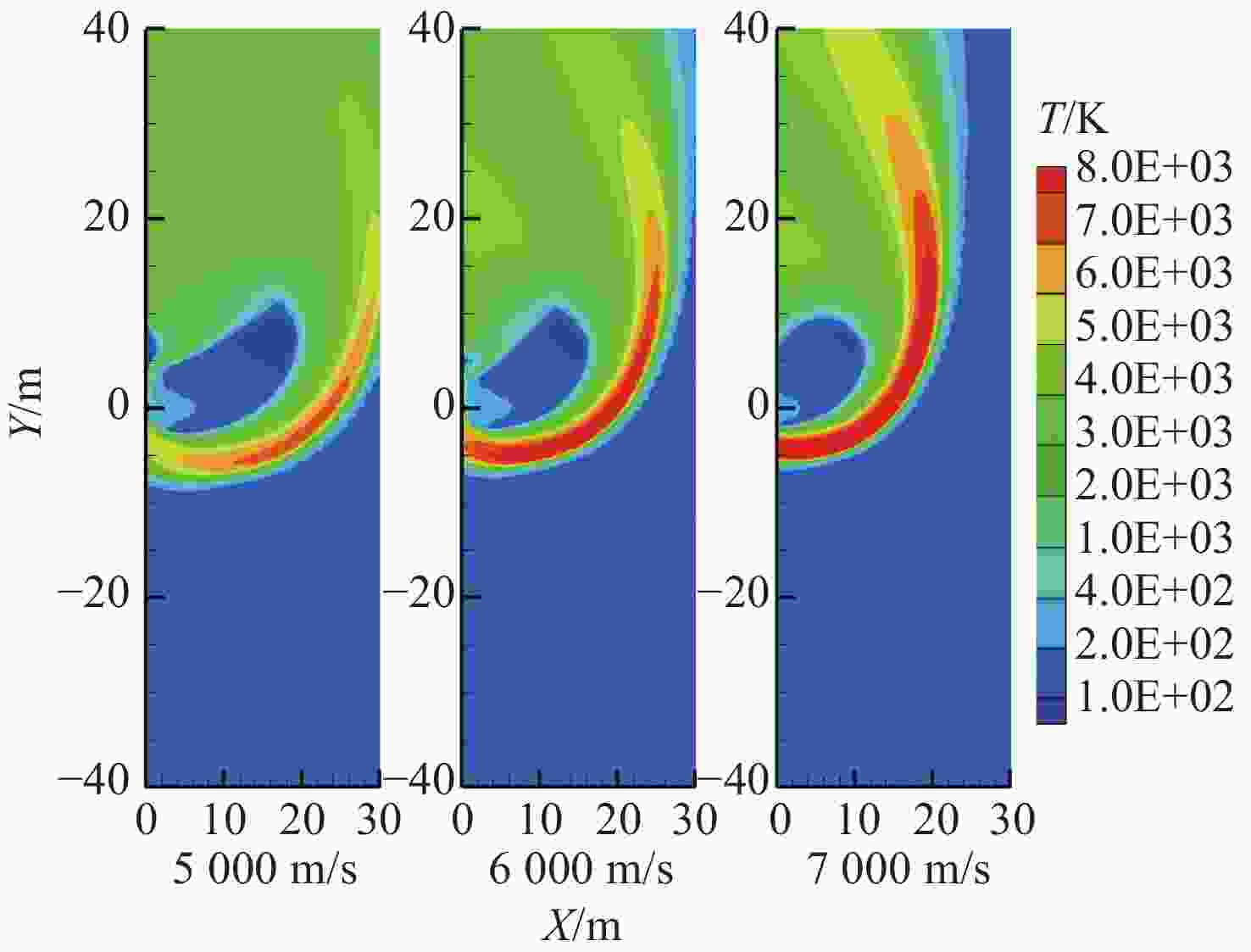
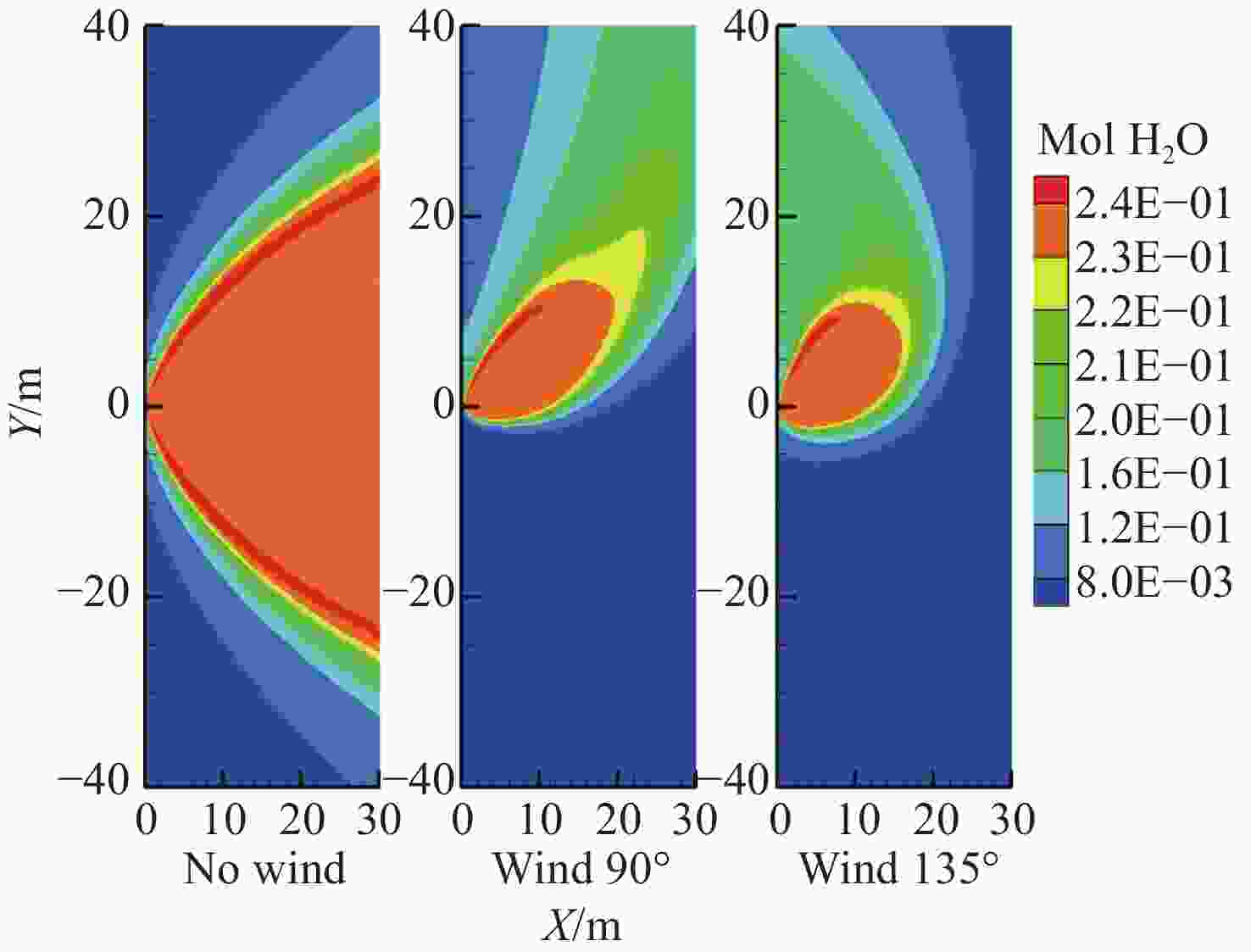
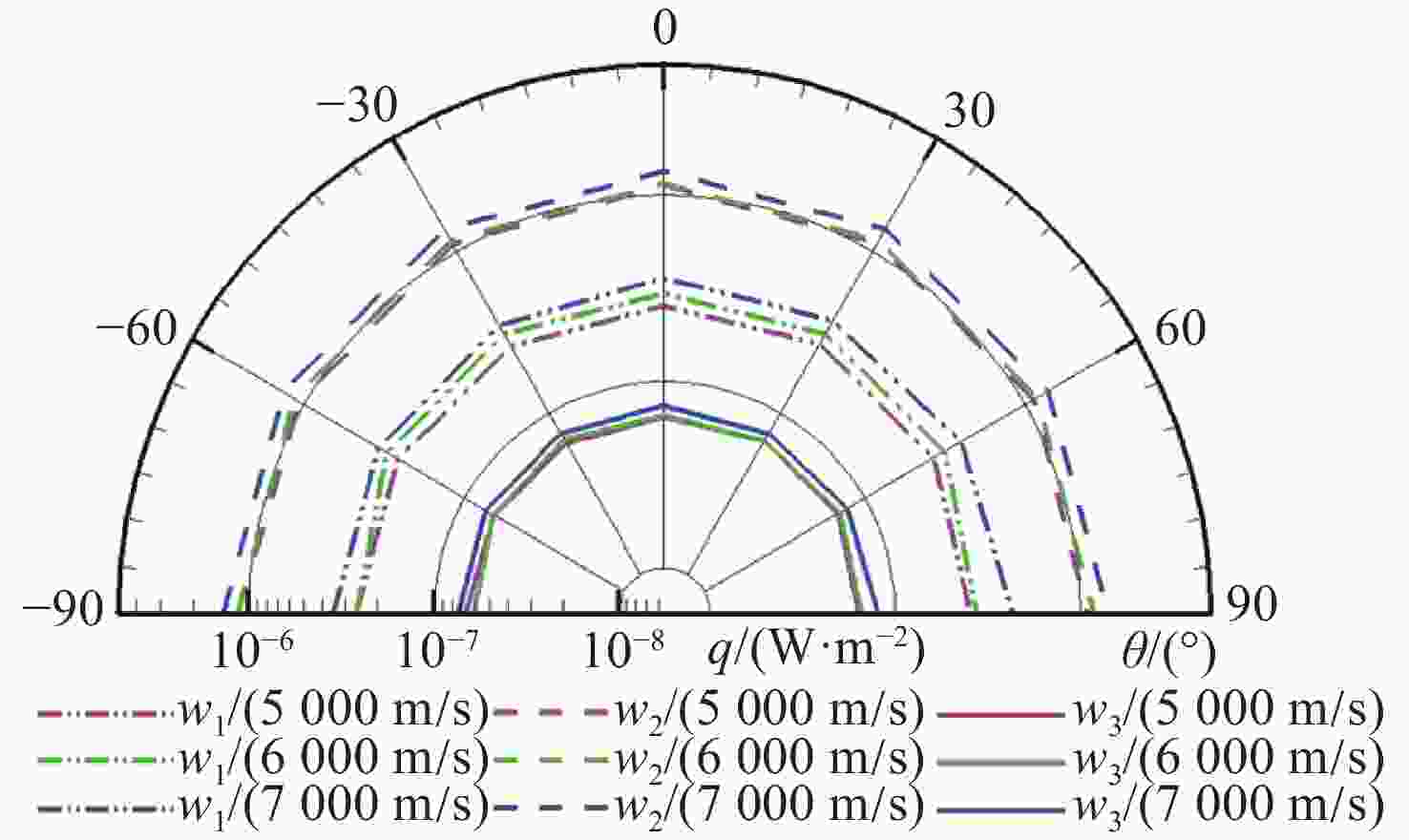
-
摘要: 高超声速飞行器大攻角机动时,其离轨发动机产生的喷流与高速稀薄的大气来流产生强烈干扰,流场情况复杂,流场红外辐射也是天基红外系统探测的标志性事件。本文针对高超声速飞行器发动机喷流与稀薄来流的相互干扰情况,采用数值求解Navier-Stokes方程模拟干扰流场,采用逐线积分法得到气体红外辐射特性,结合反向蒙特卡洛方法计算得到飞行器在94公里飞行高度下,无来流、不同来流攻角、不同来流速度下的尾焰流场红外辐射特性,并针对低轨卫星的可观测性进行了评估。仿真结果表明,对于给定观测位置,在无风条件下,红外辐射在各个波段下的强度较低,最大值在10−9 W/m2量级。而在来流攻角影响下,流场红外信号强度显著上升,且来流攻角、来流速度越大,强度越大,最大值在10−6 W/m2量级。大气衰减效应对不同观测位置的可观测性影响较大。本文结果可为高超声速飞行器红外预警和反导提供参考。Abstract: When a hypersonic vehicle maneuvers at a high angle of attack, the jet generated by its off-orbit engine interferes strongly with the high-speed thin atmospheric flow, and the flow field is complicated, and the infrared radiation generated by the flow field is also a landmark event in space-based infrared system detection. In this paper, aiming at interference situation of the jet flow of hypersonic flight vehicle engine and thin flow, Navier-Stokes equations are numerically solved to simulate the interference flow field, and the infrared radiation characteristics of gas are obtained by the line-by-line integration method. Combining with the backward Monte Carlo method, the infrared radiation characteristic of exhaust plume are obtained when the aircraft flight′s altitude is 94 kilometers, with no wind, different incoming flow attack angles and different velocities are considered, and the observability of low orbit satellites is evaluated. The simulation results show that for a given observation position, the intensity of infrared radiation in each band is low when there is no wind, and the maximum value is 10−9 W/m2. Under the influence of incoming flow attack angles, the infrared signal intensity of the flow field increases significantly with greater attack angle and velocities and the maximum value reaches 10−6 W/m2. The atmospheric attenuation effect has great influence on the observability of different observation positions. The results can provide reference for infrared warning and anti-missile of hypersonic vehicle.
-
表 1 不同观测位置的辐射热流密度
Table 1. Radiative heat fluxes at different observation positions (W/cm2)
Waveband/μm Location 1 Location 2 No wind Wind 90° Wind 135° 5000 m/s 6000 m/s No wind Wind 90° Wind 135° 5000 m/s 6000 m/s 2.65~3 5.07×10−14 1.82×10−11 3.94×10−11 2.40×10−11 2.77×10−11 1.25×10−17 6.13×10−15 1.33×10−14 7.84×10−15 8.81×10−15 3.7~4.95 7.00×10−13 7.84×10−11 1.32×10−10 1.13×10−10 1.13×10−10 5.42×10−18 1.37×10−14 2.51×10−14 2.11×10−14 2.14×10−14 8~13.5 1.79×10−14 4.37×10−12 7.22×10−12 6.40×10−12 6.32×10−12 6.60×10−17 2.24×10−14 3.74×10−14 3.31×10−14 3.25×10−14 -
[1] 赵玉杰, 杨晨, 宋琛. 空基高超声速导弹防御系统关键技术研究[J]. 战术导弹技术,2020(4):64-70.ZHAO Y J, YANG CH, SONG CH. Research on the key technologies of air-based hypersonic missile defense system[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2020(4): 64-70. (in Chinese) [2] 黄曦, 吴鑫. 基于天基红外预警系统的导弹中段弹道成像特征实时仿真[J]. 空天防御,2020,3(4):60-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4641.2020.04.009HUANG X, WU X. Real-time simulation of missile midcourse trajectory imaging characteristics based on space-based infrared early warning system[J]. Air &Space Defense, 2020, 3(4): 60-66. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4641.2020.04.009 [3] 余晓娅, 刘立拓, 李瑞, 等. 高超声速再入试验的辐射光谱定量测量[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(1):87-94. doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0087YU X Y, LIU L T, LI R, et al. Measurements of absolute radiative emissions for supersonic reentry[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(1): 87-94. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0087 [4] 杨霄, 牛青林, 贺志宏, 等. 类HTV-2高超声速滑翔飞行器红外辐射特征与可探测性分析[J]. 光学学报,2017,37(12):1204001.YANG X, NIU Q L, HE ZH H, et al. Analysis of Infrared radiation characteristics and detectability of HTV-2-like hypersonic gliding aircrafts[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(12): 1204001. (in Chinese) [5] 牛青林, 杨霄, 陈彪, 等. 高速滑翔目标点源红外辐射特征模拟及可探测性分析[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2018,47(11):1104001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.1104001NIU Q L, YANG X, CHEN B, et al. Infrared radiation characteristics and detectability analysis of point source based on high-speed sliding[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(11): 1104001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.1104001 [6] 江涛, 丁明松, 刘庆宗, 等. 印度烈火-Ⅱ导弹助推段和再入段红外辐射特性计算研究[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2020,49(5):20190493. doi: 10.3788/irla.21_2019-0493JIANG T, DING M S, LIU Q Z, et al. IR radiation characteristics of India Angi-Ⅱ at launching and reentry stage[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(5): 20190493. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/irla.21_2019-0493 [7] 王少平, 董受全, 刘亿, 等. 助推滑翔高超声速导弹红外辐射特性研究[J]. 战术导弹技术,2020(5):27-32.WANG SH P, DONG SH Q, LIU Y, et al. Research on infrared characteristics of boost-glide hypersonic missile[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2020(5): 27-32. (in Chinese) [8] 包醒东, 余西龙, 吴杰, 等. 稀薄环境下高空羽流流动与超窄谱红外辐射特性数值研究[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2020,49(S1):20200159.BAO X D, YU X L, WU J, et al. Numerical study of flow and ultra narrow spectrum infrared radiation characteristics of high-altitude plume under thin atmosphere[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(S1): 20200159. (in Chinese) [9] 任翔, 姜淇瀚, 袁军娅, 等. 高空离轨发动机喷流与来流干扰数值模拟[C]. 第四十届技术交流会暨第四届空天动力联合会议. 昆明: 中国航天第三专业信息网, 2019: 181-189.REN X, JIANG Q H, YUAN J Y, et al.. Numerical simulation of the interaction between off-orbit rocket motor jets and incoming flows at high altitude[C]. The 40th Technical Exchange Meeting and the Fourth Aerospace Power Joint Conference. Kunming: China Aerospace Third Professional Information Network, 2019: 181-189. [10] ROTHMAN L S, GORDON I E, BARBE A, et al. The HITRAN 2008 molecular spectroscopic database[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2009, 110(9-10): 533-572. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2009.02.013 [11] ROTHMAN L S, GORDON I E, BARBER R J, et al. HITEMP, the high-temperature molecular spectroscopic database[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2010, 111(15): 2139-2150. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2010.05.001 [12] 任泓帆, 朱定强. 液体火箭发动机尾焰复燃对红外辐射特性的影响[J]. 推进技术,2018,39(6):1227-1233.REN H F, ZHU D Q. Effects of afterburning on infrared radiation characteristics of liquid rocket exhaust plume[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2018, 39(6): 1227-1233. (in Chinese) [13] 董士奎, 余其铮, 谈和平, 等. 燃烧产物二氧化碳高温辐射的窄谱带模型参数[J]. 航空动力学报,2001,16(4):355-359. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8055.2001.04.012DONG SH K, YU Q ZH, TAN H P, et al. Narrow band model parameters of high temperature radiation for carbon dioxide of combustion products[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2001, 16(4): 355-359. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8055.2001.04.012 [14] 董士奎, 谈和平, 余其铮, 等. 300~3000K水蒸气红外辐射谱带模型参数[J]. 热能动力工程,2001,16(1):33-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2060.2001.01.009DONG SH K, TAN H P, YU Q ZH, et al. Infrared radiative spectral band-model parameters for water vapor in the 300 - 3000 K temperature range[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2001, 16(1): 33-38. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2060.2001.01.009 -





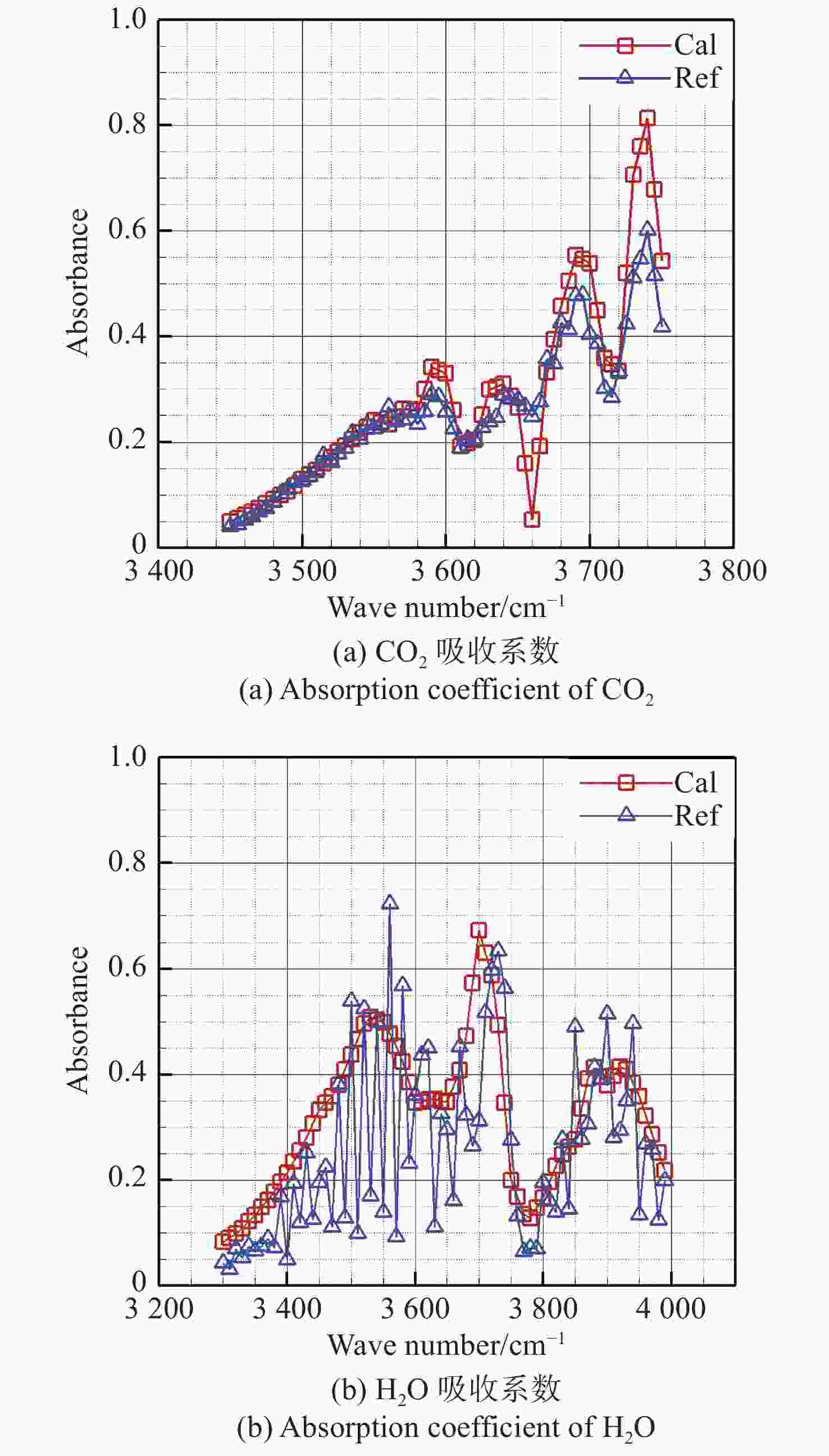
 下载:
下载: