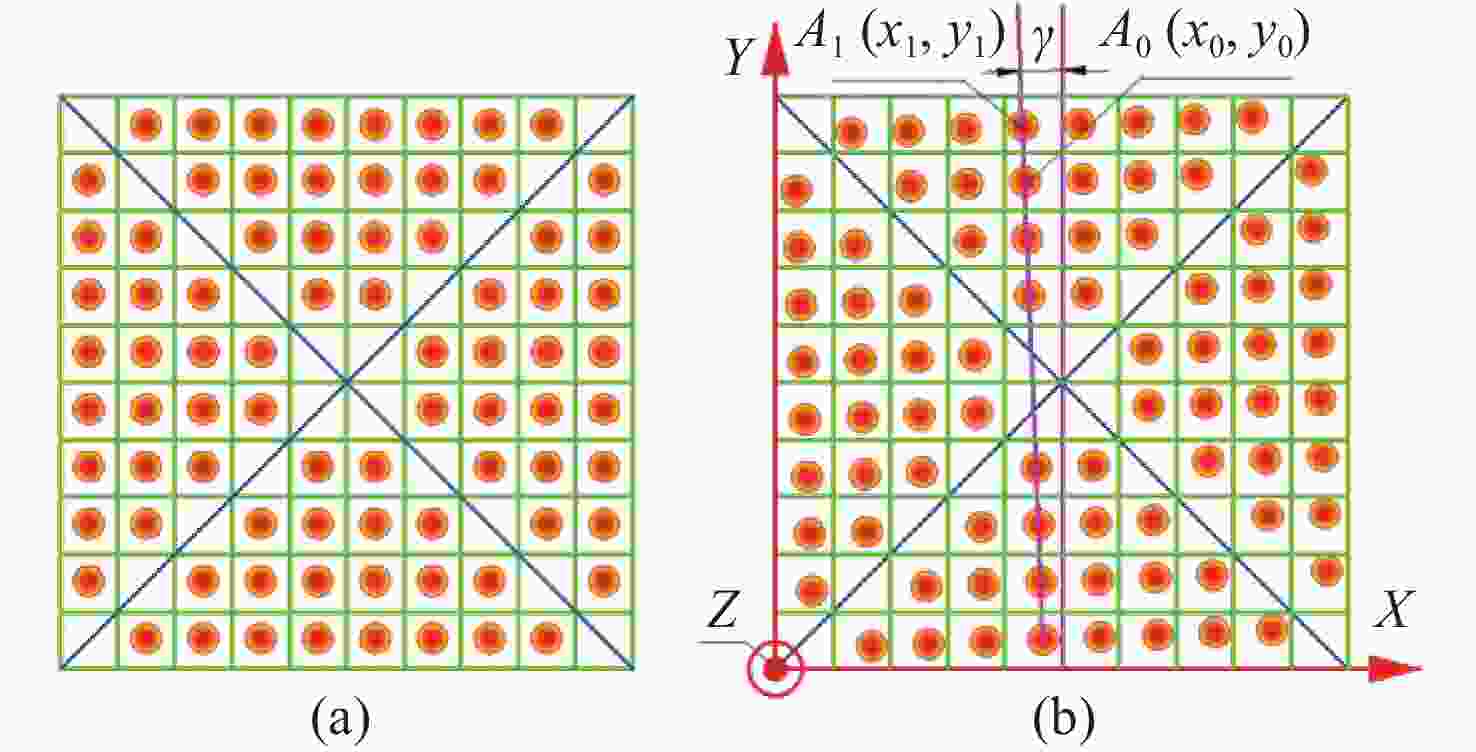
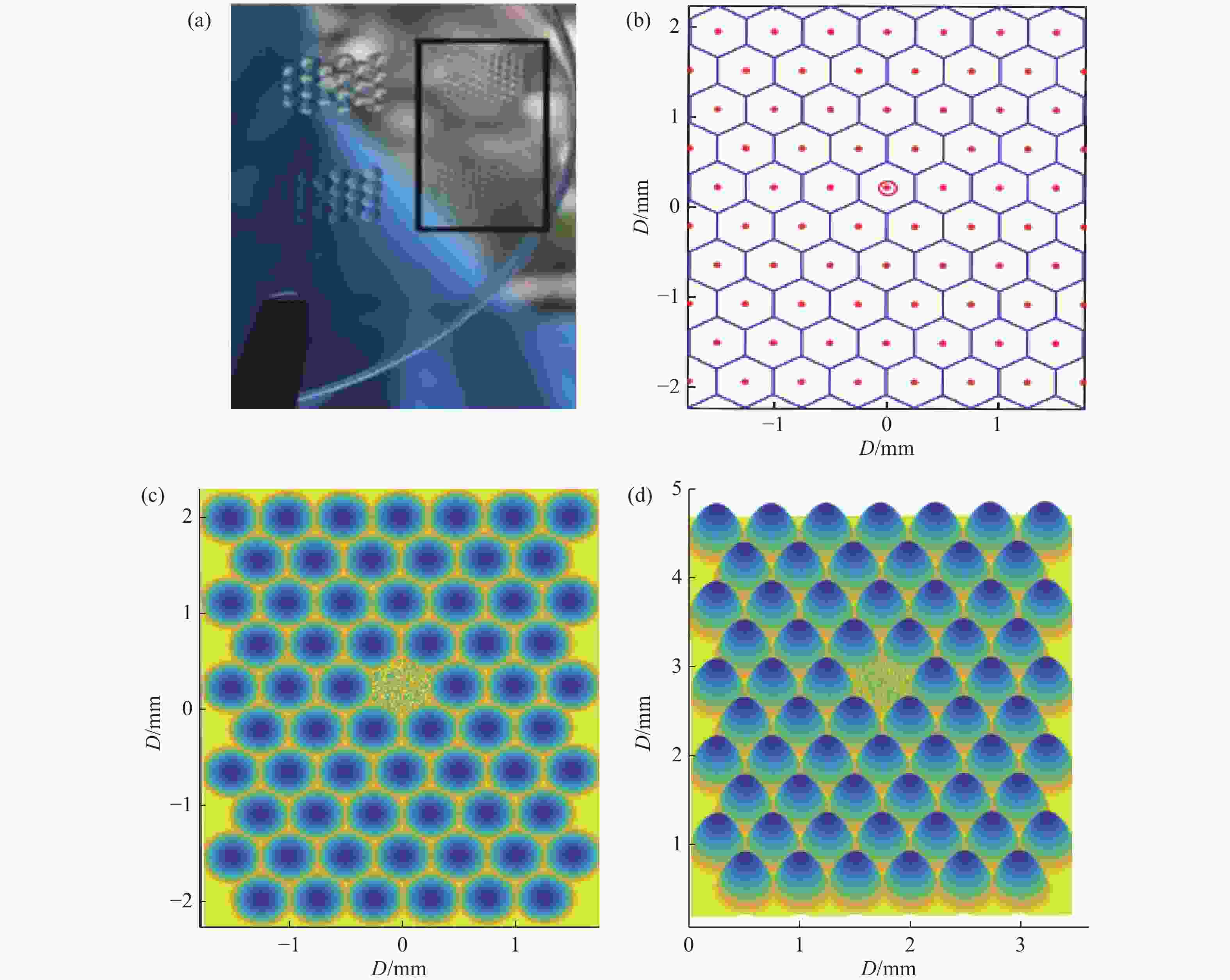
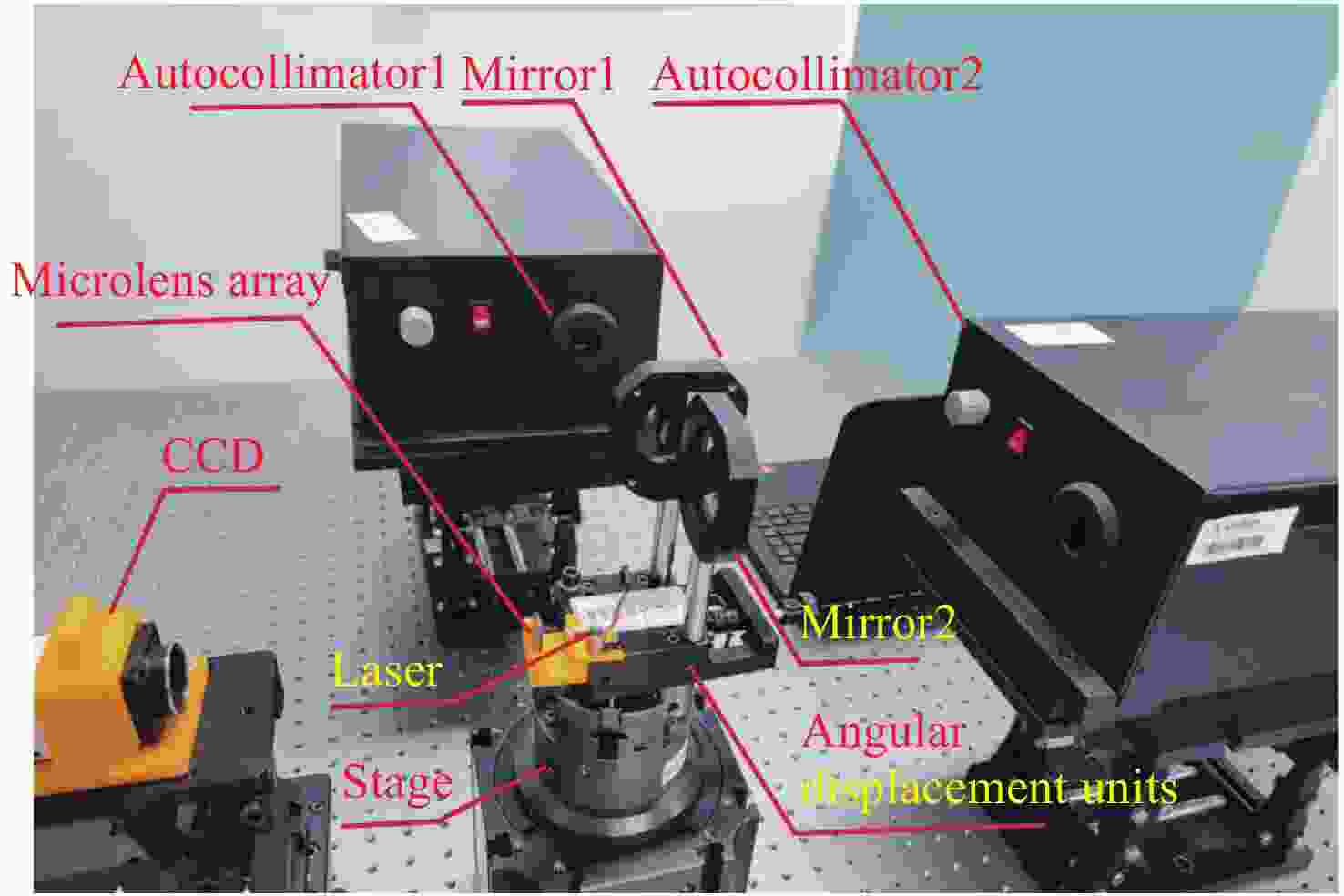
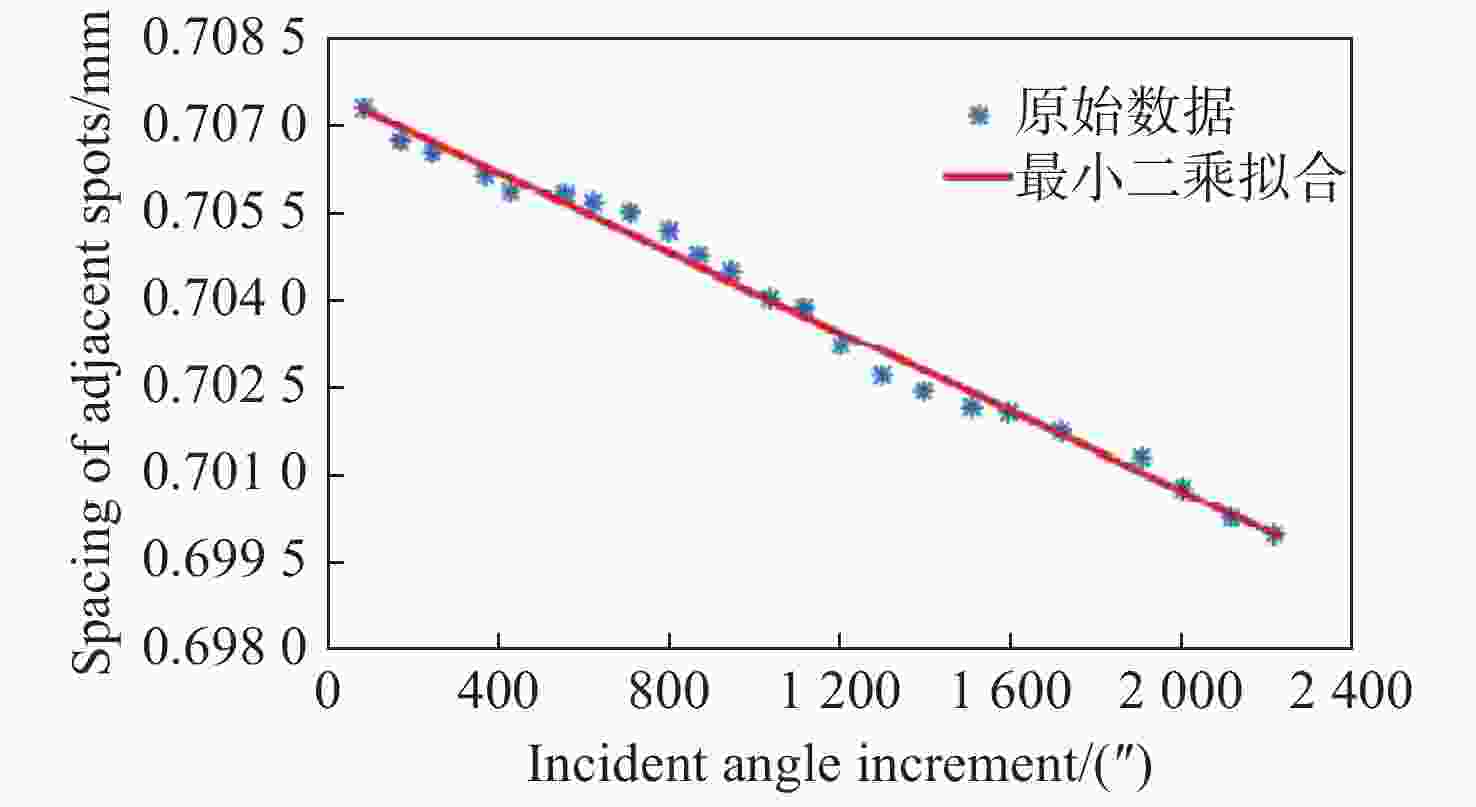
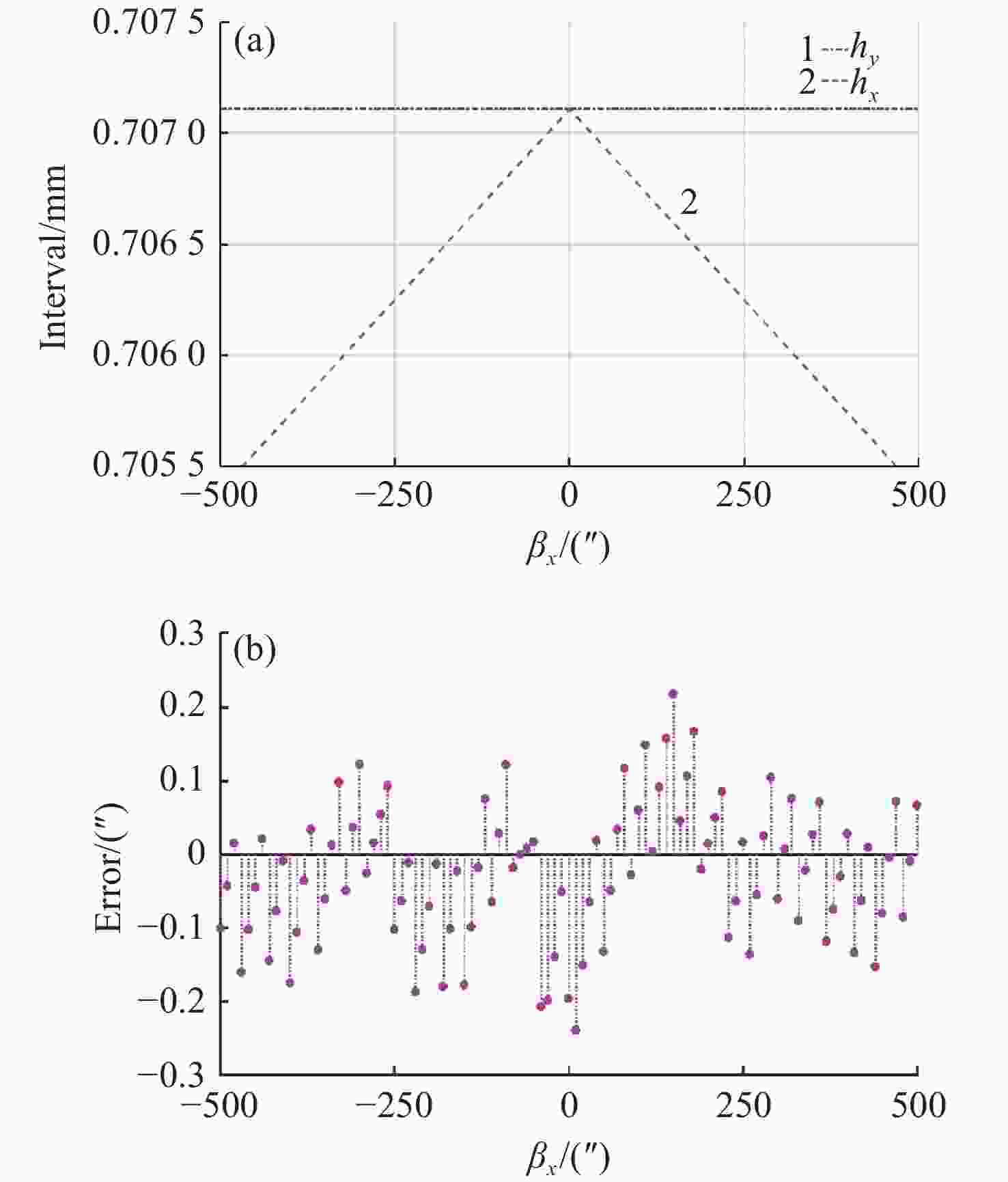
| [1] |
RAJ A A B, SELVI A J V, DURAI K D, et al. Intensity feedback-based beam wandering mitigation in free-space optical communication using neural control technique[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2014, 2014(1): 160. doi: 10.1186/1687-1499-2014-160
|
| [2] |
BAI SH, WANG J Y, QIANG J, et al. Predictive filtering-based fast reacquisition approach for space-borne acquisition, tracking, and pointing systems[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(22): 26462-26475. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.026462
|
| [3] |
HSIEH T H, CHEN P Y, JYWE W Y, et al. A geometric error measurement system for linear guideway assembly and calibration[J]. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 2019, 9(3): 574. doi: 10.3390/app9030574
|
| [4] |
HU P H, YU CH W, FAN K CH, et al. Error averaging effect in parallel mechanism coordinate measuring machine[J]. Applied Sciences, 2016, 6(12): 383. doi: 10.3390/app6120383
|
| [5] |
SCHERFF M L D, NUTTER J, FUSS-KAILUWEIT P, et al. Spectral mismatch and solar simulator quality factor in advanced LED solar simulators[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 56(8S2): 08MB24. doi: 10.7567/JJAP.56.08MB24
|
| [6] |
TANG SH ZH, WANG ZH, GAO J M, et al. Influence of tilt on collinear calibration of a laser interferometer[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(4): B46-B51. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.000B46
|
| [7] |
SAITO Y, WEI G, KIYONO S. A micro-angle sensor based on laser autocollimation[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 6052: 60520Q. doi: 10.1117/12.647981
|
| [8] |
廉孟冬, 金伟锋, 居冰峰. 二维光学自准直微角度传感器[J]. 机电工程,2010,27(12):23-26,35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2010.12.006LIAN M D, JIN W F, JU B F. 2D micro-angle sensor based on laser autocollimation[J]. Journal of Mechanical &Electrical Engineering, 2010, 27(12): 23-26,35. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2010.12.006
|
| [9] |
HSIEH H L, PAN S W. Development of a grating-based interferometer for six-degree-of-freedom displacement and angle measurements[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(3): 2451-2465. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.002451
|
| [10] |
陈琎, 杨程亮, 穆全全, 等. 基于琼斯矩阵的液晶偏振光栅扭曲角及厚度的测量方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2021,36(5):656-662. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0336CHEN J, YANG CH L, MU Q Q, et al. Method for measuring the twist angle and thickness of liquid crystal polarization grating based on Jones matrix[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2021, 36(5): 656-662. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0336
|
| [11] |
SABATYAN A, HOSEINI S A. Fresnel biprism as a 1D refractive axicon[J]. Optik, 2013, 124(21): 5046-5048. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.03.126
|
| [12] |
ZHANG E ZH, CHEN B Y, ZHANG H, et al. Note: comparison experimental results of the laser heterodyne interferometer for angle measurement based on the Faraday effect[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89(4): 046104. doi: 10.1063/1.5013630
|
| [13] |
WU Y M, CHENG H B, WEN Y F. High-precision rotation angle measurement method based on a lensless digital holographic microscope[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(1): 112-118. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.000112
|
| [14] |
YUAN J H, DAI P, LIANG D, et al. Grid deformation real-time measurement system of ion thruster based on videometrics[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(9): 1759. doi: 10.3390/app9091759
|
| [15] |
李娜, 姜志, 王军, 等. 基于Faster R-CNN的仪表识别方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2020,35(12):1291-1298. doi: 10.37188/YJYXS20203512.1291LI N, JIANG ZH, WANG J, et al. Instrument recognition method based on faster R-CNN[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2020, 35(12): 1291-1298. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/YJYXS20203512.1291
|
| [16] |
KONYAKHIN I, SAKHARIYANOVA A M, SMEKHOV A. Investigation vignetting beams in optoelectronic autocollimation angle measurement system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9526: 95260H.
|
| [17] |
CHEN Y L, SHIMIZU Y, TAMADA J, et al. Laser autocollimation based on an optical frequency comb for absolute angular position measurement[J]. Precision Engineering, 2018, 54: 284-293. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2018.06.005
|
| [18] |
樊华, 曹小文, 李臻赜, 等. 飞秒脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用
空间光场调控的微透镜阵列制备技术进展[J]. 液晶与显示,2021,36(6):827-840. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0334FAN H, CAO X W, LI ZH Z, et al. Progress in femtosecond laser fabrication of microlens array with spatial light modulators[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2021, 36(6): 827-840. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0334
|
| [19] |
SARKAR S K, BASURAY A, SENGUPTA K. A compound interferometer for angle measurement[J]. Optics Communications, 1992, 89(2-4): 153-158. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(92)90150-P
|
| [20] |
LI X J, HUI M, ZHAO ZH, et al. Differential computation method used to calibrate the angle-centroid relationship in coaxial reverse Hartmann test[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2018, 89(5): 053104. doi: 10.1063/1.5021313
|
| [21] |
SHAIKH S A, TONELLO A M. Radio source localization in multipath channels using EM lens assisted massive antennas arrays[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 9001-9012. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2891110
|
| [22] |
FUH Y K, LAI ZH H. A fast processing route of aspheric polydimethylsiloxane lenses array (APLA) and optical characterization for smartphone microscopy[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 385: 160-166. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.10.029
|
| [23] |
CHANG X F, XU K Y, XIE D, et al. Microforging technique for fabrication of spherical lens array mold[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 96(9-12): 3843-3850. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-1719-1
|
| [24] |
COPPOLA S, PAGLIARULO V, VESPINI V, et al. Direct fabrication of polymer micro-lens array[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10329: 103294Q.
|
| [25] |
LIU K H, CHEN M F, PAN C T, et al. Fabrication of various dimensions of high fill-factor micro-lens arrays for OLED package[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2010, 159(1): 126-134. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2010.02.020
|
| [26] |
吴从均, 颜昌翔, 刘伟. 像差对通信捕获光斑质心的影响分析[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用
,2013,40(10):1005004. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.1005004WU C J, YAN CH X, LIU W. Analysis of optical aberration impact on acquisition performance[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2013, 40(10): 1005004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.1005004
|
| [27] |
张艳艳, 郝晓龙, 陈洁玮. 加门限的一阶矩光斑质心探测方法[J]. 光学技术,2015,41(1):59-63. doi: 10.3788/GXJS20154101.0059ZANG Y Y, HAO X L, CHEN J W. First moment spot centroid detection with a threshold to compute the centroid[J]. Optical Technique, 2015, 41(1): 59-63. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/GXJS20154101.0059
|





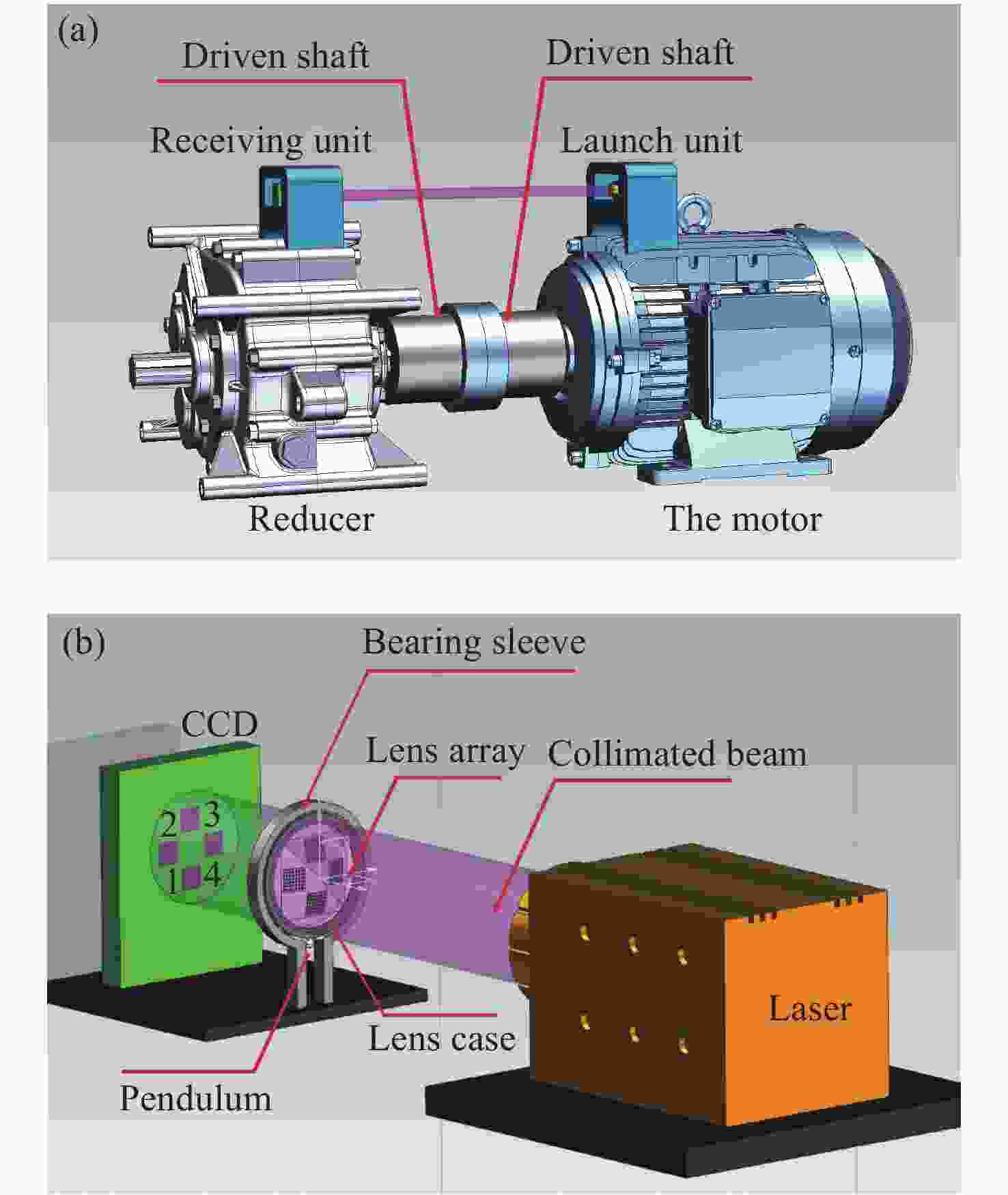
 下载:
下载: