-
摘要:
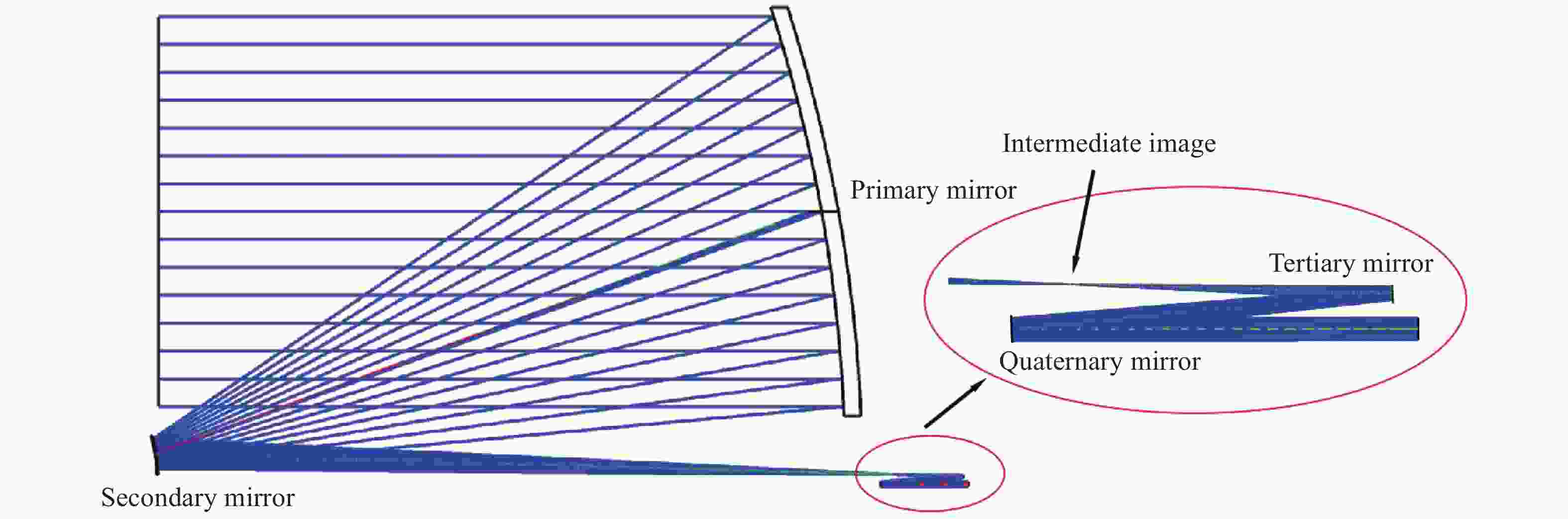
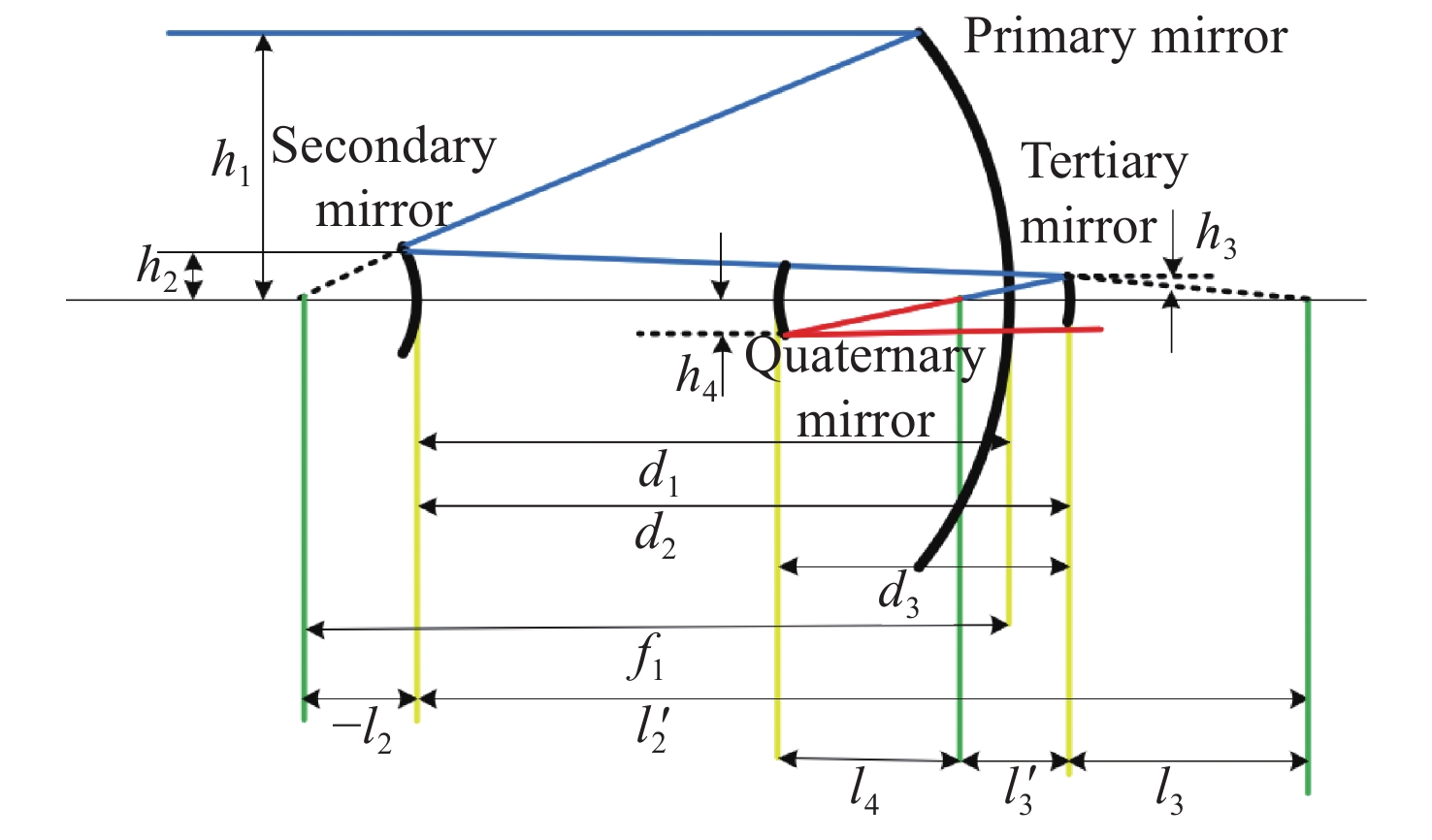
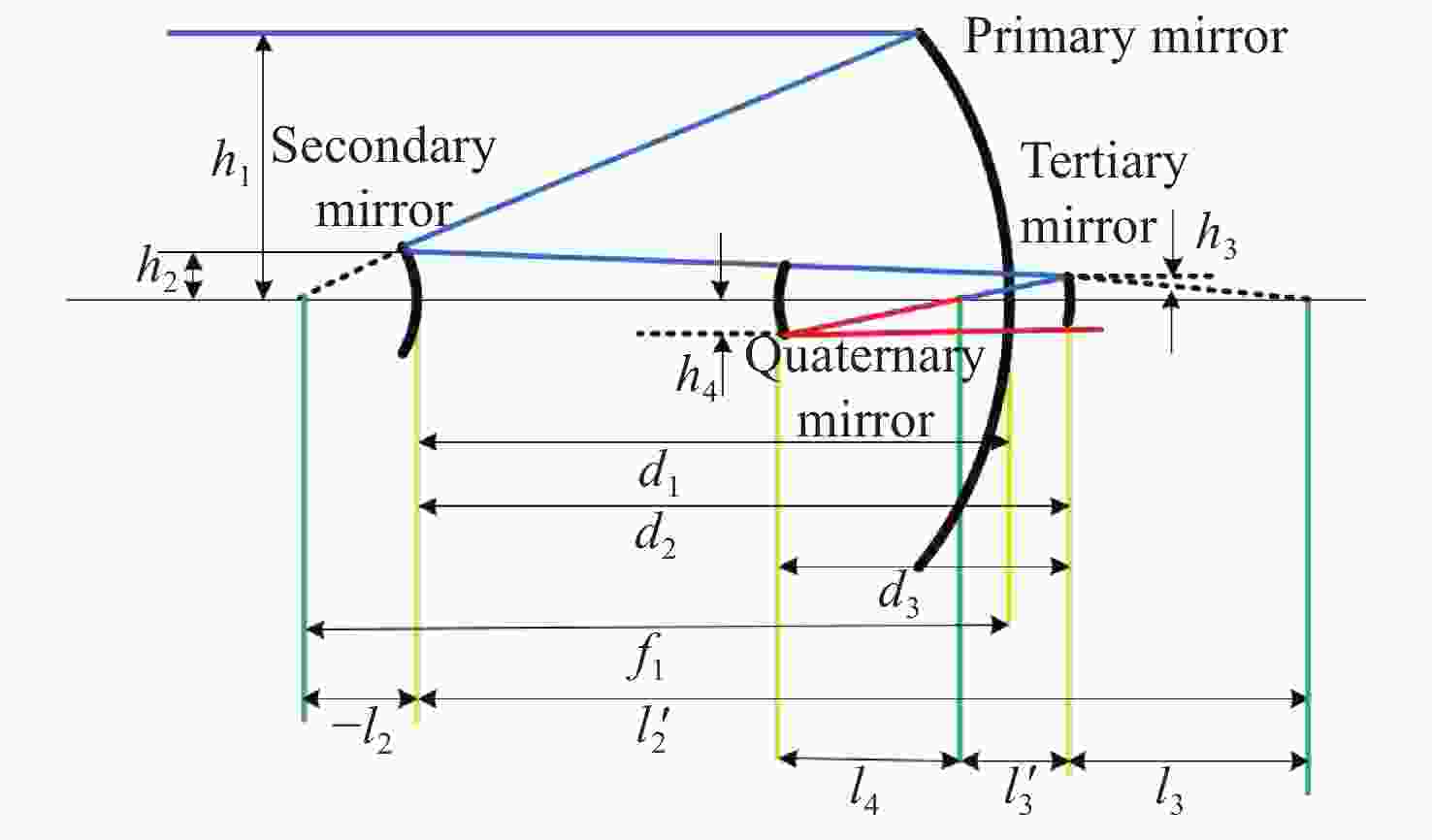
太极计划是中国探测空间引力波的一项重点任务。望远镜作为空间引力波探测中的重要组成部分,它的性能会直接影响引力波探测的精度。现有的典型空间引力波望远镜结构中次镜灵敏度高,难以满足更大口径的空间引力波望远镜对制造装调公差的要求,特别是在轨稳定性公差要求。为解决以上问题,首先,提出了一种中间像面设置于三四镜之间的新型空间引力波望远镜光学系统结构,以降低次镜灵敏度;结合高斯光学理论方法,从理论上分析并计算新型望远镜结构的初始参数。其次,通过优化设计,获得入瞳直径为400 mm,放大倍率为80倍,科学视场为±8 μrad,波前误差RMS值优于0.0063λ的望远镜光学系统。最后,建立了望远镜系统的灵敏度评价公差分配表,对比分析了现有望远镜结构与新型望远镜结构的公差情况。结果显示:相较于现有望远镜结构,新型望远镜结构的灵敏度降低了30.4%,具有低灵敏度优势,为空间引力波望远镜的设计提供了一种优选方案。
Abstract:The Taiji program is a key task for China's space gravitational wave detection, and as an important part of space gravitational wave detection, the telescope's performance will directly affect the accuracy of gravitational wave detection. For the existing typical space gravitational wave telescope structures, due to the high sensitivity of secondary mirror, it is difficult to meet the requirements for manufacturing and adjustment tolerance of larger aperture space gravitational wave telescopes, especially the tolerance requirements for in-orbit stability. In order to solve the above problems, firstly, a new optical system structure of space gravitational wave telescope with intermediate image plane set between three and four mirrors is proposed to reduce the sensitivity of the secondary mirror. Combined with the theoretical method of Gaussian optics, the initial parameters of the structure of the new telescope are theoretically analyzed and calculated. Secondly, through the optimization design, a telescope optical system with a pupil diameter of 400 mm, a magnification of 80 times, a field of view of ± 8 μrad, and a wavefront error RMS value of better than 0.0063λ was obtained. Finally, the sensitivity evaluation tolerance allocation table of the telescope system is established, and the tolerances of the existing telescope structure and the new telescope structure are compared and analyzed. Compared with the existing telescope structure, the sensitivity of the new telescope structure is reduced by 30.4%. The results show that the new telescope structure has the advantage of low sensitivity, which provides an optimal scheme for the design of space gravitational wave telescopes.
-
Key words:
- telescope /
- space gravitational wave detection /
- wavefront error /
- low sensitivity /
- optical design
-
表 1 望远镜系统的技术指标
Table 1. Specifications of telescope system
系统参数 技术指标 光学口径/mm 400 工作波长/nm 1064 捕获视场/μrad ±200 科学视场/μrad ±8 金宝搏188软件怎么用 束放大倍数 80 波前质量(科学视场内) ≤λ/30(λ=1064 nm) 表 2 本文提出光学系统的结构参数
Table 2. Structural parameters of the proposed optical system
结构参数 取值范围 取值 α2 ($0,1 $) 0.113924050 α3 ($ 0,\infty $) 0.060710194 α4 ($0,\infty$) 1.820512820 β2 (−$\infty,0$) −9.700000000 β3 ($0,\infty$) 1.471698113 表 3 优化后的光学系统镜头数据
Table 3. Lens parameters of optimized optical system
曲率半径/mm 间隔/mm 圆锥系数 Y向偏心/mm 绕X轴倾斜/(°) 主镜 −1579.701 −700.0 −1.000 −270.0 0.00 次镜 −200.025 820.0 −1.503 −270.0 0.00 三镜 360.730 −250.0 0.000 −268.0 −2.80 四镜 301.309 240.1 0.000 −288.5 −1.32 表 4 出瞳处的波前误差
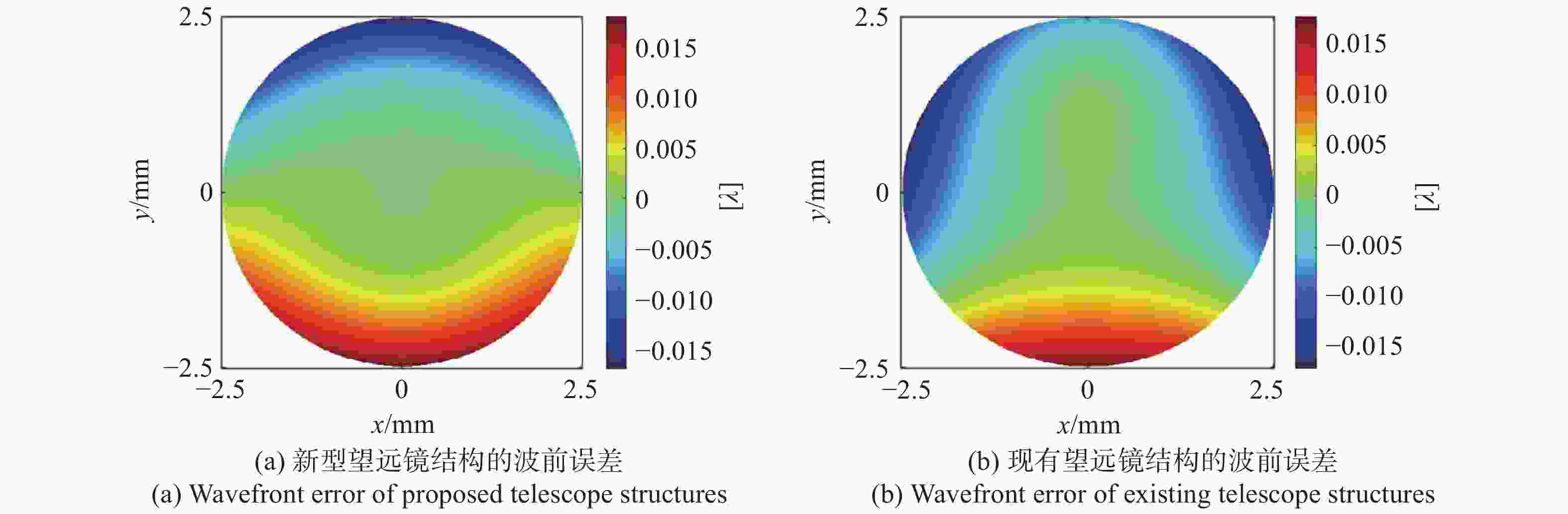
Table 4. Wavefront errors at the exit pupil
视场 /μrad RMS(λ = 1064 nm) PV(λ = 1064 nm) (0,0) 0.0063λ 0.0349λ (0,5.6) 0.0063λ 0.0351λ (0,8.0) 0.0063λ 0.0352λ (0,−5.6) 0.0063λ 0.0346λ (0,−8.0) 0.0063λ 0.0345λ (5.6,0) 0.0063λ 0.0349λ (8.0,0) 0.0063λ 0.0349λ 表 5 公差分配表
Table 5. Tolerance distribution
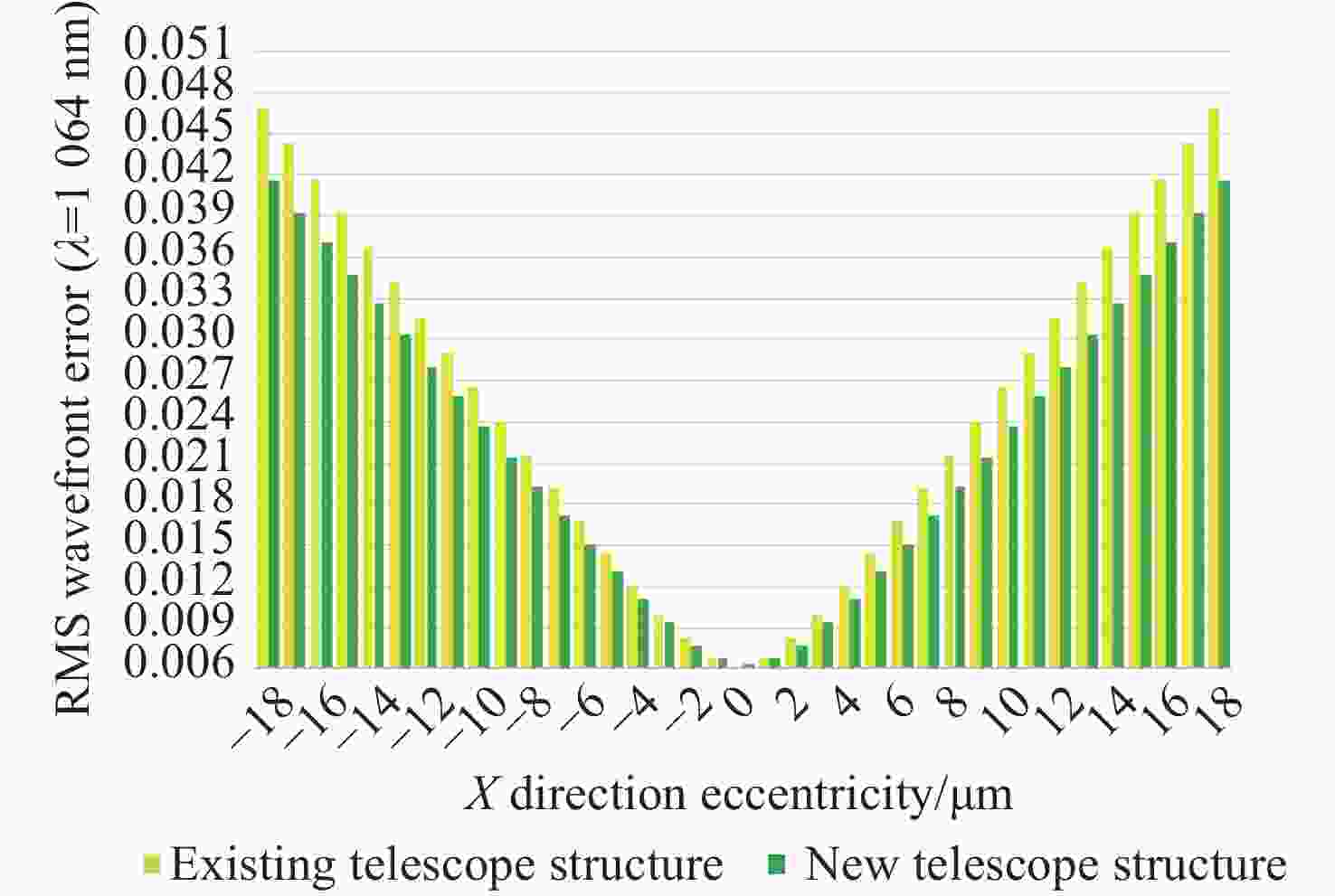
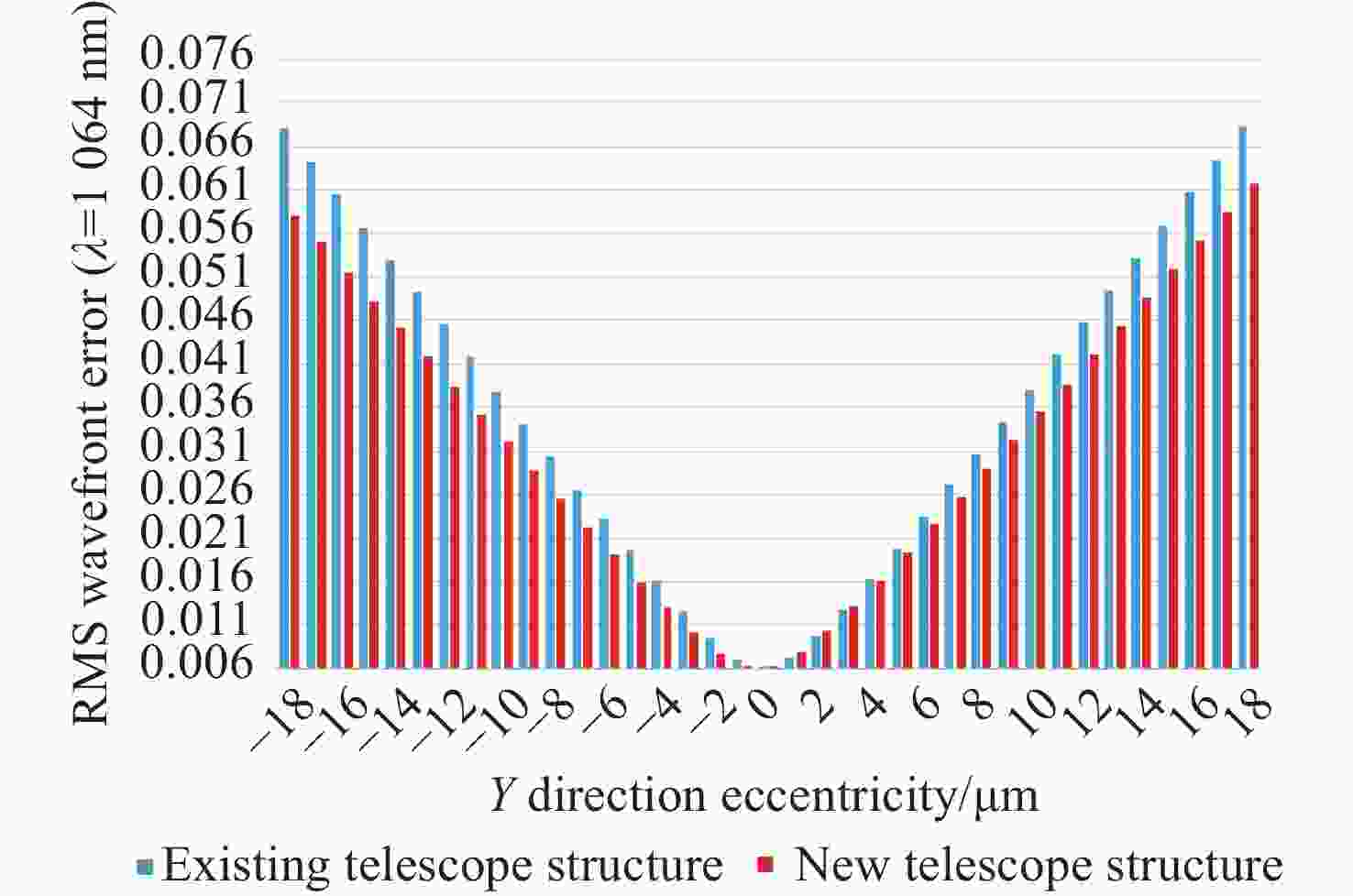
类型 公差项 主镜 次镜 三镜 四镜 加工公差 曲率半径(mm) ±0.3 ±0.2 ±0.5 ±0.1 二次曲面系数 ±0.0001 ±0.0004 - - 面型误差(λ=1064 nm) ±λ/100 ±λ/100 ±λ/200 ±λ/200 装调误差 X向偏心(μm) - ±18 ±18 ±18 Y向偏心(μm) - ±18 ±18 ±18 Z向位移(μm) - ±20 ±20 ±20 绕X轴倾斜( ″) - ±10 ±10 ±10 绕Y轴倾斜( ″) - ±10 ±10 ±10 绕Z轴倾斜( ″) - ±10 ±10 ±10 表 6 新型望远镜结构波前误差累计概率
Table 6. Cumulative probability of wavefront error of the proposed telescope structure
累计概率 全视场波前误差变化(λ=1064 nm) 2% 0.00683λ 10% 0.01126λ 20% 0.01478λ 50% 0.02255λ 80% 0.03235λ 90% 0.03859λ 98% 0.04824λ 表 7 现有望远镜结构波前误差累计概率
Table 7. Cumulative probability of wavefront error in existing telescope structures
累计概率 全视场波前误差变化(λ=1064 nm) 2% 0.00807λ 10% 0.01278λ 20% 0.01727λ 50% 0.02773λ 80% 0.04124λ 90% 0.04642λ 98% 0.05660λ 表 8 新型望远镜结构中最灵敏的10项公差项
Table 8. The 10 most sensitive tolerance terms in new telescope structure
类型 反射镜面 数值 影响量 Y向偏心(μm) 次镜 18 0.03588128 Y向偏心(μm) 次镜 −18 0.03483910 X向偏心(μm) 次镜 18 0.03354102 X向偏心(μm) 次镜 −18 0.03354102 二次曲面系数 主镜 −0.0001 0.01435808 二次曲面系数 主镜 0.0001 0.01257815 绕X轴倾斜( ″) 次镜 10 0.00846399 绕Y轴倾斜( ″) 次镜 −10 0.00752685 绕Y轴倾斜( ″) 次镜 10 0.00752685 绕X轴倾斜( ″) 次镜 −10 0.00744224 表 9 现有望远镜结构中最灵敏的10项公差项
Table 9. The 10 most sensitive tolerance terms in existing telescope structures
类型 反射镜面 数值 影响量 Y向偏心(μm) 次镜 −18 0.04193880 X向偏心(μm) 次镜 18 0.03553085 X向偏心(μm) 次镜 −18 0.03553085 Y向偏心(μm) 次镜 18 0.03329243 二次曲面系数 主镜 0.0001 0.01654640 二次曲面系数 主镜 −0.0001 0.00907945 绕X轴倾斜( ″) 次镜 10 0.00695408 曲率半径(mm) 次镜 0.2 0.00588237 面型误差(λ=1064 nm) 主镜 −λ/100 0.00479811 二次曲面系数 次镜 −0.0004 0.00368115 -
[1] MILLER M C, YUNES N. The new frontier of gravitational waves[J]. Nature, 2019, 568(7753): 469-476. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1129-z [2] ESA. LISA assessment study report (Yellow Book)[EB/OL]. https://sci.esa.int/documents/35005/36499/1567258681608-LISA_YellowBook_ESA-SRE-2011-3_Feb2011.pdf. (2011-10-11) [3] LUO Z R, WANG Y, WU Y L, et al. The Taiji program: a concise overview[J]. Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics, 2021, 2021(5): 05A108. doi: 10.1093/ptep/ptaa083 [4] TIAN Y CH. Research on the analytical development and progress of gravitational wave detection technology[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2021, 2083(2): 022043. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2083/2/022043 [5] ZHAO Y, SHEN J, FANG CH, et al. Tilt-to-length noise coupled by wavefront errors in the interfering beams for the space measurement of gravitational waves[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(17): 25545-25561. doi: 10.1364/OE.397097 [6] 王智, 沙巍, 陈哲, 等. 空间引力波探测望远镜初步设计与分析[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(1):131-151. doi: 10.3788/co.20181101.0131WANG ZH, SHA W, CHEN ZH, et al. Preliminary design and analysis of telescope for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(1): 131-151. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20181101.0131 [7] 陈胜楠, 姜会林, 王春艳, 等. 大倍率离轴无焦四反光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(1):179-188. doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0179CHEN SH N, JIANG H L, WANG CH Y, et al. Design of off-axis four-mirror afocal optical system with high magnification[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(1): 179-188. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0179 [8] 李建聪, 林宏安, 罗佳雄, 等. 空间引力波探测望远镜光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(4):761-769. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0018LI J C, LIN H A, LUO J X, et al. Optical design of space gravitational wave detection telescope[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(4): 761-769. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0018 [9] ZHAO Y, SHEN J, FANG CH, et al. Far-field optical path noise coupled with the pointing jitter in the space measurement of gravitational waves[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(2): 438-444. doi: 10.1364/AO.405467 [10] 范纹彤, 赵宏超, 范磊, 等. 空间引力波探测望远镜系统技术初步分析[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),2021,60(1):178-185. doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2020.11.02.2020b111FAN W T, ZHAO H CH, FAN L, et al. Preliminary analysis of space gravitational wave detection telescope system technology[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2021, 60(1): 178-185. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2020.11.02.2020b111 [11] QIN Z CH, WANG X D, REN CH M, et al. Design method for a reflective optical system with low tilt error sensitivity[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(26): 43464-43479. doi: 10.1364/OE.447556 [12] FAN Z CH, ZHAO L J, CAO SH Y, et al. High performance telescope system design for the TianQin project[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2022, 39(19): 195017. doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ac8b57 [13] 赵宇宸, 胡长虹, 吕恒毅, 等. 紧凑型偏视场多光路耦合同轴四反光学系统设计[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2021,50(3):20200197. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200197ZHAO Y CH, HU CH H, LV H Y, et al. Design of high-density coaxial four-mirror optical system with field-bias and multi-light-channel coupled[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(3): 20200197. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200197 [14] 陈太喜, 伍雁雄, 宋绍漫, 等. 折叠式离轴三反光学系统设计与装调[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与光电子学进展,2021,58(17):1722001.CHEN T X, WU Y X, SONG SH M, et al. Design and alignment of folded off-axis three-mirror optical system[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(17): 1722001. (in Chinese) [15] 马烈, 陈波. 三维成像载荷共孔径光学系统设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(9):2326-2333. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182609.2326MA L, CHEN B. Optical design of a co-aperture system for 3-D remote sensing payload[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(9): 2326-2333. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182609.2326 -





 下载:
下载: