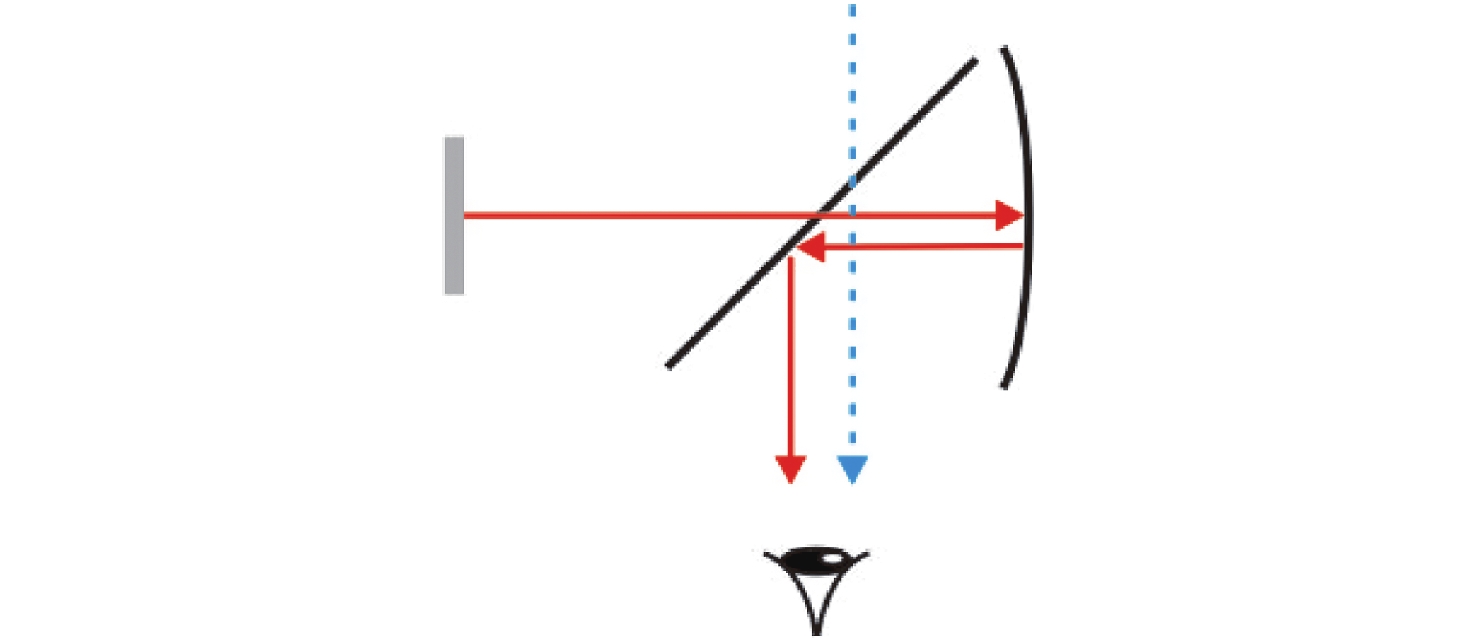
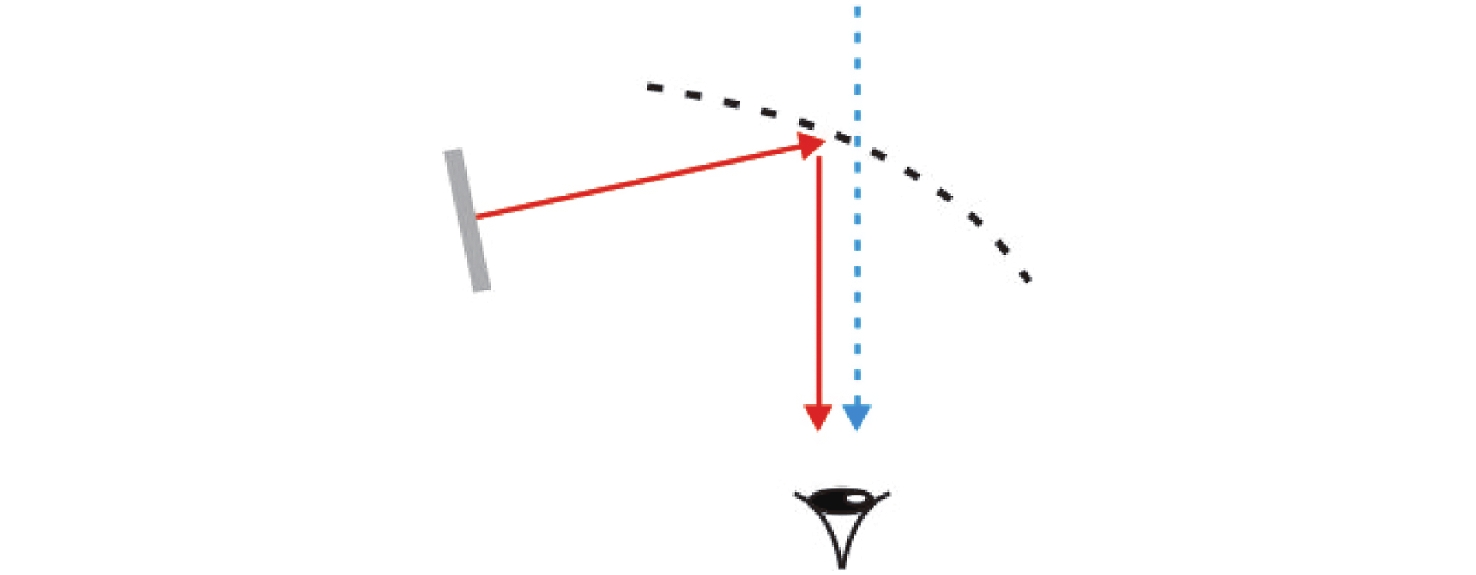
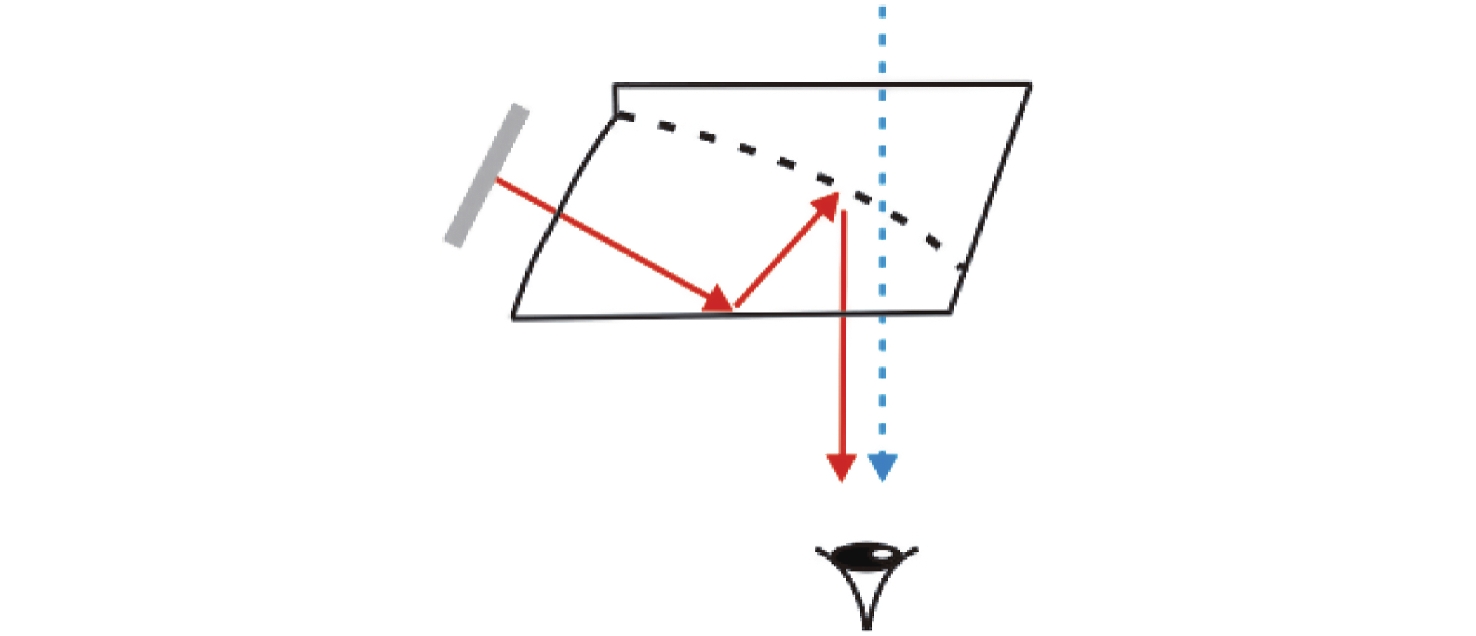
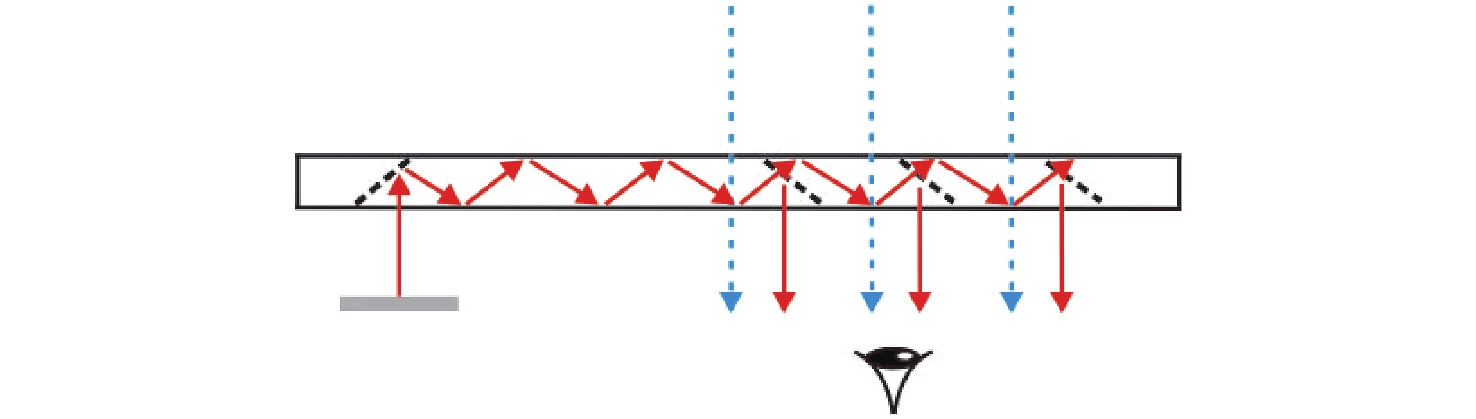
-
摘要: 增强现实显示技术近年来发展迅速,已成为全球信息技术及产业的研究热点和发展重点,有望彻底改变人们感知和处理各种数字信息的方式。同时,微显示技术和光学技术的最新进展为增强现实显示技术的进一步发展指明了方向。本文分析了人眼视觉系统对增强现实头戴式显示器的光学性能要求,将目前增强现实头戴式显示器可实现的规格与之进行比较,说明了现阶段增强现实显示技术的发展水平和面临的主要挑战;重点阐述了增强现实显示技术中各种微显示器和光学组合器的基本原理和所能达到的参数指标,说明了它们的技术先进性和可实现性,同时对它们的发展前景进行了展望。Abstract: Augmented reality (AR) display technology has developed rapidly in recent years, and has become a research hotspot and development focus of the global information technology industry. It has the potential to revolutionize the ways we perceive and interact with various digital information. Recent advances in micro-displays and optical technologies offer new development directions to further advance AR display technology. This review analyzes the optical requirements of human visual systems for AR head-mounted displays and compares them with current specifications of AR head-mounted displays to demonstrate their current levels of development and main challenge. The basic principles and parameters of various micro-displays and optical combiners in AR head-mounted displays are introduced to explain their advantages and practicability, and their development trends are summarized.
-
Key words:
- augmented reality /
- head-mounted displays /
- micro-displays /
- optical combiners
-
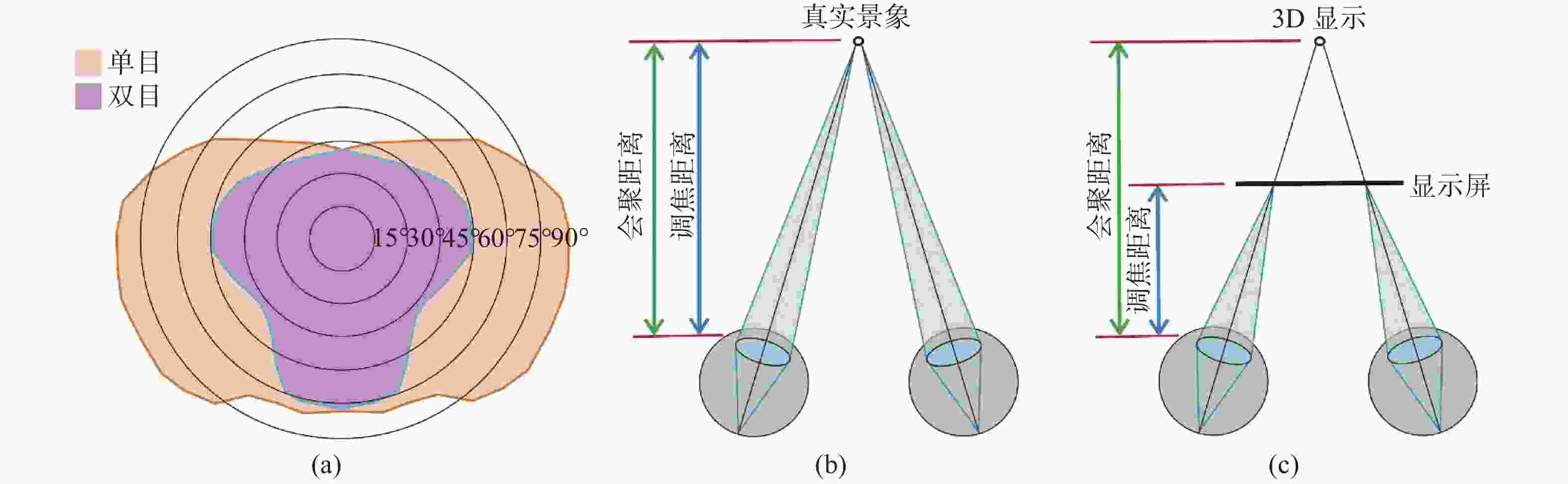
图 1 (a)人眼视场角分布[5];(b)人眼观察真实景象时,会聚距离与调焦距离一致;(c)人眼观察显示屏上的虚拟物体时,会聚距离与调焦距离不一致
Figure 1. (a) The profile of human FOV[5]; (b) accommodation cue coincides with vergence cue when viewing a real object; (c) accommodation cue mismatches with vergence cue when viewing a virtual object displayed at a fixed plane
表 1 几种AR微显示器之间的性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of different types of AR micro-displays
LCoS DLP OLED μLED MEMS RSD 成熟度 高 高 中等 低 中等 亮度(nits) ${10^4}$~${10^5}$ ${10^4}$~${10^5}$ ${10^3}$~${10^4}$ ${10^5}$~${10^6}$ $ > {10^4}$ 对比度 ~${10^3}:1$ ~${10^3}:1$ ~${10^4}:1$ ~${10^5}:1$ ~${10^5}:1$ 光效 低 中等 高 高 高 体积 大 中等 小 小 小 光学系统复杂度 中等 中等 低 低 高 表 2 AR光学组合器的性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison of AR optical combiners
效率 体积 带宽 视场角 色彩均匀性 批量生产工艺 Birdbath $ < 25\% $ 大 大 ~$52^\circ $ 良好 注塑/涂层 自由曲面反射镜 $ < 50\% $ 大 大 ~$90^\circ $ 良好 注塑/涂层 自由曲面棱镜 $ < 50\% $ 大 大 ~$120^\circ $ 良好 注塑/涂层 阵列波导 $ < 20\% $ 中等 大 ~$40^\circ $ 良好 切割/涂层/抛光 SRG $ < 10\% $ 中等 大 ~$52^\circ $ 需要补偿 纳米压印 离轴全息透镜 $ < 20\% $ 小 小 ~$15^\circ $ 需要补偿 曝光 传统体全息光栅 $ < 10\% $ 中等 小 ~$40^\circ $ 需要补偿 曝光 HPDLC $ < 10\% $ 中等 中等 ~$50^\circ $ 好 曝光 PVG $ < 10\% $ 中等 中等 ~$50^\circ $ 好 曝光 -
[1] CARMIGNIANI J, FURHT B, ANISETTI M, et al. Augmented reality technologies, systems and applications[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2011, 51(1): 341-377. doi: 10.1007/s11042-010-0660-6 [2] 何泽浩, 隋晓萌, 赵燕, 等. 基于全息光学的虚拟现实与增强现实技术进展[J]. 科技导报,2018,36(9):8-17.HE Z H, SUI X M, ZHAO Y, et al. The development trend of virtual reality and augmented reality technology based on holographic optics[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2018, 36(9): 8-17. (in Chinese) [3] 范丽亚, 马介渊, 张克发, 等. 增强现实硬件产业的发展及展望[J]. 科技导报,2019,37(15):114-124.FAN L Y, MA J Y, ZHANG K F, et al. The development status and prospect of augmented reality hardware industry[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2019, 37(15): 114-124. (in Chinese) [4] CHANG CH L, BANG K, WETZSTEIN G, et al. Toward the next-generation VR/AR optics: a review of holographic near-eye displays from a human-centric perspective[J]. Optica, 2020, 7(11): 1563-1578. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.406004 [5] WHEELWRIGHT B, SULAI Y, GENG Y, et al. Field of view: not just a number[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10676: 1067604. [6] ZHAN T, YIN K, XIONG J H, et al. Augmented reality and virtual reality displays: perspectives and challenges[J]. iScience, 2020, 23(8): 101397. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101397 [7] CURCIO C A, SLOAN K R, KALINA R E, et al. Human photoreceptor topography[J]. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 1990, 292(4): 497-523. doi: 10.1002/cne.902920402 [8] DOBROWOLSKI J A, SULLIVAN B T, BAJCAR R C. Optical interference, contrast-enhanced electroluminescent device[J]. Applied Optics, 1992, 31(28): 5988-5996. doi: 10.1364/AO.31.005988 [9] CHEN H W, TAN G J, WU S T. Ambient contrast ratio of LCDs and OLED displays[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(26): 33643-33656. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.033643 [10] LEE Y H, ZHAN T, WU S T. Prospects and challenges in augmented reality displays[J]. Virtual Reality &Intelligent Hardware, 2019, 1(1): 10-20. [11] SCHOWENGERDT B T, LIN D M, ST HILAIRE P. Multi-layer diffractive eyepiece: US, 2018052277A1[P]. 2018-02-22. [12] HOFFMAN D M, GIRSHICK A R, AKELEY K, et al. Vergence-accommodation conflicts hinder visual performance and cause visual fatigue[J]. Journal of Vision, 2008, 8(3): 33. doi: 10.1167/8.3.33 [13] KRAMIDA G. Resolving the vergence-accommodation conflict in head-mounted displays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2016, 22(7): 1912-1931. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2015.2473855 [14] ZHAN T, XIONG J H, ZOU J Y, et al. Multifocal displays: review and prospect[J]. PhotoniX, 2020, 1: 10. doi: 10.1186/s43074-020-00010-0 [15] TAY S, BLANCHE P A, VOORAKARANAM R, et al. An updatable holographic three-dimensional display[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 694-698. doi: 10.1038/nature06596 [16] YARAŞ F, KANG H, ONURAL L. State of the art in holographic displays: a survey[J]. Journal of Display Technology, 2010, 6(10): 443-454. doi: 10.1109/JDT.2010.2045734 [17] WETZSTEIN G, LANMAN D, HIRSCH M, et al. Tensor displays: compressive light field synthesis using multilayer displays with directional backlighting[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(4): 80. [18] YUUKI A, ITOGA K, SATAKE T. A new Maxwellian view display for trouble-free accommodation[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2012, 20(10): 581-588. doi: 10.1002/jsid.122 [19] STEVENS R E, RHODES D P, HASNAIN A, et al. Varifocal technologies providing prescription and VAC mitigation in HMDs using Alvarez lenses[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10676: 106760J. [20] DUNN D, TIPPETS C, TORELL K, et al. Wide field of view varifocal near-eye display using see-through deformable membrane mirrors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2017, 23(4): 1322-1331. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2017.2657058 [21] 刘澍鑫, 李燕, 苏翼凯. 基于液晶散射膜的多平面增强现实显示[J]. 液晶与显示,2020,35(7):725-732.LIU SH X, LI Y, SU Y K. Review on multi-plane augmented reality display based on liquid crystal scattering films[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2020, 35(7): 725-732. (in Chinese) [22] LIU SH, HUA H. A systematic method for designing depth-fused multi-focal plane three-dimensional displays[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(11): 11562-11573. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.011562 [23] ZHAN T, LEE Y H, WU S T. High-resolution additive light field near-eye display by switchable Pancharatnam-Berry phase lenses[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(4): 4863-4872. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.004863 [24] LIU SH X, LI Y, ZHOU P CH, et al. Full-color multi-plane optical see-through head‐mounted display for augmented reality applications[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2018, 26(12): 687-693. doi: 10.1002/jsid.739 [25] HUANG Y G, LIAO E, CHEN R, et al. Liquid-crystal-on-silicon for augmented reality displays[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(12): 2366. doi: 10.3390/app8122366 [26] KIM J, KOMANDURI R K, LAWLER K F, et al. Efficient and monolithic polarization conversion system based on a polarization grating[J]. Applied Optics, 2012, 51(20): 4852-4857. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.004852 [27] DU T, FAN F, TAM A M W, et al. Complex nanoscale-ordered liquid crystal polymer film for high transmittance holographic polarizer[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(44): 7191-7195. doi: 10.1002/adma.201502395 [28] WANG CH, HSU R. 18‐4: Invited Paper: Digital modulation on micro display and spatial light modulator[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2017, 48(1): 238-241. doi: 10.1002/sdtp.11678 [29] KANAZAWA M, HAMADA K, KONDOH I, et al. An ultrahigh-definition display using the pixel-offset method[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2004, 12(1): 93-103. doi: 10.1889/1.1824245 [30] STERLING R. JVC D-ILA high resolution, high contrast projectors and applications[C]. Proceedings of the 2008 Workshop on Immersive Projection Technologies/Emerging Display Technologiges, ACM, 2008: 1-6. [31] HUANG Y P, LIN F CH, SHIEH H P D. Eco-displays: the color LCD's without color filters and polarizers[J]. Journal of Display Technology, 2011, 7(12): 630-632. doi: 10.1109/JDT.2011.2166056 [32] LEE Y H, ZHAN T, WU S T. Enhancing the resolution of a near-eye display with a Pancharatnam-Berry phase detector[J]. Optics Letters, 2017, 42(22): 4732-4735. [33] PETTITT G, FERRI J, THOMPSON J. 47.1: invited paper: practical application of TI DLP® technology in the next generation head-up display system[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2015, 46(1): 700-703. doi: 10.1002/sdtp.10269 [34] FIRTH M. Turning automotive windows into the Ultimate HMIs[J]. Information Display, 2020, 36(4): 16-20. doi: 10.1002/msid.1129 [35] MOTOYAMA Y, SUGIYAMA K, TANAKA H, et al. High‐efficiency OLED microdisplay with microlens array[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2019, 27(6): 354-360. doi: 10.1002/jsid.784 [36] GHOSH A, DONOGHUE E P, KHAYRULLIN I, et al. 18-1: invited paper: ultra-high-brightness 2K x 2K Full-color OLED microdisplay using direct patterning of OLED emitters[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2017, 48(1): 226-229. doi: 10.1002/sdtp.11674 [37] LIN J Y, JIANG H X. Development of microLED[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2020, 116(10): 100502. doi: 10.1063/1.5145201 [38] HUANG Y, HSIANG E L, DENG M Y, et al. Mini-LED, Micro-LED and OLED displays: Present status and future perspectives[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2020, 9(1): 105. [39] 韩洪松, 齐爱想, 刘俊国, 等. Micro-LED在机载上的应用[J]. 液晶与显示,2021,36(3):439-447. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0096HAN H S, QI A X, LIU J G, et al. Application of Micro-LED technology in airborne display[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2021, 36(3): 439-447. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0096 [40] QUESNEL E, LAGRANGE A, VIGIER M, et al. Dimensioning a full color LED microdisplay for augmented reality headset in a very bright environment[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2021, 29(1): 3-16. doi: 10.1002/jsid.884 [41] 郝斌, 赵文武, 郁建元, 等. 荧光粉Ba5-3x/2B4O11:xEu3+的制备及发光性能[J]. 应用化学,2019,36(5):548-553. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2019.05.180276HAO B, ZHAO W W, YU J Y, et al. Preparation and luminescence property of Ba5-3x/2B4O11∶xEu3+ phosphor[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2019, 36(5): 548-553. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2019.05.180276 [42] 刘伟强, 崔荣朕, 武瑞霞, 等. 蓝色延迟荧光材料及器件的研究进展[J]. 应用化学,2019,36(1):1-9. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2019.01.180071LIU W Q, CUI R ZH, WU R X, et al. Recent progress on blue delayed fluorescent materials and devices[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2019, 36(1): 1-9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2019.01.180071 [43] 黄国斌, 骆登峰, 张茂升. 多色高发光效率CsPbX3(X=Cl, Br, I)钙钛矿量子点的制备及其在发光二极管中的应用[J]. 应用化学,2019,36(8):932-938. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2019.08.190016HUANG G B, LUO D F, ZHANG M SH. Preparation of CsPbX3(X=Cl, Br, I) perovskite quantum dots with multicolor and high luminescence efficiency and its application in light emitting diode devices[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2019, 36(8): 932-938. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2019.08.190016 [44] ALEXANDER S, BAILEY M, MORRISON V R, et al.. Systems, devices, and methods for eyebox expansion in wearable heads-up displays: US, 9989764[P]. 2018-06-05. [45] HAAS G. 40-2: invited paper: microdisplays for augmented and virtual reality[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2018, 49(1): 506-509. doi: 10.1002/sdtp.12445 [46] CADO H, MOLITON R. Polarization splitter, method of manufacturing same and ophthalmic lens incorporating projection inserts containing it: US, 20040136082[P]. 2004-07-15. [47] MARTINEZ M A, SAEEDI E, AMIRPARVIZ B. Head-mounted display including integrated projector: US, 9128285[P]. 2015-09-08. [48] WANG J H, LIANG Y CH, XU M. Design of a see-through head-mounted display with a freeform surface[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of Korea, 2015, 19(6): 614-618. doi: 10.3807/JOSK.2015.19.6.614 [49] TAKAHASHI K. Head or face mounted image display apparatus: US, 5701202[P]. 1997-12-23. [50] AMITAI Y. Substrate-guided optical device utilizing thin transparent layer: US, 7724443[P]. 2010-05-25. [51] CHENG D W, WANG Y T, XU CH, et al. Design of an ultra-thin near-eye display with geometrical waveguide and freeform optics[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(17): 20705-20719. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.020705 [52] GU L, CHENG D W, WANG Q W, et al. Design of a two-dimensional stray-light-free geometrical waveguide head-up display[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(31): 9246-9256. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.009246 [53] KRESS B C. Optical waveguide combiners for AR headsets: features and limitations[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11062: 110620J. [54] 刘明欢, 付秀华, 王菲, 等. 增强现实显示衍射光波导的设计[J]. 液晶与显示,2021,36(3):389-397. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0214LIU M H, FU X H, WANG F, et al. Design of augmented reality display diffraction optical waveguide[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2021, 36(3): 389-397. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0214 [55] MUKAWA H, AKUTSU K, MATSUMURA I, et al. A full-color eyewear display using planar waveguides with reflection volume holograms[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2009, 17(3): 185-193. doi: 10.1889/JSID17.3.185 [56] KRESS B C, CUMMINGS W J. 11-1: invited paper: towards the ultimate mixed reality experience: hololens display architecture choices[J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2017, 48(1): 127-131. doi: 10.1002/sdtp.11586 [57] SCHOWENGERDT B T, LIN D M, ST HILAIRE P. Multi-layer diffractive eyepiece: US, 20200284967[P]. 2020-09-10. [58] GLEESON M R, SHERIDAN J T. A review of the modelling of free-radical photopolymerization in the formation of holographic gratings[J]. Journal of Optics A:Pure and Applied Optics, 2009, 11(2): 024008. doi: 10.1088/1464-4258/11/2/024008 [59] BRUDER F K, FÄCKE T, HAGEN R, et al. Diffractive optics with high Bragg selectivity: volume holographic optical elements in Bayfol® HX photopolymer film[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9626: 96260T. [60] YEOM H J, KIM H J, KIM S B, et al. 3D holographic head mounted display using holographic optical elements with astigmatism aberration compensation[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(25): 32025-32034. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.032025 [61] LIN W K, MATOBA O, LIN B S, et al. Astigmatism correction and quality optimization of computer-generated holograms for holographic waveguide displays[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(4): 5519-5527. doi: 10.1364/OE.381193 [62] MAIMONE A, GEORGIOU A, KOLLIN J S. Holographic near-eye displays for virtual and augmented reality[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): 85. [63] SUTHERLAND R L, TONDIGLIA V P, NATARAJAN L V, et al. Electrically switchable volume gratings in polymer‐dispersed liquid crystals[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1994, 64(9): 1074-1076. doi: 10.1063/1.110936 [64] FENG X Y, LU L, YAROSHCHUK O, et al. Closer look at transmissive polarization volume holograms: geometry, physics, and experimental validation[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(3): 580-592. doi: 10.1364/AO.412589 [65] NYS I. Patterned surface alignment to create complex three-dimensional nematic and chiral nematic liquid crystal structures[J]. Liquid Crystals Today, 2020, 29(4): 65-83. doi: 10.1080/1358314X.2020.1886780 [66] WENG Y SH, XU D M, ZHANG Y N, et al. Polarization volume grating with high efficiency and large diffraction angle[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(16): 17746-17759. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.017746 [67] LEE Y H, YIN K, WU S T. Reflective polarization volume gratings for high efficiency waveguide-coupling augmented reality displays[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(22): 27008-27014. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.027008 [68] LEE Y H, TAN G J, ZHAN T, et al. Recent progress in Pancharatnam-Berry phase optical elements and the applications for virtual/augmented realities[J]. Optical Data Processing and Storage, 2017, 3(1): 79-88. [69] SAKHNO O, GRITSAI Y, SAHM H, et al. Fabrication and performance of efficient thin circular polarization gratings with Bragg properties using bulk photo-alignment of a liquid crystalline polymer[J]. Applied Physics B, 2018, 124(3): 52. doi: 10.1007/s00340-018-6920-2 [70] LEE Y H, TAN G J, YIN K, et al. Compact see-through near-eye display with depth adaption[J]. Journal of the Society for Information Display, 2018, 26(2): 64-70. doi: 10.1002/jsid.635 -





 下载:
下载: