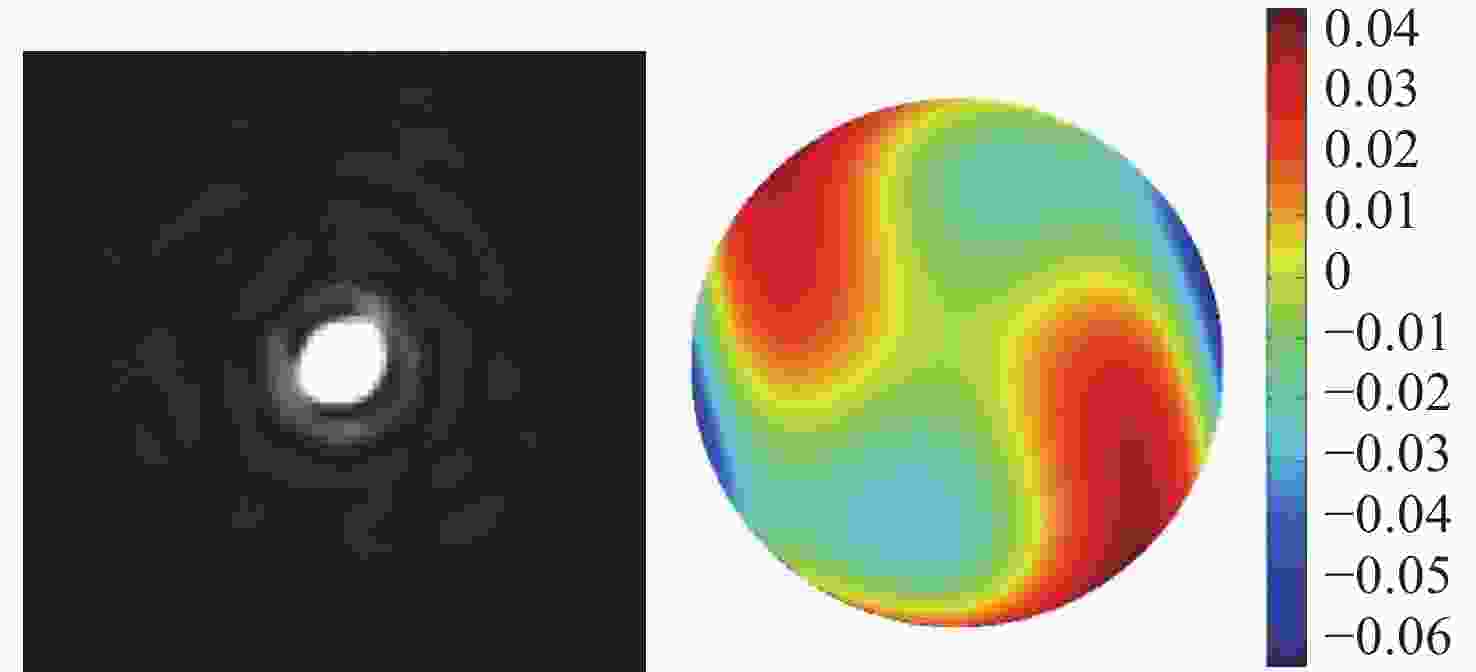Staticaberration correction technique for adaptive optics system based on focal-plane copy approach
-
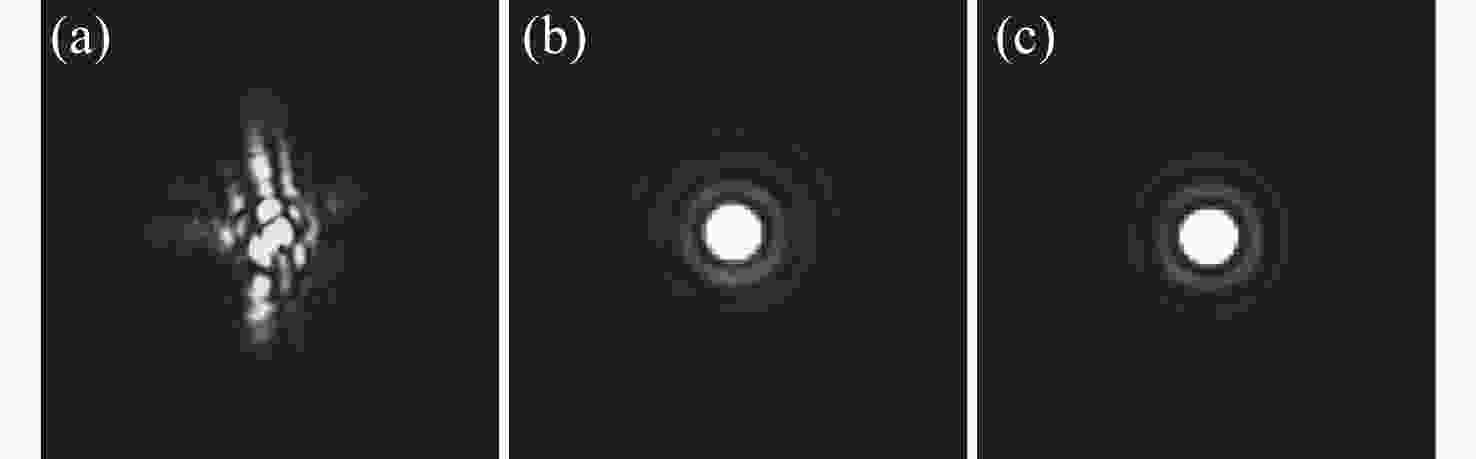
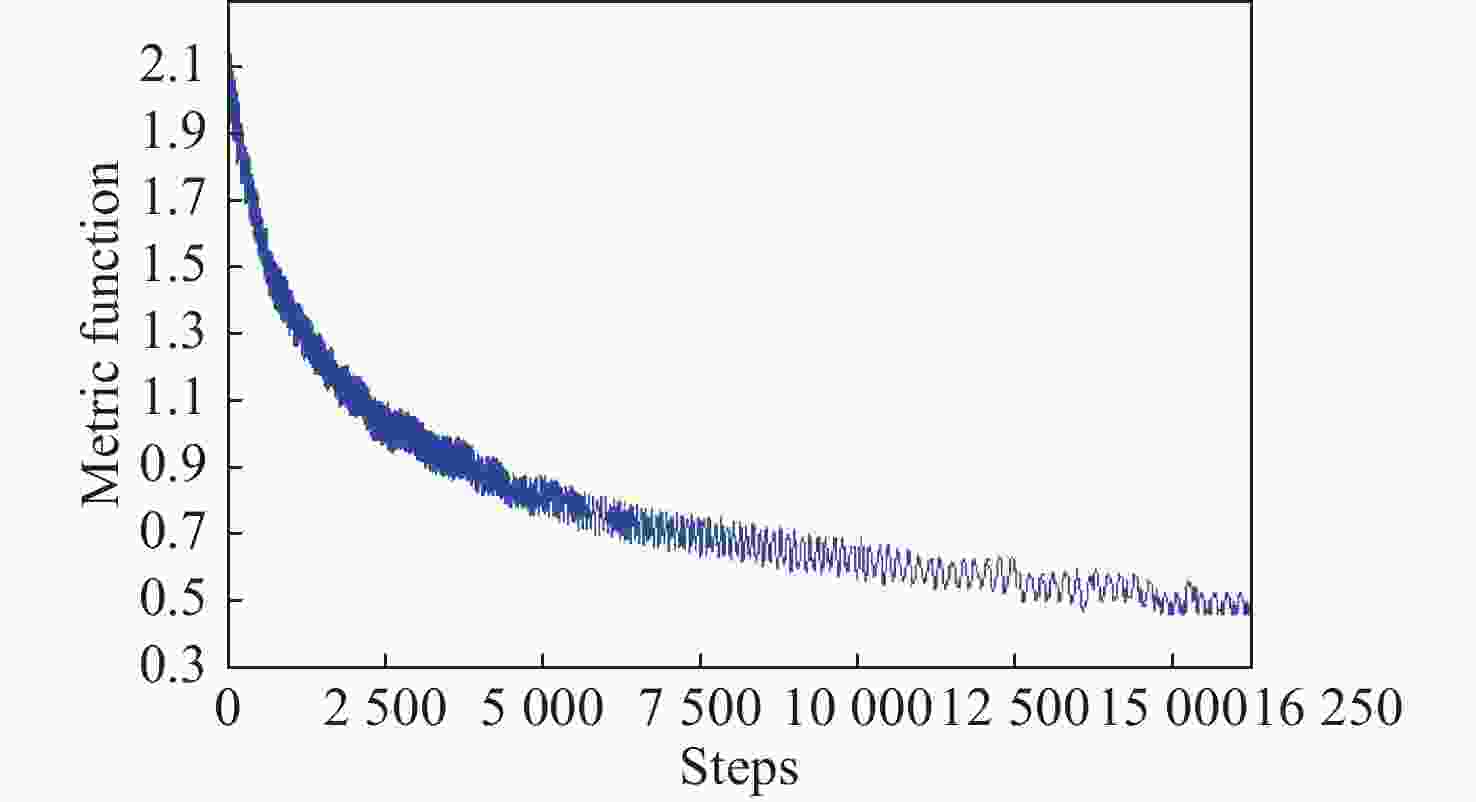
摘要: 限制自适应光学(Adaptive Optics, AO)系统表现的一个关键因素是由波前传感器所在路径和科学成像路径之间差异引起的非共光路像差(Non-Common Path Aberration,NCPA),同时AO系统共光路部分也会不可避免地引入静态像差。为此,本文提出了一种基于焦面点扩散函数(Point Spread Function,PSF)复制的技术,用于校正AO系统中的静态像差。此技术利用点光源产生的PSF图像作为参考图像,通过迭代优化算法控制可变形镜改变其面型,将参考PSF图像复制到AO系统科学成像路径。实验结果表明,校正后的斯特列尔比(Strehl Ratio,SR)从初始的0.312提高到0.995。此技术可以稳定、快速地获得全局校正结果,特别是在系统具有较大的初始静态像差时。Abstract: A key factor limiting the performance of Adaptive Optics (AO) systems is the Non-Common Path Aberration (NCPA) caused by the difference between the wavefront sensor path and the science imaging path. Meanwhile, a static aberration will inevitably be introduced in the common path of the AO system. This paper proposes a correction technology based on a copy of the focal-plane Point Spread Function (PSF) to correct static aberration in the scientific imaging path of AO systems. This technology uses the PSF generated by the laser point light source as the reference PSF, and copies that to the science imaging path of the AO system through iterative optimization algorithms. Experimental results show that the Strehl Ratio (SR) increases from the initial 0.312 to 0.995 after correction. This technology can still stably and quickly obtain global optimization results, especially when the initial static aberration of the system is large.
-
Key words:
- adaptive optics /
- aberration correction /
- high-contrast imaging
-
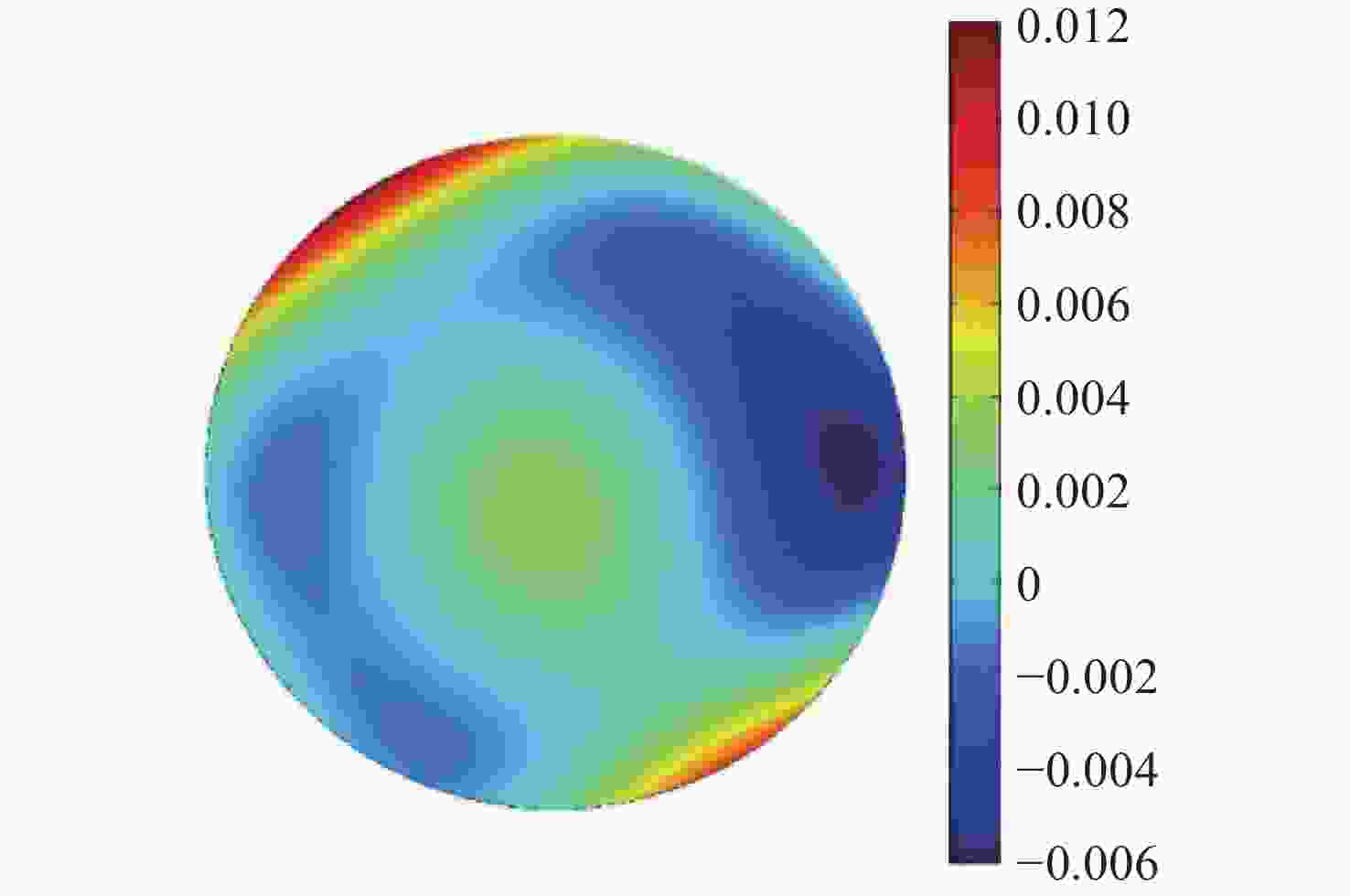
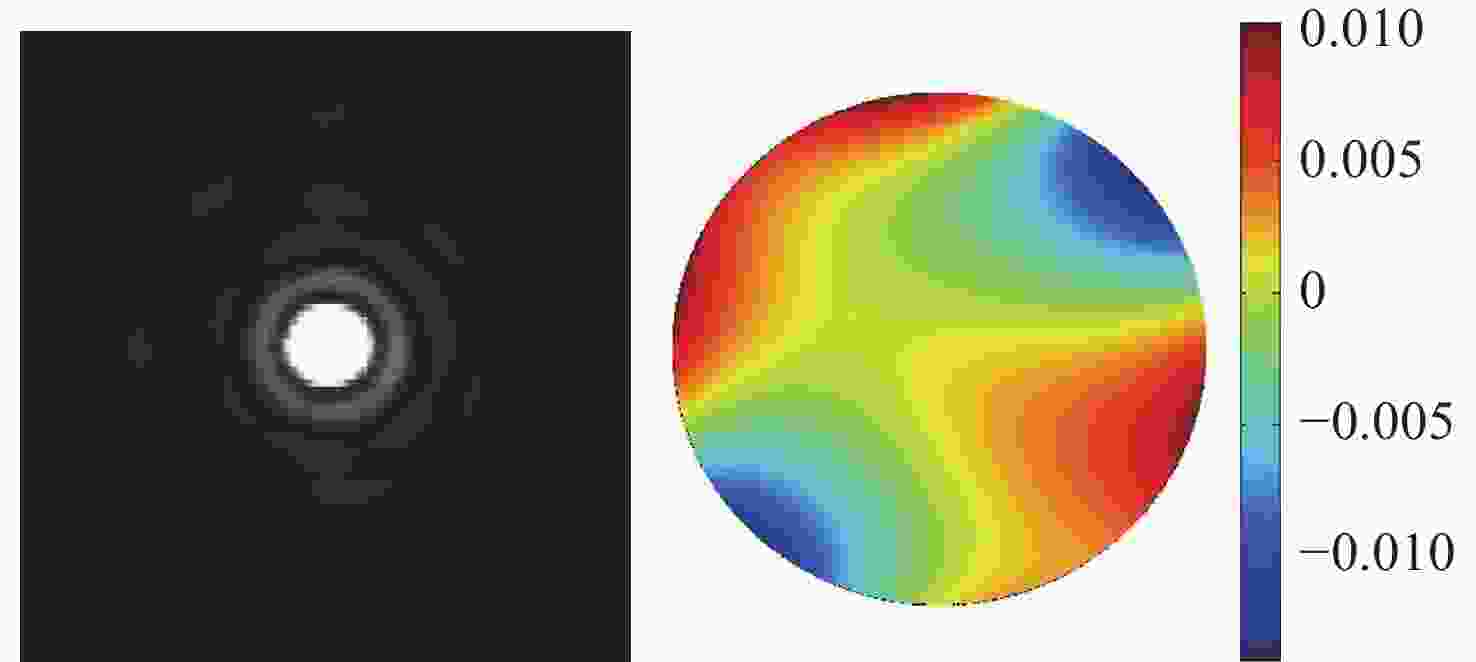
表 1 校正前后系统各项Zernike系数
Table 1. Zernike coefficients of the system before and after correction
Zernike多项式系数 校正前 校正后 Astigmatism y −0.029 0.001 Astigmatism x 0.127 -0.003 Trefoil y 0.013 0.000 Coma x −0.038 −0.002 Coma y −0.035 0.001 Trefoil x 0.028 −0.004 Tetrafoil y 0.009 −0.000 Secondary Astigmatism y −0.040 −0.000 Primary Spherical −0.061 0.003 Secondary Astigmatism x 0.035 0.000 Tetrafoil x 0.111 −0.002 表 2 3种方法校正后Zernike系数
Table 2. Zernike coefficients corrected by 3 kinds of methods
Zernike
多项式系数焦面能量
优化法瞳面
校正法焦面
复制技术Astigmatism y 0.039 0.009 0.001 Astigmatism x 0.003 0.002 −0.003 Trefoil y 0.001 0.002 0.000 Coma x 0.007 −0.002 −0.002 Coma y −0.008 −0.001 0.001 Trefoil x 0.006 0.000 −0.004 Tetrafoil y 0.005 0.001 −0.000 Secondary Astigmatism y −0.004 0.000 −0.000 Primary Spherical −0.004 0.001 0.003 Secondary Astigmatism x −0.034 −0.001 0.000 Tetrafoil x −0.013 0.005 −0.002 -
[1] ZHU Y T, DOU J P, ZHANG X, et al. Portable adaptive optics for exoplanet imaging[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2021, 21(4): 082. doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/21/4/82 [2] KHORRAMI Z, LANGLOIS M, VAKILI F, et al. Extreme adaptive optics astrometry of R136[J]. Astronomy &Astrophysics, 2021, 649: L8. [3] SAHU P, MAZUMDER N. Improving the way we see: adaptive optics based optical microscopy for deep-tissue imaging[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2021, 9: 654868. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2021.654868 [4] 郑贤良, 刘瑞雪, 夏明亮, 等. 液晶自适应光学视网膜校正成像技术研究[J]. 中国光学,2014,7(1):98-104.ZHENG X L, LIU R X, XIA M L, et al. Retinal correction imaging system based on liquid crystal adaptive optics[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(1): 98-104. (in Chinese) [5] CHEN Y W, HE Y, WANG J, et al. Automated cone cell identification on adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscope images based on TV-L1 optical flow registration and K-means clustering[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(5): 2259. doi: 10.3390/app11052259 [6] 刘立新, 张美玲, 吴兆青, 等. 自适应光学在荧光显微镜中的应用[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与光电子学进展,2020,57(12):120001.LIU L X, ZHANG M L, WU ZH Q, et al. Application of adaptive optics in fluorescence microscope[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(12): 120001. (in Chinese) [7] MILLER D T, KUROKAWA K. Cellular-scale imaging of transparent retinal structures and processes using adaptive optics optical coherence tomography[J]. Annual Review of Vision Science, 2020, 6: 115-148. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-030320-041255 [8] 朱沁雨, 韩国庆, 彭建涛, 等. 双波长视网膜成像自适应光学系统的轴向色差补偿方法[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(1):79-89. doi: 10.37188/CO.EN.2021-0009ZHU Q Y, HAN G Q, PENG J T, et al. Longitudinal chromatic aberration compensation method for dual-wavelength retinal imaging adaptive optics systems[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(1): 79-89. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.EN.2021-0009 [9] 潘国涛, 闫钰锋, 于信, 等. 矩形大口径金宝搏188软件怎么用 光束质量评价光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):306-317. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0130PAN G T, YAN Y F, YU X, et al. Design of optical system for quality evaluation of large rectangular aperture laser beam[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 306-317. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0130 [10] ANGEL J R P. Ground-based imaging of extrasolar planets using adaptive optics[J]. Nature, 1994, 368(6468): 203-207. doi: 10.1038/368203a0 [11] FUSCO T, SAUVAGE J F, PETIT C, et al. Final performance and lesson-learned of SAXO, the VLT-SPHERE extreme AO: from early design to on-sky results[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9148: 91481U. [12] POYNEER L A, PALMER D W, MACINTOSH B, et al. Performance of the Gemini Planet Imager's adaptive optics system[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(2): 323-340. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.000323 [13] HIPPLER S. Adaptive optics for extremely large telescopes[J]. Journal of Astronomical Instrumentation, 2019, 8(2): 1950001. doi: 10.1142/S2251171719500016 [14] BAUDOZ P, MAS M, GALICHER R, et al. Focal plane wavefront sensor sensitivity for ELT planet finder[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7736: 77365S. doi: 10.1117/12.858272 [15] 王亮, 陈涛, 刘欣悦, 等. 适用于波前处理器的自适应光学系统非共光路像差补偿方法[J]. 光子学报,2015,44(5):0511001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154405.0511001WANG L, CHEN T, LIU X Y, et al. Compensation of the non-common path aberrations in an adaptive optics system with a wavefront processor[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2015, 44(5): 0511001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154405.0511001 [16] REN D Q, DONG B, ZHU Y T, et al. Correction of non-common-path error for extreme adaptive optics[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2012, 124(913): 247-253. doi: 10.1086/664947 [17] REN D Q, ZHANG T Y, WANG G. A low-cost and high-performance technique for adaptive optics static wavefront correction[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2021, 21(7): 181. doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/21/7/181 [18] VORONTSOV M A, CARHART G W, RICKLIN J C. Adaptive phase-distortion correction based on parallel gradient-descent optimization[J]. Optics Letters, 1997, 22(12): 907-909. doi: 10.1364/OL.22.000907 [19] VORONTSOV M A, SIVOKON V P. Stochastic parallel-gradient-descent technique for high-resolution wave-front phase-distortion correction[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1998, 15(10): 2745-2758. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.15.002745 [20] VORONTSOV M A, YU M. Compensation of distant phase-distorting layers. II. Extended-field-of-view adaptive receiver system[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2004, 21(9): 1659-1668. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.21.001659 -





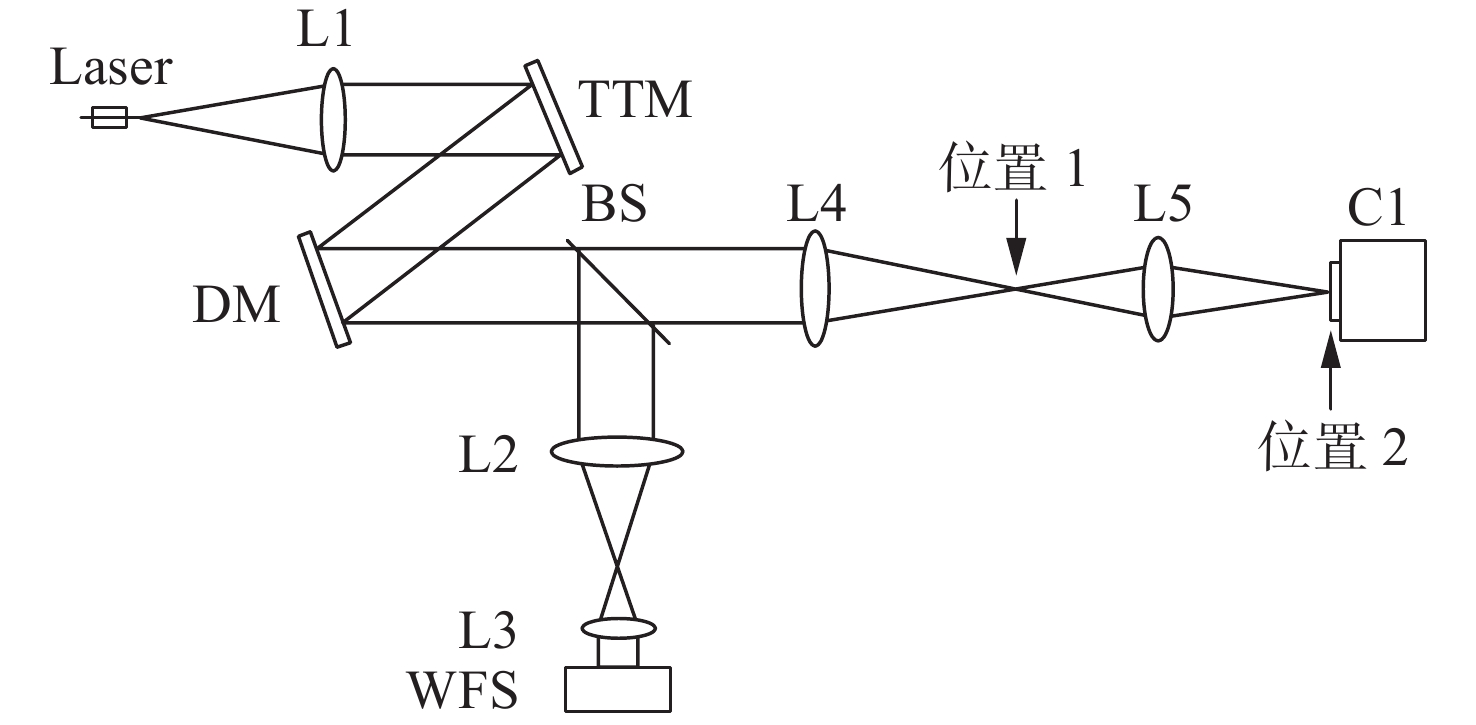
 下载:
下载: