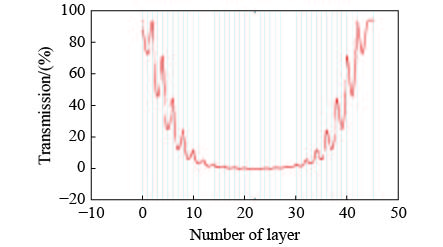
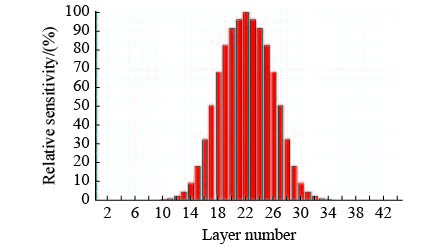
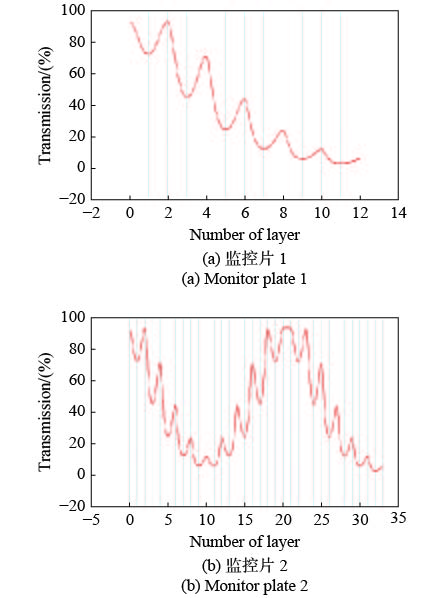
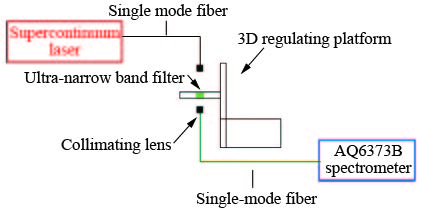
Fabrication of an ultra-narrow band-pass filter with 60 pm bandwidth in green light band
doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0092
-
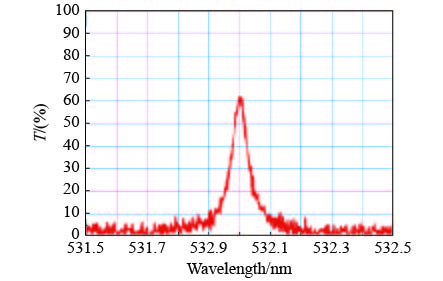
摘要: 波长为532 nm的绿色金宝搏188软件怎么用 在大气层中有较强的穿透能力,可用于自由空间光通信和金宝搏188软件怎么用 三维测绘,为了抑制背景光的干扰,需要半功率带宽小于100 pm的光谱滤波器。因此,设计并研制了基于光学干涉薄膜的超窄带滤光片。将五氧化二钽(Ta2O5)和二氧化硅(SiO2)分别作为高低折射率膜层材料,将熔石英作为基片,采用双离子束溅射沉积方法制备出所设计的光学薄膜。利用可调谐金宝搏188软件怎么用 器和功率计测量滤光片的透射光谱,其半功率带宽为(60±2) pm,透过率达到62.6%。
-
关键词:
- 光学薄膜 /
- 薄膜滤光片 /
- 皮米带宽 /
- 绿光波段 /
- 空间金宝搏188软件怎么用 测绘
Abstract: Owing to the strong penetrating ability in the atmosphere, 532 nm-wavelength green laser has wide applications including free-space optical communications and laser three-dimensional mapping. A spectral filter, with a half-power bandwidth of less than 100 pm, is an important optical element to suppress the interference of background light. Therefore, an ultra-narrow band-pass filter based on optical interference film is designed and fabricated in this paper. The high and low refractive index film are made of tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5) and silicon dioxide (SiO2), respectively. The designed optical thin films are deposited on a fused quartz substrate by double-ion-beam sputtering deposition method. The transmission spectra of the filters are measured by a tunable laser and a power meter. The half-power bandwidths of the filters are (60±2) pm, and the transmittance reaches 62.6%.-
Key words:
- optical thin film /
- thin film filter /
- picometer bandwidth /
- green light band /
- space laser mapping
-
表 1 Comparison of main filtering techniques for sub-nanometer spectrum in visible light band
Table 1. Comparison of main filtering techniques for sub-nanometer spectrum in visible light band
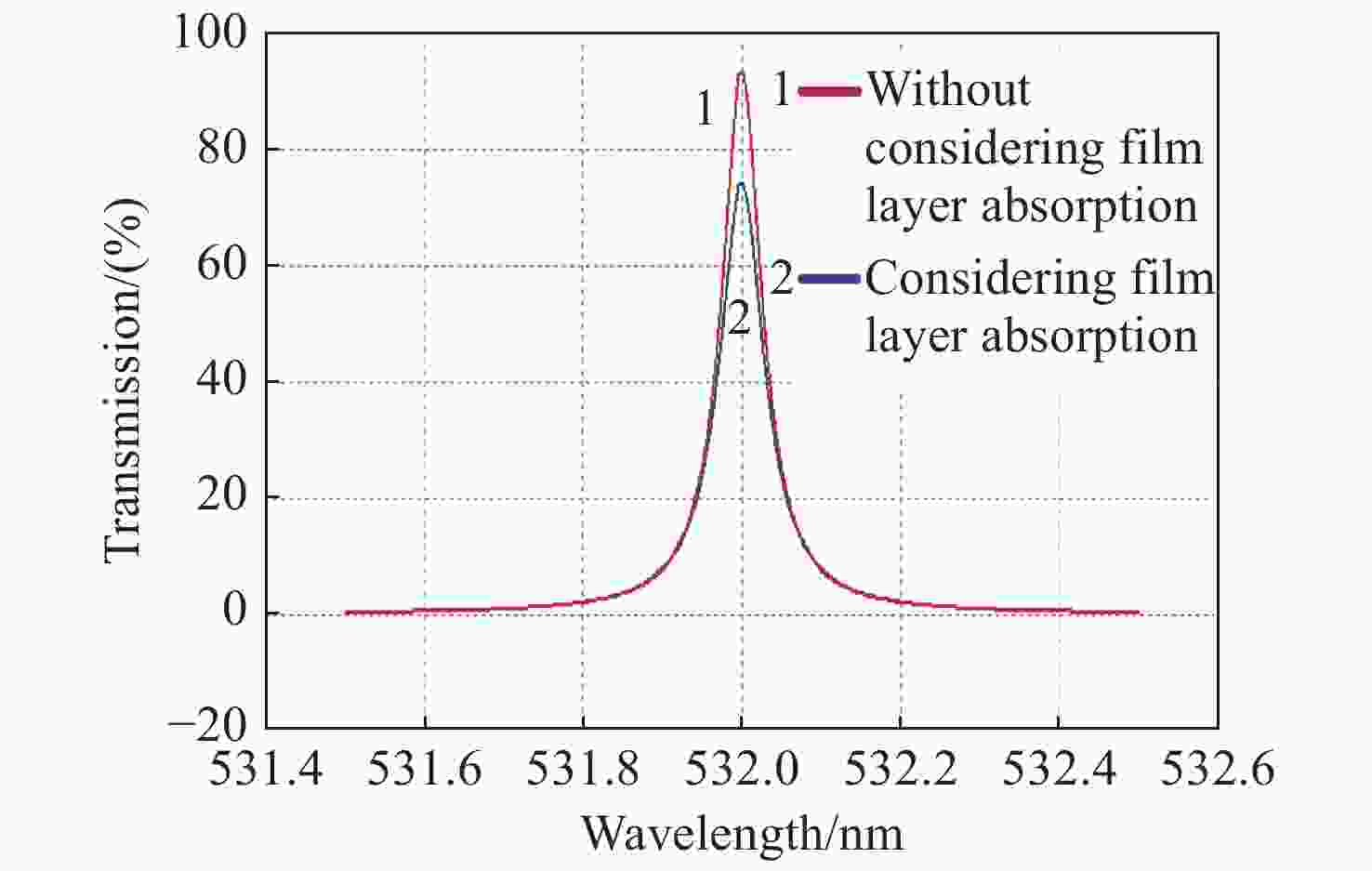
Spectral filtering technique Spectral fineness Optical efficiency Wave option Structure Stability Acoustoptic modulation 1~0.01 nm Medium Fast modulated Complex Good Atomic filtering 1~0.001 nm High−low Fixed, fewer options Complex Not bad F-P etalon 1~0.002 nm High Fixed, more options Somewhat complex Good Film interference 1~0.03 nm High Fixed, more options Simple Very good 表 2 Data of measured and designed transmission spectrum
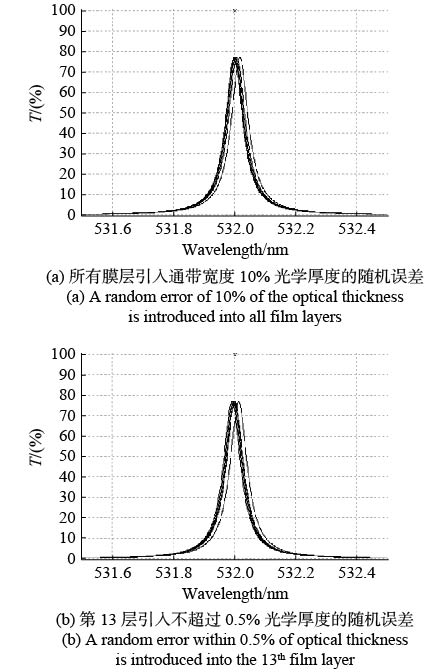
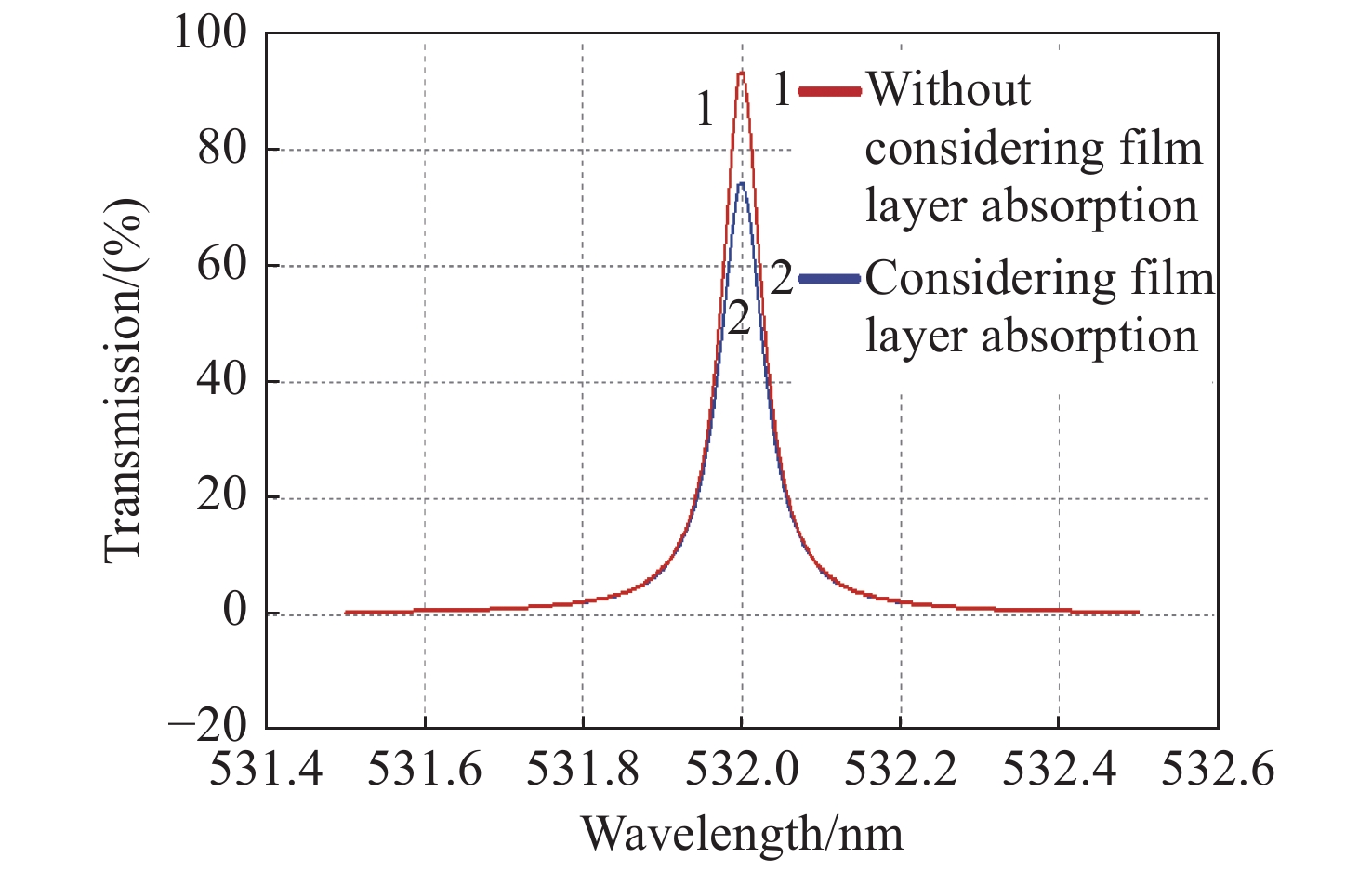
Table 2. Data of measured and designed transmission spectrum
Bandwidth
(pm)Peak transmittance
(%)Central wavelength
(nm)A. Design value
(without absorption)57 93.4 532.00 B. Design value
(with absorption)63 74.3 532.00 C. Measured value 62 62.6 532.009 D. Deviation value
(from B)−1 −11.7 +0.009 表 3 Optical and thermal properties of substrates and thin films in this study[12, 21-22]
Table 3. Optical and thermal properties of substrates and thin films in this study[12, 21-22]
Materials Refractive index,
n@ 532nm,20~40 ℃Refractive-index temperature coefficient,
dn/dT (10−6/℃)Linear expansion coefficient, α
(10−6/℃)
@0~100 ℃Crystal Quartz (CQ) 1.55 5.2 13.4 Fused quartz (JGS-1) 1.46 10.0 0.55 Glass ceramics (Zerodur) 1.54 14.3 0.05 Glass (K9, BK7) 1.52 3.0 7.4 Sapphire (Al2O3) 1.77 13.1 6.7 SiO2 film 1.44 9.0 0.55 Ta2O5 film 2.11 20.0 1.1 -
[1] YU A W, STEPHEN M A, LI S X, et al. Space laser transmitter development for ICESat-2 mission[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7578: 757809. doi: 10.1117/12.843342 [2] SAWRUK N W, STEPHEN M A, LITVINOVITCH S, et al. Space qualified laser transmitter for NASA’s ICESat-2 mission[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8599: 85990O. doi: 10.1117/12.2005590 [3] GAO SH J, WU J B, LIU Y K, et al. Development status and trend of micro-satellite laser communication systems[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1171-1181. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0033 [4] DONG Q R, CHEN T, GAO SH J, et al. Progress of research on satellite-borne laser communication technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(6): 1260-1270. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1260 [5] TROUPAKI E, DENNY Z H, WU S, et al. Space qualification of the optical filter assemblies for the ICESat-2/ATLAS instrument[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9346: 93460H. [6] WANG J Y, SHU R, LIU Y N, et al.. Introduction to Imaging Spectroscopy[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 90-110. (in Chinese) [7] HAN F, LIU H J, SUN D S, et al. An ultra-narrow bandwidth filter for daytime wind measurement of direct detection Rayleigh lidar[J]. Current Optics and Photonics, 2020, 4(1): 69-80. [8] GAYEN S K, BILLMERS R I, CONTARINO V M, et al. Induced-dichroism-excited atomic line filter at 532 nm[J]. Optics Letters, 1995, 20(12): 1427-1429. doi: 10.1364/OL.20.001427 [9] XU CH, XIAO O L, MA J Y, et al. High temperature annealing effect on structure, optical property and laser-induced damage threshold of Ta2O5 films[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254(20): 6554-6559. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.04.034 [10] ZHAO Q, PU Y T, HAO L, et al. Residual stress and laser-induced damage of ion-beam sputtered Ta2O5/SiO2 mixture coatings[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2015, 592: 221-224. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2015.06.023 [11] LV Q P, HUANG M L, ZHANG SH Q, et al. Effects of annealing on residual stress in Ta2O5 films deposited by dual ion beam sputtering[J]. Coatings, 2018, 8(4): 150. doi: 10.3390/coatings8040150 [12] KIM S H, HWANGBO C K. Derivation of the center-wavelength shift of narrow-bandpass filters under temperature change[J]. Optics Express, 2004, 12(23): 5634-5639. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.12.005634 [13] TANG J F, GU P F, LIU X, et al.. Modern Optical Thin Film Technology[M]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press, 2006: 144-146. (in Chinese) [14] MACLEOD H A. Thin-Film Optical Filters[M]. Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis, 2010: 310-313. [15] CHEN G. Research on the near infrared optical properties of several metal oxide thin films and narrow bandpass filters for space remote sensing[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020: 56-68. (in Chinese) [16] CHANELIERE C, AUTRAN J L, DEVINE R A B, et al. Tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5) thin films for advanced dielectric applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:R:Reports, 1998, 22(6): 269-322. doi: 10.1016/S0927-796X(97)00023-5 [17] YUAN W J, SHEN W D, ZHENG X W, et al. Optical and mechanical properties and microstructures of Nb2O5, Ta2O5 and SiO2 thin films prepared by ion beam sputtering[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(12): 1231001. (in Chinese) [18] JIANG Y G, LIU H S, CHEN D, et al. Ultraviolet absorption film technology based on ion beam sputtering Ta2O5 thin films[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(3): 527-532. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192703.0527 [19] SHANG P, XIONG SH M, LI L H, et al. Optical constants and properties of dual-ion-beam sputtering Ta2O5/SiO2 thin film by spectroscopy[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2014, 34(5): 0531002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201434.0531002 [20] WU Q D. Nucleation and growth of vapor phase deposition on solid surfaces[J]. Vacuum, 1990, 41(4-6): 1431-1433. doi: 10.1016/0042-207X(90)93980-W [21] WAKAKI M, KUDO K, SHIBUYA T. Physical Properties and Data of Optical Materials[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2007: 301-330. [22] ZHU X D, ZHANG R J, ZHENG Y X, et al. Spectroscopic ellipsometry and its applications in the study of thin film materials[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(6): 1195-1234. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1195 -





 下载:
下载: