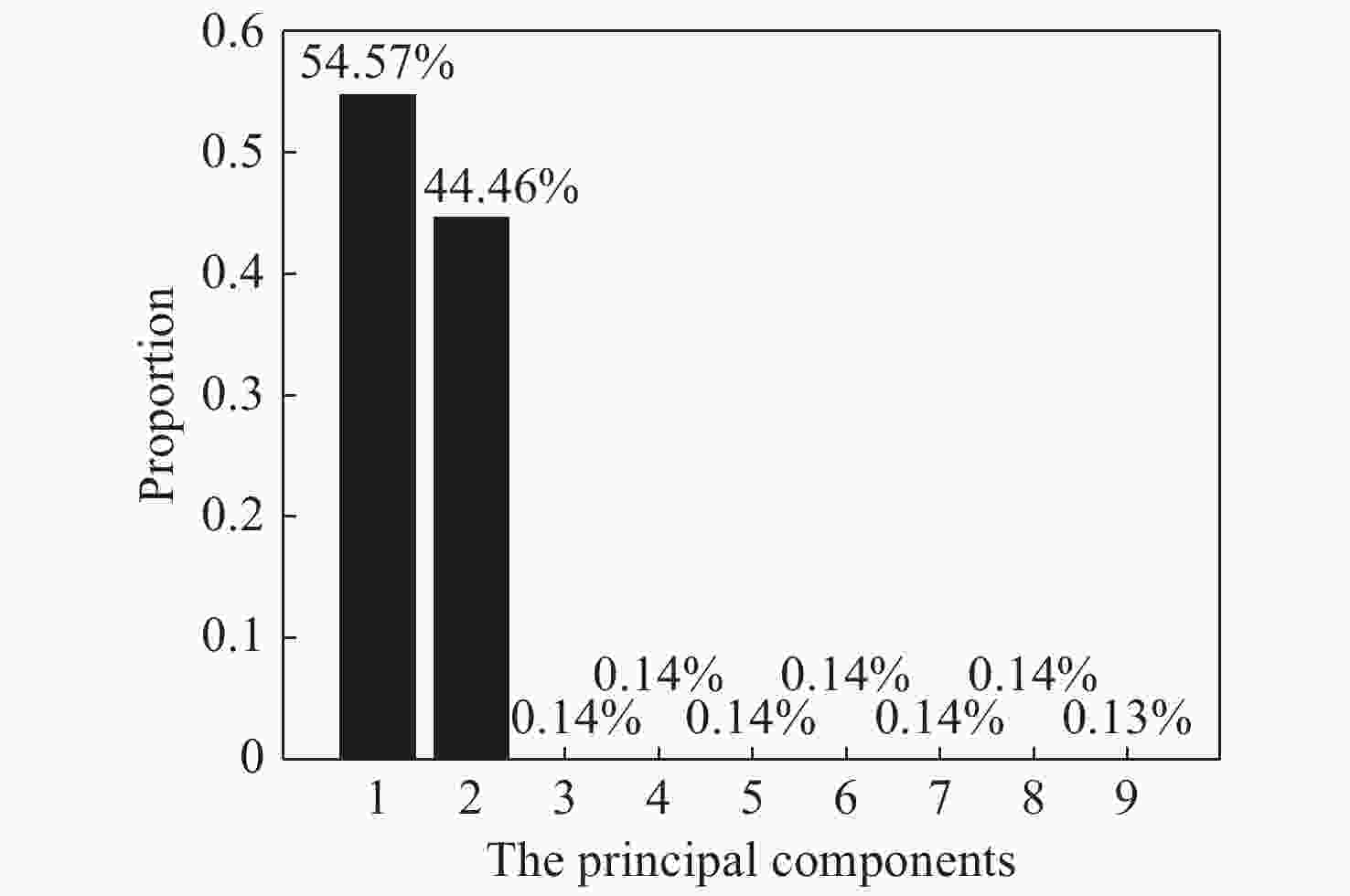
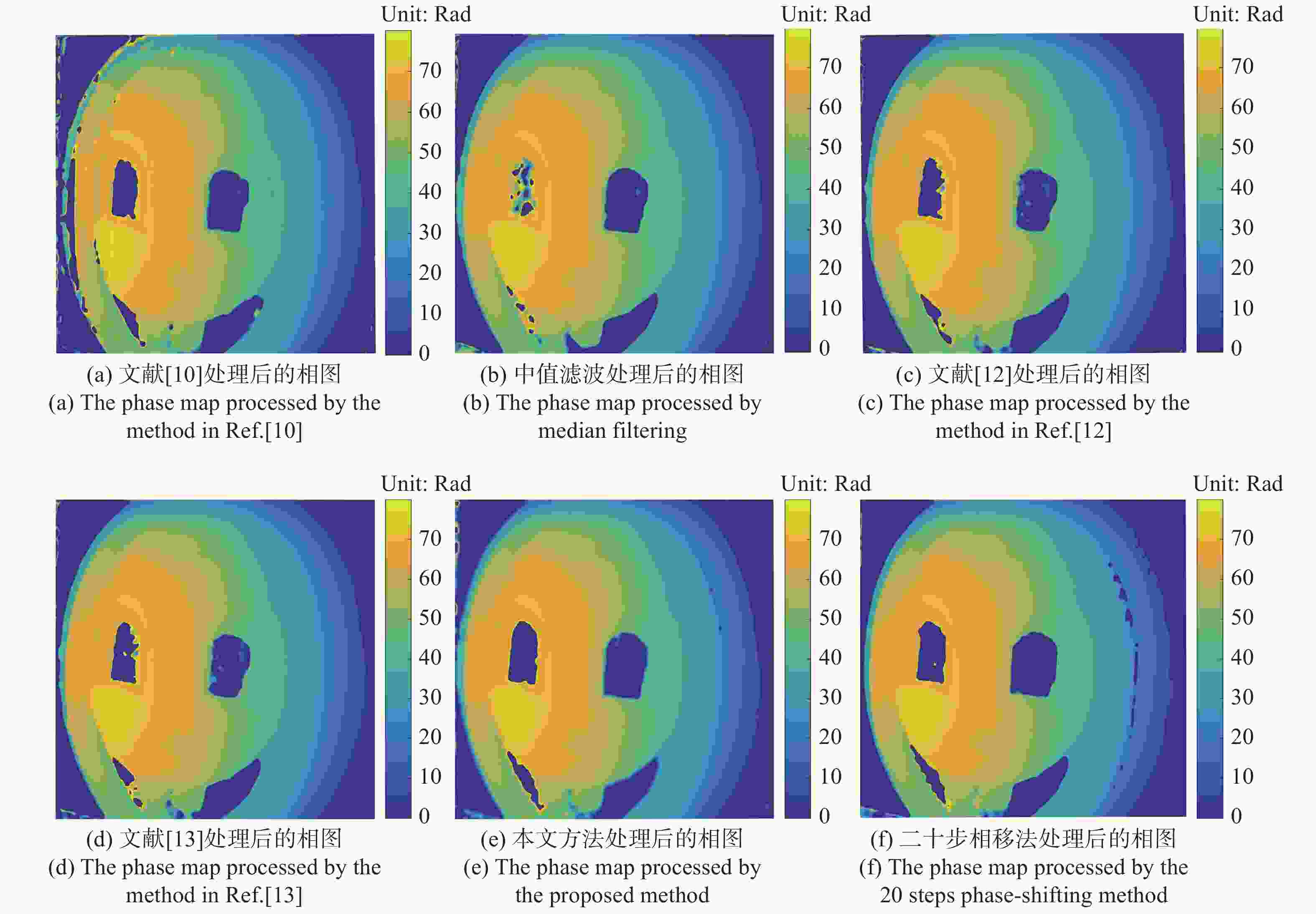
摘要: 基于正弦光栅条纹投影的三维测量技术是当前研究的热点问题。然而,受噪声的影响,采集到的光栅条纹图像质量降低,导致提取的相位发生扰动,而相位的提取结果直接决定着测量结果的准确性。实际测量中噪声未知,针对这一问题,本文提出了一种盲去噪方法。首先,根据残差模型,完成光栅条纹图像的真值图像与噪声图像的分离,然后,引入主成分分析技术估计出噪声图像的方差值。最后,根据噪声方差的估计值,利用基于相图的高斯滤波方法,将针对多帧光栅图像的噪声滤波转换到提取的相位图上完成。由实验结果可知,和对比方法相比,本文方法的均方根相位误差最高下降了88.5%,所提方法处理后的相位更加接近测量体的真值相位。本文方法可在最短的执行时间内实现对噪声导致的相位扰动进行抑制。所提方法能够快速处理光栅图像噪声引起的相位误差,在光栅投影测量中具有较强的实用性。Abstract: The three-dimensional measurement technology based on the projection of sine grating fringe image is a hot-topic. However, due to the influence of noise, the quality of the captured grating image is worse, resulting in the disturbance of the extracted phase, which directly determines the accuracy of the measurement. Since the noise is unknown in actual measurement, a blind denoising method is proposed in this paper. Firstly, according to the residual model, the grating fringe image is separated into the true value and the noise, then the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) technology is introduced to estimate the variance of the noise. Finally, according to the estimated value of the variance, the filtering on multi-frame fringe images is replaced by employing Gaussian filtering on the phase map. In contrast to other methods, the results of the proposed method showed that the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) decreased by 88.5% (up to most), which indicated that the phase values of the proposed method were closer to the ground-truth of the measured object. By employing the proposed method, the phase disturbance caused by noise were significantly suppressed in the shortest execution time. The proposed method can quickly deal with the phase error caused by the noise of the grating image and has strong practicability in the grating image projection measurement.
-
Key words:
- grating image /
- blind denoising /
- PCA /
- phase map filtering
-
表 1 仪器设备型号和参数
Table 1. The instrument types and parameters
仪器设备 型号 主要性能及参数 投影仪 DLP4500 分辨率912 pixel×1140 pixel 工业相机 MV-UB130M 分辨率1024 pixel×1280 pixel
曝光时间:200 ms
帧率:30 frame/s
信噪比:45 dB电脑 Intel Core (TM)
i5-8250U CPU主频:1.6 GHz 表 2 各种方法的噪声方差估计值
Table 2. The estimated noise variances of different methods
表 3 几种算法的量化指标对比
Table 3. Comparison of quantitative indicators for different methods
表 4 几种算法的执行时间对比
Table 4. Comparison of computing time for different methods
(s) -
[1] 王建华, 杨延西. 基于彩色编码光栅投影的双N步相移轮廓术[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(3):616-627. doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0616WANG J H, YANG Y X. Double N-step phase-shifting profilometry using color-encoded grating projection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 616-627. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0616 [2] 张申华, 杨延西. 一种针对投影仪gamma效应的相位误差补偿方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2019,40(11):1-8.ZHANG SH H, YANG Y X. A phase error compensation method for the gamma effect of projector[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2019, 40(11): 1-8. (in Chinese) [3] 邓吉, 李健, 封皓, 等. 不连续相位跳变点的三维深度分割[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(11):2459-2466. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192711.2459DENG J, LI J, FENG H, et al. Three-dimensional depth segmentation technique utilizing discontinuities of wrapped phase sequence[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(11): 2459-2466. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192711.2459 [4] 丁超, 唐力伟, 曹立军, 等. 深孔内表面结构光图像几何畸变校正[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(10):2555-2564. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182610.2555DING CH, TANG L W, CAO L J, et al. Geometric distortion correction for structured-light image of deep-hole inner-surface[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(10): 2555-2564. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182610.2555 [5] 韩玉兰, 赵永平, 王启松, 等. 稀疏表示下的噪声图像超分辨率重构[J]. 光学 精密工程,2017,25(6):1619-1626. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172506.1619HAN Y L, ZHAO Y P, WANG Q S, et al. Reconstruction of super resolution for noise image under the sparse representation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(6): 1619-1626. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172506.1619 [6] 谢斌, 黄安, 黄辉. 本征图像分解的稀疏表示彩色图像去噪算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(11):1104-1114. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193411.1104XIE B, HUANG A, HUANG H. Color image denoising algorithm based on intrinsic image decomposition and sparse representation[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(11): 1104-1114. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193411.1104 [7] 马逸东, 周顺勇. 基于连通性检测的图像椒盐噪声滤波算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2020,35(2):167-172. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203502.0167MA Y D, ZHOU SH Y. Salt and pepper noise filtering algorithm based on connectivity detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2020, 35(2): 167-172. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203502.0167 [8] WANG J H, YANG Y X. An efficient phase error self-compensation algorithm for nonsinusoidal gating fringes in phase-shifting profilometry[J]. Review of Scientific Instrument, 2018, 89(6): 063115. doi: 10.1063/1.5025593 [9] WANG H X, QIAN K M, GAO W J, et al. Fringe pattern denoising using coherence-enhancing diffusion[J]. Optics Letters, 2009, 34(8): 1141-1143. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.001141 [10] TANG CH, HAN L, REN H W, et al. Second-order oriented partial-differential equations for denoising in electronic-speckle-pattern interferometry fringes[J]. Optics Letters, 2008, 33(19): 2179-2181. doi: 10.1364/OL.33.002179 [11] ZHOU Q L, TANG CH, LI B Y, et al. Adaptive oriented PDEs filtering methods based on new controlling speed function for discontinuous optical fringe patterns[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2018, 100: 111-117. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2017.07.018 [12] DONOHO D L, JOHNSTONE I M. Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage[J]. Biometrika, 1994, 81(3): 425-455. doi: 10.1093/biomet/81.3.425 [13] PYATYKH S, HESSER J, ZHENG L. Image noise level estimation by principal component analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(2): 687-699. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2221728 [14] LIU X H, TANAKA M, OKUTOMI M. Single-image noise level estimation for blind denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(12): 5226-5237. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2283400 [15] 汪浩然, 夏克文, 任苗苗, 等. 结合PCA及字典学习的高光谱图像自适应去噪方法[J]. 计算机应用,2016,36(12):3411-3417, 3422. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2016.12.3411WANG H R, XIA K W, REN M M, et al. Adaptive denoising method of hyperspectral remote sensing image based on PCA and dictionary learning[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2016, 36(12): 3411-3417, 3422. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2016.12.3411 [16] 肖进胜, 朱力, 赵博强, 等. 基于主成分分析的分块视频噪声估计[J]. 自动化学报,2018,44(9):1618-1625.XIAO J SH, ZHU L, ZHAO B Q, et al. Block-based video noise estimation algorithm via principal component analysis[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(9): 1618-1625. (in Chinese) [17] 乔双, 吴晓阳, 赵辰一, 等. 基于PCA和BM3D的噪声估计方法及其在中子图像去噪中的应用[J]. 原子能科学技术,2018,52(4):729-736. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2017.youxian.0457QIAO SH, WU X Y, ZHAO CH Y, et al. Noise level estimation method based on PCA and BM3D for neutron image denoising[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2018, 52(4): 729-736. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7538/yzk.2017.youxian.0457 [18] 杨华. 基于稀疏主成分分析的图像噪声估计方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(9):913-920. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193409.0913YANG H. Image noise estimation method based on sparse principal component analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(9): 913-920. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193409.0913 [19] 叶杨, 徐志伟, 陈仁文, 等. 基于KPCA和SVM的直升机旋翼桨叶损伤源定位[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报,2020,34(4):118-123.YE Y, XU ZH W, CHEN R W, et al. Damage source location of helicopter rotor blade based on KPCA and SVM[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2020, 34(4): 118-123. (in Chinese) [20] 吴疆, 尤飞, 蒋平. 基于回归分析和主成分分析的噪声方差估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报,2018,40(5):1195-1201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170624WU J, YOU F, JIANG P. Noise variance estimation method based on regression analysis and principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(5): 1195-1201. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11999/JEIT170624 [21] ZUO CH, HUANG L, ZHANG M L, et al. Temporal phase unwrapping algorithms for fringe projection profilometry: a comparative review[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2016, 85: 84-103. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2016.04.022 [22] JIANG P, WANG Q, WU J. Efficient noise-level estimation based on principal image texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(7): 1987-1999. [23] TOWERS C E, TOWERS D P, JONES J D C. Absolute fringe order calculation using optimised multi-frequency selection in full-field profilometry[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2005, 43(7): 788-800. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2004.08.005 [24] ZUO CH, FENG SH J, HUANG L, et al. Phase shifting algorithms for fringe projection profilometry: a review[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2018, 109: 23-59. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2018.04.019 [25] MAO C L, LU R S, LIU Z J. A multi-frequency inverse-phase error compensation method for projector nonlinear in 3D shape measurement[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 419: 75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.03.006 [26] ZHANG CH W, ZHAO H, ZHANG L, et al. Full-field phase error detection and compensation method for digital phase-shifting fringe projection profilometry[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2015, 26(3): 035201. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/26/3/035201 [27] GAI SH Y, DA F P, LIU CH. Multiple-gamma-value based phase error compensation method for phase measuring profilometry[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(35): 10290-10299. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.010290 -






 下载:
下载: