Electrostatic discharge failure characteristics of oxide vertical cavity surface emitting lasers
-
摘要:
氧化型垂直腔面发射金宝搏188软件怎么用 器(VCSEL)在数据通信等领域具有广泛的应用,然而氧化型VCSEL是一种静电敏感型器件,静电放电(ESD)是导致其失效的主要原因之一,并且器件失效后很难判断问题的原因。本文对氧化型VCSEL进行了包括人体模式(HBM)、机器模式(MM)和元件充电模式(CDM)3种不同的ESD模式和过度电应力(EOS)冲击,以分析其具体失效原因。其中,在HBM模式中研究了不同极性的电压冲击对应的失效特征,然后分别采用反向I-V、正向L-I-V测试、发光显微镜(EMMI)和透射电子显微镜(TEM)等手段进行表征。结果表明,不同ESD模式表现出截然不同的损伤电压阈值,氧化型VCSEL容易遭受HBM和MM损伤,而对CDM模式不敏感。研究发现和ESD失效关联的特性及缺陷特征包括反向漏电增加、出光功率衰减、EMMI亮点等,而TEM作为最为直接有效的分析手段,不同ESD模式表现出不同的缺陷大小和位置等性质。这些研究结果有助于区分ESD故障和其它故障机制,并且能够精确地判断出引起失效的具体ESD模式,具有重要的意义。
-
关键词:
- 垂直腔面发射金宝搏188软件怎么用 器 /
- 静电放电(ESD) /
- 失效分析
Abstract:Oxide Vertical Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) are widely used in data communication. However, VCSELs are sensitive to ElectroStatic Discharge (ESD), which is one of the main reasons for their failure. It is difficult to identify the root cause of this problem. Therefore, 3 different ESD models including Human Body Model (HBM), Machine Model (MM) and Charge Device Model (CDM) and Electrical OverStress (EOS) shocks were applied to carry out the failure analysis of oxide VCSELs. Among them, voltage shocks of different polarities were used for HBM while reverse I-V, forward L-I-V scan, emission microscopy (EMMI) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) were used for characterization. The results show that different ESD models show significantly different damage voltage thresholds, and the oxide VCSEL is susceptible to damage in the HBM and MM models but insensitive in the CDM model. Defect characteristics associated with ESD failure were found including increased reverse leakage, degradation of optical output power, and bright spots in the EMMI. TEM was the most direct and effective method where different ESD events showed different defect sizes and locations. These research results are of great significance to confirm whether the failure mode is caused by ESD and to judge the specific ESD models in detail.
-
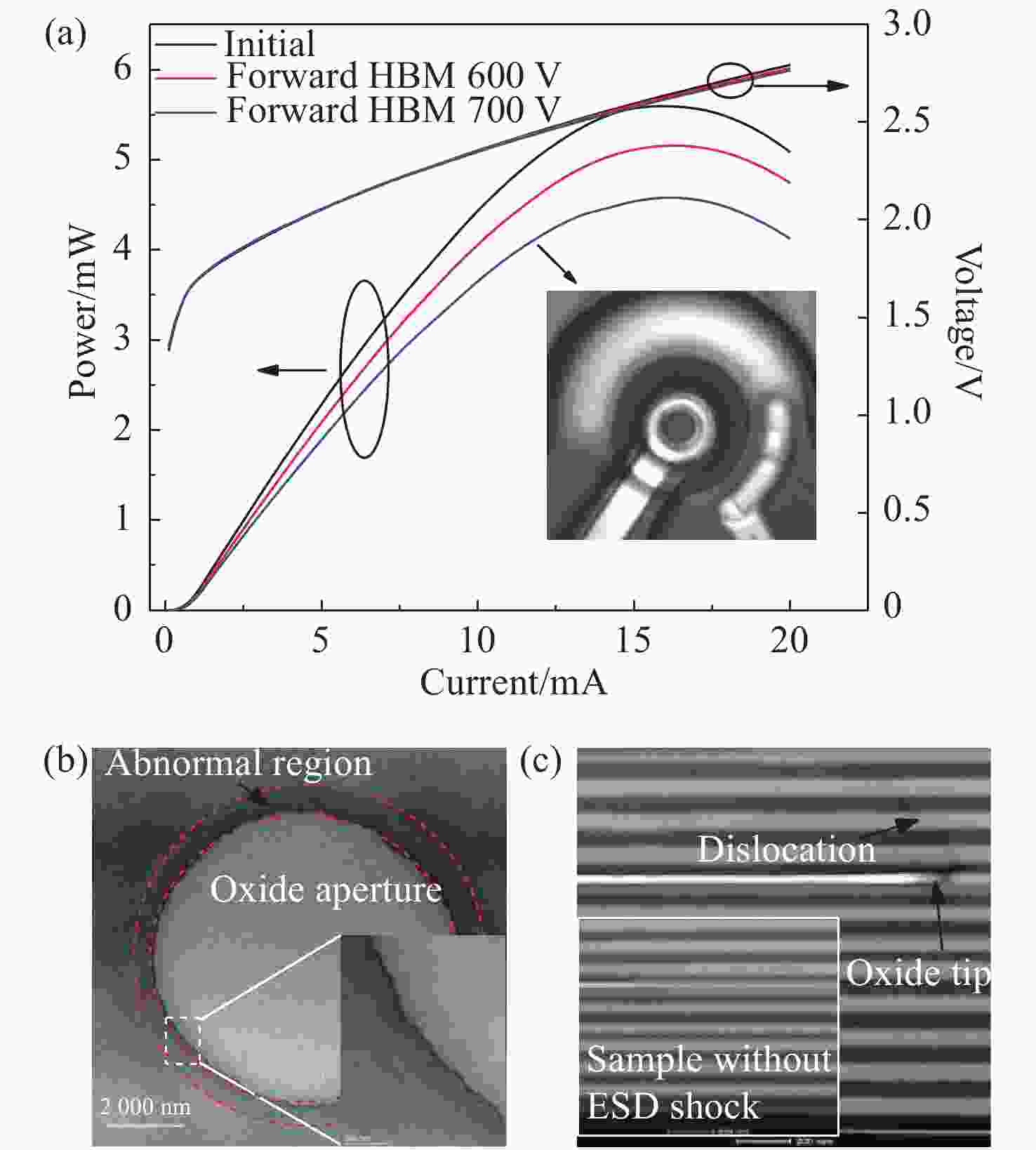
图 2 (a)正向HBM模式冲击前后L-I-V曲线对比(插图为700 V冲击电压下对应的EMMI图像);(b)正向HBM 700 V冲击后失效样品的PV-TEM(插图为白色虚框部分的放大图)和(c)XS-TEM(插图为未经ESD冲击样品的氧化层尖端附近的XS-TEM)
Figure 2. (a) Comparison of L-I-V curve before and after forward HBM shock. Inset is an EMMI image under 700 V impulse voltage. (b) PV-TEM, the insert is an enlarged view of the white dotted part and (c) XS-TEM after forward HBM shock under 700 V impulse voltage, the insert is XS-TEM near the oxide tip of sample without an ESD shock
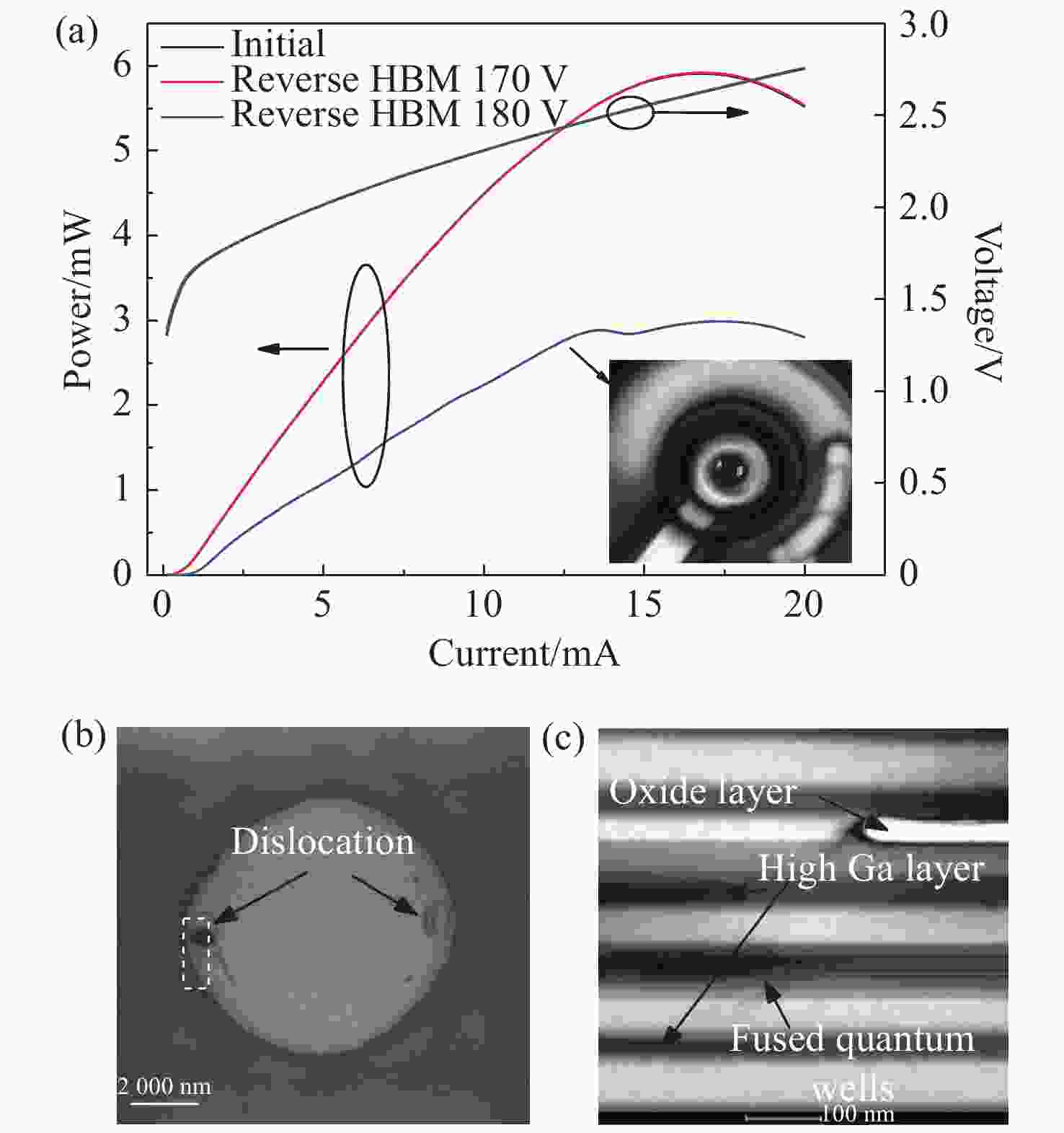
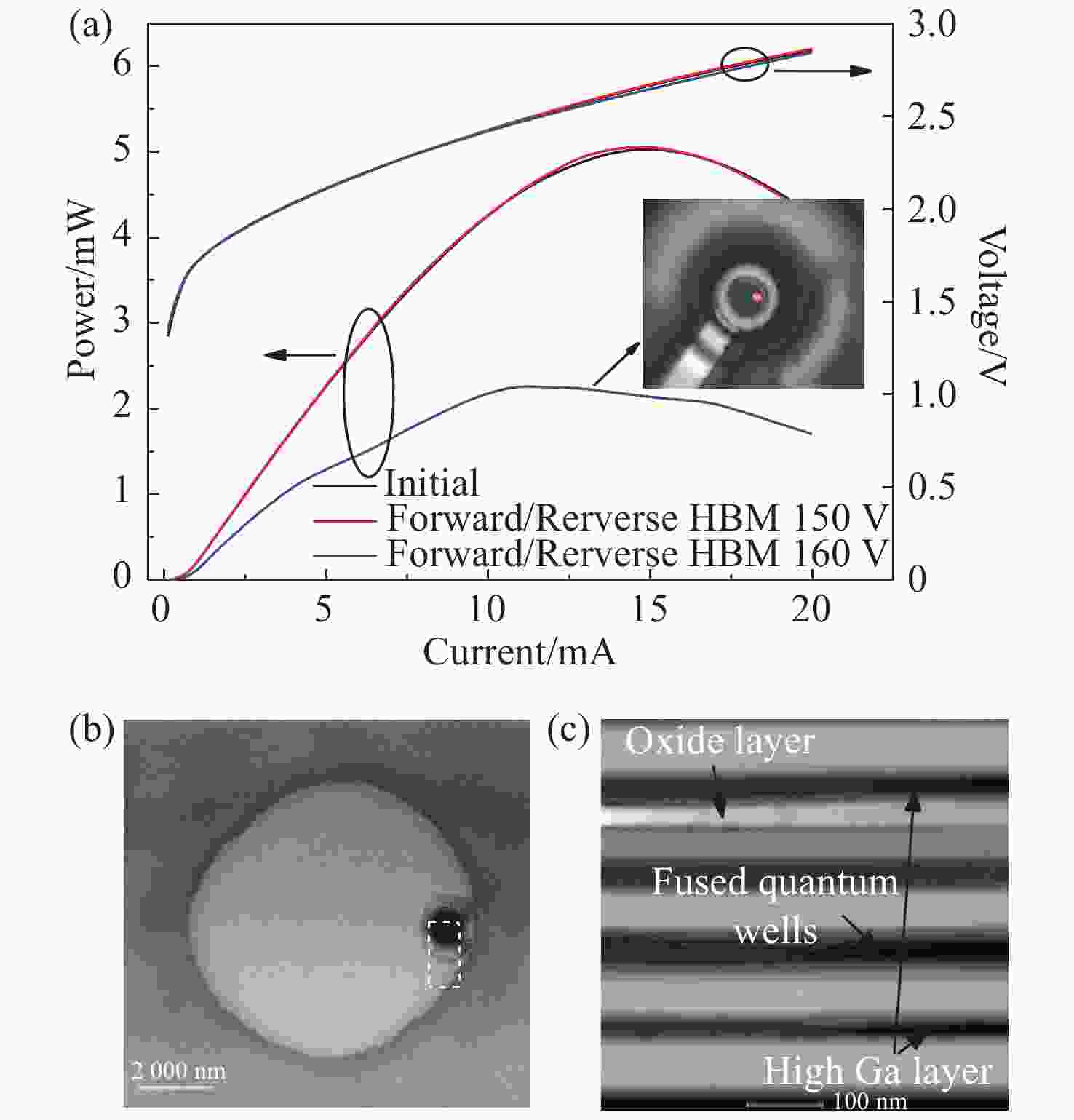
图 4 (a)正/反向HBM模式冲击前后L-I-V曲线对比,插图为160 V冲击电压对应的EMMI图像;正反向HBM 160 V冲击电压下(b)PV-TEM和(c)XS-TEM结果
Figure 4. (a) Comparison of L-I-V curve before and after forward/reverse HBM shock. The insert is an EMMI image under 160 V impulse voltage. (b) PV-TEM and (c) XS-TEM after forward/reverse HBM shock under an 160 V impulse voltage
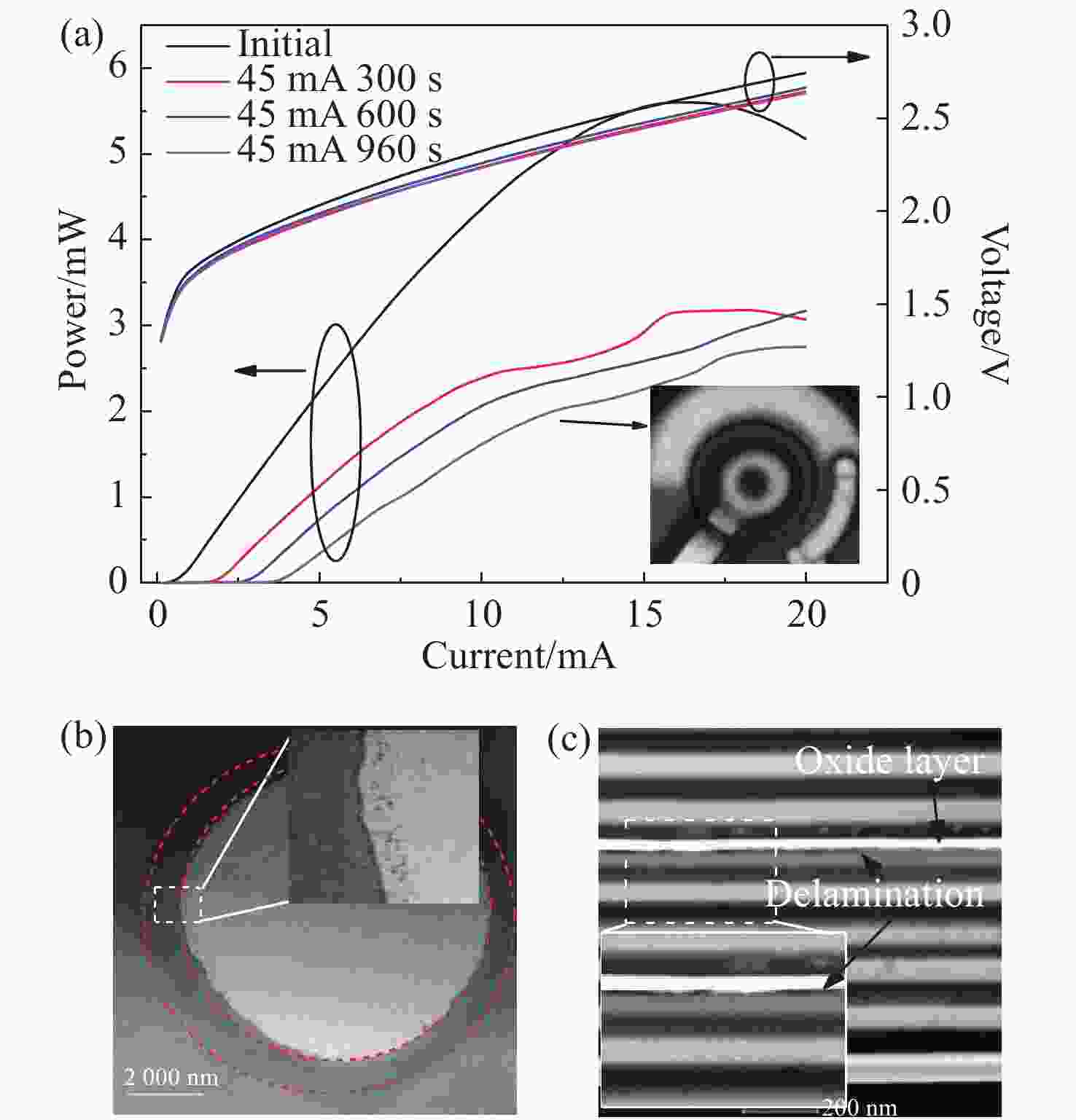
图 7 (a)EOS模式冲击前后L-I-V曲线对比,插图为45 mA 960 s对应的EMMI图像以及相应的(b)PV-TEM和(c)XS-TEM,插图为局部放大图
Figure 7. (a) Comparison of L-I-V curve before and after EOS shock. The inset is an EMMI image under a 45 mA 960 s surge; (b) PV-TEM and (c) XS-TEM after EOS shock under a 45 mA 960 s surge. The inserts are partial enlarged views.
表 1 氧化型VCSEL中不同ESD模式的失效特征汇总
Table 1. Summary of failure characteristics corresponding to different ESD models in oxide VCSELs
ESD模式 损伤阈值 光电特性 EMMI和TEM失效特征 可能的失效机理 正向HBM 700 V 出光功率逐渐下降,阈值小幅度增加,反向漏电不变,高电流下电压微降 EMMI无亮点;器件内部无集中的击穿位错,在氧化孔边缘出现位错,有源区未出现明显的损伤 焦耳热产生的过量热应力导致在应力集中的氧化尖端出现位错;
氧化层对该ESD模式的脉冲表现为电阻特性反向HBM −180 V 出光功率快速下降,阈值增加,反向漏电变大,正向I-V特性无明显变化 EMMI有亮点,和TEM集中的击穿位错位置吻合;比正向HBM模式的位错密度高,击穿位错出现在靠近氧化孔边缘的出光孔内,有源区出现局部融合现象,DBR中含高镓层的缺陷较为严重 隧道击穿效应;
氧化层对该ESD模式的脉冲表现为电阻特性正/反向HBM ±160 V 出光功率快速下降,阈值增加,反向漏电变大,高电流下电压微增 EMMI有亮点,和TEM集中的击穿位错位置吻合;与反向HBM失效特征相似,位错大小为微米量级,氧化孔边缘和有源区出现永久性损伤 隧道击穿和热的累积效应;
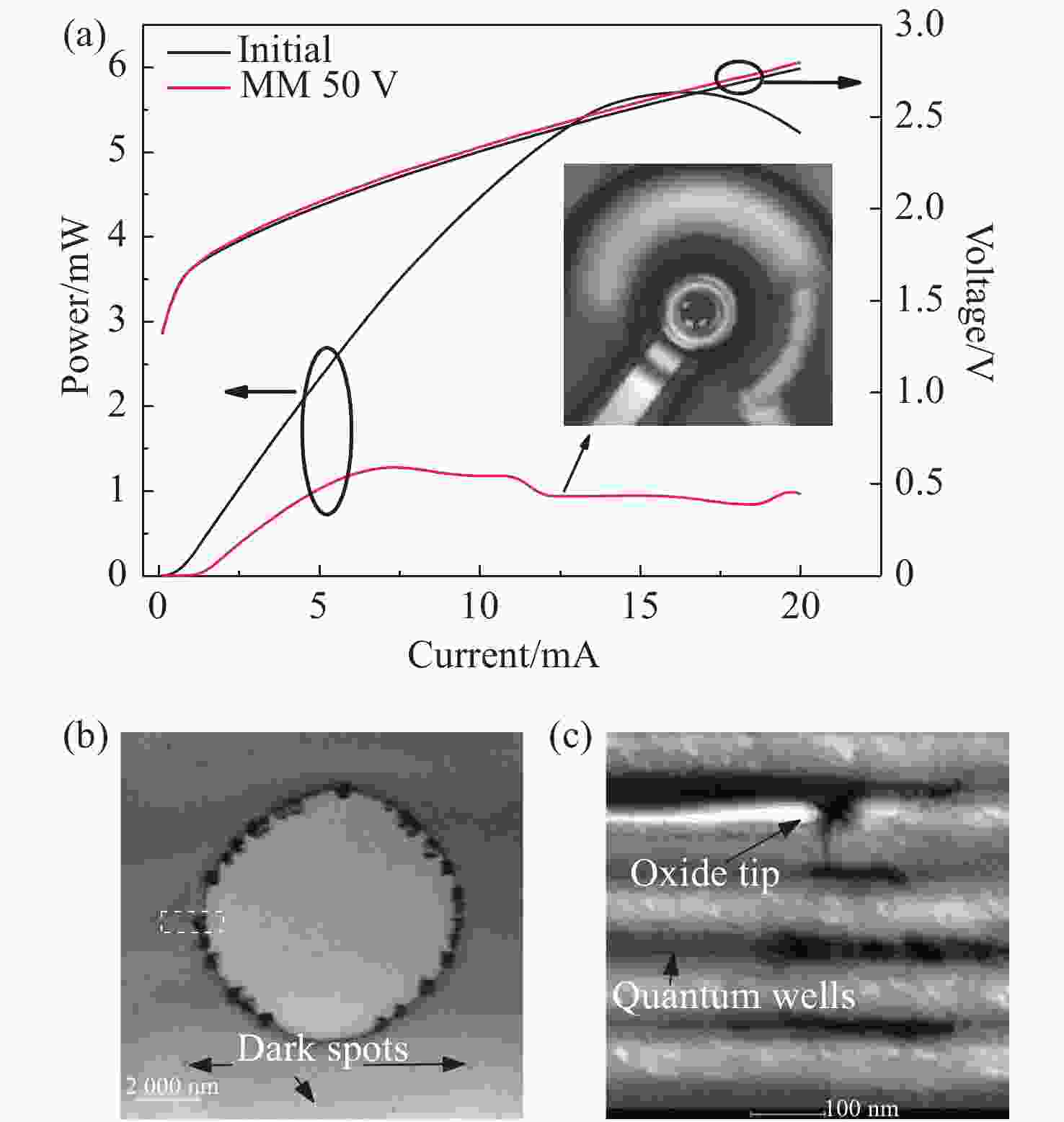
氧化层对该ESD模式的脉冲表现为电阻特性MM 50 V 出光功率快速下降,阈值增加,反向漏电变大,正向电压增加 EMMI有亮点,和TEM集中的击穿位错位置吻合;氧化孔边缘的两侧出现大量位错,直径大小为数百纳米量级。位错从氧化层以上延伸到有源区,高镓含量层位错密度较高。有时会出现轻微的氧化层介质击穿现象 隧道击穿效应;
氧化层相对于该ESD模式的脉冲表现为部分电容特性部分电阻特性CDM 2000 V L-I-V特性基本不变,高电流时出光功率微降,阈值不变,反向漏电微增,正向电压下降 EMMI无亮点;器件内部无集中的击穿位错,整个氧化层出现介质击穿,分布在氧化孔的周围,并呈现出环状图案。在氧化孔边缘和有源区未观察到明显的缺陷 介质击穿;
氧化层相对于该ESD模式的脉冲等效为电容特性EOS / 出光功率逐渐下降,阈值增加,反向漏电增大,正向电压下降 EMMI无亮点;器件内部无集中的击穿位错,高电流密度的应力驱动下,氧化孔边缘出现暗点缺陷和分层现象 焦耳热产生的过量热应力 -
[1] 张继业, 李雪, 张建伟, 等. 垂直腔面发射金宝搏188软件怎么用 器研究进展[J]. 发光学报,2020,41(12):1443-1459. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20200339ZHANG J Y, LI X, ZHANG J W, et al. Research progress of vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2020, 41(12): 1443-1459. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJL.20200339 [2] 杨卓凯, 田思聪, LARISCH G, 等. 基于PAM4调制的高速垂直腔面发射金宝搏188软件怎么用 器研究进展[J]. 发光学报,2020,41(4):399-413. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20204104.0399YANG ZH K, TIAN S C, LARISCH G, et al. High-speed vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers based on PAM4 modulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2020, 41(4): 399-413. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20204104.0399 [3] 何晓颖, 董建, 胡帅, 等. 采用BCB平整技术的高速850nm垂直面发射金宝搏188软件怎么用 器[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(2):190-197. doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0190HE X Y, DONG J, HU SH, et al. High-speed 850 nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers with BCB planarization technique[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(2): 190-197. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0190 [4] 张玉岐, 左致远, 阚强, 等. 氧化型垂直腔面发射金宝搏188软件怎么用 器的常见失效模式和机理分析[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):187-209. doi: 10.37188/CO.EN.2021-0012ZHANG Y Q, ZUO ZH Y, KAN Q, et al. Common failure modes and mechanisms in oxide vertical cavity surface emitting lasers[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 187-209. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.EN.2021-0012 [5] HELMS C J, AEBY I, LUO W L, et al. Reliability of oxide VCSELs at Emcore[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5364: 183-189. doi: 10.1117/12.539282 [6] KRUEGER J J, SABHARWAL R, MCHUGO S A, et al. Studies of ESD-related failure patterns of Agilent oxide VCSELs[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4994: 162-172. doi: 10.1117/12.482632 [7] 张建华, 陈章福, 徐小雪, 等. 人体静电放电对有机发光二极管的影响[J]. 发光学报,2018,39(2):169-174. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183902.0169ZHANG J H, CHEN ZH F, XU X X, et al. Analysis of organic light emitting diode under electrostatic discharge stresses[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(2): 169-174. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183902.0169 [8] UEDA O. Reliability and degradation of III-V optical devices focusing on gradual degradation[M]//UEDA O, PEARTON S J. Materials and Reliability Handbook for Semiconductor Optical and Electron Devices. New York, NY: Springer, 2013: 87-122. [9] HSU C L, DAS S, WU Y S, et al. Spectrally resolved optical beam-induced current imaging of ESD induced defects on VCSELs[J]. OSA Continuum, 2021, 4(2): 711-719. doi: 10.1364/OSAC.414086 [10] VANZI M, MURA G, MARCELLO G, et al. ESD tests on 850 nm GaAs-based VCSELs[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2016, 64: 617-622. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2016.07.023 [11] MCHUGO S A, KRISHNAN A, KRUEGER J J, et al. Characterization of failure mechanisms for oxide VCSELs[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4994: 55-66. doi: 10.1117/12.482637 [12] MATHES D, GUENTER J, TATUM J, et al. AOC moving forward: the impact of materials behavior[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6132: 613203. doi: 10.1117/12.646447 [13] GUENTER J K, TATUM J A, HAWTHORNE III R A, et al. VCSELs at Honeywell: the story continues[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5364: 34-46. doi: 10.1117/12.540129 [14] WEIDBERG A R. VCSEL reliability in ATLAS and development of robust arrays[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2012, 7: C01098. [15] MATHES D T, GUENTER J, HAWKINS B, et al. . An atlas of ESD failure signatures in vertical cavity surface emitting lasers[C]. Proceedings of ISTFA, ISTFA, 2005: 330-336. [16] UEDA O, HERRICK R W. Failure analysis of semiconductor optical devices[M]//UEDA O, PEARTON S J. Materials and Reliability Handbook for Semiconductor Optical and Electron Devices. New York: Springer, 2013: 19-53. [17] MOKHTARI M, PAGNOD-ROSSIAUX P, LEVALLOIS C, et al. Mechanical strain mapping of GaAs based VCSELs[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 118(9): 091102. doi: 10.1063/5.0040386 [18] MUKHERJEE K. Materials science of defects in GaAs-based semiconductor lasers[M]//HERRICK R W, UEDA O. Reliability of Semiconductor Lasers and Optoelectronic Devices. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2021: 113-176. [19] GUENTER J K, TATUM J A, HAWTHORNE III R A, et al. A plot twist: the continuing story of VCSELs at AOC[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5737: 20-34. doi: 10.1117/12.601831 [20] HUANG J J SH, JAN Y H, CHANG H S, et al. . ESD polarity effect study of monolithic, integrated DFB-EAM EML for 100/400G optical networks[C]. Proceedings of 2017 Conference on Lasers and Electro-optics Pacific Rim, IEEE, 2017: 1-4. [21] HUANG J S. Reliability of optoelectronics[M]//SWINGLER J. Reliability Characterisation of Electrical and Electronic Systems. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2015: 83-114. [22] HUANG J SH, OLSON T, ISIP E. Human-body-model electrostatic-discharge and electrical-overstress studies of buried-heterostructure semiconductor lasers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Device and Materials Reliability, 2007, 7(3): 453-461. doi: 10.1109/TDMR.2007.907425 [23] TWU Y, CHENG L S, CHU S N G, et al. Semiconductor laser damage due to human-body-model electrostatic discharge[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 74(3): 1510-1520. doi: 10.1063/1.354850 [24] MEIER H, SANTSCHI R, ODERMATT S, et al. A TCAD approach to robust ESD design in oxide-confined VCSELs[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6484: 648405. doi: 10.1117/12.698997 -





 下载:
下载: