-
摘要:
全景内窥成像技术可有效减小体内器官的观察盲区,具有缩短手术时间、降低术中出血风险、改善手术预后、缩短术后恢复时间等多种优点,在微创手术和术前检查中有重要应用价值,是近年来的研究热点。本文从原理和产品应用两个方面对全景内窥成像技术进行了梳理。首先,综述了基于二维和三维成像的各种全景内窥成像技术,阐述了它们各自的实现方式,并分析了其关键指标和性能。其次,对比分析了由全景内窥成像技术衍生出来的胶囊内窥镜、全景结直肠镜等多种不同类型的产品,并展望了全景内窥成像技术的发展趋势和应用前景。
Abstract:Panoramic endoscopic imaging technology can effectively reduce the observation blind area of internal organs. It has many advantages, such as shortening the operation time, reducing the risk of intraoperative bleeding, improving the prognosis and shortening the postoperative recovery time. It has important application value in minimally invasive surgery and preoperative examination. It is a research hotspot in recent years. This paper combs the panoramic endoscopic imaging technology from two aspects: principle and product applications. Firstly, various panoramic endoscopic imaging technologies based on two-dimensional and three-dimensional imaging are reviewed, their implementation methods are described, and their key indexes and performances are analyzed. Secondly, the capsule endoscope, panoramic enteroscope and other different types of products derived from panoramic endoscopic imaging technology are compared and analyzed, and the development trend and application prospect of panoramic endoscopic imaging technology are prospected.
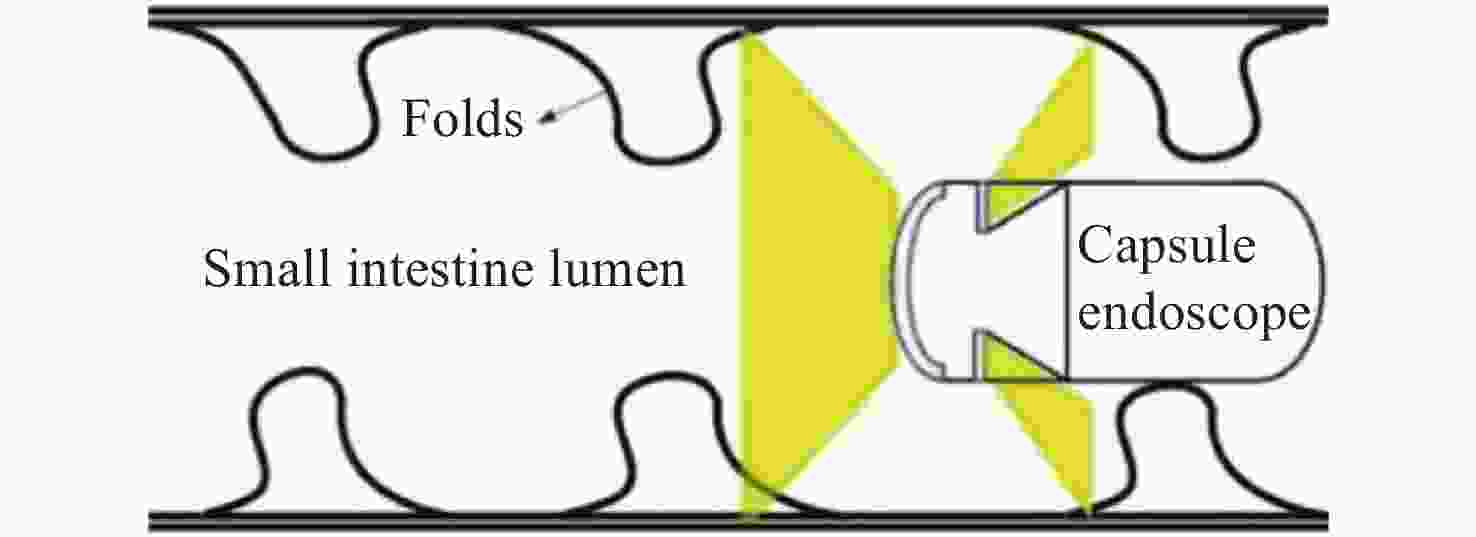
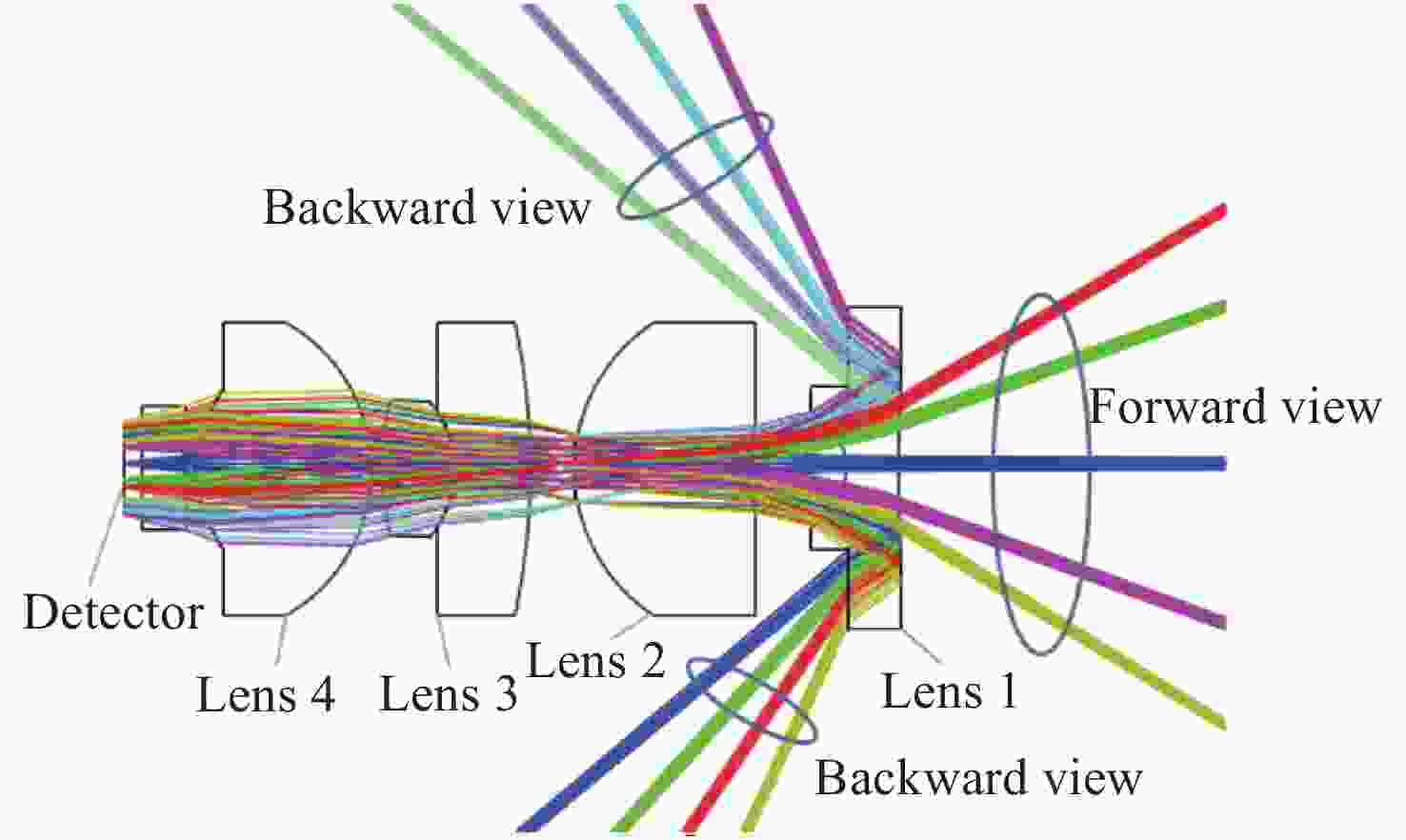
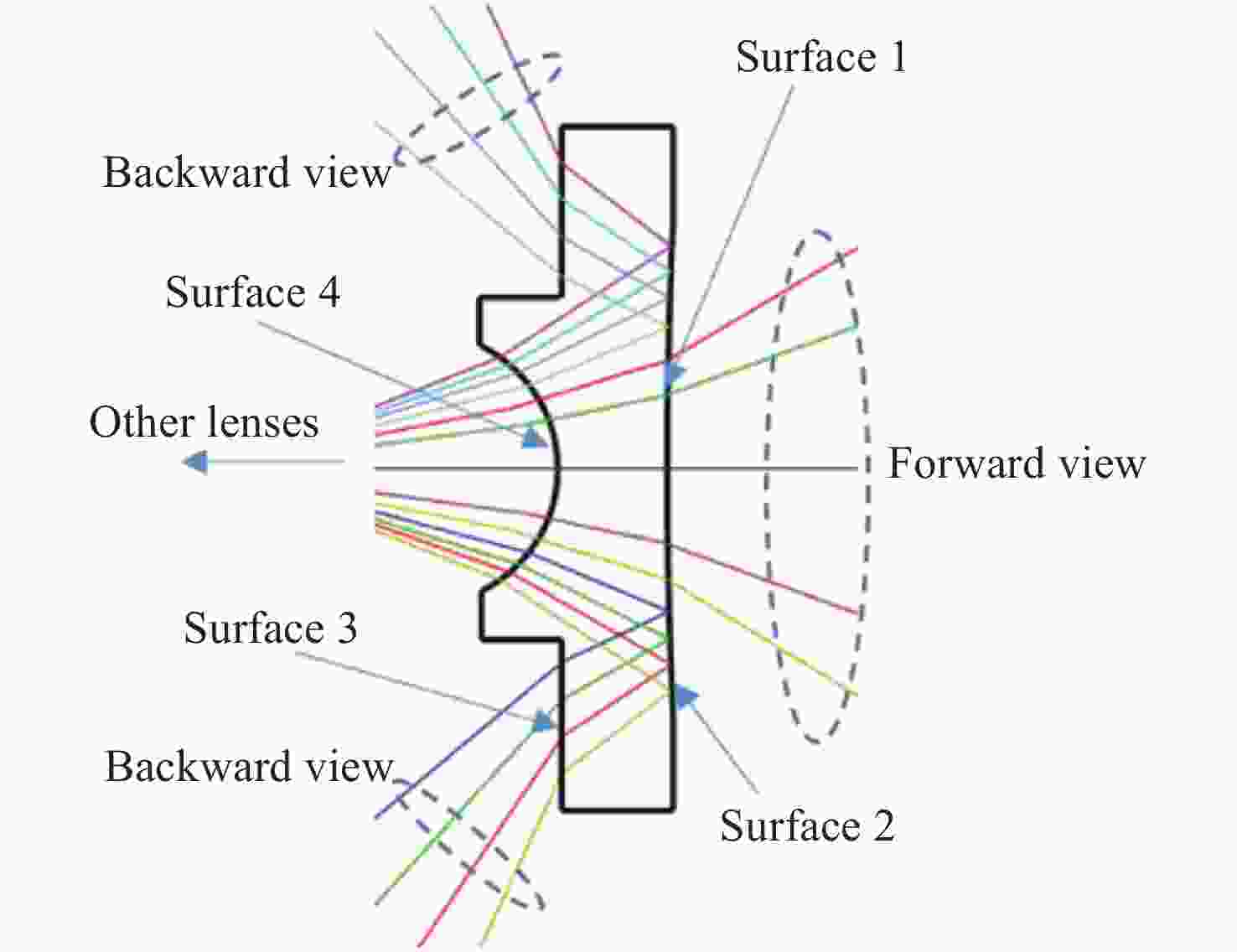
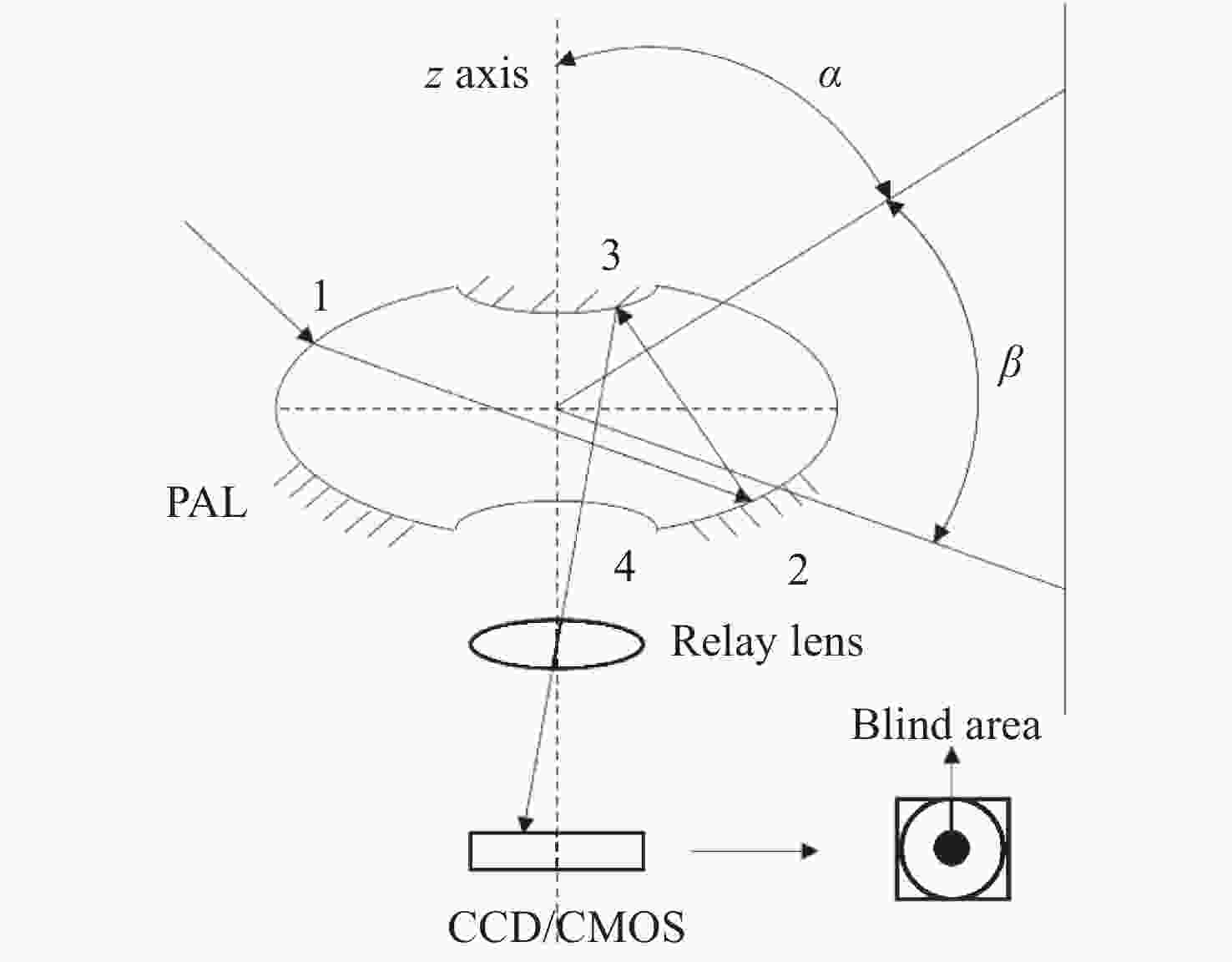
-
Key words:
- endoscope /
- panoramic imaging /
- 3D reconstruction /
- image stitching
-
图 11 真实内窥镜图像视差图。(a)输入图像(左);(b)SGBM视差图;(c)StereoNet视差图[59]
Figure 11. Disparity results of real endoscopic images. (a) Input image (left); (b) disparity map produced by the SGBM algorithm; (c) disparity map produced by StereoNet
图 13 实验场景及全景三维点云图[66]
Figure 13. Experiment scene and full-view 3D point clouds
表 1 不同全景镜头技术对比
Table 1. Comparison of different panoramic lens technologyies
表 2 常用商用胶囊内镜
Table 2. Common commercial capsule endoscopes
产品 厂家 国家 帧率 摄像头
数量视场角 PillCam SB3 Medtronic 美国 2~6 1 156° PillCam Crohn’s
CapsuleMedtronic 美国 4~35 2 336° EndoCapsule 10 Olympus 日本 2 1 160° MiroCam MC1600 IntroMedic 韩国 6 1 170° MiroCam MC2000 IntroMedic 韩国 3(per
camera)2 340° OMOM RC100 Jinshan 中国 2~8 1 160° CapsoCam Plus Capso
Vision美国 12-20 4 360° 表 3 商用结肠内镜
Table 3. Commercial colonoscopies
产品 厂家 国家 视场角 摄像头
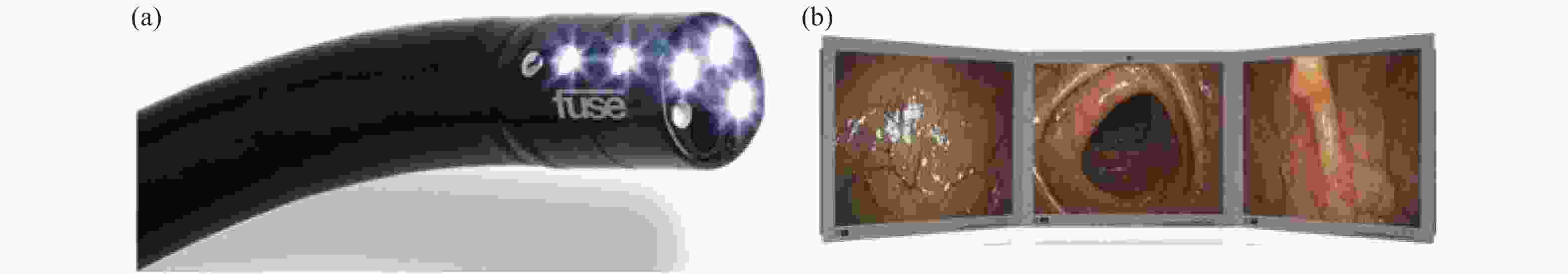
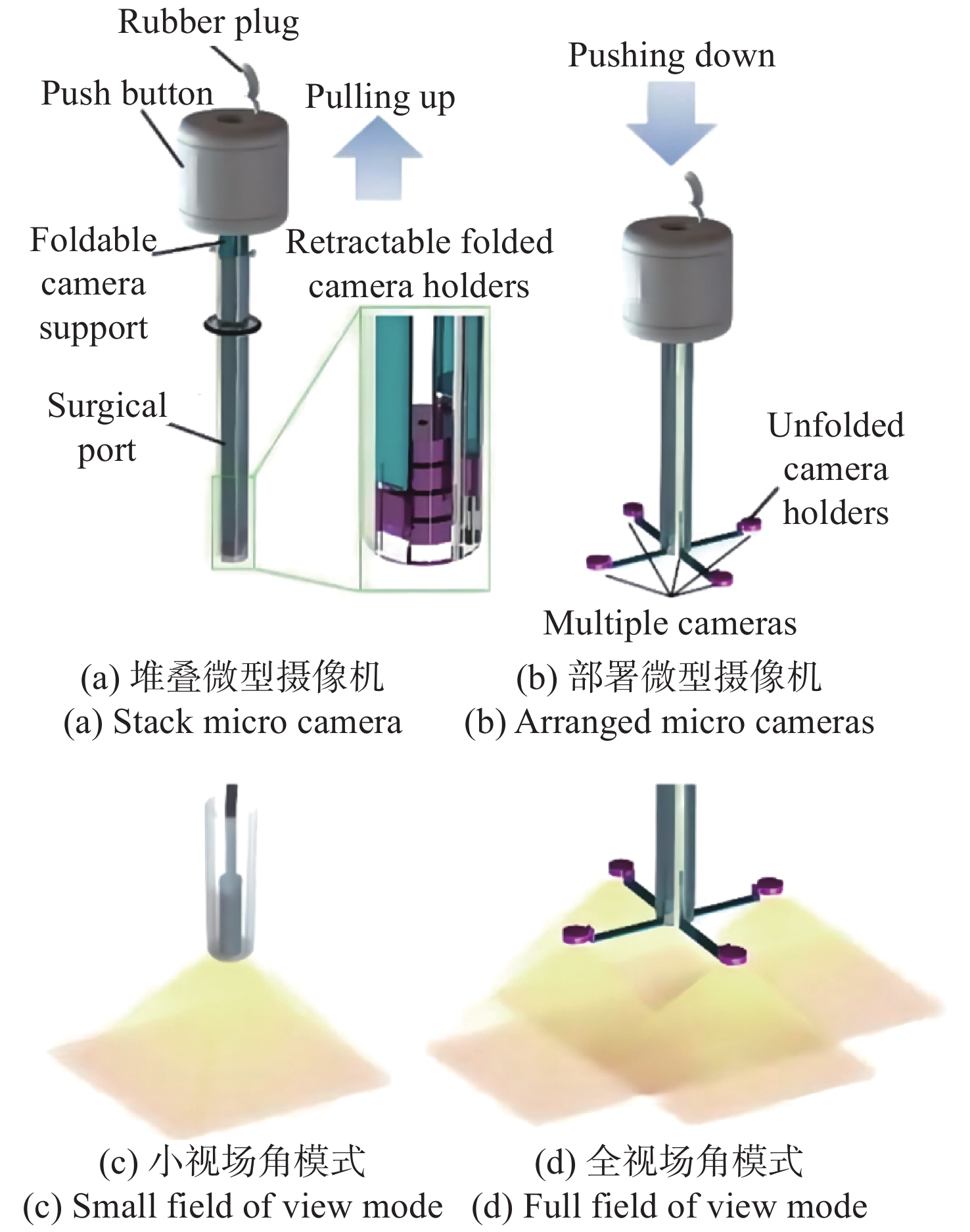
个数实现方式 CF-HQ290 Olympus 日本 170° 1 超广角 FUSE Endo Choice 美国 330° 3 多视角显示 EWAVE Olympus 日本 232° 3 多摄像头拼接 Third Eye
PanoromicAvantis 美国 >300° 3 多视角显示 -
[1] 熊兴波, 樊淑梅, 江镇州, 等. 胶囊内镜在胃肠道疾病中的诊断价值研究[J]. 中国实用医药,2021,16(19):85-87. doi: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2021.19.030XIONG X B, FAN SH M, JIANG ZH ZH, et al. Research on the diagnostic value of capsule endoscopy in gastrointestinal diseases[J]. China Practical Medicine, 2021, 16(19): 85-87. (in Chinese) doi: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2021.19.030 [2] 国擎. 腹腔镜辅助与开腹直肠癌根治术治疗直肠癌的近期效果对比[J]. 中国实用医药,2022,17(3):30-32. doi: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2022.03.010GUO Q. Comparison of the recent effect of laparoscopic-assisted resection and open radical resection of rectal cancer in the treatment of rectal cancer[J]. China Practical Medicine, 2022, 17(3): 30-32. (in Chinese) doi: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2022.03.010 [3] 高志强. 内镜联合腹腔镜在胃肠道病变手术治疗中的临床应用[J]. 影像研究与医学应用,2022,6(1):188-190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3807.2022.01.064GAO ZH Q. Clinical application of endoscopy combined with laparoscopy in the surgical treatment of gastrointestinal lesions[J]. Journal of Imaging Research and Medical Applications, 2022, 6(1): 188-190. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3807.2022.01.064 [4] VAN KEULEN K E, SOONS E, SIERSEMA P D. The role of behind folds visualizing techniques and technologies in improving adenoma detection rate[J]. Current Treatment Options in Gastroenterology, 2019, 17(3): 394-407. doi: 10.1007/s11938-019-00242-5 [5] FRIEDRICH K, GEHRKE S, STREMMEL W, et al. First clinical trial of a newly developed capsule endoscope with panoramic side view for small bowel: a pilot study[J]. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2013, 28(9): 1496-1501. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12280 [6] ZAMMIT S C, MCALINDON M E, SIDHU R. PTU-084 the use of panoramic capsule endoscopy in obscure gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(S2): A233. [7] ZWINGER L L, SIEGMUND B, STROUX A, et al. CapsoCam SV-1 versus PillCam SB 3 in the detection of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding: results of a prospective randomized comparative multicenter study[J]. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, 2019, 53(3): e101-e106. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000994 [8] BRANCHI F, FERRETTI F, ORLANDO S, et al. Small-bowel capsule endoscopy in patients with celiac disease, axial versus lateral/panoramic view: Results from a prospective randomized trial[J]. Digestive Endoscopy, 2020, 32(5): 778-784. doi: 10.1111/den.13575 [9] NAYA Y, NAKAMURA K, ARAKI K, et al. Usefulness of panoramic views for novice surgeons doing retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy[J]. International Journal of Urology, 2009, 16(2): 177-180. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2008.02215.x [10] ELOSUA A, RULLAN M, RUBIO S, et al. Does capsule endoscopy impact clinical management in established Crohn's disease?[J]. Digestive and Liver Disease, 2022, 54(1): 118-124. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2021.08.014 [11] POPOVIC V, SEYID K, COGAL Ö, et al. . State-of-the-art multi-camera systems[M]//POPOVIC V, SEYID K, COGAL Ö, et al. . Design and Implementation of Real-Time Multi-Sensor Vision Systems. Cham: Springer, 2017: 13-31. [12] ZENG J L, CHENG Y H, WU T Y, et al. . MicroEYE: a wireless multiple-lenses panoramic endoscopic system[C]. International Conference on Advanced Engineering Theory and Applications, Springer, 2017: 190-200. [13] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [14] ROSTEN E, DRUMMOND T. Machine learning for high-speed corner detection[C]. 9th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2006: 430-443. [15] BAY H, TUYTELAARS T, VAN GOOL L. Surf: Speeded up robust features[C]. 9th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2006: 404-417. [16] RUBLEE E, RABAUD V, KONOLIGE K, et al. . ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]. International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, 2011: 2564-2571. [17] MUJA M, LOWE D G. Fast approximate nearest neighbors with automatic algorithm configuration[C]. Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, INSTICC Press, 2009. [18] FISCHLER M A, BOLLES R C. Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1981, 24(6): 381-395. doi: 10.1145/358669.358692 [19] PENG C H, CHENG C H. A panoramic endoscope design and implementation for Minimally Invasive Surgery[C]. 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), IEEE, 2014: 453-456. [20] CHENG C H, PENG C H, GUO J I, et al. A two-lens minimally invasive surgical panoramic endoscope design and implementation[J]. International Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2014, 21(6): 235-241. [21] CHENG C H, HUNG SH P, GUO J I, et al. . A wireless panoramic endoscope system design and implementation for minimally invasive surgery[C]. 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), IEEE, 2015: 1895-1895. [22] KIM D T, CHENG C H. A panoramic stitching vision performance improvement technique for Minimally Invasive Surgery[C]. 2016 5th International Symposium on Next-Generation Electronics (ISNE), IEEE, 2016: 1-2. [23] KIM D T, NGUYEN V T, CHENG C H, et al. Speed improvement in image stitching for panoramic dynamic images during minimally invasive surgery[J]. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2018, 2018: 3654210. [24] KIM D T, CHENG C H, LIU D G, et al. Designing a new endoscope for panoramic-view with focus-area 3D-vision in minimally invasive surgery[J]. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 2020, 40(2): 204-219. doi: 10.1007/s40846-019-00503-9 [25] KIM D T, CHENG C H, LIU D G, et al. Performance improvement for two-lens panoramic endoscopic system during minimally invasive surgery[J]. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2019, 2019: 2097284. [26] KIM J J, WATRAS A, LIU H W, et al. Large-field-of-view visualization utilizing multiple miniaturized cameras for laparoscopic surgery[J]. Micromachines, 2018, 9(9): 431. doi: 10.3390/mi9090431 [27] ZHANG Z Y, WANG L X, ZHENG W F, et al. Endoscope image mosaic based on pyramid ORB[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 71: 103261. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103261 [28] JANG J, YOO H J. A capsule endoscope system for wide visualization field and location tracking[C]. 2018 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), IEEE, 2018: 1-4. [29] SHEU M J, CHIANG C W, SUN W S, et al. Dual view capsule endoscopic lens design[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(7): 8565-8575. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.008565 [30] JANG J, LEE J, LEE K R, et al. . 4-Camera VGA-resolution capsule endoscope with 80 MB/s body-channel communication transceiver and Sub-cm range capsule localization[C]. 2018 IEEE International Solid - State Circuits Conference - (ISSCC), IEEE, 2018: 282-284. [31] TAMADAZTE B, AGUSTINOS A, CINQUIN P, et al. Multi-view vision system for laparoscopy surgery[J]. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2015, 10(2): 195-203. doi: 10.1007/s11548-014-1064-2 [32] LIN CH H, HSIAO L J, HSAIO J T, et al. Front view and panoramic side view videoscope lens system design[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(29): H146-H152. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.00H146 [33] KATKAM R, BANERJEE B, HUANG C Y, et al. Compact dual-view endoscope without field obscuration[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2015, 20(7): 076007. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.20.7.076007 [34] LIU Q, BAI J, LUO Y J. Design of high resolution panoramic endoscope imaging system based on freeform surface[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2016, 680: 012011. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/680/1/012011 [35] SAHLI S, WANG R C C, MURTHY A, et al. A 360 degree side view endoscope for lower GI tract mapping[J]. Physics in Canada, 2015, 71: 18-20. [36] DALLAIRE X, THIBAULT S. Design of a foveated wide-angle endoscopic lens[J]. Optical Engineering, 2016, 55(4): 047106. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.55.4.047106 [37] TSENG S M, HUANG C W, HSU Y T, et al. . Panoramic annular lens design of endoscope[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW), IEEE, 2017: 101-102. [38] TSENG S M, YU J C, HSU Y T, et al. Panoramic endoscope based on convex parabolic mirrors[J]. Optical Engineering, 2018, 57(3): 033102. [39] TSENG Y C, HAN P, HSU H C, et al. A flexible FOV capsule endoscope design based on compound lens[J]. Journal of Display Technology, 2016, 12(12): 1798-1804. [40] COGAL O, LEBLEBICI Y. An insect eye inspired miniaturized multi-camera system for endoscopic imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2017, 11(1): 212-224. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2016.2547388 [41] CHEN L, YUAN Q, YE J F, et al. Design of a compact dual-view endoscope based on a hybrid lens with annularly stitched aspheres[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 453: 124346. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.124346 [42] PENNE J, HÖLLER K, STÜRMER M, et al. . Time-of-flight 3-D endoscopy[C]. 12th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Springer, 2009: 467-474. [43] KÖHLER T, HAASE S, BAUER S, et al. . ToF meets RGB: novel multi-sensor super-resolution for hybrid 3-D endoscopy[C]. 16th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 2013: 139-146. [44] STOLYAROV R, BUHARIN V, VAL M, et al. Sub-millimeter precision 3D measurement through a standard endoscope with time of flight[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2022, 11949: 119490E. [45] ISHII I, YAMAMOTO K,DOI K, et al.. High-speed 3D image acquisition using coded structured light projection[C]. 2007 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IEEE, 2007: 925-930. [46] 朱高杰. 基于相位结构光的三维测量内窥镜系统研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.ZHU G J. Research on three-dimensional measurement endoscope system based on phase-shifting structure light[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. (in Chinese) [47] HUANG P S, ZHANG S. Fast three-step phase-shifting algorithm[J]. Applied Optics, 2006, 45(21): 5086-5091. doi: 10.1364/AO.45.005086 [48] VALKENBURG R J, MCIVOR A M. Accurate 3D measurement using a structured light system[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 1998, 16(2): 99-110. doi: 10.1016/S0262-8856(97)00053-X [49] POSDAMER J L, ALTSCHULER M D. Surface measurement by space-encoded projected beam systems[J]. Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 1982, 18(1): 1-17. doi: 10.1016/0146-664X(82)90096-X [50] HEIKE C L, UPSON K, STUHAUG E, et al. 3D digital stereophotogrammetry: a practical guide to facial image acquisition[J]. Head &Face Medicine, 2010, 6(1): 18. [51] MAURICE X, ALBITAR C, DOIGNON C, et al. . A structured light-based laparoscope with real-time organs' surface reconstruction for minimally invasive surgery[C]. 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, IEEE, 2012: 5769-5772. [52] GRIFFIN P M, NARASIMHAN L S, YEE S R. Generation of uniquely encoded light patterns for range data acquisition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 1992, 25(6): 609-616. doi: 10.1016/0031-3203(92)90078-W [53] DESJARDINS D, PAYEUR P. Dense stereo range sensing with marching pseudo-random patterns[C]. Fourth Canadian Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV'07), IEEE, 2007: 216-226. [54] GORTHI S S, RASTOGI P. Fringe projection techniques: whither we are?[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2010, 48: 133-140. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2009.09.001 [55] CLANCY N T, STOYANOV D, MAIER-HEIN L, et al. Spectrally encoded fiber-based structured lighting probe for intraoperative 3D imaging[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2011, 2(11): 3119-3128. doi: 10.1364/BOE.2.003119 [56] STOYANOV D, YANG G ZH. Soft tissue deformation tracking for robotic assisted minimally invasive surgery[C]. 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, IEEE, 2009: 254-257. [57] HIRSCHMULLER H. Stereo processing by semiglobal matching and mutual information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 30(2): 328-341. [58] KHAMIS S, FANELLO S, RHEMANN C, et al. . Stereonet: Guided hierarchical refinement for real-time edge-aware depth prediction[C]. 15th Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Springer, 2018: 573-590. [59] YU H, ZHOU CH J, ZHANG W, et al. A three-dimensional measurement method for binocular endoscopes based on deep learning[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology &Electronic Engineering, 2022, 23(4): 653-660. [60] ZHOU CH J, YU H, YUAN B, et al. Three-dimensional stitching of binocular endoscopic images based on feature points[J]. Photonics, 2021, 8(8): 330. doi: 10.3390/photonics8080330 [61] MUR-ARTAL R, MONTIEL J M M, TARDÓS J D. ORB-SLAM: a versatile and accurate monocular SLAM system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2015, 31(5): 1147-1163. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671 [62] MUR-ARTAL R, TARDÓS J D. ORB-SLAM: tracking and mapping recognizable features[C]. Workshop on Multi View Geometry in Robotics (MVIGRO), 2014: 2. [63] MUR-ARTAL R, TARDÓS J D. Orb-slam2: An open-source slam system for monocular, stereo, and rgb-d cameras[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017, 33(5): 1255-1262. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103 [64] CAMPOS C, ELVIRA R, RODRÍGUEZ J J G, et al. Orb-slam3: An accurate open-source library for visual, visual–inertial, and multimap slam[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021, 37(6): 1874-1890. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3075644 [65] WHELAN T, LEUTENEGGER S, SALAS-MORENO R, et al. . ElasticFusion: Dense SLAM without a pose graph[C]. Robotics: Science and Systems XI, 2015. [66] DOCEA R, PFEIFFER M, BODENSTEDT S, et al. Simultaneous localisation and mapping for laparoscopic liver navigation: a comparative evaluation study[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2021, 11598: 115980B. [67] CHEN L, TANG W, JOHN N W, et al. SLAM-based dense surface reconstruction in monocular minimally invasive surgery and its application to augmented reality[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2018, 158: 135-146. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.02.006 [68] NEWCOMBE R A, LOVEGROVE S J, DAVISON A J. DTAM: Dense tracking and mapping in real-time[C]. 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2011: 2320-2327. [69] ENGEL J, STURM J, CREMERS D. Semi-dense visual odometry for a monocular camera[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2013: 1449-1456. [70] CHEN R J, BOBROW T L, ATHEY T, et al. . Slam endoscopy enhanced by adversarial depth prediction[Z]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1907.00283, 2019. [71] WIDYA A R, MONNO Y, OKUTOMI M, et al. Whole stomach 3D reconstruction and frame localization from monocular endoscope video[J]. IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine, 2019, 7: 1-10. [72] TONTINI G E, CAVALLARO F, NEUMANN H, et al. . Extensive small-bowel Crohn’s disease detected by the newly introduced 360° panoramic viewing capsule endoscopy system[J]. Endoscopy, 2014, 46(S 01): E353-E354. [73] VOGELSTEIN B, FEARON E R, HAMILTON S R, et al. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development[J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 1988, 319(9): 525-532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901 [74] LEGGETT B, WHITEHALL V. Role of the serrated pathway in colorectal cancer pathogenesis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2010, 138(6): 2088-2100. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.12.066 [75] GRALNEK I M, CARR-LOCKE D L, SEGOL O, et al. Comparison of standard forward-viewing mode versus ultrawide-viewing mode of a novel colonoscopy platform: a prospective, multicenter study in the detection of simulated polyps in an in vitro colon model (with video)[J]. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 2013, 77(3): 472-479. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.12.011 [76] RUBIN M, BOSE K P, KIM S H. Mo1517 successful deployment and use of third eye panoramic™ a novel side viewing video CAP fitted on a standard colonoscope[J]. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 2014, 79(S5): AB466. -






 下载:
下载: