-
摘要: 在消色差的结构优化中,超构透镜的尺寸、消色差带宽及数值孔径具有内在制约关系,很难获得高效率的大尺寸消色差透镜。离散波长消色差设计将打破宽带消色差的参数制约,有望获得更高效率的成像性能。本文通过引入相位色散空间的概念,理论上阐明了离散波长消色差的效率变化规律,证明了离散波长消色差超构透镜在聚焦效率上优于宽带消色差超构透镜。计算结果表明,双波长消色差超构透镜效率大概为宽带消色差超构透镜的4倍,相关结果通过设计相应的超构透镜进行仿真模拟得到验证。进一步揭示并解释了离散波长消色差的聚焦效率会随消色差的频率间隔增大呈现出先下降后上升的规律。Abstract: Due to the intrinsic constraints of metalenses’ achromatic bandwidth, lens size, and numerical aperture, it’s hard to create a high-performance large scale broadband achromatic metalens. Discrete multi-wavelength achromatic metalenses can exceed multiple of these restrictions of these parameters, which means they could perform more suitably. Here, we introduce a phase-dispersion space, by which we prove that multiwavelength achromatic metalenses are theoretically more efficient than broadband achromatic metalenses. The efficiency of dualwavelength achromatic metalenses is 4 times that of broadband achromatic metalenses when calculated by simulation. We also analyze the relationship between efficiency and the frequency interval of multiwavelength achromatic metalens, and conclude that efficiency will decrease first and then increase as the frequency interval increases.
-
Key words:
- metalens /
- achromatic /
- multiwavelength /
- frequency interval /
- efficiency
-
图 1 理论分析示意图。(a)两个频率ω1与ω2的相位分布示意图;(b)相位色散空间示意图;(c)离散消色差与宽带消色差超构透镜相位处理上的差异;(d)约化后的相位色散空间。
Figure 1. Diagram for analyzation. (a) The phase distribution at frequency ω1and ω2; (b) phase-dispersion space; (c) difference in multiwavelength metalens and broadband metalens when it comes to phase processing; (d) phase-dispersion space after mod 2π.
图 3 设计样品对应的光场分布及聚焦效率。(a)离散消色差超构透镜在设计波长处轴向光场分布。比例尺为500 nm;(b)宽带消色差超构透镜在6个波长处轴向光场分布。比例尺为1 μm;(c)离散消色差超构透镜和宽带消色差超构透镜在设计波长处的聚焦效率;(d)离散消色差超构透镜在平均聚焦效率随设计波长数目的变化
Figure 3. The light fields and focus efficiencies of the designed samples. (a) Light field of multiwavelength metalens at the wavelengths 450 nm and 650 nm along the propagation axis. Scale bar, 500 nm; (b) light field of broadband achromatic metalens at six wavelengths along the propagation axis. Scale bar, 1 μm; (c) the focus efficiency of multiwavelength metalens and broadband achromatic metalens at the designed wavelengths; (d) the distribution of focus efficiency with respect to the number of designed wavelength
图 4 结构提供的色散分布和实际所需色散分布。(a)不同频率下结构所能提供的相位色散分布;(b)不同频率下实现离散消色差超构透镜所需的相位色散分布。每一列的两幅图对应频率相同。
Figure 4. The phase-dispersion provided by meta-unit and required for achromatic performance. (a) The phase-dispersion provided by meta-unit at different frequencies; (b) the phase-dispersion required for achromatic performance at different frequencies. Diagrams in the same column has the same frequencies
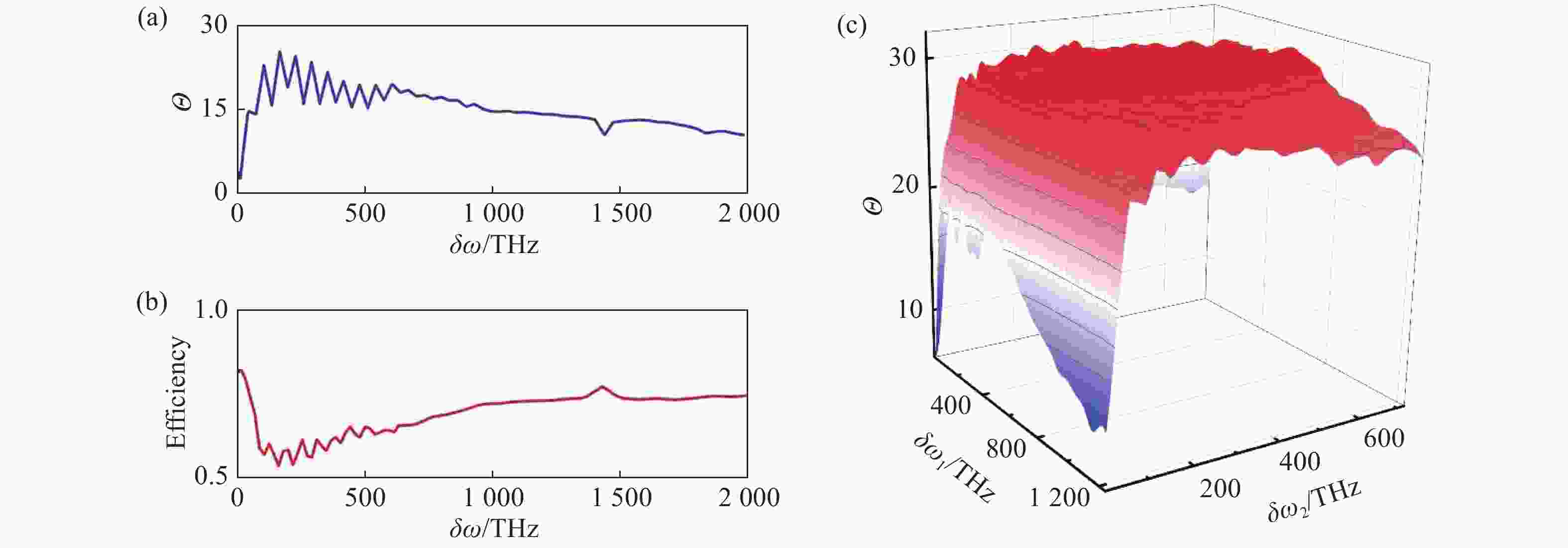
图 5 相位色散误差及聚焦效率随频率间隔的分布。(a)双波长离散消色差超构透镜对应的相位色散误差;(b)双波长离散消色差超构透镜平均聚焦效率;(c)三波长离散消色差超构透镜对应的相位色散误差Θ随频率间隔δω1和δω2的分布。
Figure 5. The distributions of the phase-dispersion error and focus efficiency with respect to frequency interval. (a) The phase-dispersion error of dual-wavelength achromatic metalens. (b) The average focus efficiency of dual-wavelength achromatic metalens. (c) The phase-dispersion error of three-wavelength achromatic metalens.
-
[1] MANSURIPUR M. Classical Optics and its Applications[M]. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press, 2009: 9-22. [2] O'SHEA D C, SULESKI T J, KATHMAN A D, et al.. Diffractive Optics: Design, Fabrication, and Test[M]. Washington USA: SPIE Press, 2004: 57-82. [3] ARBABI A, HORIE Y, BALL A J, et al. Subwavelength-thick lenses with high numerical apertures and large efficiency based on high-contrast transmit arrays[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 7069. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8069 [4] KHORASANINEJAD M, CHEN W T, DEVLIN R C, et al. Metalenses at visible wavelengths: diffraction-limited focusing and subwavelength resolution imaging[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6290): 1190-1194. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf6644 [5] KHORASANINEJAD M, SHI ZH J, ZHU A Y, et al. Achromatic metalens over 60 nm bandwidth in the visible and metalens with reverse chromatic dispersion[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(3): 1819-1824. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b05137 [6] WANG SH M, WU P C, SU V C, et al. Broadband achromatic optical metasurface devices[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 187-195. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00166-7 [7] SHRESTHA S, OVERVIG A C, LU M, et al. Broadband achromatic dielectric metalenses[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2018, 7(1): 85. [8] CHEN W T, ZHU Z Y, SANJEEV V, et al. A broadband achromatic metalens for focusing and imaging in the visible[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2018, 13(3): 220-226. doi: 10.1038/s41565-017-0034-6 [9] WANG SH M, WU P C, SU V C, et al. A broadband achromatic metalens in the visible[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2018, 13(3): 227-232. doi: 10.1038/s41565-017-0052-4 [10] BALLI F, SULTAN M, LAMI S K, et al. A hybrid achromatic metalens[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3892. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17646-y [11] 肖行健, 祝世宁, 李涛. 宽带消色差平面透镜的设计与参量分析[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2020,49(9):20201032. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201032XIAO X J, ZHU SH N, LI T. Design and parametric analysis of the broadband achromatic flat lens[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(9): 20201032. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201032 [12] PALUM R. Image sampling with the Bayer color filter array[C]. PICS 2001: Image Processing, Image Quality, Image Capture, Systems Conference, Proceedings, 2001: 239-245. [13] AIETA F, KATS M A, GENEVET P, et al. Multiwavelength achromatic metasurfaces by dispersive phase compensation[J]. Science, 2015, 347(6228): 1342-1345. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa2494 [14] ARBABI E, ARBABI A, KAMALI S M, et al. Multiwavelength polarization-insensitive lenses based on dielectric metasurfaces with meta-molecules[J]. Optica, 2016, 3(6): 628-633. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.000628 [15] AVAYU O, ALMEIDA E, PRIOR Y, et al. Composite functional metasurfaces for multispectral achromatic optics[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 14992. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14992 [16] LI ZH Y, LIN P, HUANG Y W, et al. Meta-optics achieves RGB-achromatic focusing for virtual reality[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(5): eabe4458. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abe4458 [17] AIETA F, GENEVET P, KATS M A, et al. Aberration-free ultrathin flat lenses and axicons at telecom wavelengths based on plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(9): 4932-4936. doi: 10.1021/nl302516v [18] LIANG H W, MARTINS A, BORGES B H V, et al. High performance metalenses: numerical aperture, aberrations, chromaticity, and trade-offs[J]. Optica, 2019, 6(12): 1461-1470. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.001461 [19] HOOKE R, JEEVES T A. “Direct Search”solution of numerical and statistical problems[J]. Journal of the ACM, 1961, 8(2): 212-229. doi: 10.1145/321062.321069 -






 下载:
下载: