-
摘要:
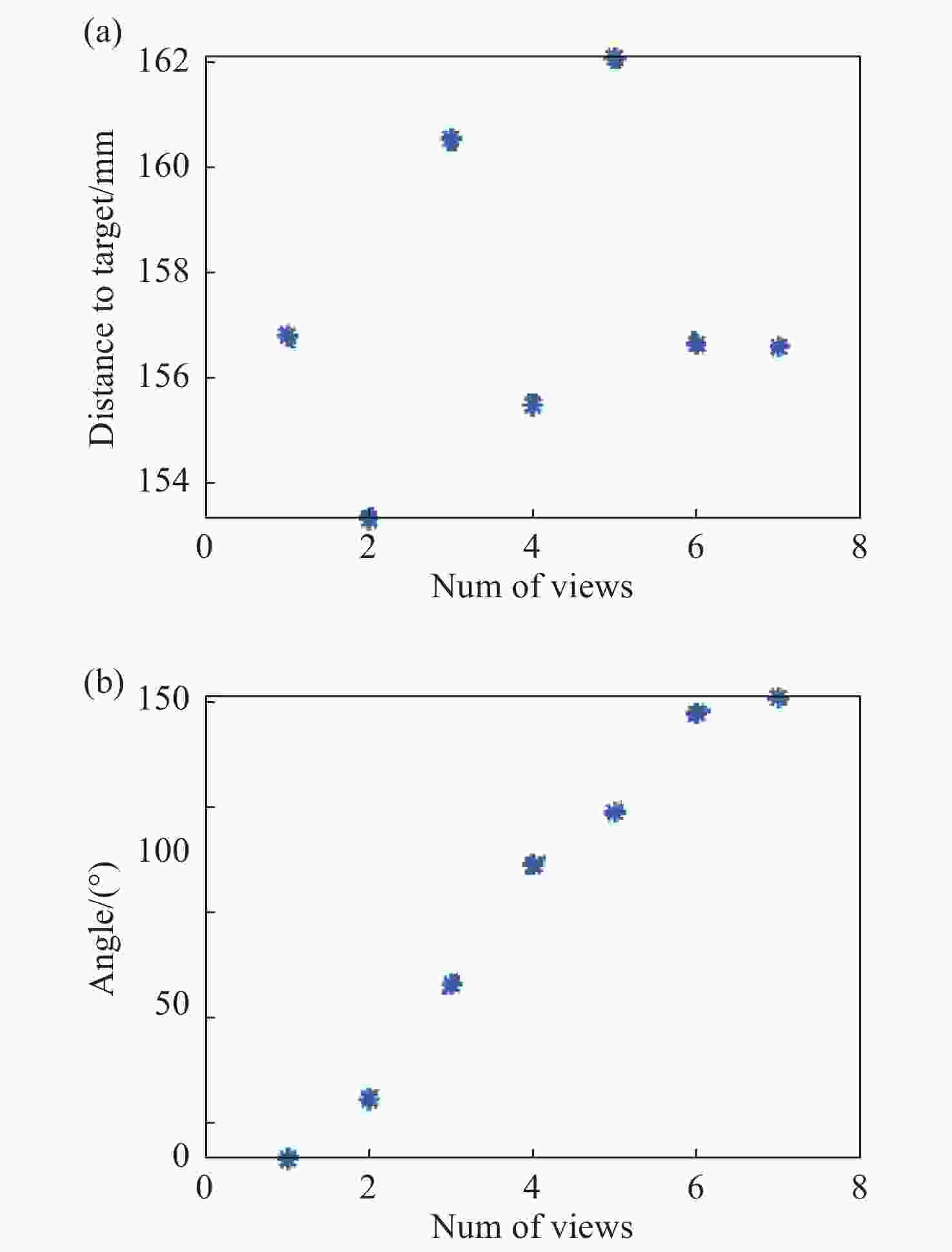
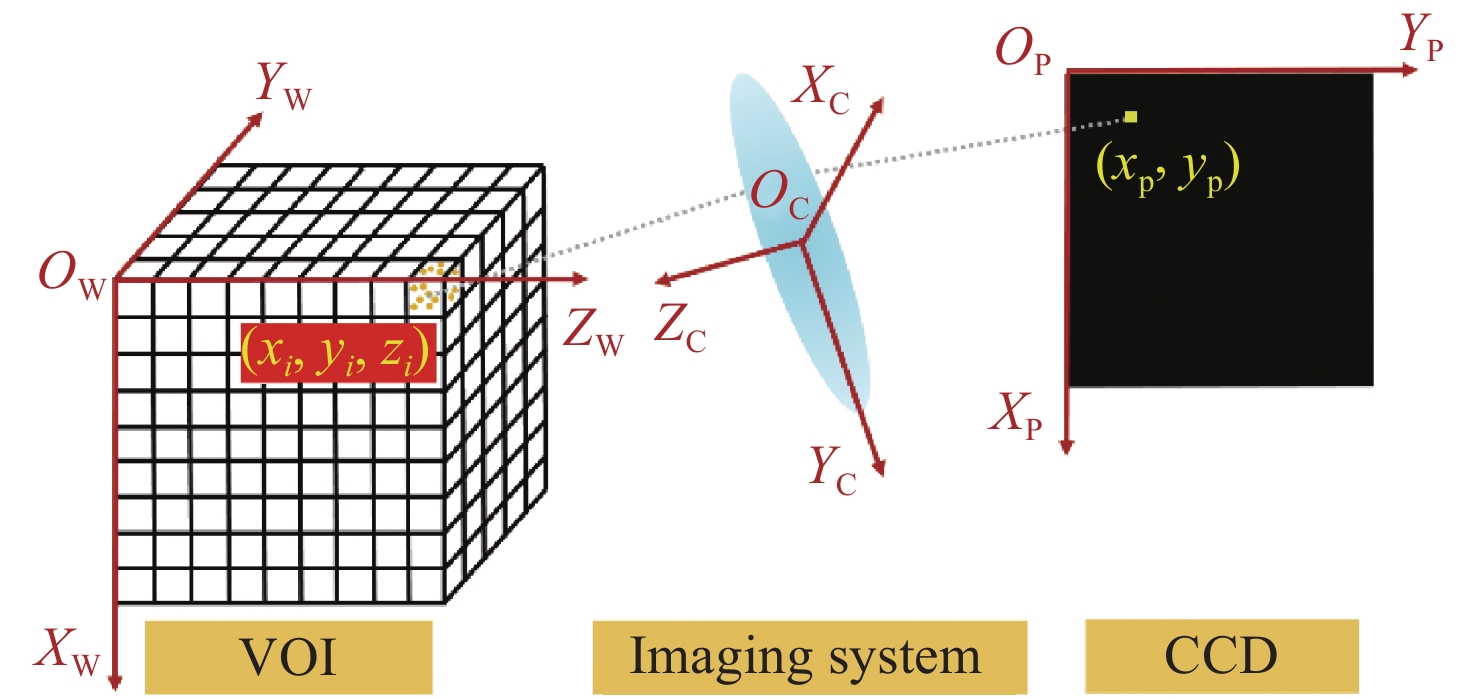
为了对金宝搏188软件怎么用 光强分布进行准确测量,本文提出基于层析成像技术的金宝搏188软件怎么用 光强分布测量方法。首先,通过数值仿真计算,对采用的成像模型的准确性以及重建算法的收敛性进行验证。对不同金宝搏188软件怎么用 光强分布模型以及不同随机噪声等级时的重建精度进行评估。经计算,采用不同典型金宝搏188软件怎么用 光强模型时其重建误差均小于等于7.02%;在施加10%以内随机噪声时,重建误差均小于8.5%。设计并搭建了层析成像系统,采用定制的一分七光纤束实现7七个角度信号的测量。7个角度分布在垂直于金宝搏188软件怎么用 光束平面内的近半圆周内,各个角度距重建区域的距离约为160 mm,且7个角度的角度覆盖范围约为150°。实验通过探测金宝搏188软件怎么用 光束穿过若丹明-乙醇溶液之后的体金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导荧光信号,结合后续的数据处理过程间接实现金宝搏188软件怎么用 光强三维分布的反演。在数据处理过程中,采用交替迭代重建算法对探测信号进行吸收矫正的三维重建,可间接地获得金宝搏188软件怎么用 光强分布。为了定量评估测量精度,在进行重建时仅采用其中6个角度,将余下一角度的重建反投影以及投影数据间的相关性用来间接证明此重建方法的可行性。计算结果表明,该角度投影以及反投影之间的相关性系数为0.9802,可间接的验证该方法的可行性。可以预见,本工作提出的金宝搏188软件怎么用 光强三维测量方案在金宝搏188软件怎么用 应用领域具有广泛的前景。
-
关键词:
- 光学诊断 /
- 计算成像 /
- 层析成像 /
- 三维重建 /
- 金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导荧光
Abstract:In order to accurately measure the laser intensity distribution, we propose a method based on tomographic imaging. Firstly, numerical studies were performed to validate the correctness of the imaging model and convergence of the reconstruction algorithm. Reconstruction errors were less than or equal to 7.02% with different laser intensity distribution phantoms employed and less than 8.5% with the addition of different random noise levels under 10%. Additionally, a demonstration experiment was performed with the employment of a customized fiber bundle to realize the measurement from seven views. Seven views are distributed along a semi-circle plane which is perpendicular to the propagation direction of the laser beam. The distance from the laser beam to each view is nearly 160 mm and the angle coverage range of the seven views is about 150°. Laser-induced fluorescence obtained after the laser passed through a rhodamine-ethanol solution was collected by the tomographic imaging system. Then, the laser intensity distribution was obtained through absorption-corrected three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction. The correlation of the projection and re-projection of the one view was used to quantitatively access the accuracy after the other six views were adopted in the reconstruction. The results show the feasibility of the method with a correlation coefficient of 0.9802. It can be predicted that the 3D laser intensity measurement scheme proposed in this work has a broad prospect in the field of laser applications.
-
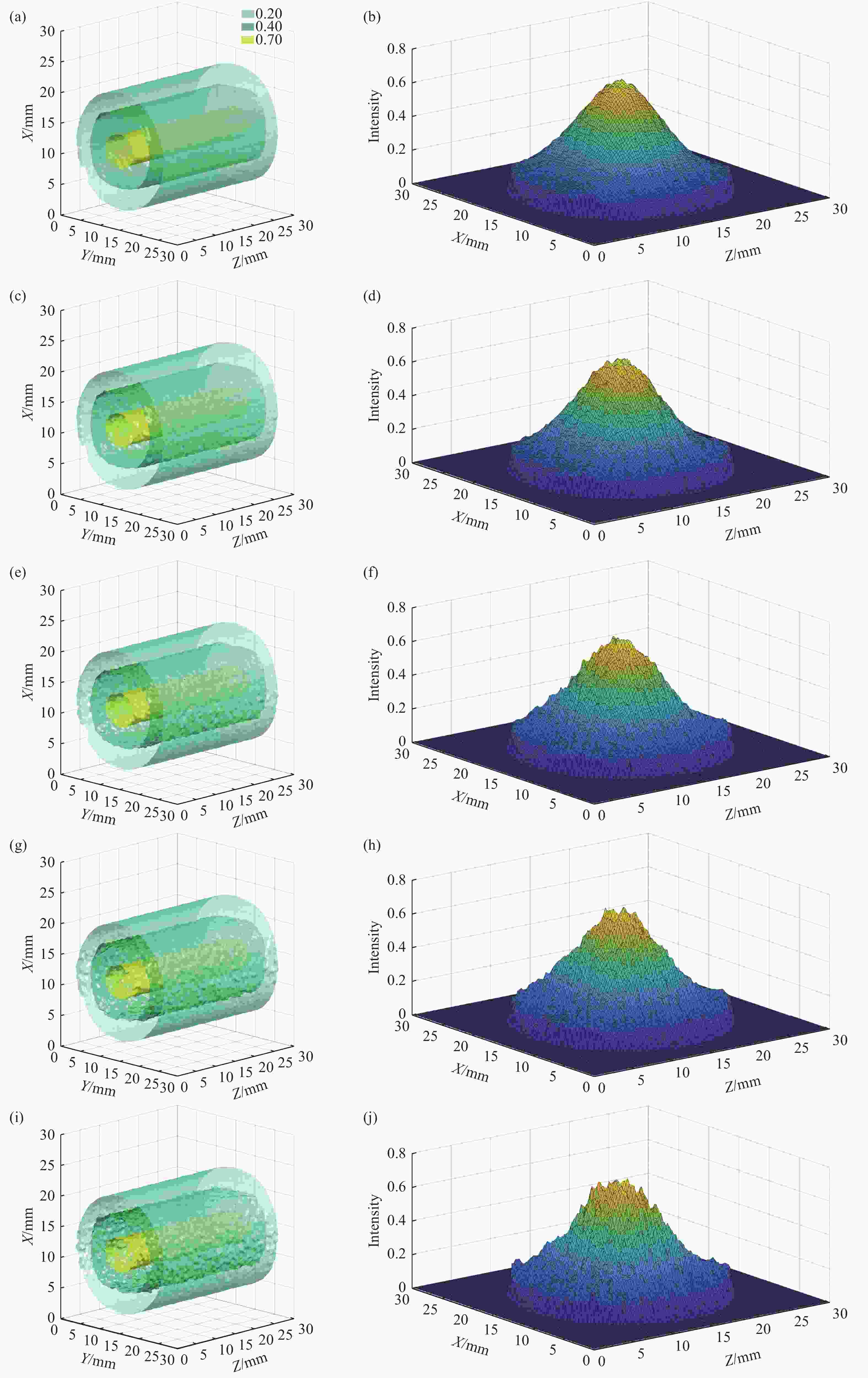
图 2 不同金宝搏188软件怎么用 光强三维分布phantom及其重建结果等值面示意图:(a−b)为沿着光束传播方向光强无变化的高斯分布;(c−d)为沿着光束传播方向光强分布有变化的分布;(e−f)为沿着光束传播方向光强无变化的非高斯分布;(a)、(c)、(e)为原始phantom,(b)、(d)、(f)为对应的重建结果
Figure 2. Isosurfaces of laser intensity distribution 3D phantoms and the corresponding reconstructions: (a−b) laser intensity with Gaussian distribution, kept unhanged along the propagation direction of the beam; (c−d) laser intensity with Gaussian distribution, changed along the propagation direction of the beam; (e−f) laser intensity with non-Gaussian distribution, unhanged along the propagation direction of the beam; (a), (c) and (e) are original phantoms and (b), (d) and (f) are the corresponding reconstructions
图 3 不同信噪比下金宝搏188软件怎么用 光强分布三维重建等值面结果及中间截面金宝搏188软件怎么用 光强二维分布示意图:(a−b)、(c−d)、(e−f)、(g−h)和(i−j)分别为施加2%, 4%, 6%, 8%和10%的随机噪声
Figure 3. Isosurfaces of laser intensity distribution 3D reconstructions under different signal-to-noise ratios and the corresponding 2D slices for the middle section: (a−b), (c−d), (e−f), (g−h) and (i−j) are corresponding to adding 2%, 4%, 6%, 8% and 10% random noise, respectively
-
[1] 王家乐. 基于光斑图像的金宝搏188软件怎么用 能量密度分布测量技术[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2013WANG J L. Measurement technology of energy density distribution based on spot image[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2013. (in Chinese) [2] 王艳茹, 王建忠, 冉铮惠, 等. 高能金宝搏188软件怎么用 光束质量β因子的影响因素分析[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(2):353-360. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0137WANG Y R, WANG J ZH, RAN ZH H, et al. Analysis of effects on the beam quality β factor of high power laser[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(2): 353-360. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0137 [3] 郜魏柯, 杜小平, 王阳, 等. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 散斑目标探测技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1182-1193. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0049GAO W K, DU X P, WANG Y, et al. Review of laser speckle target detection technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1182-1193. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0049 [4] 文康, 李和章, 马壮, 等. 光斑尺寸对连续金宝搏188软件怎么用 辐照铝合金温度响应影响研究[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(5):1023-1031. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0022WEN K, LI H ZH, MA ZH, et al. Effects of spot size on the temperature response of an aluminum alloy irradiated by a continuous laser[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(5): 1023-1031. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0022 [5] 庞淼, 袁学文, 高学燕, 等. 散射成像法测量金宝搏188软件怎么用 强度分布中的光斑畸变校正[J]. 光学学报,2010(2):5. doi: CNKI:SUN:GXXB.0.2010-02-029PANG M, YUAN X W, GAO X Y, et al. Spot distortion calibration in measurement of laser intensity distribution based on imaging by scattering[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2010(2): 5. (in Chinese) doi: CNKI:SUN:GXXB.0.2010-02-029 [6] 王飞, 徐作冬, 戢运峰, 等. 采用扫描式漫反射成像法的金宝搏188软件怎么用 强度分布测量装置[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2014,43(7):4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.07.033WANG F, XU Z D, JI Y F, et al. Measurement system for laser intensity distribution based on scanning diffuse reflection imaging[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(7): 4. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.07.033 [7] ZHU ZH, WANG Y ZH, YI Y X, et al. Novel direct-detection scheme for measuring energy distribution of laser spots in outfield[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2005, 32(11): 49-53. [8] CHO K Y, SATIJA A, POURPOINT T L, et al. High-repetition-rate three-dimensional OH imaging using scanned planar laser-induced fluorescence system for multiphase combustion[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(3): 316-326. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.000316 [9] NYGREN J, HULT J, RICHTER M, et al. Three-dimensional laser induced fluorescence of fuel distributions in an HCCI engine[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2002, 29(1): 679-685. doi: 10.1016/S1540-7489(02)80087-6 [10] 陈琦, 徐熙平, 姜肇国, 等. 基于光场相机的深度面光场计算重构[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(3):708-714. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182603.0708CHEN Q, XU X P, JIANG ZH G, et al. Light field computational reconstruction from focal planes based on light field camera[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(3): 708-714. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182603.0708 [11] SUN J, XU CH L, ZHANG B, et al. Three-dimensional temperature field measurement of flame using a single light field camera[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(2): 1118-1132. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.001118 [12] LILLO P M, GREENE M L, SICK V. Plenoptic single-shot 3D imaging of in-cylinder fuel spray geometry[J]. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 2015, 229(4): 549-560. [13] SAMARASINGHE J, PELUSO S, SZEDLMAYER M, et al. Three-dimensional chemiluminescence imaging of unforced and forced swirl-stabilized flames in a lean premixed multi-nozzle can combustor[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2013, 135(10): 101503. doi: 10.1115/1.4024987 [14] CAI W W, LI X S, MA L. Practical aspects of implementing three-dimensional tomography inversion for volumetric flame imaging[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(33): 8106-8116. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.008106 [15] CAI W W, LI X S, LI F, et al. Numerical and experimental validation of a three-dimensional combustion diagnostic based on tomographic chemiluminescence[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(6): 7050-7064. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.007050 [16] SHI SH X, WANG J H, DING J F, et al. Parametric study on light field volumetric particle image velocimetry[J]. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 2016, 49: 70-88. doi: 10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2016.05.006 [17] ZHOU G X, LI F, WANG K L, et al. Research on a quantitative method for three-dimensional computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(17): 5310-5318. doi: 10.1364/AO.393225 [18] WINDLE C I, ANDERSON J, BOYD J, et al. In situ imaging of 4D fire events in a ground vehicle testbed using customized fiber-based endoscopes[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2021, 224: 225-232. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2020.11.022 [19] WANG Q, YU T, LIU H C, et al. Optimization of camera arrangement for volumetric tomography with constrained optical access[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2020, 37(4): 1231-1239. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.385291 [20] LIU H C, PAOLILLO G, ASTARITA T, et al. Computed tomography of chemiluminescence for the measurements of flames confined within a cylindrical glass[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(19): 4793-4796. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.004793 [21] ZHANG ZH Y. Flexible camera calibration by viewing a plane from unknown orientations[C]. Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 1999: 666-673. [22] YU T, LIU H C, CAI W W. On the quantification of spatial resolution for three-dimensional computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(20): 24093-24108. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.024093 [23] YU T, TIAN B, CAI W W. Development of a beam optimization method for absorption-based tomography[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(6): 5982-5999. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.005982 [24] WEI CH Y, PINEDA D I, PAXTON L, et al. Mid-infrared laser absorption tomography for quantitative 2D thermochemistry measurements in premixed jet flames[J]. Applied Physics B, 2018, 124(6): 123. doi: 10.1007/s00340-018-6984-z [25] YU T, LI Z M, RUAN C, et al. Development of an absorption-corrected method for 3D computed tomography of chemiluminescence[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2019, 30(4): 045403. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab01c1 [26] LIU H C, SUN B, CAI W W. kHz-rate volumetric flame imaging using a single camera[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 437: 33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.12.036 [27] LIU H C, YU T, ZHANG M, et al. Demonstration of 3D computed tomography of chemiluminescence with a restricted field of view[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(25): 7107-7115. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.007107 -






 下载:
下载: