-
摘要:
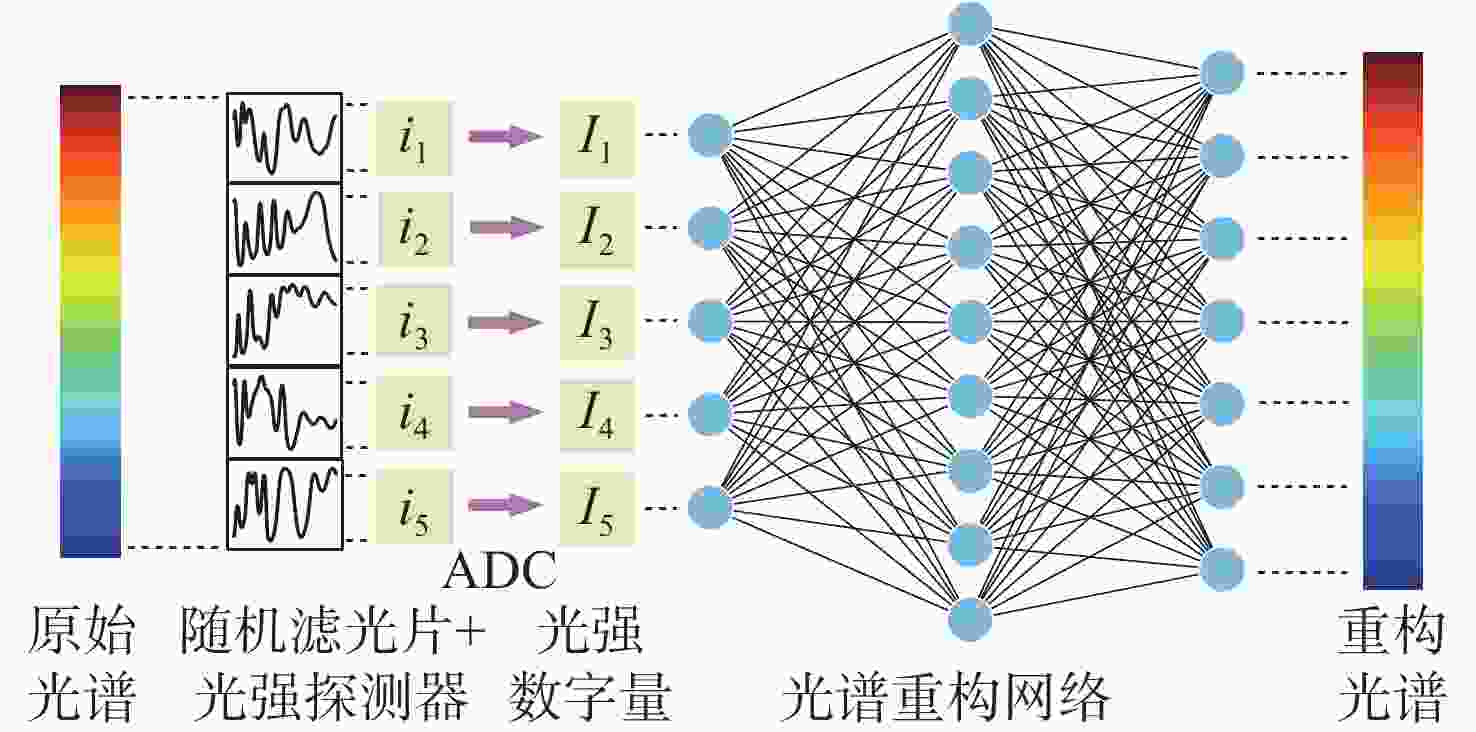
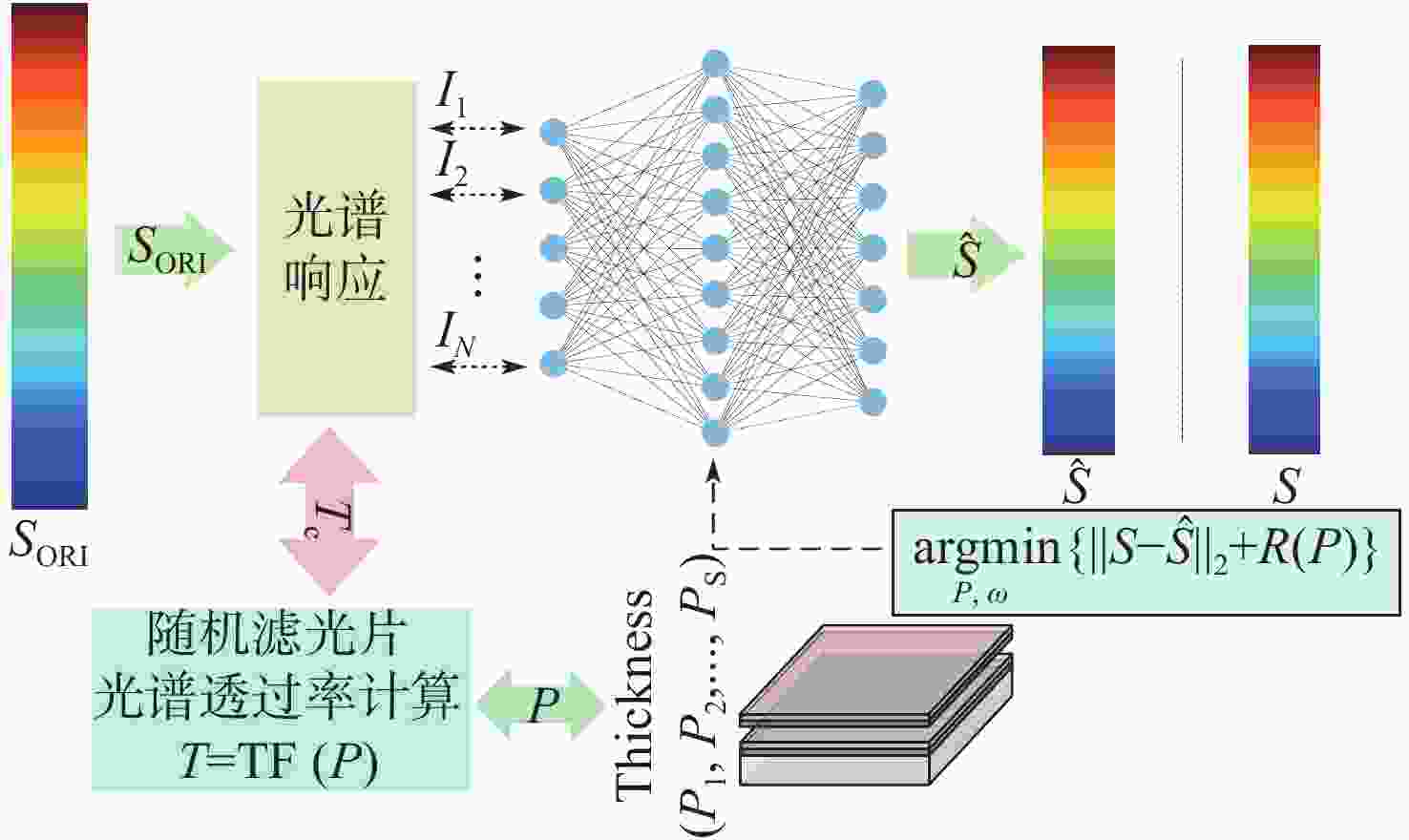
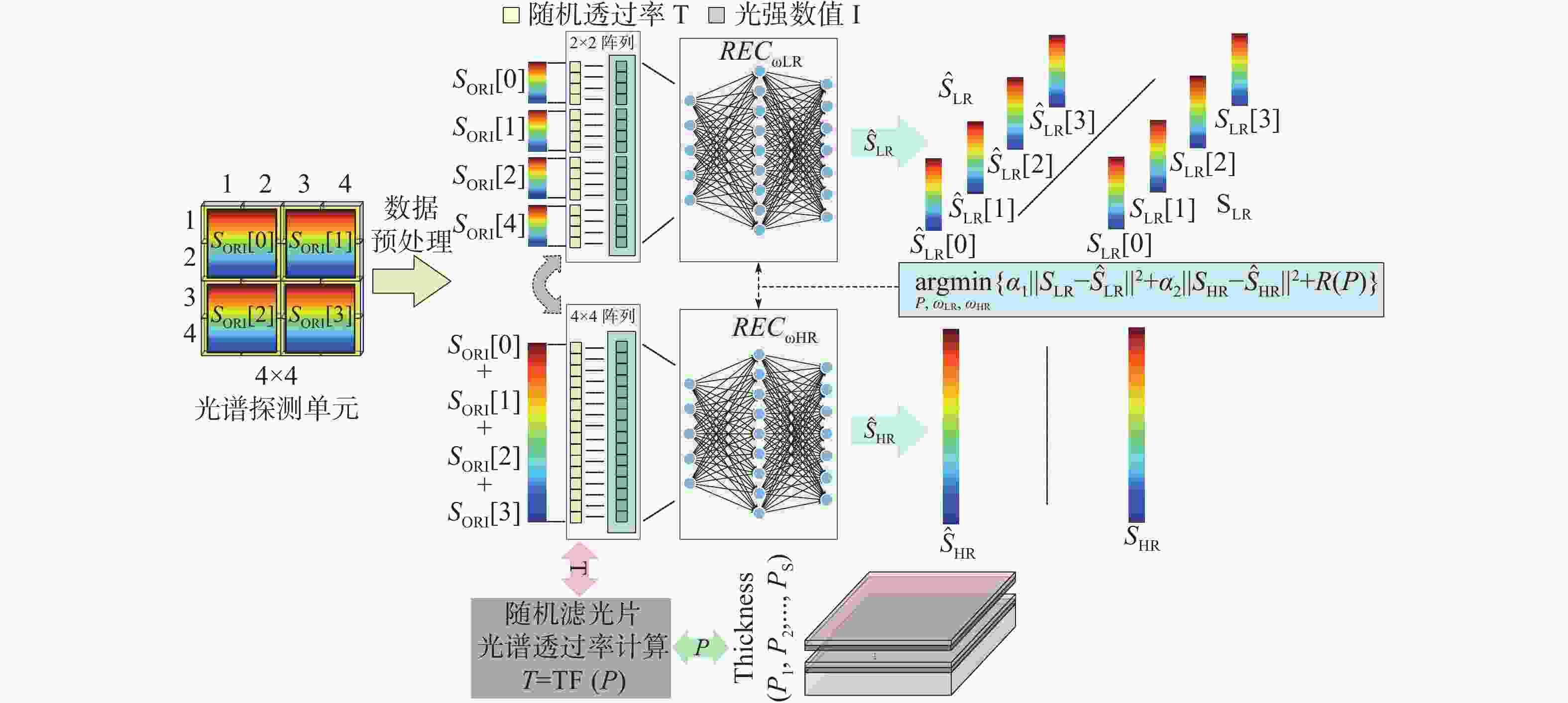
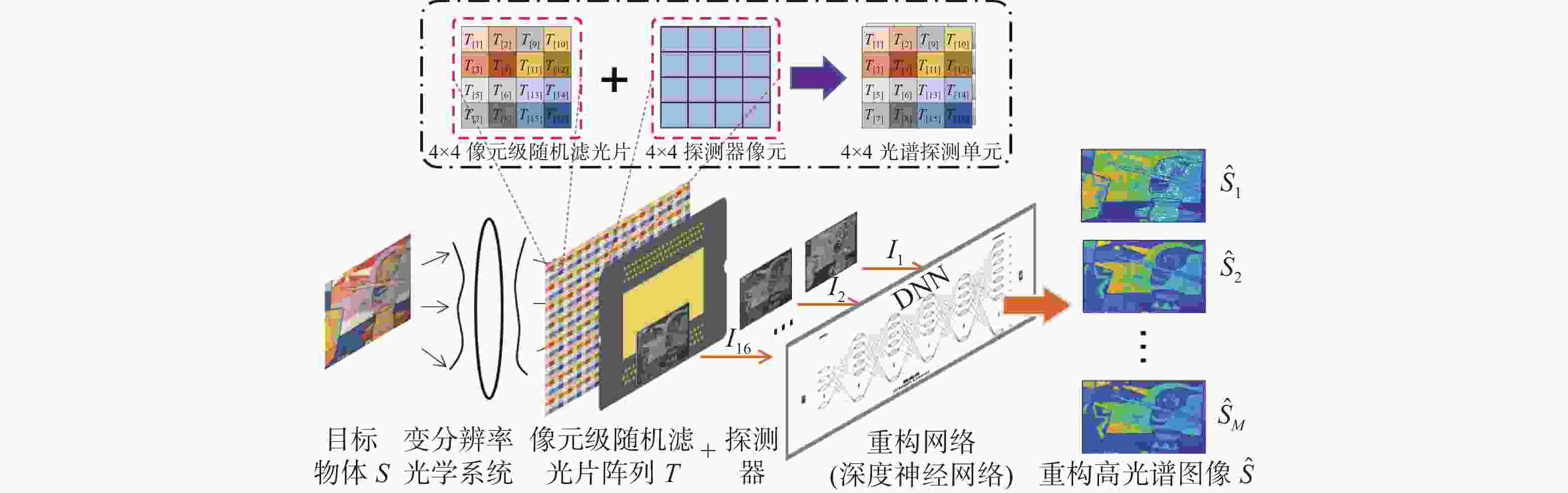
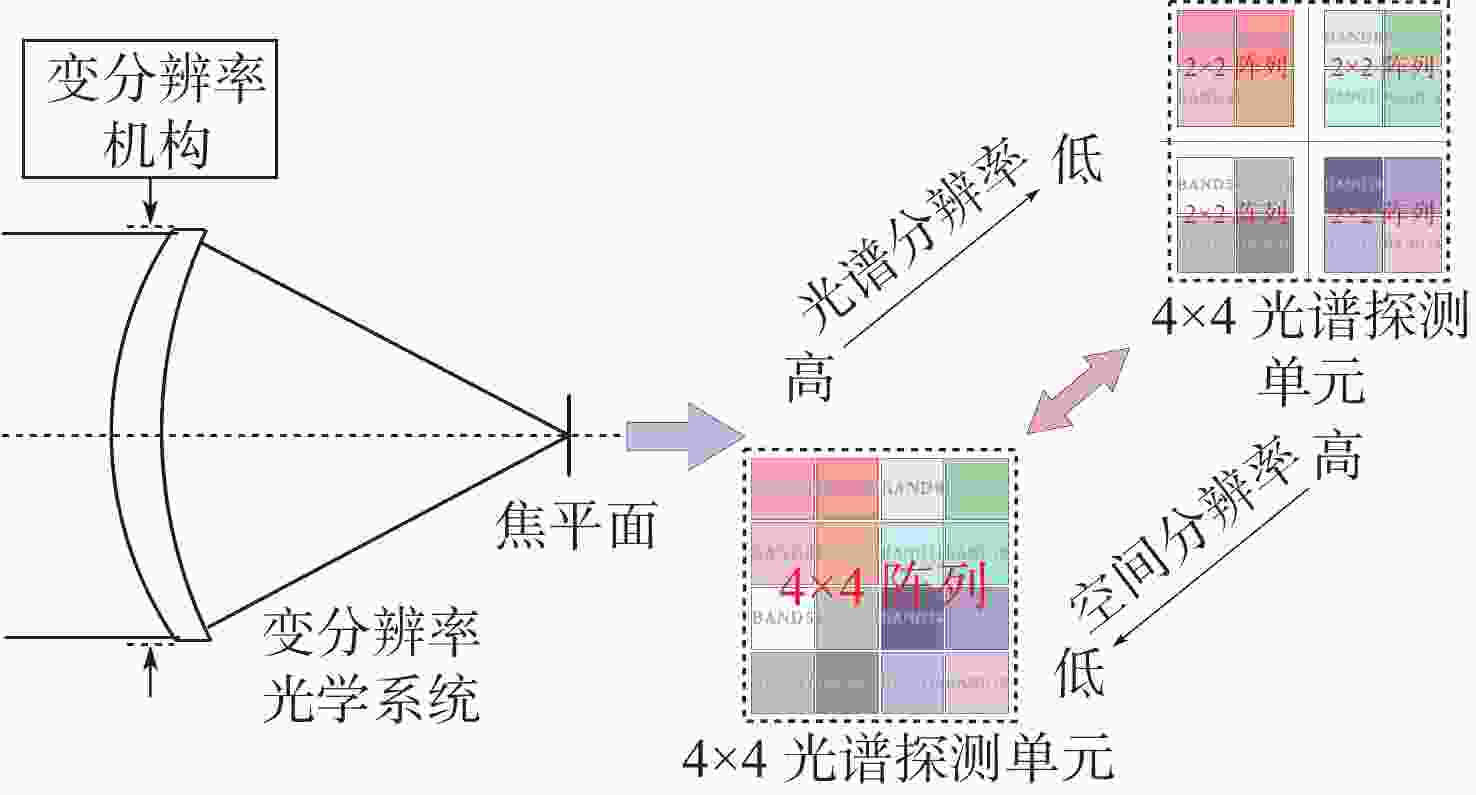
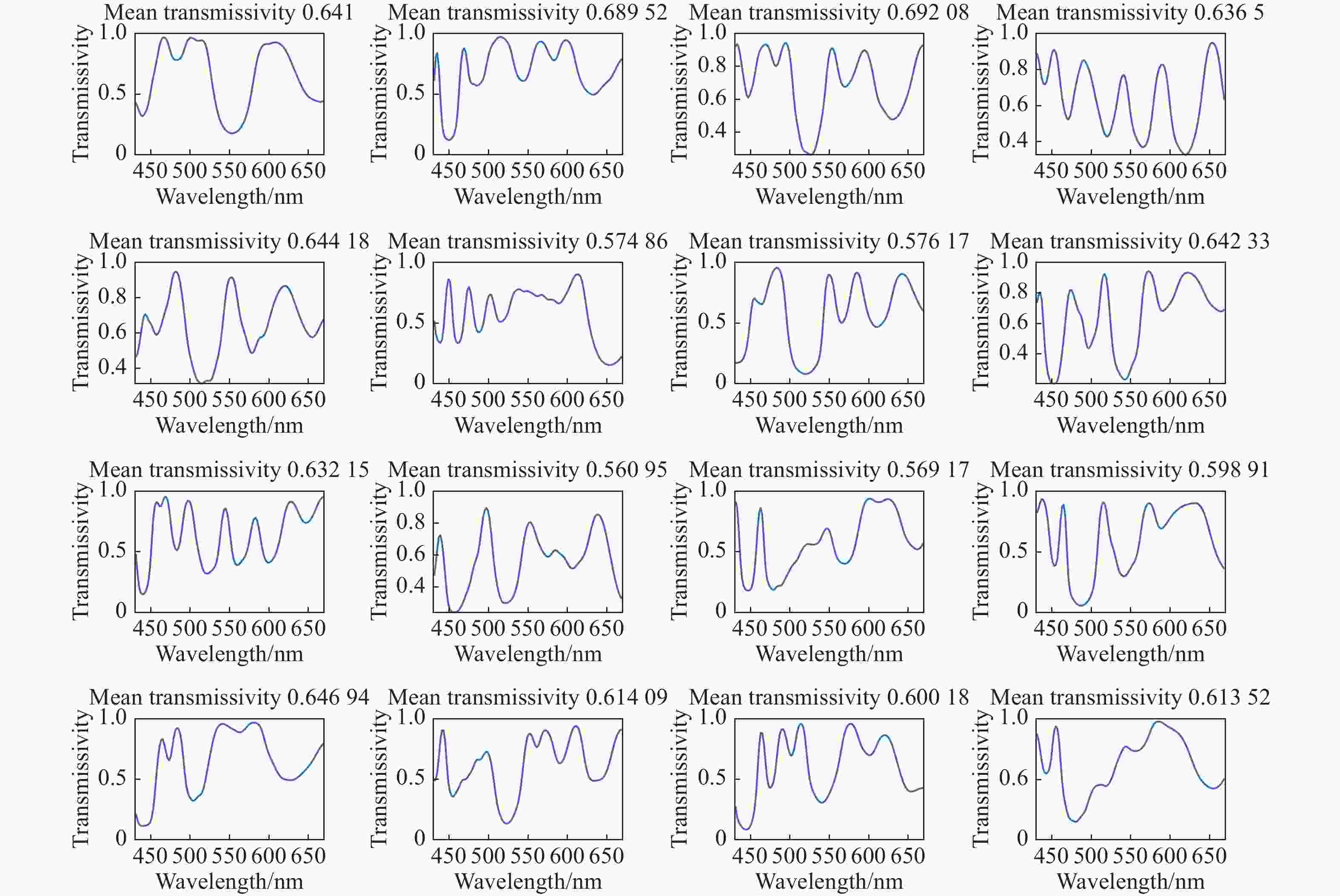
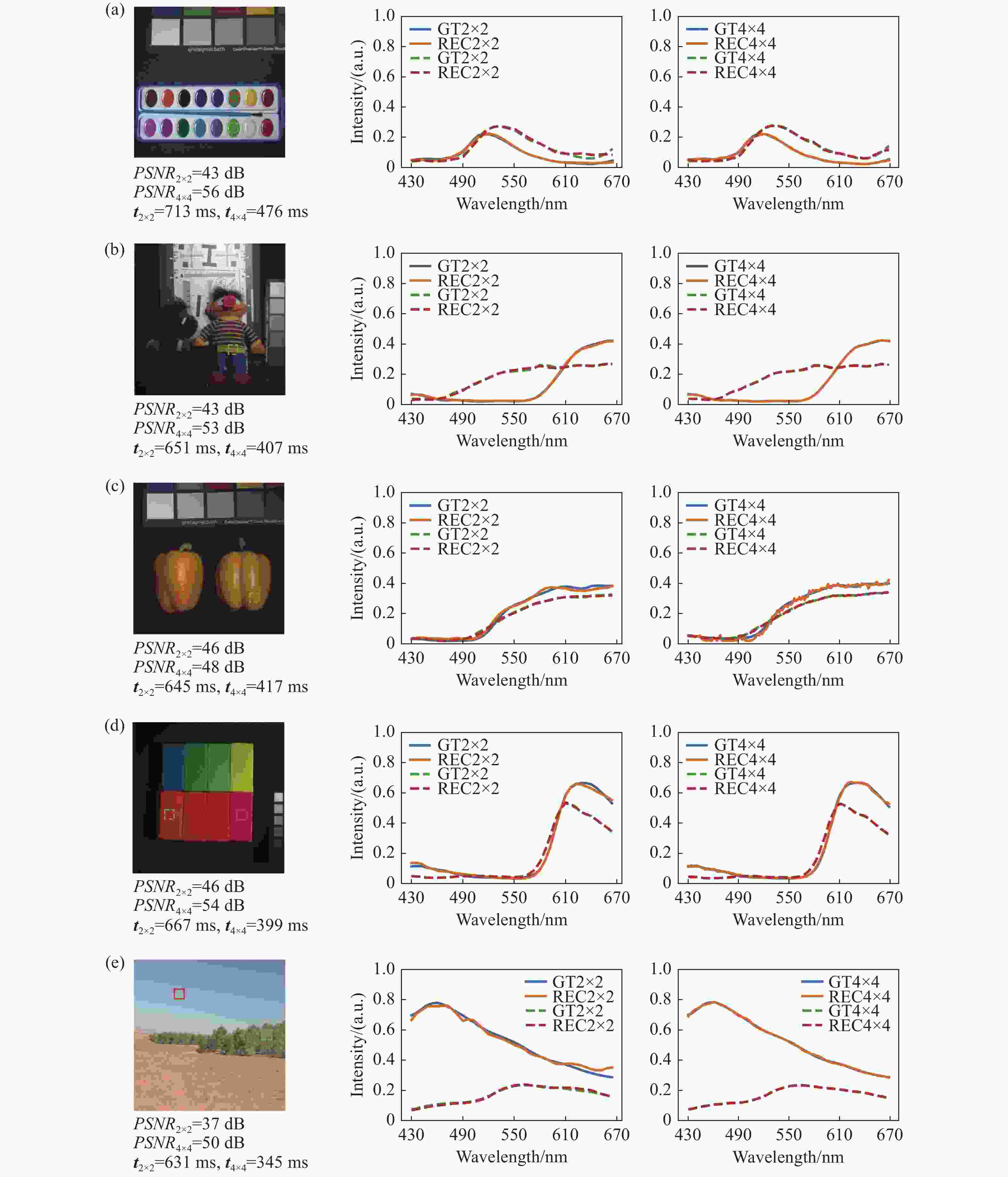
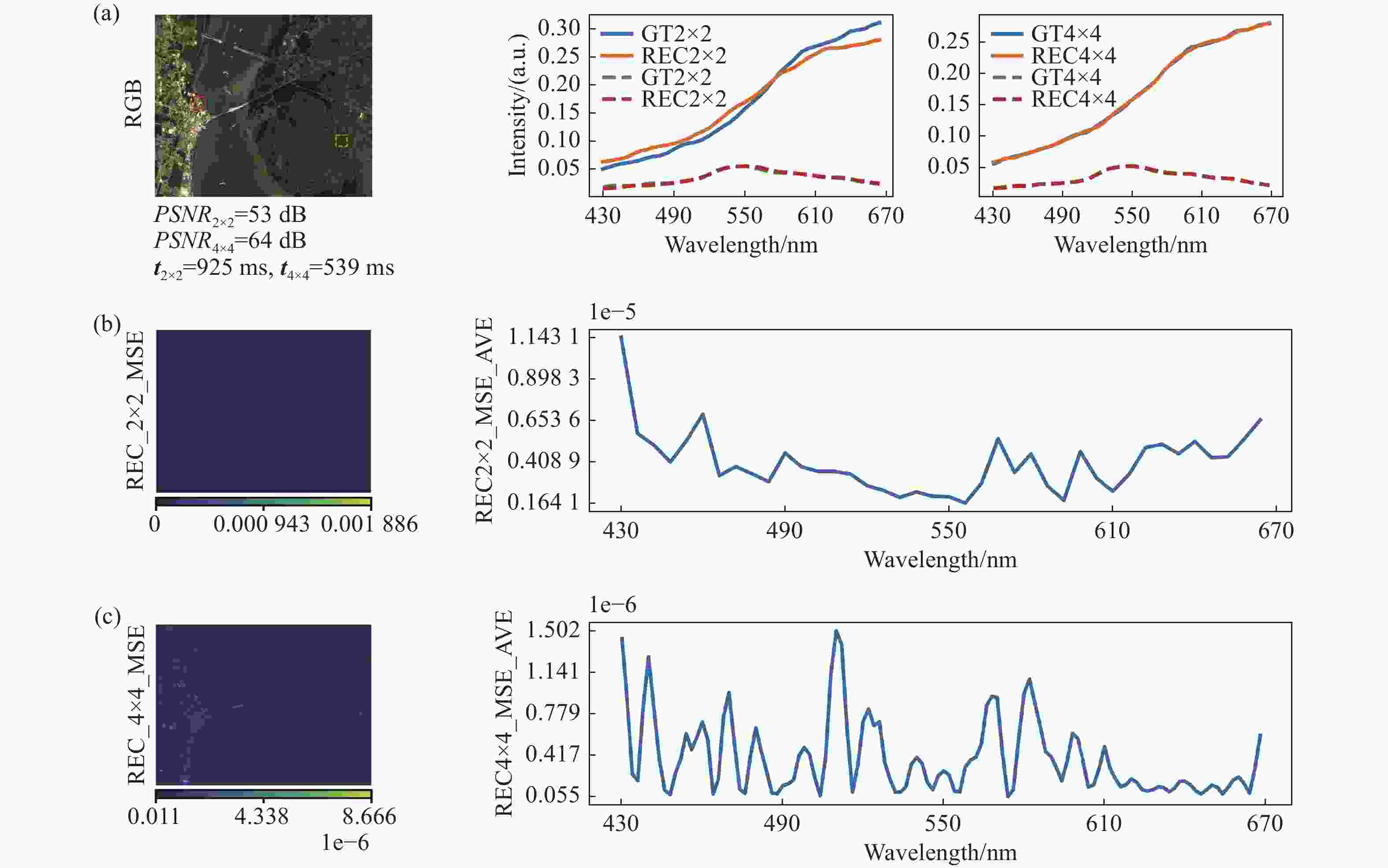
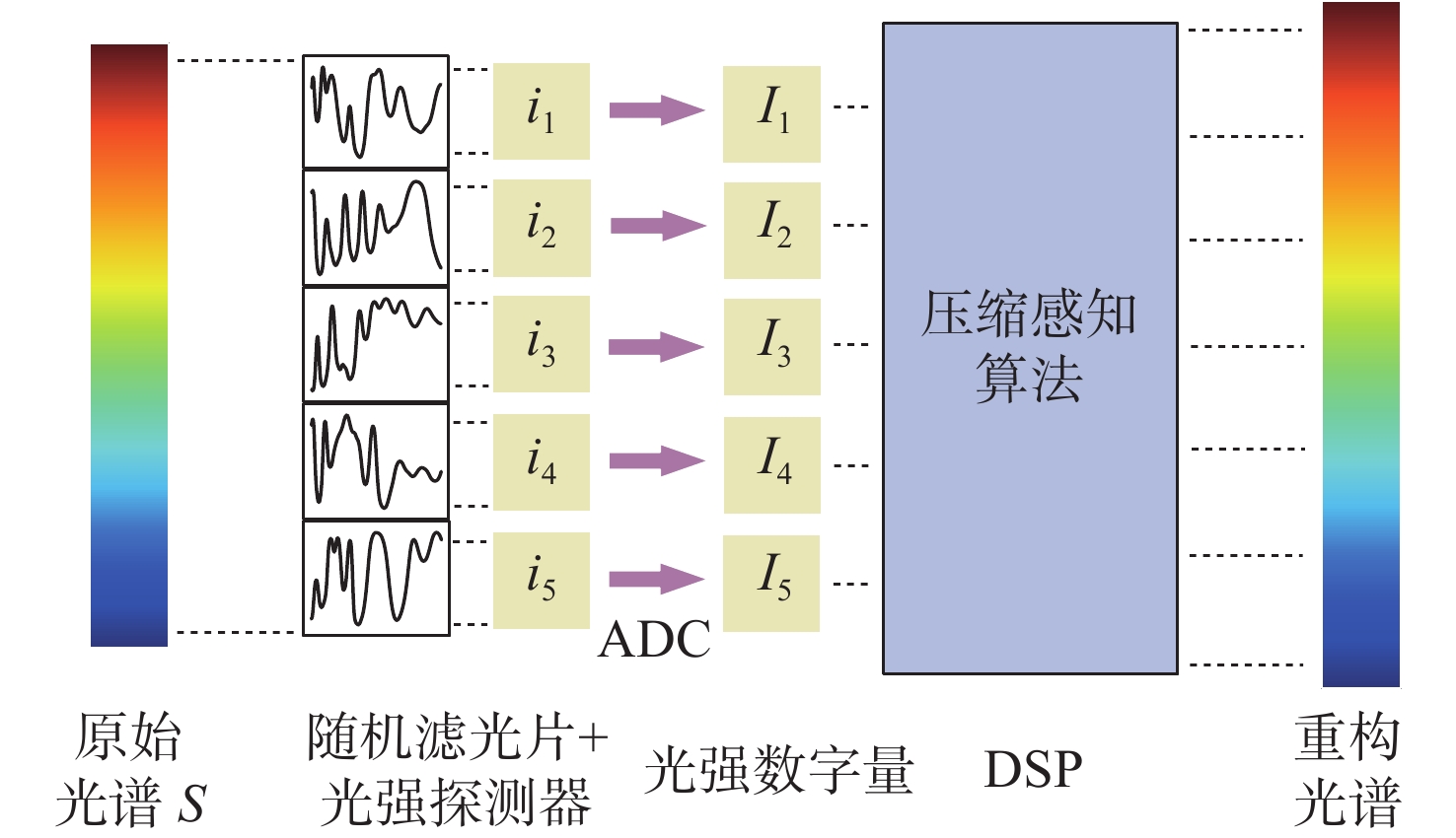
本文讨论了随机滤光片光谱编码-解码的基本原理与重构方法,利用深度学习欠完备自编码器的自动特征提取机制,构建了高精度、低延时的像元映射变分辨率光谱成像重构网络,通过变换像元映射关系完成了2×2、4×4像元阵列光谱重构网络的并行训练。最后,利用512×512、120谱段(430 ~670 nm)的遥感光谱图像对重构网络进行验证,实现了2×2像元阵列/40谱段重构峰值信噪比达53 dB、均方误差小于0.002、重构用时0.87 s与4×4像元阵列/120谱段重构峰值信噪比达64 dB、均方误差小于10−5、重构用时0.52 s的变分辨率光谱图像重构。实验结果表明像元映射变分辨率光谱成像重构网络具备高精度、低延时的动态变换性能。
Abstract:In this paper, the basic principle and reconstruction method of random filter spectral coding-decoding are discussed. According to the automatic feature extraction mechanism of a deep learning undercomplete autoencoder, a pixel mapping variable-resolution spectral imaging reconstruction network with high reconstruction accuracy and low delay is constructed. The parallel training of a 2×2 and 4×4 pixel array spectral reconstruction network is implemented by transforming the pixel mapping relationship. Finally, the network’s performance is verified by the remote sensing data with 512×616 with 120 bands spectral images. For a 2×2 pixel array with 40 bands, the reconstruction PSNR is 53 dB, the reconstruction MSE is less than 0.002, and the reconstruction time is 0.85 s. For a 4×4 pixel array with 120 bands, the reconstruction PSNR is 64 dB, the reconstruction MSE is less than 10−5, and the reconstruction time is 0.5 s. The experimental results show that the pixel mapping variable-resolution spectral imaging reconstruction network has the dynamic transformation performance of high accuracy and low delay.
-
Key words:
- variable-resolution spectral imaging /
- pixel mapping /
- random filter /
- deep learning
-
-
[1] LOBO J, DIAS J. Vision and inertial sensor cooperation using gravity as a vertical reference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(12): 1597-1608. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1251152 [2] CORKE P, LOBO J, DIAS J. An introduction to inertial and visual sensing[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2007, 26(6): 519-535. doi: 10.1177/0278364907079279 [3] HAGEN N A, KUDENOV M W. Review of snapshot spectral imaging technologies[J]. Optical Engineering, 2013, 52(9): 090901. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.52.9.090901 [4] YANG Z Y, ALBROW-OWEN T, CAI W W, et al. Miniaturization of optical spectrometers[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6528): eabe0722. doi: 10.1126/science.abe0722 [5] 左超, 陈钱. 计算光学成像: 何来, 何处, 何去, 何从?[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2022,51(2):20220110. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220110ZUO CH, CHEN Q. Computational optical imaging: an overview[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(2): 20220110. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220110 [6] ZHU X X, BIAN L H, FU H, et al. Broadband perovskite quantum dot spectrometer beyond human visual resolution[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2020, 9: 73. [7] YANG Z Y, ALBROW-OWEN T, CUI H X, et al. Single-nanowire spectrometers[J]. Science, 2019, 365(6457): 1017-1020. doi: 10.1126/science.aax8814 [8] WANG ZH, YI S, CHEN A, et al. Single-shot on-chip spectral sensors based on photonic crystal slabs[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1020. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08994-5 [9] LEE W B, OLIVER J, KIM S C, et al. . Random optical scatter filters for spectrometers: implementation and estimation[C]. Propagation Through and Characterization of Distributed Volume Turbulence 2013, Optical Society of America, 2013: JTu4A. 33. [10] XIONG J, CAI X SH, CUI K Y, et al. Dynamic brain spectrum acquired by a real-time ultraspectral imaging chip with reconfigurable metasurfaces[J]. Optica, 2022, 9(5): 461-468. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.440013 [11] ZHANG W Y, SONG H Y, HE X, et al. Deeply learned broadband encoding stochastic hyperspectral imaging[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2021, 10: 108. [12] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289-1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [13] OLIVER J, LEE W, PARK S, et al. Improving resolution of miniature spectrometers by exploiting sparse nature of signals[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(3): 2613-2625. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.002613 [14] BARANIUK R, DAVENPORT M, DEVORE R, et al. A simple proof of the restricted isometry property for random matrices[J]. Constructive Approximation, 2008, 28(3): 253-263. doi: 10.1007/s00365-007-9003-x [15] CANDÈS E J. Compressive sampling[C]. Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians, 2006: 1-20. [16] HUANG L Q, LUO R CH, LIU X, et al. Spectral imaging with deep learning[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2022, 11: 61. [17] 王雅思, 姚鸿勋, 孙晓帅, 等. 深度学习中的自编码器的表达能力研究[J]. 计算机科学,2015,42(9):56-60,65. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2015.09.012WANG Y S, YAO H X, SUN X SH, et al. Representation ability research of auto-encoders in deep learning[J]. Computer Science, 2015, 42(9): 56-60,65. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2015.09.012 [18] 冯驰, 常军, 杨海波. 双小凹光学成像系统设计[J]. 物理学报,2015,64(3):034201. doi: 10.7498/aps.64.034201FENG CH, CHANG J, YANG H B. Design of dually foveated imaging optical system[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(3): 034201. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.64.034201 [19] CHENG Y, CAO J, HAO Q, et al. Compound eye and retina-like combination sensor with a large field of view based on a space-variant curved micro lens array[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(12): 3502-3509. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.003502 [20] ARAD, BEN-SHAHAR, et al.. Sparse recovery of hyperspectral signal from natural RGB images[C]. Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, 19–34. Springer. -






 下载:
下载: