Spatial pulse position modulation multi-classification detector based on deep learning
-
摘要:
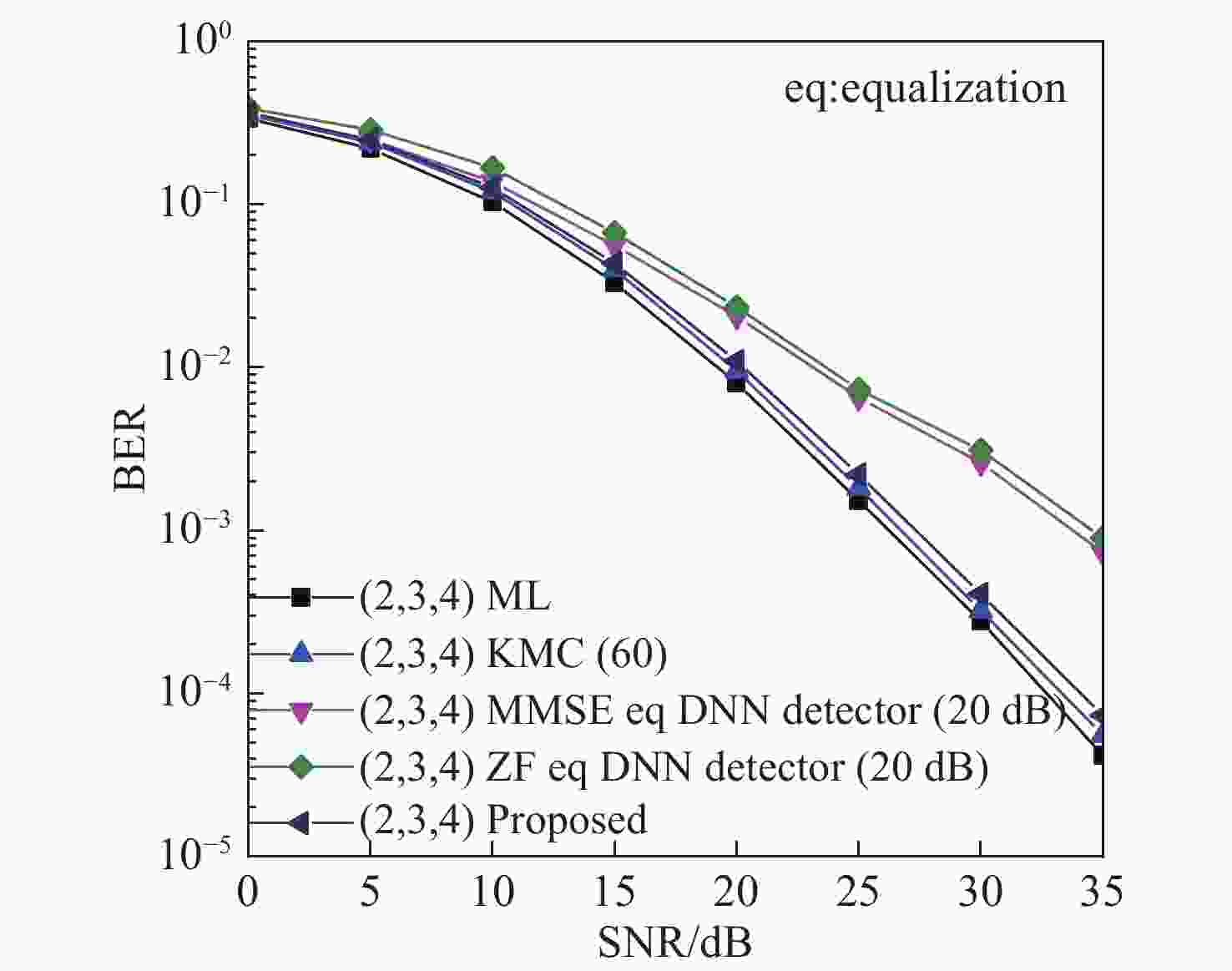
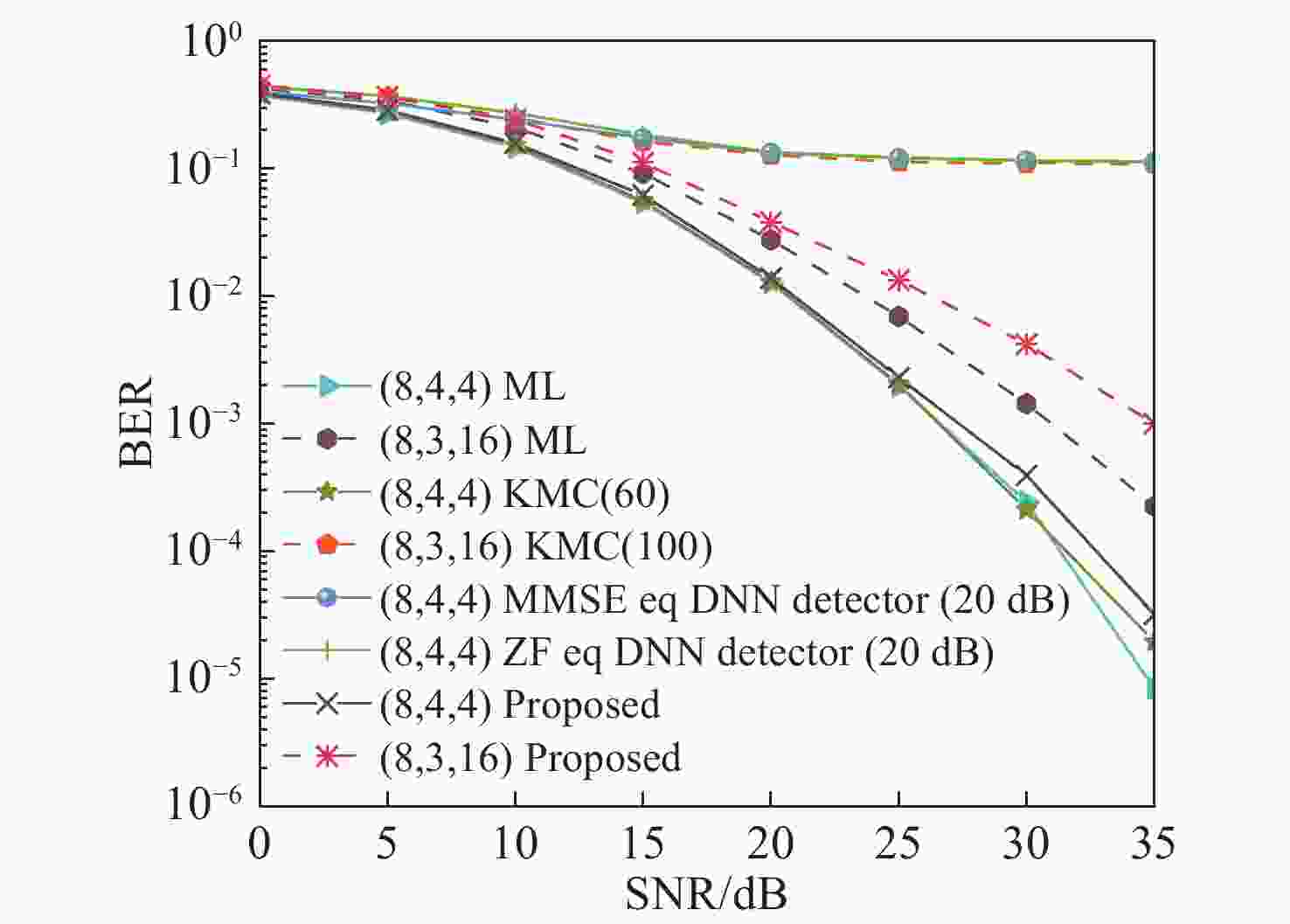
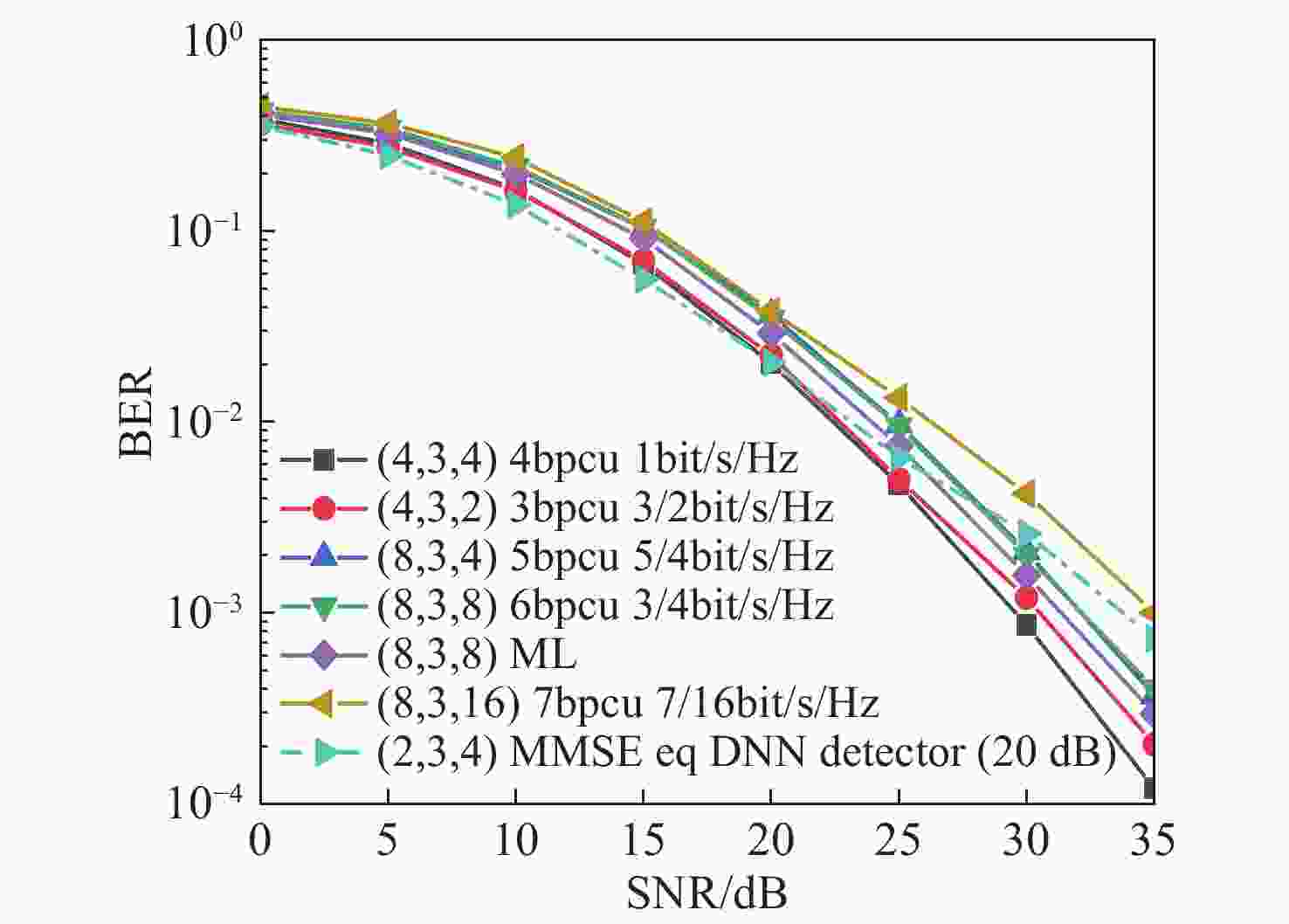
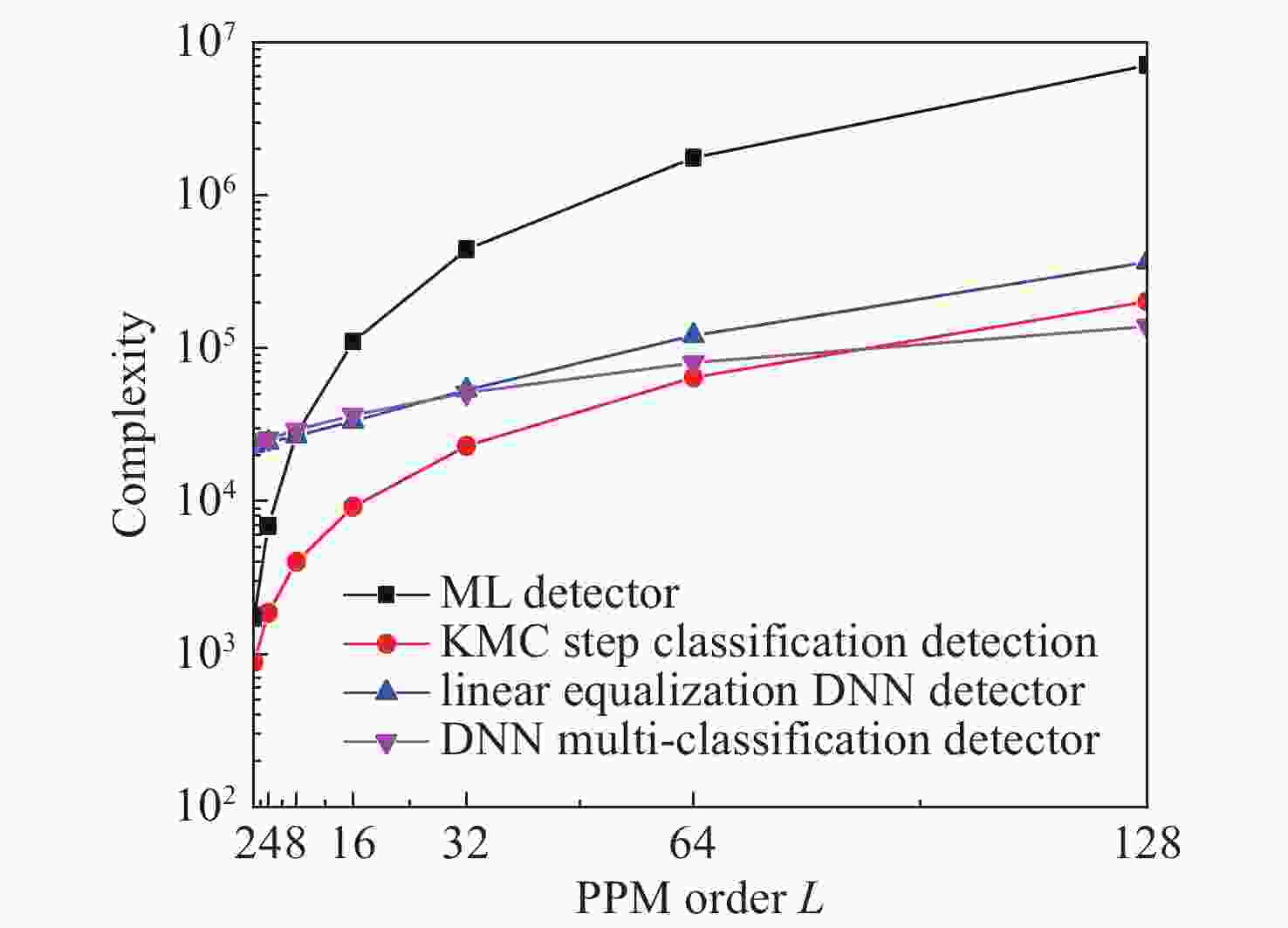
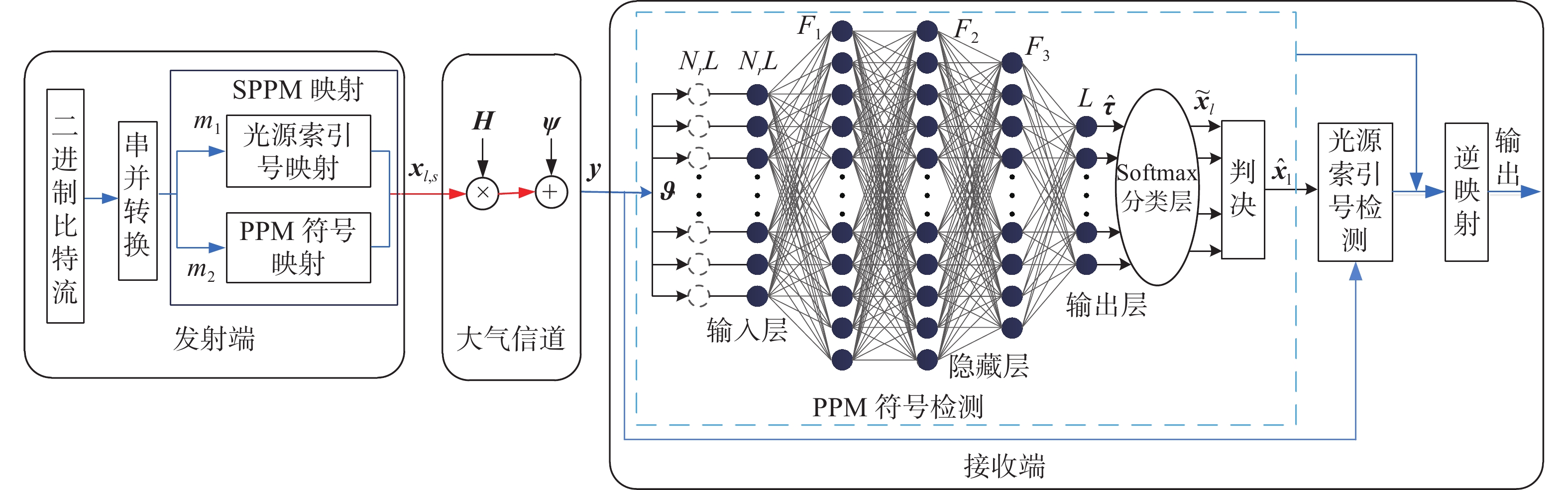
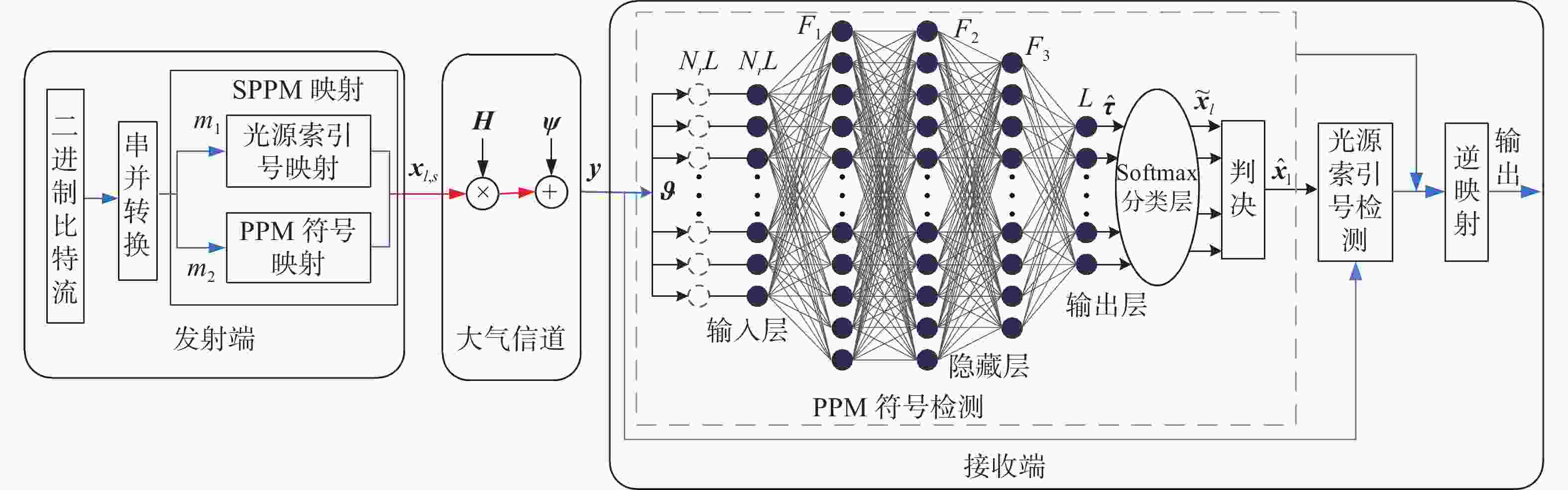
为有效避免最大似然(ML)检测复杂的计算过程,根据空间脉冲位置调制(SPPM)信号的特点,将深度神经网络(DNN)与分步检测相结合,提出了一种基于深度学习的SPPM多分类检测器。在该检测器中,利用DNN建立接收信号与PPM符号间的非线性关系,并以此为准则完成在线接收PPM符号的检测,从而有效避免了对PPM符号的穷搜索检测过程。结果表明,采用本文检测器后,SPPM系统在大幅降低检测复杂度的前提下,取得了近似最优的误比特性能,同时还克服了K均值聚类(KMC)分步分类检测所出现的错误平台效应。当PPM阶数为64时,本文方法较ML检测和线性均衡DNN检测器的计算复杂度分别降低了约95.45%、33.54%。
Abstract:In order to effectively avoid high computational complexity when using Maximum Likelihood (ML) detection, a deep learning-based Spatial Pulse Position Modulation (SPPM) multi-classification detector is proposed by combining a Deep Neural Network (DNN) and step detection. In the detector, the DNN is used to establish a non-linear relationship between the received signal and the PPM symbols. Thereafter, the subsequent received PPM symbols are detected according to this relationship, so as to avoid the exhaustive search process of PPM symbol detection. The simulation results show that with the proposed detector, the SPPM system approximately achieves optimal bit error performance on the premise of greatly reducing detection complexity. Meanwhile, it overcomes the error platform effect caused by K-Means Clustering (KMC) step classification detection. When the PPM order is 64, the computational complexity of the proposal is about 95.45% and 33.54% lower than that of ML detectors and linear equalization DNN detectors, respectively.
-
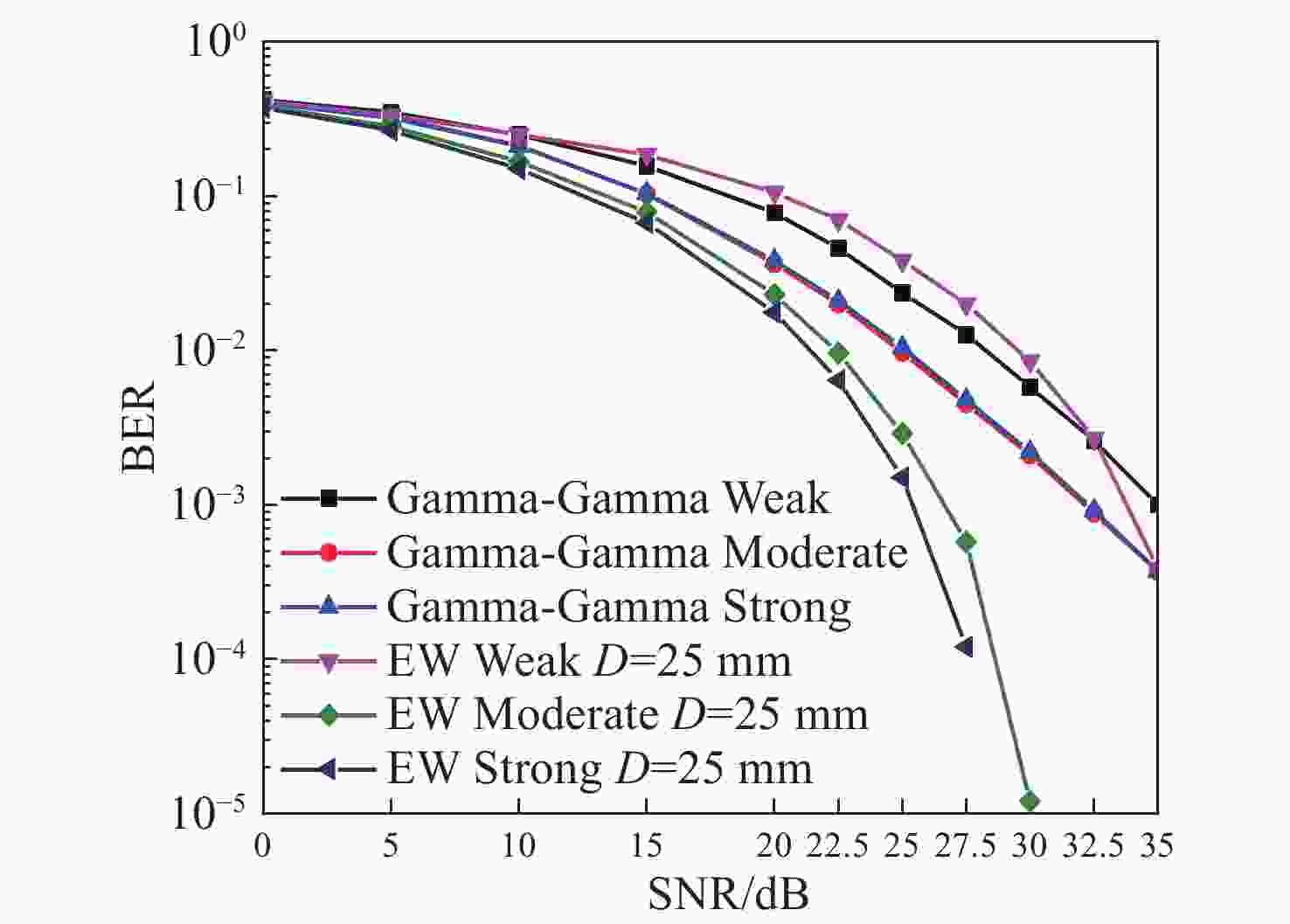
表 1 湍流模型参数
Table 1. Turbulence model parameters
表 2 多分类检测器的超参数
Table 2. Hyperparameters of the multi-classification detector
超参数 值 各隐藏层神经元数目 F1=64,F2=98,F3=48 Batch 1.25×104 Batch_size 24 轮次Epoch 50 激活函数 Relu+Sigmoid 损失函数 Cross Entropy Loss 优化器 SGD 学习率 0.001 表 3 各算法计算复杂度
Table 3. Computational complexity of each algorithm
检测算法 计算复杂度/Flops ML 检测 $ {N_t}L\left( {2{N_t}{N_r}L + 2{N_r}L - 1} \right) $ KMC分步分类检测[23] $ {N_t}\left( {2{N_t}{N_r}L + {\text{2}}{N_r}L - 1} \right) + L\left( {3{N_r}L - 1} \right) $ 线性均衡DNN检测器[17] $ 2\left( {{{\left( {{N_r}L} \right)}^2} + {N_r}L{F_1} + {F_1}{F_2} + {F_2}{F_3} + {F_3}{{\log }_2}\left( {{N_t}L} \right)} \right) + {\log _2}\left( {{N_t}L} \right) $ DNN多分类检测器 $ 2\left( {{N_r}L{F_1} + {F_1}{F_2} + {F_2}{F_3} + {F_3}L + N_t^2{N_r}L + {N_t}{N_r}L} \right) + 3L - {N_t} - 1 $ -
[1] LI Y Y, YANG P, DI RENZO M, et al. Precoded optical spatial modulation for indoor visible light communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(4): 2518-2531. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3041766 [2] REN Y X, WANG ZH, XIE G D, et al. Atmospheric turbulence mitigation in an OAM-based MIMO free-space optical link using spatial diversity combined with MIMO equalization[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(11): 2406-2409. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.002406 [3] HAJJARIAN Z, FADLULLAH J, KAVEHRAD M. MIMO free space optical communications in turbid and turbulent atmosphere[J]. Journal of Communications, 2009, 4(8): 524-532. [4] ZHONG X, CHEN CH, FU SH, et al. . OFDM-based generalized spatial modulation for optical wireless communication[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 16th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, IEEE, 2021: 1311-1316. [5] ANANDKUMAR D, SANGEETHA R G. A survey on performance enhancement in free space optical communication system through channel models and modulation techniques[J]. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 2021, 53(1): 1-39. doi: 10.1007/s11082-020-02629-6 [6] YU S Y, GENG CH, ZHONG J, et al. Performance analysis of optical spatial modulation over a correlated Gamma-Gamma turbulence channel[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(8): 2025-2035. doi: 10.1364/AO.447644 [7] 张悦, 王惠琴, 曹明华, 等. 无线光通信中的增强型光空间调制[J]. 光学学报,2020,40(3):0306001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0306001ZHANG Y, WANG H Q, CAO M H, et al. Enhanced optical spatial modulation in wireless optical communication[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(3): 0306001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0306001 [8] INOUE K. Analysis of BER degradation owing to multiple crosstalk channels in optical QPSK/QAM signals[J]. IEICE Transactions on Communications, 2021, E104.B(4): 370-377. doi: 10.1587/transcom.2020EBP3098 [9] BHOWAL A, KSHETRIMAYUM R S. Advanced optical spatial modulation techniques for FSO communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(2): 1163-1174. [10] 徐宪莹, 岳殿武. 可见光通信中正交频分复用调制技术[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(3):516-527. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0051XU X Y, YUE D W. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing modulation techniques in visible light communication[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(3): 516-527. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0051 [11] KUMAR D A, SANGEETHA R G. Power series based gamma-gamma fading MIMO/FSO link analysis with atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors[J]. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 2021, 53(9): 505. doi: 10.1007/s11082-021-03103-7 [12] 王惠琴, 宋梨花, 曹明华, 等. 湍流信道下光空间调制信号的压缩感知检测[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(11):2669-2674. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182611.2669WANG H Q, SONG L H, CAO M H, et al. Compressed sensing detection of optical spatial modulation signal in turbulent channel[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(11): 2669-2674. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182611.2669 [13] XIE Y H, TEH K C, KOT A C. Deep learning-based joint detection for OFDM-NOMA scheme[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(8): 1-27. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3077878 [14] BAEK M S, KWAK S W, JUNG J Y. Implementation methodologies of deep learning-based signal detection for conventional MIMO transmitters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2019, 65(3): 636-642. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2019.2891051 [15] SHAMASUNDAR B, CHOCKALINGAM A. A DNN architecture for the detection of generalized spatial modulation signals[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(12): 2770-2774. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3018260 [16] AMIRABADI M A, KAHAEI M H, NEZAMALHOSSEINI S A. Deep learning based detection technique for FSO communication systems[J]. Physical Communication, 2020, 43: 101229. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2020.101229 [17] WANG T J, YANG F, SONG J. Deep learning-based detection scheme for visible light communication with generalized spatial modulation[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(20): 28906-28915. doi: 10.1364/OE.404463 [18] LUONG T V, KO Y, VIEN N A, et al. Deep learning-based detector for OFDM-IM[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(4): 1159-1162. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2909893 [19] 周畅, 于笑楠, 姜会林, 等. 基于APD自适应增益控制的近地无线金宝搏188软件怎么用 通信信道大气湍流抑制方法研究[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2022,49(4):0406002. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.0406002ZHOU CH, YU X N, JIANG H L, et al. Atmospheric turbulence suppression methods for near the earth wireless laser communication channels based on avalanche photodiode adaptive gain control[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(4): 0406002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.0406002 [20] BARRIOS R, DIOS F. Exponentiated Weibull model for the irradiance probability density function of a laser beam propagating through atmospheric turbulence[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2013, 45(1): 13-20. [21] PHAM H T T, DANG N T. Performance improvement of spatial modulation-assisted FSO systems over Gamma-Gamma fading channels with geometric spreading[J]. Photonic Network Communications, 2017, 34(2): 213-220. [22] 劳陈哲, 孙建锋, 周煜, 等. 多孔径接收相干合束系统性能研究[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2019,46(7):0705003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0705003LAO CH ZH, SUN J F, ZHOU Y, et al. Performance of coherent beam combining system with multiple aperture receiver[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2019, 46(7): 0705003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0705003 [23] 王惠琴, 侯文斌, 彭清斌, 等. 基于K均值聚类的SPPM分步分类检测算法[J]. 通信学报,2022,43(1):161-171. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022010WANG H Q, HOU W B, PENG Q B, et al. Step-by-step classification detection algorithm of SPPM based on K-means clustering[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(1): 161-171. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022010 [24] 霍婷婷, 张冬冬, 施祥蕾, 等. 基于碳纳米薄膜/砷化镓范德华异质结的高性能自驱动光电探测器研究[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):373-386. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0149HUO T T, ZHANG D D, SHI X L, et al. High-performance self-powered photodetectors based on the carbon nanomaterial/GaAs vdW heterojunctions[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 373-386. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0149 [25] O’SHEA T, HOYDIS J. An introduction to deep learning for the physical layer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2017, 3(4): 563-575. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2017.2758370 [26] AMIRABADI M A, KAHAEI M H, NEZAMALHOSSENI S A. Low complexity deep learning algorithms for compensating atmospheric turbulence in the free space optical communication system[J]. IET Optoelectronics, 2022, 16(3): 93-105. -





 下载:
下载: