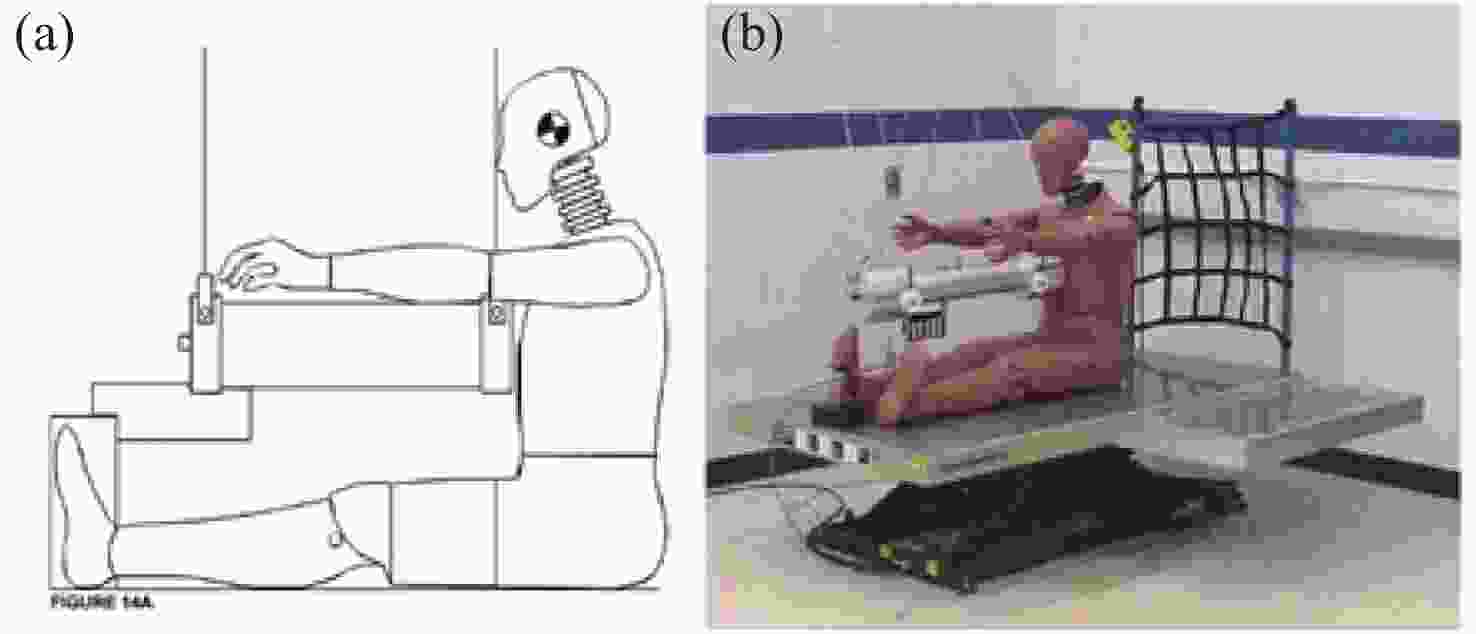
Design and simulation of the dummy thoracic finite element model based on mashine vision
-
摘要:
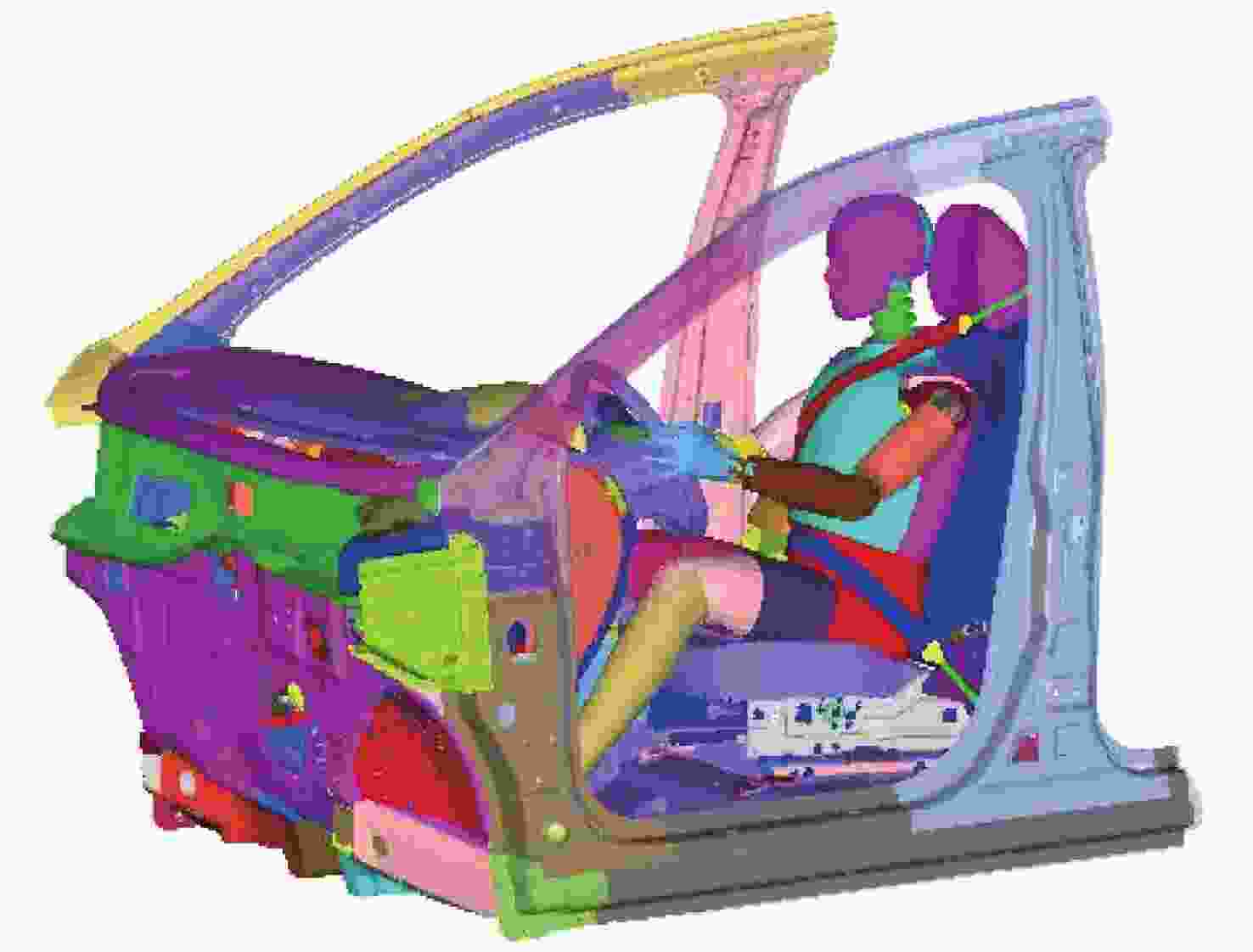
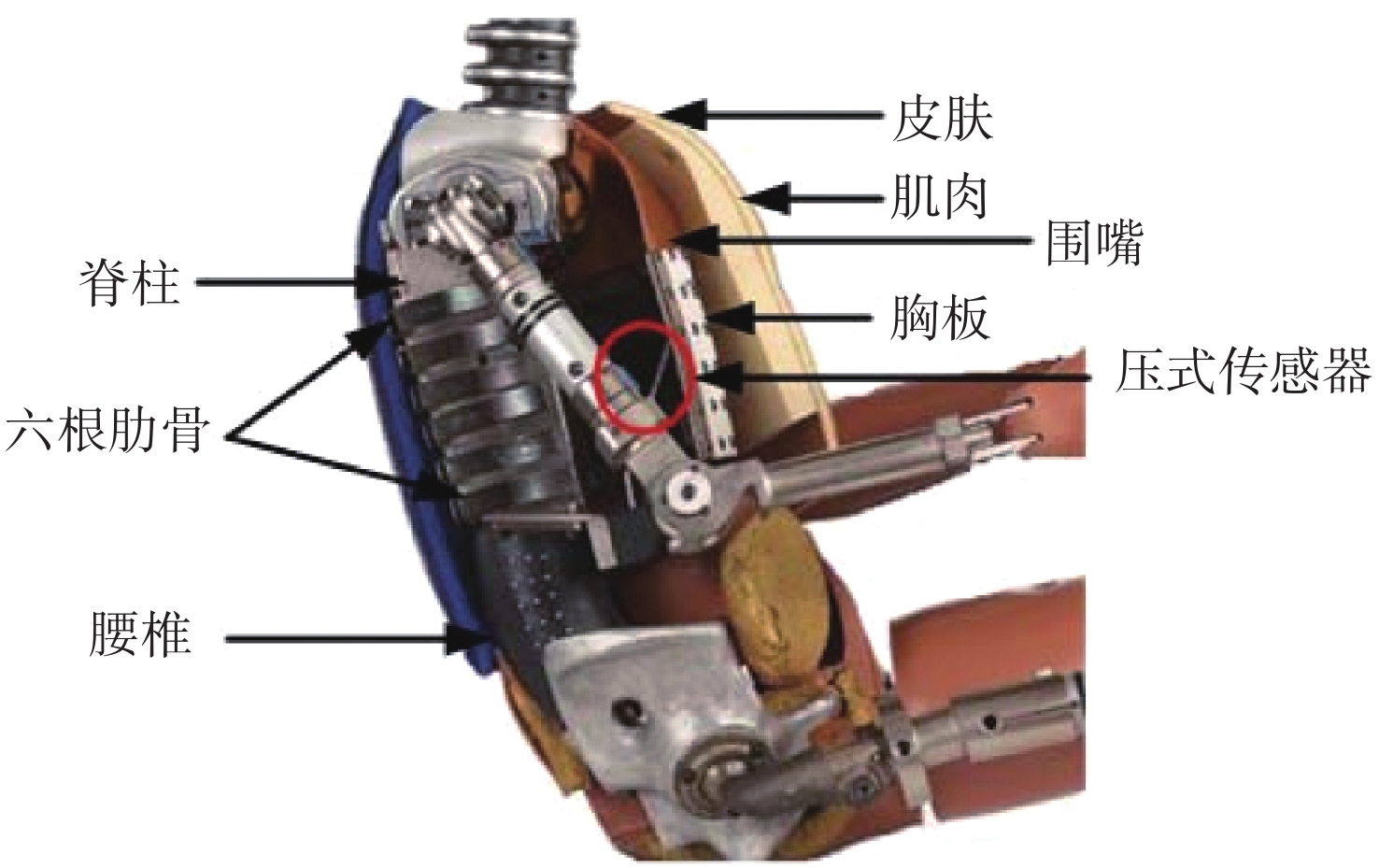
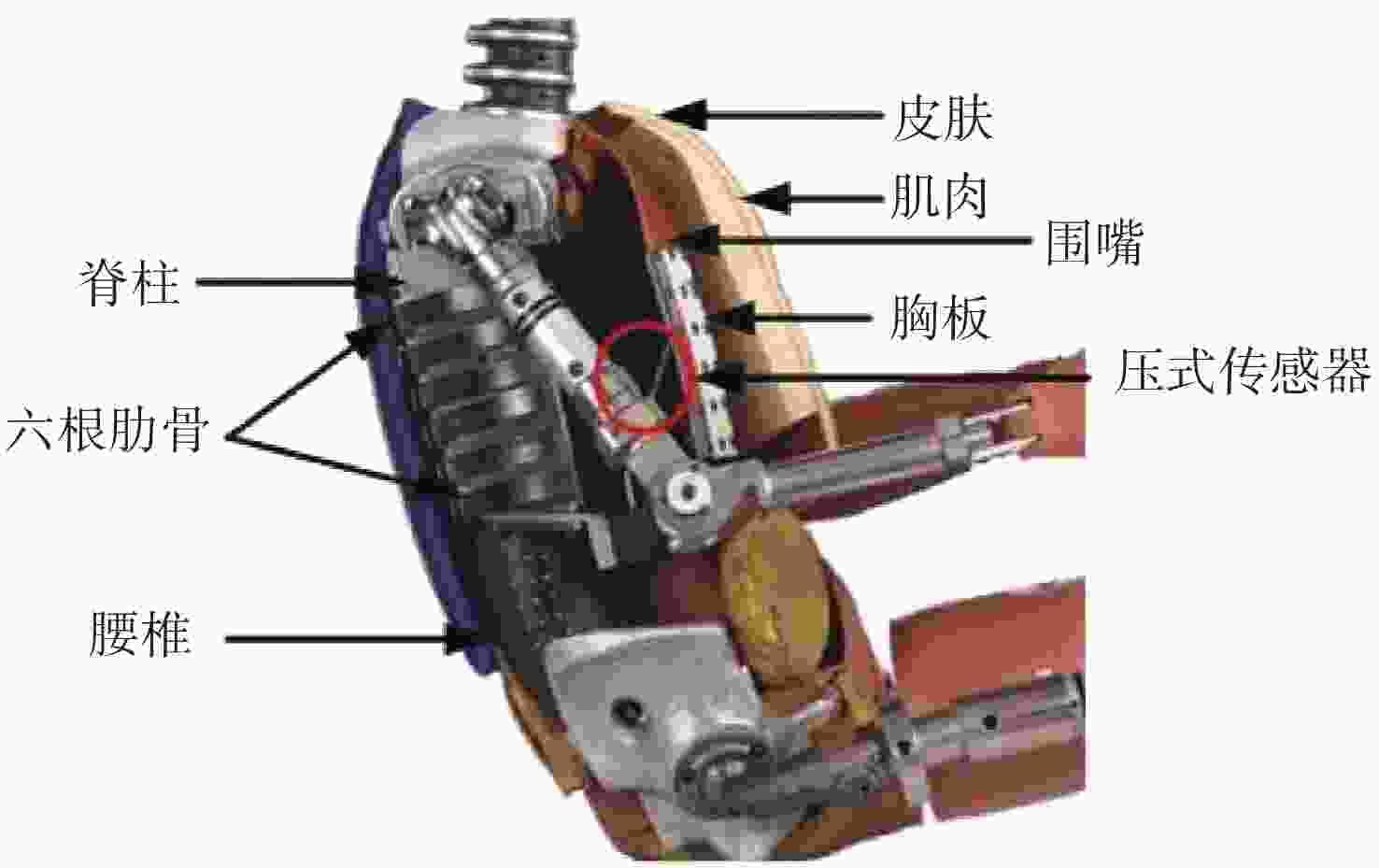
在汽车被动安全领域,对于驾驶员正碰撞击中胸部的研究具有重要的意义。本文基于机器视觉的方法,通过Hybrid Ⅲ 50th汽车碰撞实体假人,构建假人胸部模型。利用遗传算法进行参数优化,优化后标定试验的所有指标均符合法规要求,仿真结果与试验测试结果相符,误差小于5%。随后将含有胸部模型的有限元假人模型放入整车系统进行正碰仿真分析,结果表明:胸部伤害得分值为80%,与试验测试结果相比,仿真结果误差不超过10%。实验结果表明该模型有较好的仿真度,可用于汽车碰撞安全性能的研究。
-
关键词:
- 机器视觉 /
- 遗传算法 /
- Hybrid Ⅲ 50th
Abstract:This paper focuses on the field of automobile passive safety in my country. By scanning the Hybrid III 50th automobile crash dummy, a finite element simulation model of the dummy chest is constructed. The genetic algorithm is used to optimize the parameters. After optimization, all the indicators of the calibration test meet the requirements of the regulations. The simulation results are consistent with the experimental test results, and the error is less than 5%. Then we put the finite element dummy model containing the chest model into the vehicle system for frontal collision simulation analysis. The results show that the score of chest injury is 80%, and the error of the simulation results is less than 10% compared with the test results. The model has a good degree of simulation and can be used for the study of vehicle crash safety performance.
-
Key words:
- machine vision /
- genetic algorithm /
- Hybrid Ⅲ 50th
-
表 1 胸部模型部分材料参数
Table 1. Partial material parameters of chest model
参数 弹性材料
MAT1弹塑性材料
MAT3刚体材料
MAT20弹性模量E/GPa 0.5 205 205 泊松比μ 0.30 0.31 0.31 屈服强度σ/MPa / 0.6 / 切线模量/GPa / 0.5 / 表 2 胸部肋骨材料(弹性材料MAT1)参数
Table 2. Material parameters of thoracic rib (elastic material MAT1)
参数 参数值 体积模量(BULK) 0.33 GPa 短效剪切模量(G0) 0.11 MPa 衰减常数(BETA) 0.15 长效剪切模量(GI) 0.024 MPa 表 3 胸部泡沫材料(MAT57)参数
Table 3. Chest foam material (MAT57) parameters
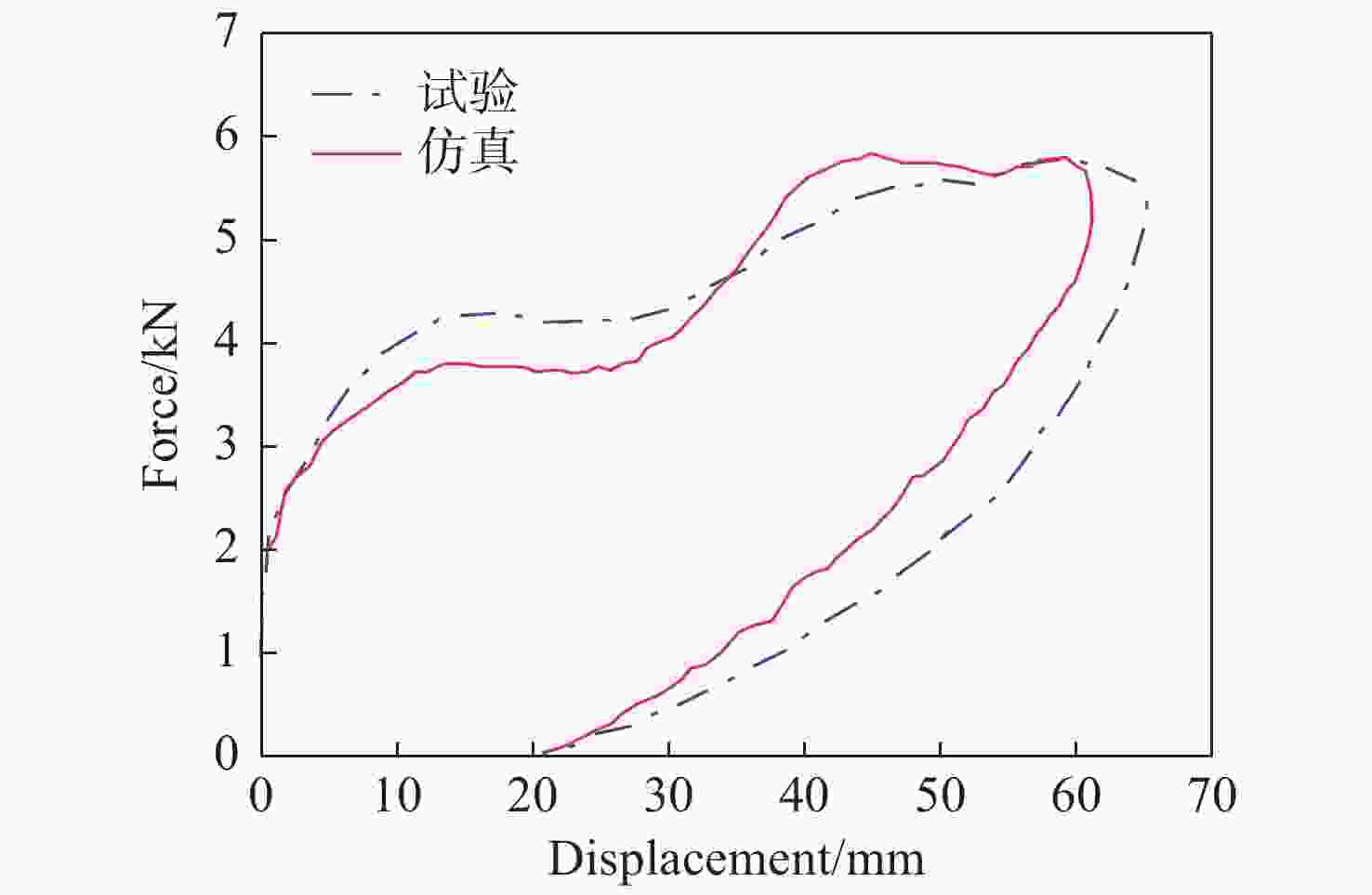
参数 参数值 杨氏模量(E) 0.005 MPa 拉应力(TC) 0.1 滞后卸载系数(HU) 1.0 粘滞系数(DAMP) 0.1 衰减常数(BETA) 0.1 表 4 胸部标定试验与仿真结果
Table 4. Calibration test and simulation results of chest
类型 位移峰值(mm) 摆锤力峰值(kN) 滞后率(%) 要求 63.5~72.6 5.16~5.89 69~85 试验 65.402 5.788 73.98 仿真 61.117 5.865 70 误差 -6.55 1.33 -5.37 表 5 优化结果对比
Table 5. Comparison of optimization results
x1(MPa) x2(Mpa) x3 x4(Mpa) Dmax(mm) Fmax(kN) 滞后率(%) 原参数 0.11 0.253 0.15 0.5 61.117 5.865 70.00 优化后 0.087 0.234 0.172 0.439 64.401 5.615 71.13 标定要求 / / / / 63.5~72.6 5.16~5.89 69~85 试验 / / / / 65.402 5.788 73.98 误差(%) / / / / −1.5 −2.9 −3.85 表 6 实车试验和仿真假人胸部伤害指标对比
Table 6. Comparison of chest injury index between real vehicle test and dummy
损伤指标 胸部加速度C3ms(g) 胸部压缩量ThPC(mm) 性能限值 38~60 22~50 试验值 38.47 29.21 仿真值 42.13 28.16 误差 9.51% −3.59% 得分率 81.2% 78% -
[1] 中国汽车技术研究中心有限公司. 中国汽车安全发展报告(2020)[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2020.China Automotive Technology and Research Center. Annual Report on Automobile Safety in China (2020)[M]. Beijing: Social Sciences Academic Press, 2020. (in Chinese) [2] 凯-乌韦·施密特, 彼得 F. 尼德雷尔, 马库斯 H. 穆塞尔, 等. 汽车与运动损伤生物力学[M]. 曹立波, 译. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2012.SCHMITT K U, NIEDERER P F, MUSER M H, et al.. Trauma Biomechanics: Accidental Injury in Traffic and Sports[M]. CAO L B, trans. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2012. (in Chinese) [3] HAMMON W M. Impact injury and crash protection[J]. Military Medicine, 1970, 135(7): 616. [4] MERTZ H J, IRWIN A L, MELVIN J W, et al. . Size, weight and biomechanical impact response requirements for adult size small female and large male dummies[C]. SAE International Congress and Exposition, SAE International, 1989: 133-144. [5] PATRICK L M, MERTZ H J, KROELL C K. Cadaver knee, chest and head impact loads[C]. 11th Stapp Car Crash Conference, SAE International, 1967: 2932-2940. [6] KROELL C K, SCHNEIDER D C, NAHUM A M. Impact tolerance and response of the human thorax II[C]. 18th Stapp Car Crash Conference, SAE International, 1974: 383-457. [7] RIDELLA S A, VIANO D C. Determining tolerance to compression and viscous injury in frontal and lateral impacts[C]. Stapp Car Crash Conference, SAE International, 1990: 349-356. [8] 陈嘉鑫. 基于中国体征的正碰假人仿真研究与应用[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021.CHEN J X. Research on simulation of frontal impact dummy with Chinese physical sign and its application[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021. (in Chinese) [9] FOSTER J K, KORTGE J O, WOLANIN M J. Hybrid III-A biomechanically-based crash test dummy[C]. 21st Stapp Car Crash Conference, SAE International, 1977. [10] XU T, SHENG X M, ZHANG T Y, et al. Development and validation of dummies and human models used in crash test[J]. Applied Bionics and Biomechanics, 2018, 2018: 3832850. [11] PHILIPPENS M, NIEBOER J J, WISMANS J. An advanced database of the 50th percentile hybrid III dummy[C]. International Congress & Exposition, SAE International, 1991: 121-129. [12] RUAN J, EL-JAWAHRI R, CHAI L, et al. . Prediction and analysis of human thoracic impact responses and injuries in cadaver impacts using a full human body finite element model[C]. 47th Stapp Car Crash Conference, SAE International, 2003: 299-321. [13] 肖森, 杨济匡, 肖志, 等. 基于正面碰撞实验的胸部损伤有限元分析[J]. 力学学报,2017,49(1):191-201.XIAO S, YANG J K, XIAO ZH, et al. Analysis of chest injury in frontal impact via finite element modelling based on biomechanical experiment[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2017, 49(1): 191-201. (in Chinese) [14] 邓世宽, 李盼东, 王洪川, 等. 汽车正碰后排假人胸压伤害原因分析和优化[J]. 汽车工程师,2019(11):27-30.DENG SH K, LI P D, WANG H CH, et al. Cause analysis and optimization of thoracic pressure injury of rear dummy in frontal crash[J]. Automotive Engineer, 2019(11): 27-30. (in Chinese) [15] 刘志新, 武永强, 马伟杰. 中国体征碰撞测试假人开发路径研究[J]. 中国工程科学,2019,21(3):103-107.LIU ZH X, WU Y Q, MA W J. Development path of anthropomorphic test device with Chinese physical signs[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2019, 21(3): 103-107. (in Chinese) [16] 赵长福, 丁红昌, 曹国华, 等. 图像辅助汽车制动主缸补偿孔法线测量[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(5):1212-1223. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0219ZHAO CH F, DING H CH, CAO G H, et al. Image aided measurement of the automotive brake master cylinder compensation hole normal line[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(5): 1212-1223. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0219 [17] 姜涛, 张桂林, 高俊鹏. 面向机器视觉检测的缸体横孔照明[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1285-1292. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0054JIANG T, ZHANG G L, GAO J P. Illumination of a cylinder block transverse hole for machine vision inspection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1285-1292. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0054 [18] 中国汽车技术研究中心有限公司. 中国新车评价规程(C-NCAP) 2021年版[S]. 天津: 中国汽车技术研究中心有限公司, 2021.China Automotive Technology and Research Center. China-new car assessment programme, version 2021[S]. Tianjin: China Automotive Technology and Research Center, 2021. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: