-
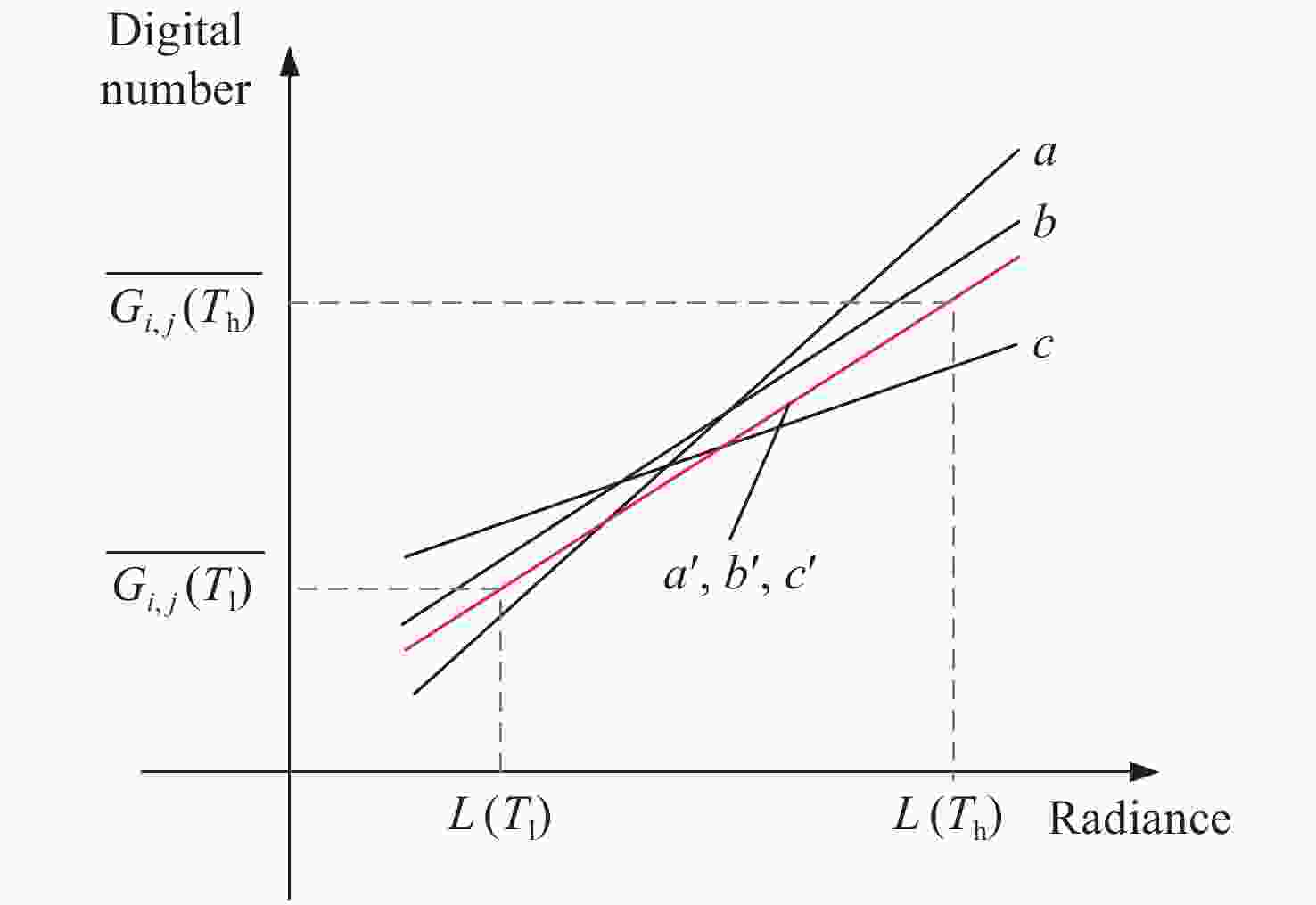
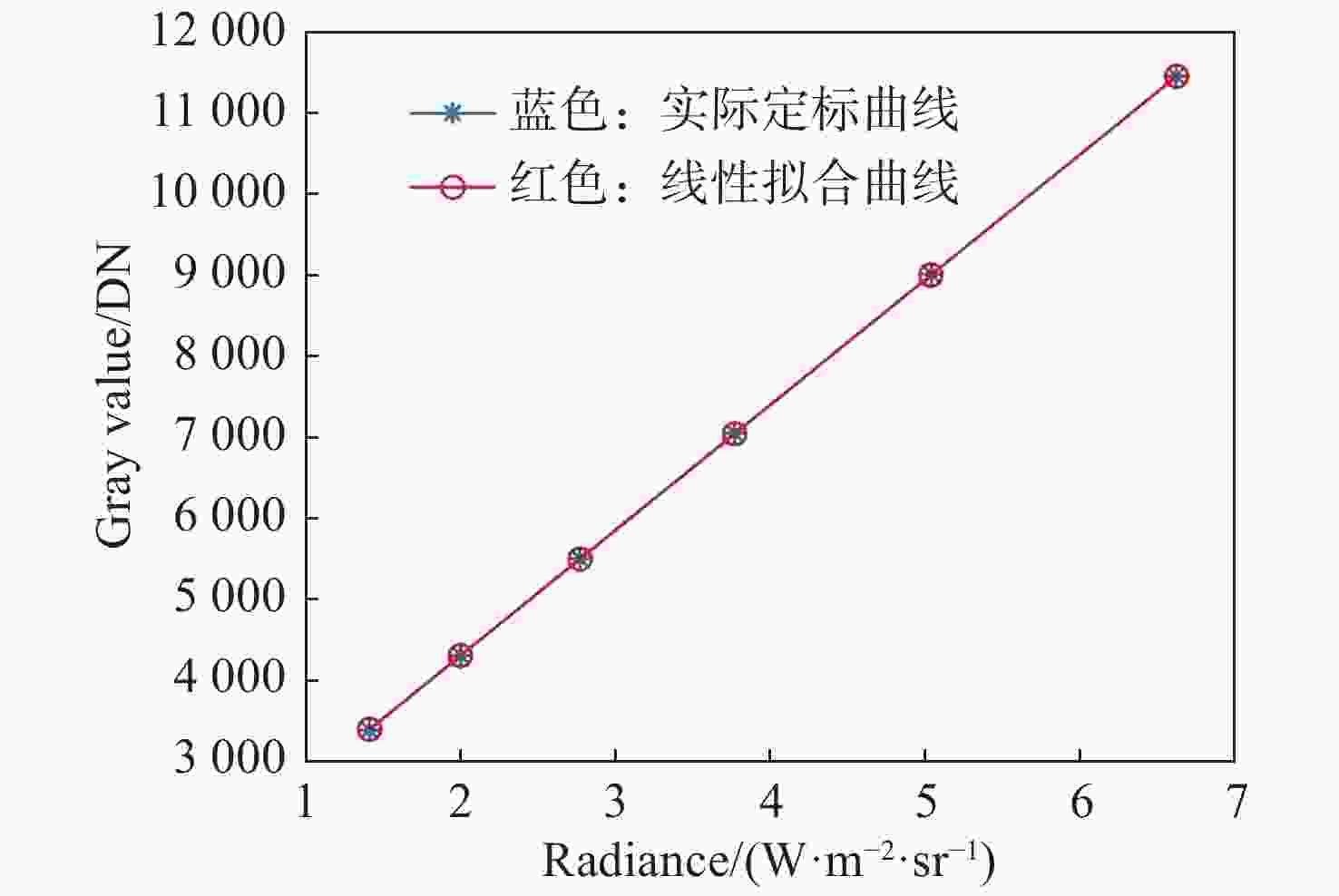
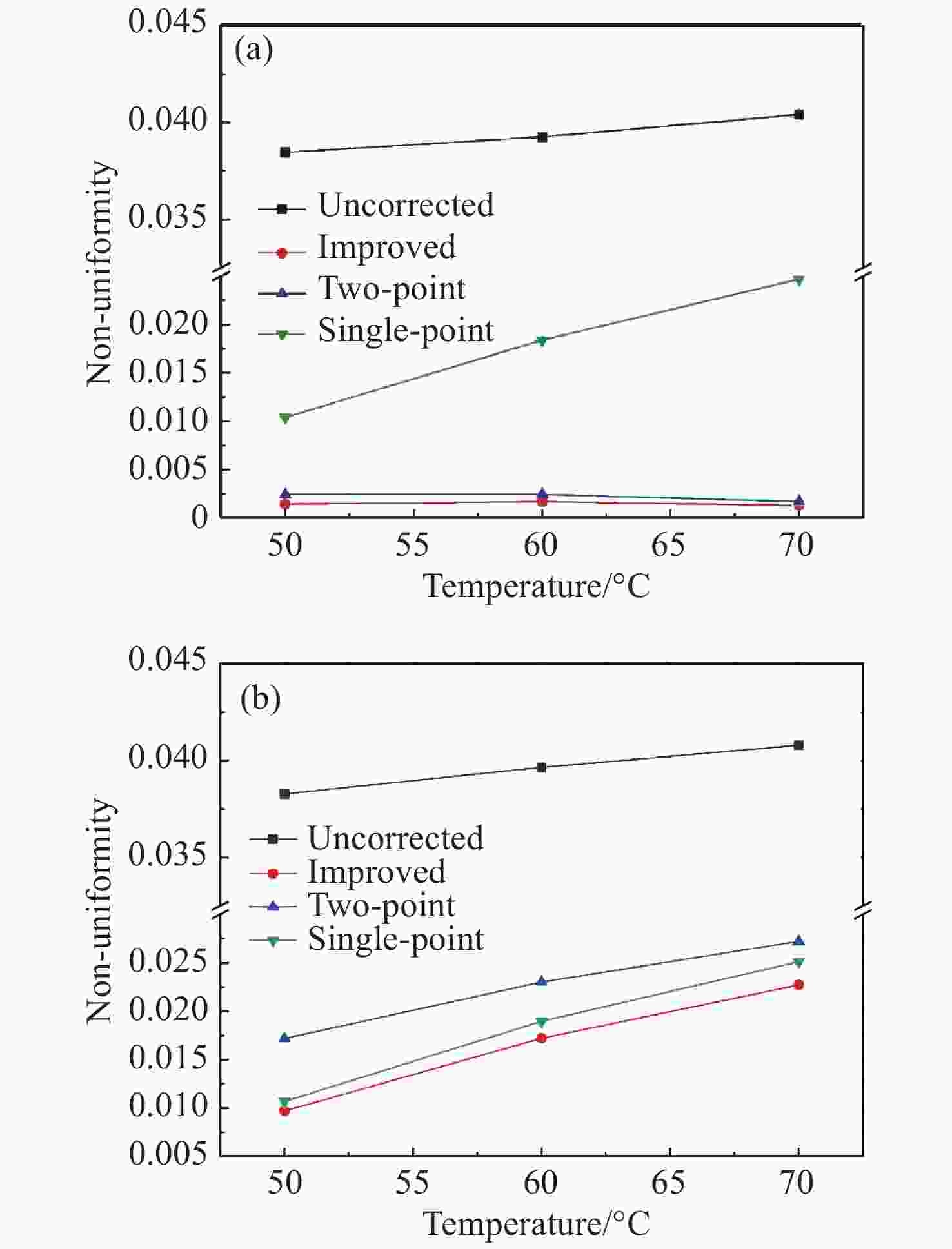
摘要: 红外辐射测量系统的成像性能以及测量精度受到焦平面阵列非均匀性的严重影响,原始红外图像的非均匀性需通过后期图像处理算法进行校正。为进一步提高制冷型红外探测器的非均匀性校正(NUC)效果,本文提出了一种基于定标的非均匀性改进算法。该算法以单点定标和两点定标非均匀性校正方法为基础,既保留两点定标非均匀性校正方法增益校正系数的一致性优势,又结合了单点定标偏置校正系数的稳定性,使得改进算法具有更好的校正效果。为了验证该改进算法的校正效果,本文以640 pixel×512 pixel大小的制冷型中波红外探测器为研究对象,采用入瞳直径为25 mm的红外成像系统对提出的算法进行实验验证。实验结果表明:在1 ms积分时间下,单点定标方法、两点定标方法及改进算法校正后的图像非均匀性分别为1.7833%、0.2190%和0.1481%;2 ms积分时间下的非均匀性分别为1.8257%、2.2474%和1.6546%。改进算法整体上进一步降低了图像的非均匀性,校正效果更好、精度更高。Abstract: The imaging performance and measurement accuracy of infrared radiation measurement systems are seriously affected by the non-uniformity of the focal plane array. Therefore, the non-uniformity of the raw infrared image needs to be corrected by the image processing algorithm. In order to further improve the Non-Uniformity Correction (NUC) effect of cooled infrared detectors, an improved non-uniformity algorithm based on calibration is proposed in this paper. The algorithm is based on the single-point calibration and the two-point calibration NUC methods, which not only retains the consistency advantage of the two-point calibration NUC method in gain correction coefficient, but also combines the stability of the single-point calibration in the offset correction coefficient. The improved algorithm has a better correction effect. In order to verify the correction effect of the improved algorithm, a cooled medium wave infrared detector with a size of 640 pixel×512 pixel is taken as the research object, and an infrared imaging system with a pupil diameter of 25 mm is used to verify the performance of the proposed algorithm. The experimental results show that under the 1ms integral time, the single-point calibration method, the two-point calibration method and the improved algorithm correct the image's non-uniformity to 1.7833%, 0.2190% and 0.1481%, respectively. And under the 2 ms integral time,they correct the image's non-uniformity to 1.8257%, 2.2474% and 1.6546%, respectively. The improved algorithm further reduces the image's non-uniformity more effectively, so it's correction effect is better and the accuracy is higher.
-
表 1 制冷型红外相机参数
Table 1. Parameters of cooled infrared camera
Parameters Requirement Materials HgCdTe Spectral range 3.7 µm~4.8 µm Aperture f/2 Pixel size 15 µm×15 µm Pixel depth 14 Resolution 640(H)×512(V) Operating temperature −40 °C~+60 °C 表 2 面源黑体参数
Table 2. Parameters of area source blackbody
Parameters Requirement Blackbody emitter size 100 mm×100 mm Temp. range 0 °C ~125 °C Set point resolution 0.001 °C Emissivity 0.98±0.02 Operating temp. head −20 °C~70 °C Operating temp. controller 0 °C ~50 °C 表 3 NUC实验结果
Table 3. Results of NUC experiment
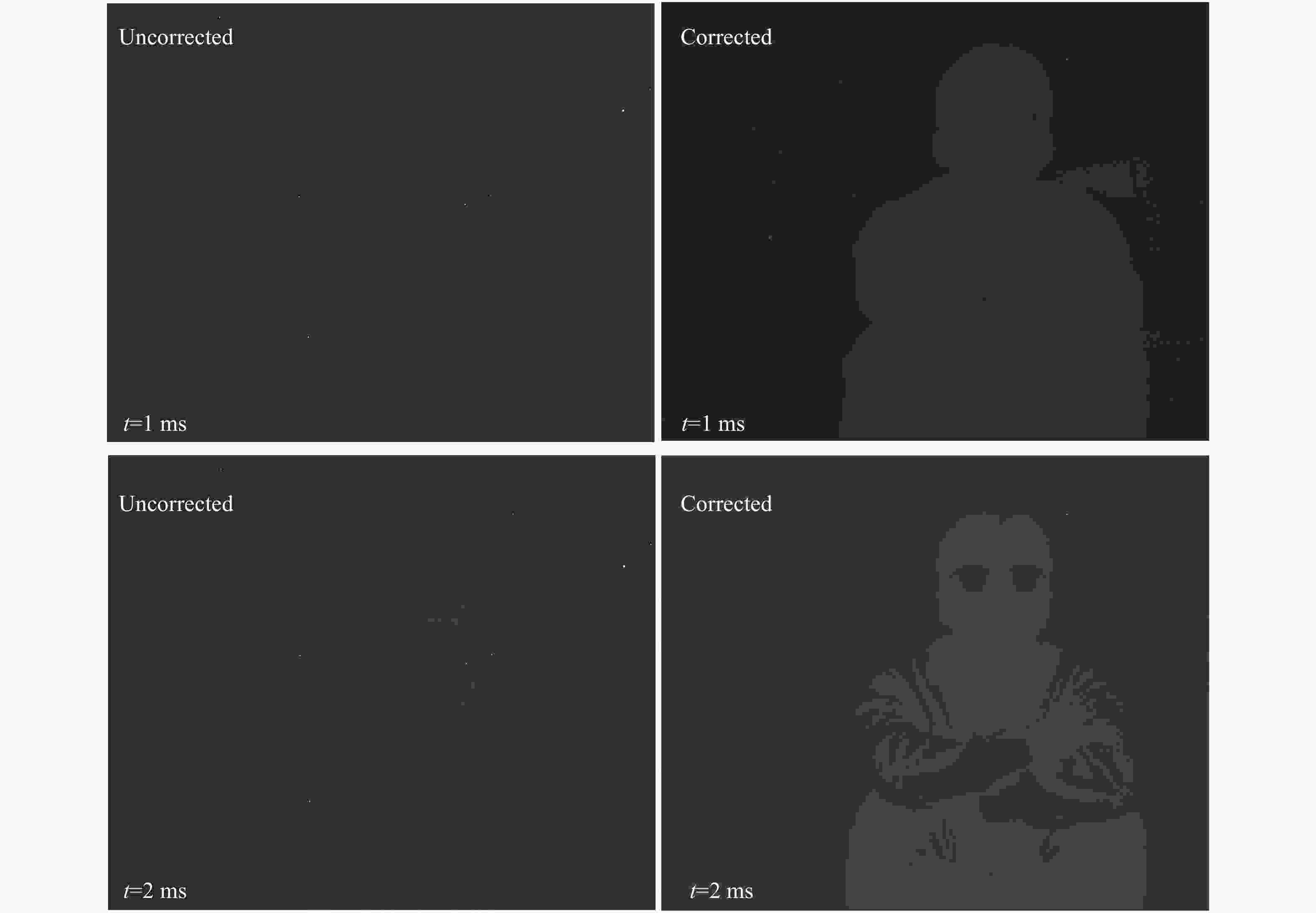
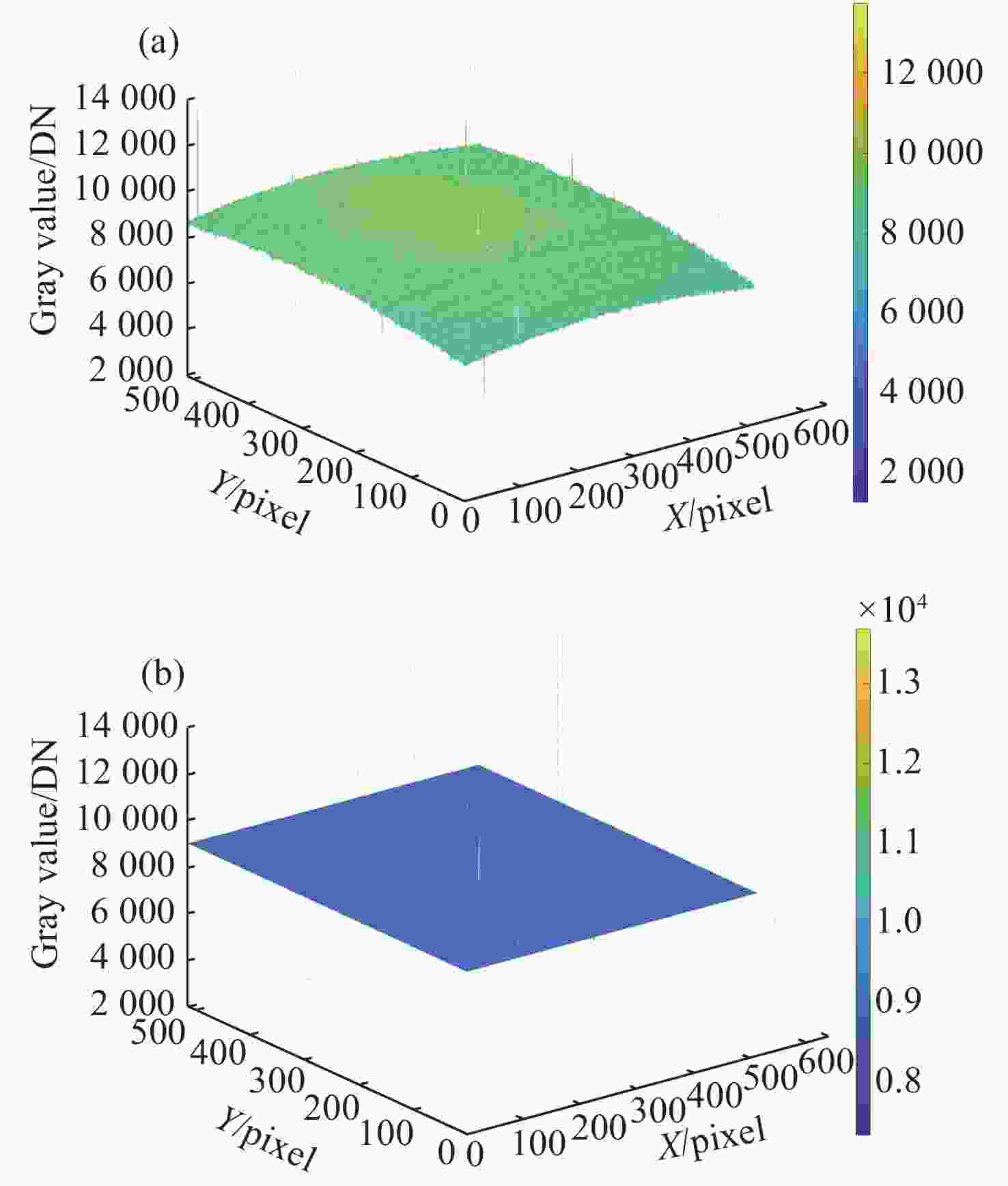
Integral time/ms Blackbody temperature/°C Non-uniformity/% Uncorrected Single-point NUC Two-point NUC Improved NUC 1 50 3.8453 1.0403 0.2437 0.1451 60 3.9253 1.8394 0.2427 0.1695 70 4.0417 2.4703 0.1704 0.1297 Average 3.9374 1.7833 0.2190 0.1481 2 50 3.8274 1.0697 1.7184 0.9707 60 3.9642 1.8963 2.3016 1.7212 70 4.0780 2.5112 2.7223 2.2718 Average 3.9565 1.8257 2.2474 1.6546 -
[1] A. F. Milton, F. R. Barone, M. R. Kruer. Influence of nonuniformity on infrared focal plane array performance[J]. Optical Engineering, 1985, 24(5): 855-862. [2] M. Schulz, L. Caldwell. Nonuniformity correction and correctability of infrared focal plane arrays[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 1994, 36: 763-777. [3] CAO Y P, Christel-L T. Shutterless solution for simultaneous focal plane array temperature estimation and nonuniformity correction in uncooled long-wave infrared camera[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(25): 6266-6271. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.006266 [4] Clay S, Doug M, Ron D. Analysis and implications of resistive emitter array non-uniformity correction (NUC) between sensors with different spectral bands[C]. Technologies for Synthetic Environments: Hardware-in-the-Loop Testing III, SPIE (3368), 1998.138-156. [5] Joe LV, Greg F, Kevin S, et al. LWIR NUC Using an Uncooled Microbolometer Camera[C]. Technologies for Synthetic Environments: Hardware-in-the-Loop Testing XV SPIE(7663), 2010.766306. [6] CAO Y P, Christel-L T. Solid-state temperature-dependent NUC (Non-Uniformity Correction) in uncooled LWIR (Long-Wave Infra-Red) Imaging System[C]. Infrared Technology and Applications XXXIX, SPIE (8704), 2013.87042W. [7] SHENG Y C, DUN X, QIU S, et al. On-orbit non-uniformity correction method for infrared remote sensing systems using controllable internal calibration sources[J]. J. Infrared Millim. Waves, 2021, 40(5): 655-663. [8] 张明杰, 李岩, 马文坡, 等. 盛一成, 顿雄, 裘溯, 等. 基于可控内定标源的星上红外遥感相机非均匀性校正方法[J]. 红外技术,2021,43(4):324-333.ZHANG M J, LI Y, MA W P, LIU Z Y. Non-uniformity Correction for Large Format Array Infrared Detectors Based on Regional Correction[J]. Infrared Technology, 2021, 43(4): 324-333. (in Chinese) [9] 赵振男, 宋鸿飞, 任宏凯. 一种改进的基于场景的非均匀性校正方法[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,43(2):53-57.ZHAO ZH N, SONG H F, REN H K. An Improved Scene-based Non-uniformity Correction Method[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition) , 2020, 43(2): 53-57. (in Chinese) [10] LIU CH W, SUI X B. Improved calibration-based non-uniformity correction method for uncooled infrared camera[C]. Infrared Sensors, Devices, and Applications VII, SPIE(10404), 2017.104040X. [11] 余毅, 常松涛, 王旻, 等. 宽动态范围红外测量系统的快速非均匀性校正[J]. 光学精密工程,2015,23(7):1932-1938.YU Y, CHANG S T, WANG M, et al. Fast non-uniformity correction for high dynamic infrared radiometric system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(7): 1932-1938. (in Chinese) [12] 关同辉, 张同贺. 一种新型实时两点非均匀性校正方法[J]. 航空兵器,2021,28(4):112-117. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2020.0003Gun T H, Zhang T H. A New Real-time two-Point Nonuniformity Correction method[J]. AERO WEAPONRY, 2021, 28(4): 112-117. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2020.0003 [13] 王跃明, 陈建新, 刘银年, 等. 红外焦平面器件二点多段非均匀性校正算法研究[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2003,22(6):415-418.WANG Y M CHEN J X, LIU Y N, et al. Study on two-point multi-section IRFPA non-uniformity correction algorithm[J]. Infrared Millim. Waves, 2003, 22(6): 415-418. (in Chinese) [14] 孙志远, 常松涛, 朱玮. 大口径、宽动态范围红外测量系统辐射定标方法[J]. 光学学报,2014,53(27):6274-6279.SUN Z Y, CHANG S T, ZHU W. Radiation calibration method for infrared system with large aperture and broad dynamic range[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2014, 53(27): 6274-6279. (in Chinese) [15] CHANG S T, ZHANG Y Y, SUN Z Y, et al. Method to remove the effect of ambient temperature on radiometric calibration[J]. Applied optics, 2014, 53(27): 6274-6279. [16] 黄宇, 张宝辉, 吴杰, 等. 自适应多点定标非均匀性校正算法[J]. 红外技术,2020,42(7):637-643.HUANG Y, ZHANG B H, WU J, et al. Adaptive Multipoint Calibration Non-uniformity Correction Algorithm[J]. Infrared Technology, 2020, 42(7): 637-643. (in Chinese) [17] 刘会通, 易新建. 红外焦平面阵列非均匀性的两点校正及依据[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2004,33(1):76-78.LIU H T, YI X J. Two-point nonuniformity correction for IRFPA and its physical motivation[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2004, 33(1): 76-78. (in Chinese) [18] 中国科学院上海技术物理研究所, GB/T 17444-1998 红外焦平面阵列特性参数测试技术规范[S], 中国质检出版社, 北京, 1988.Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of Chinese Academy of Sciences, GB/T 17444-1998 The technical norms of measurement and test of characteristic parameters of infrared focal plane arrays [S], China Zhijian Publishing House, Beijing, 1988. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: