Research progress on the related physical mechanism of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
-
摘要:
金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱技术(Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy,LIBS)是利用强脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用 与物质相互作用所产生的等离子体光谱来实现对物质组成元素定性和定量分析的一种新方法。在脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导等离子体的过程中,不同的金宝搏188软件怎么用 参数(能量、脉宽、波长)、检测过程中的环境条件以及材料本身的特性等,对金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导等离子体的物理机制都有不同程度的影响,进而影响LIBS定量分析的结果。本文综述了现阶段LIBS技术中包括LIBS基本原理、金宝搏188软件怎么用 参数区别、环境和材料特性差异所涉及的物理机制。为深入理解金宝搏188软件怎么用 与物质相互作用、提升LIBS检测能力提供了依据。
-
关键词:
- 金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱(LIBS) /
- 物理机制
Abstract:Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) is a new method for qualitative and quantitative analysis of the constituents of a material using plasma spectra produced by the interaction of a strong pulsed laser with the material. In the process of pulsed laser-induced plasma, different laser parameters (energy, pulse width, wavelength), environmental conditions during the detection process and the properties of the material itself have different degrees of influence on the physical mechanism of laser-induced plasma, which in turn affects the results of LIBS quantitative analysis. We review the physical mechanisms of LIBS technology in the current state, including the basic principles of LIBS, the differences in laser parameters, and the physical mechanisms involved in the differences in environmental and material properties. It provides a basis for a deeper understanding of laser-matter interactions and for improving the detection capabilities of LIBS.
-
表 1 LIBS定量分析性能的物理机制影响因素及受影响特性
Table 1. Influencing factors and affected properties of physical mechanisms for LIBS quantitative analysis performance
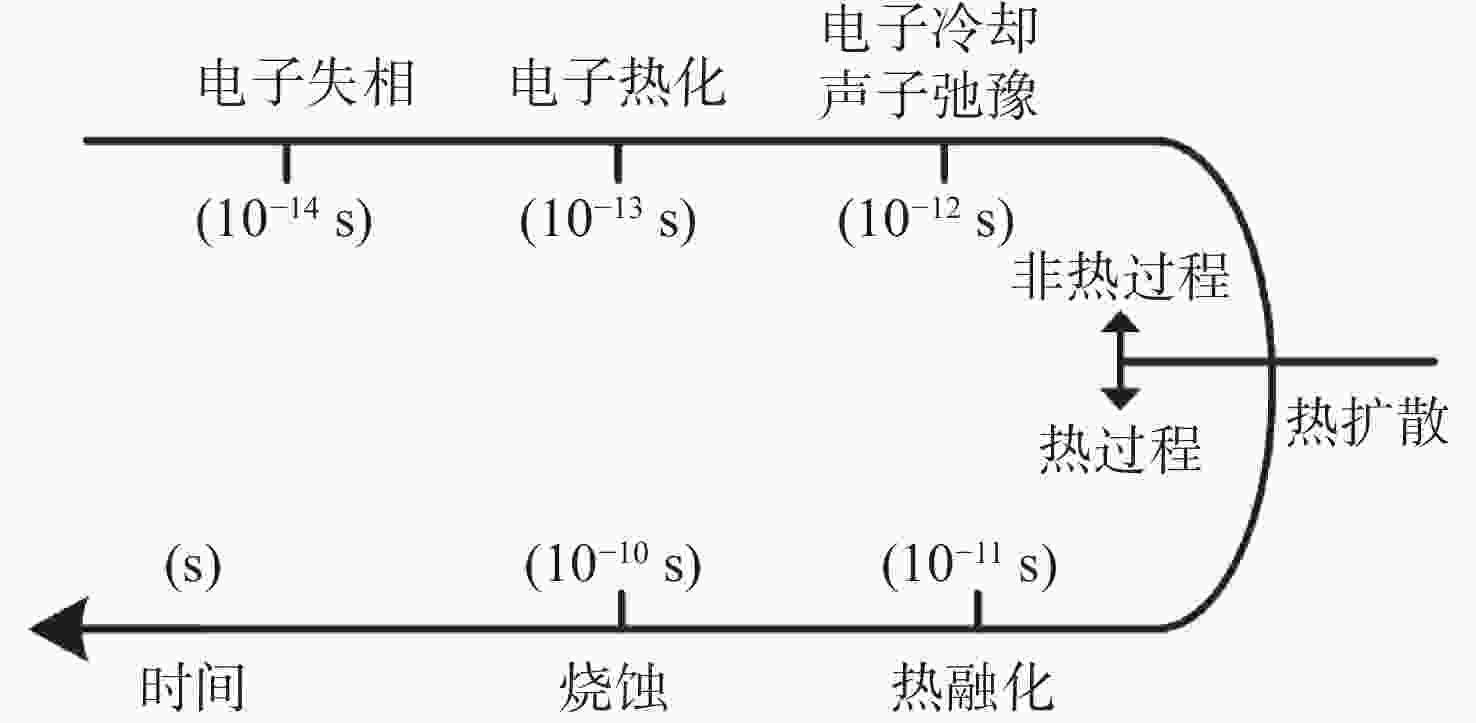
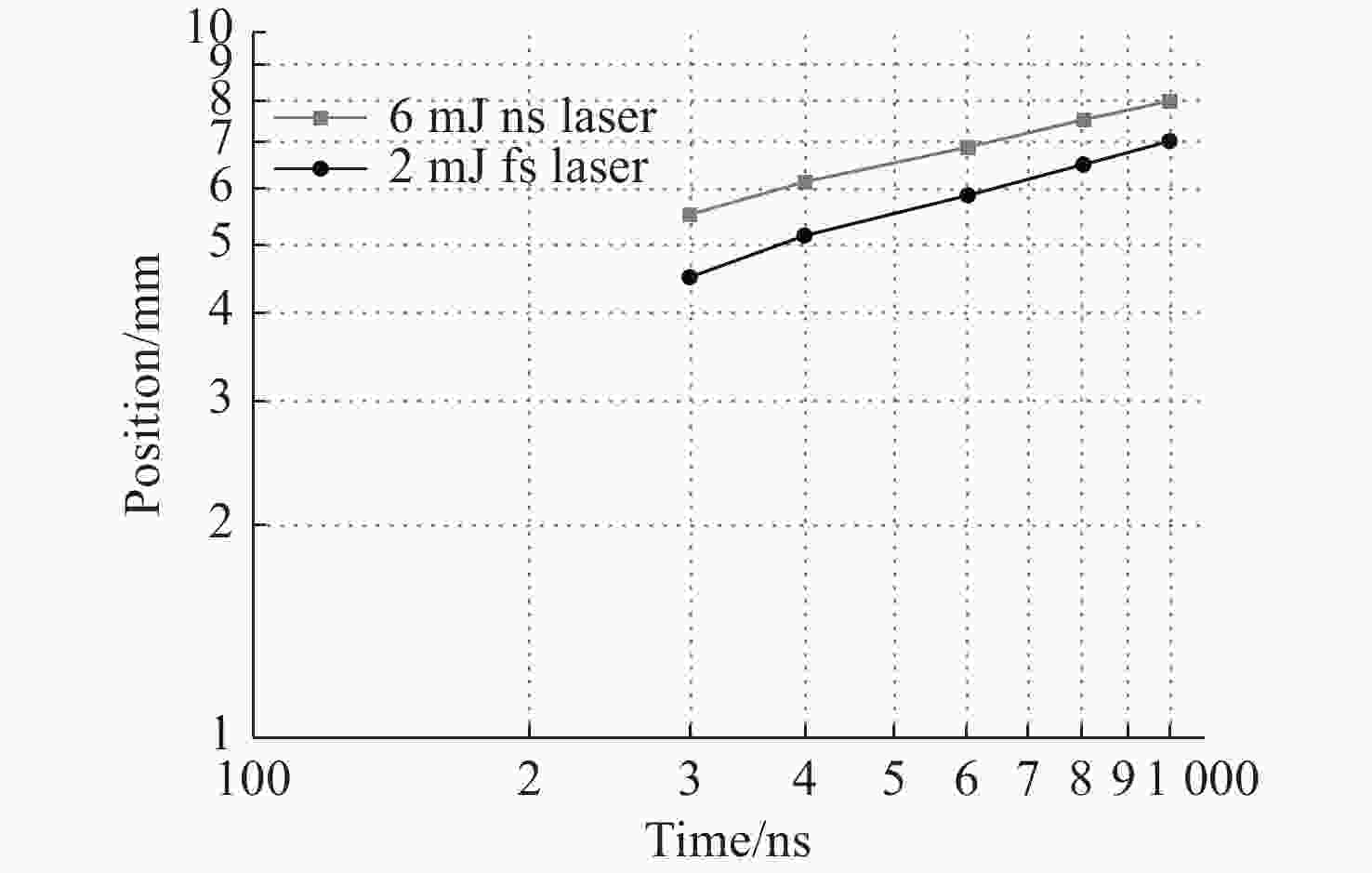
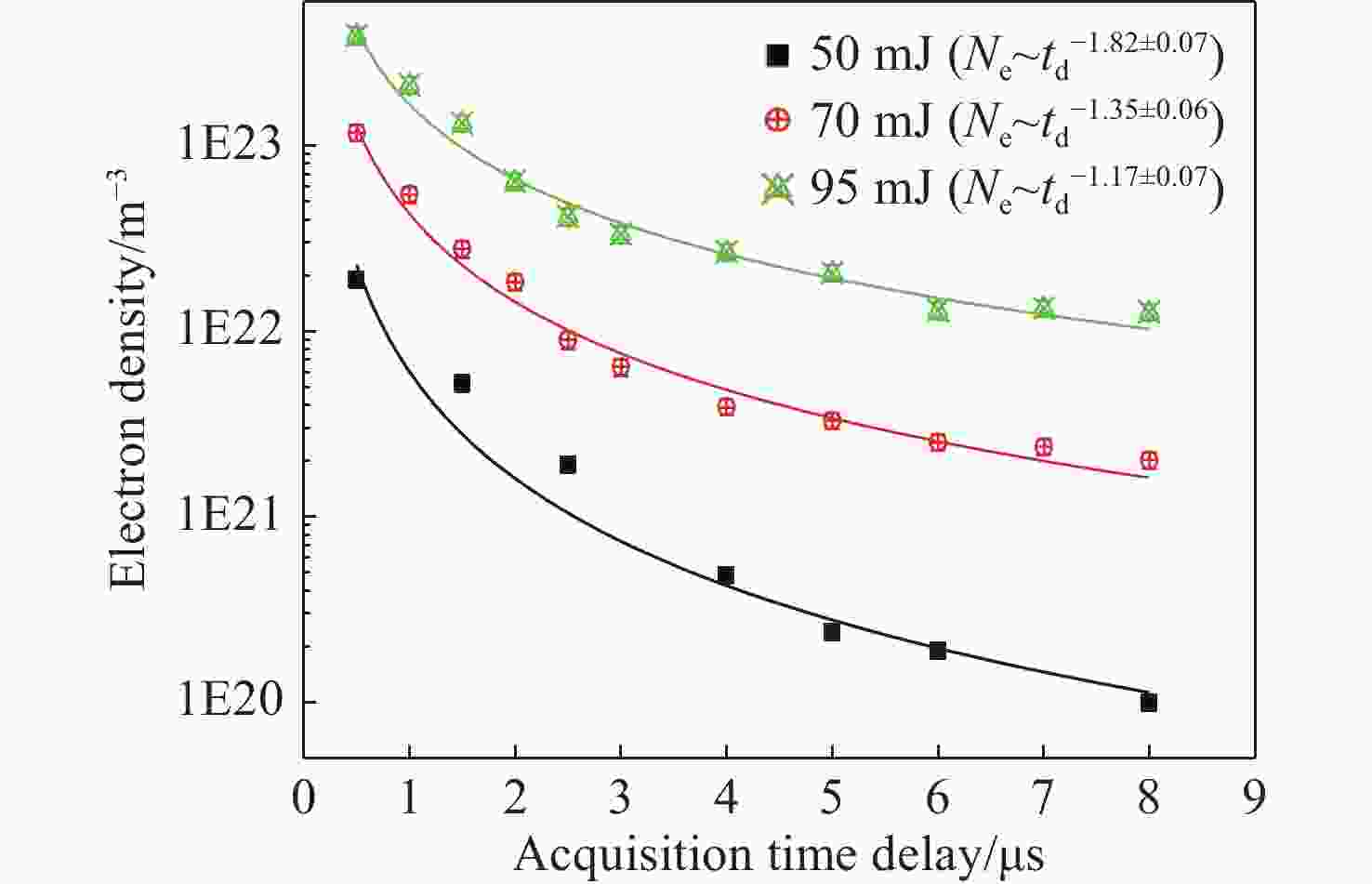
影响因素 受影响特性 双脉冲 ①等离子体的寿命,第一束金宝搏188软件怎么用 剥蚀出的颗粒不仅被第一束金宝搏188软件怎么用 产生的等离子体激发,还被第二束金宝搏188软件怎么用 产生的等离子体再次激发,等离子体寿命被延长;②电子温度,第一束金宝搏188软件怎么用 产生的等离子体对样品进行加热,使得第二束金宝搏188软件怎么用 剥蚀量增加,电子温度升高;③样品表面气体环境密度,第一束金宝搏188软件怎么用 产生的高温和等离子体的膨胀使样品表面产生一个大气密度较低的区域,第二束金宝搏188软件怎么用 在此区域内对剥蚀颗粒进行激发可以获得更好的信号强度 脉冲宽度 ①在相同的延迟时间下,等离子温度会随金宝搏188软件怎么用 脉冲宽度的增加而升高;②在相同的延迟时间下ns脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用 的谱线强度比fs脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用 的谱线强度更高;③对于fs金宝搏188软件怎么用 脉冲,烧蚀过程是直接从固体向蒸汽(或固向等离子体)转变,不存在热传导过程;对于ps金宝搏188软件怎么用 脉冲,金宝搏188软件怎么用 烧蚀伴随着电子热传导和目标内熔融区的形成;对于ns金宝搏188软件怎么用 脉冲,会产生相对较大的熔融材料层 金宝搏188软件怎么用 能量 ①在同一延迟时间下,金宝搏188软件怎么用 能量越高等离子体温度和电子数密度越大;②随着金宝搏188软件怎么用 能量的增加,吸收呈指数增长,在高能量下达到饱和;③在较高能量时,烧蚀质量增加,等离子体内部具有更高的能量而呈半球状向外膨胀;而能量较低时,烧蚀质量较小,等离子体趋向于盘状 环境气体 ①环境气体对等离子体的屏蔽效应影响很大,相比于空气环境氩气产生较高的等离子体温度,高的电子密度,消融速率较低,被探测元素的辐射强度较高;②在低的环境压力下,消融蒸汽可以自由的扩散,等离子体外部比内部的温度低,因为外部损失的能量较大。当提高压力时,由于环境气体限制了能量损失,使能量扩散更均一 靶材性质 ①在只考虑金属样品时,基体效应对等离子体参数的影响很弱;②样品的物理性质和结构以及组分都会对等离子体产生影响,并且烧蚀质量与靶材硬度成反比。③靶材温度也会影响光谱强度和等离子体性质,谱强度随着温度的升高而增强 等离子体寿命 ①等离子体寿命的变化会影响光谱信号的宽度和强度。当等离子体寿命较短时,产生的光谱信号较窄且信号强度较弱,而当等离子体寿命较长时,产生的光谱信号将更宽且信号强度更大 延时时间和积分时间 ①当延时时间较短时,等离子体没有充分形成,所得到的光谱信号较小;而当延时时间过长时,等离子体可能因为散射或扩散而消失,同样会降低光谱信号的强度。②较短的积分时间可能会导致噪声的增加,而较长的积分时间则会提高信号质量,提高光谱信号的信噪比,但会降低测量速度 -
[1] KUMAR A, YUEH F Y, SINGH J P, et al. Characterization of malignant tissue cells by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(28): 5399-5403. doi: 10.1364/AO.43.005399 [2] GALIOVÁ M, KAISER J, NOVOTNÝ K, et al. Investigation of heavy-metal accumulation in selected plant samples using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Applied Physics A, 2008, 93(4): 917-922. doi: 10.1007/s00339-008-4747-0 [3] BLEVINS L G, SHADDIX C R, SICKAFOOSE S M, et al. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy at high temperatures in industrial boilers and furnaces[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(30): 6107-6118. doi: 10.1364/AO.42.006107 [4] 程军杰, 曹智, 杨灿然, 等. 便携式远程金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱系统及其定量分析性能[J]. 应用化学, 2022, 39(9): 1447-1452.CHENG J J, CAO ZH, YANG C R, et al. Quantitative analysis with a portable remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(9): 1447-1452. [5] 黄慧, 周亦辰, 彭宇, 等. 基于量子级联金宝搏188软件怎么用 器中红外光谱技术的幽门螺旋杆菌呼气诊断的可行性研究[J]. 分析化学, 2022, 50(9): 1328-1335.HUANG H, ZHOU Y CH, PENG Y, et al. Feasibility study of breath diagnosis in Helicobacter pylori based on quantum cascade laser mid-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 50(9): 1328-1335. [6] GRÖNLUND R, LUNDQVIST M, SVANBERG S. Remote imaging laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and remote cultural heritage ablative cleaning[J]. Optics Letters, 2005, 30(21): 2882-2884. doi: 10.1364/OL.30.002882 [7] POULI P, MELESSANAKI K, GIAKOUMAKI A, et al. Measuring the thickness of protective coatings on historic metal objects using nanosecond and femtosecond laser induced breakdown spectroscopy depth profiling[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2005, 60(7-8): 1163-1171. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2005.05.028 [8] HUSSAIN T, GONDAL M A. Detection of toxic metals in waste water from dairy products plant using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2008, 80(6): 561-565. doi: 10.1007/s00128-008-9418-5 [9] 李悦, 张国霞, 蔡朝晴, 等. 大气压辉光放电结合圆柱约束增强金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱应用于土壤中稀土元素的检测[J]. 分析化学, 2022, 50(9): 1384-1390.LI Y, ZHANG G X, CAI ZH Q, et al. Atmospheric pressure glow discharge combined with cylindrical confinement enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for determination of rare earth in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 50(9): 1384-1390. [10] 李岩, 祁昱, 李赫. 拉曼光谱在感染性疾病诊断中的应用进展[J]. 分析化学, 2022, 50(3): 317-326.LI Y, QI Y, LI H. Advances of Raman spectroscopy in diagnosis of infectious diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 50(3): 317-326. (in Chinese) [11] BOGAERTS A, CHEN ZH Y, GIJBELS R, et al. Laser ablation for analytical sampling: what can we learn from modeling[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2003, 58(11): 1867-1893. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2003.08.004 [12] VASANTGADKAR N A, BHANDARKAR U V, JOSHI S S. A finite element model to predict the ablation depth in pulsed laser ablation[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2010, 519(4): 1421-1430. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2010.09.016 [13] ZHANG Y, ZHANG D X, WU J J, et al. A thermal model for nanosecond pulsed laser ablation of aluminum[J]. AIP Advances, 2017, 7(7): 075010. doi: 10.1063/1.4995972 [14] WANG Y D, LIU CH, LI CH L. Evolution of ns pulsed laser induced shock wave on aluminum surface by numerical simulation[J]. Results in Physics, 2021, 22: 103920. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.103920 [15] LIN X M, SUN H R, LIN J J. Comparison of SP-LIBS and DP-LIBS on metal and non-metal testing based on LIBS[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10457: 430-438. [16] IKEDA Y, SORIANO J K, KAWAHARA N, et al. Spatially and temporally resolved plasma formation on alumina target in microwave-enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2022, 197: 106533. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2022.106533 [17] MOHAMED W T Y. Improved LIBS limit of detection of Be, Mg, Si, Mn, Fe and Cu in aluminum alloy samples using a portable Echelle spectrometer with ICCD camera[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2008, 40(1): 30-38. [18] WERHEIT P, FRICKE-BEGEMANN C, GESING M, et al. Fast single piece identification with a 3D scanning LIBS for aluminium cast and wrought alloys recycling[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2011, 26(11): 2166-2174. doi: 10.1039/c1ja10096c [19] SHAO X X, ZANG CH X, LIN X M. A method for detecting the stability of lasers based on LIBS plasma morphology[C]. 2017 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), IEEE, 2017: 1715-1720. [20] SAMEK O, KUROWSKI A, KITTEL S, et al. Ultra-short laser pulse ablation using shear-force feedback: Femtosecond laser induced breakdown spectroscopy feasibility study[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2005, 60(7-8): 1225-1229. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2005.05.032 [21] ELAND K L, STRATIS D N, LAI T SH, et al. Some comparisons of LIBS measurements using nanosecond and picosecond laser pulses[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2001, 55(3): 279-285. doi: 10.1366/0003702011951894 [22] SEMEROK A, SALLÉ B, WAGNER J F, et al. Femtosecond, picosecond, and nanosecond laser microablation: laser plasma and crater investigation[J]. Laser and Particle Beams, 2002, 20(1): 67-72. doi: 10.1017/S0263034602201093 [23] BENEDETTI P A, CRISTOFORETTI G, LEGNAIOLI S, et al. Effect of laser pulse energies in laser induced breakdown spectroscopy in double-pulse configuration[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2005, 60(11): 1392-1401. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2005.08.007 [24] LE DROGOFF B, CHAKER M, MARGOT J, et al. Influence of the laser pulse duration on spectrochemical analysis of solids by laser-induced plasma spectroscopy[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2004, 58(1): 122-129. doi: 10.1366/000370204322729559 [25] RIEGER G W, TASCHUK M, TSUI Y Y, et al. Comparative study of laser-induced plasma emission from microjoule picosecond and nanosecond KrF-laser pulses[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2003, 58(3): 497-510. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(03)00014-4 [26] CAHOON E M, ALMIRALL J R. Wavelength dependence on the forensic analysis of glass by nanosecond 266 nm and 1064 nm laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(13): C49-C57. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.000C49 [27] WANG X SH, WAN S SH, HE Y G, et al. Rapid determination of all element in MAPbI3 thin films using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2021, 178: 106123. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2021.106123 [28] ARAGÓN C, AGUILERA J A. Characterization of laser induced plasmas by optical emission spectroscopy: A review of experiments and methods[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2008, 63(9): 893-916. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2008.05.010 [29] CREMERS D A, RADZIEMSKI L J. Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy[M]. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2006. [30] MIZIOLEK A W, PALLESCHI V, SCHECHTER I. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS): Fundamentals and Applications[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006. [31] VON DER LINDE D, SOKOLOWSKI-TINTEN K, BIALKOWSKI J. Laser-solid interaction in the femtosecond time regime[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1997, 109-110: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(96)00611-3 [32] 李业秋. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱增强特性及应用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019.LI Y Q. Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy enhancement characteristic and application research[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019. (in Chinese) [33] 刘杨. 样品温度对金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导等离子体膨胀动力学的影响[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.LIU Y. The effect of sample temperature on the expansion dynamics of laser induced plasma[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. (in Chinese) [34] GAUTIER C, FICHET P, MENUT D, et al. Study of the double-pulse setup with an orthogonal beam geometry for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2004, 59(7): 975-986. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2004.05.002 [35] DE GIACOMO A, DELL'AGLIO M, COLAO F, et al. Double pulse laser produced plasma on metallic target in seawater: basic aspects and analytical approach[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2004, 59(9): 1431-1438. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2004.07.002 [36] ST-ONGE L, DETALLE V, SABSABI M. Enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using the combination of fourth-harmonic and fundamental Nd: YAG laser pulses[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2002, 57(1): 121-135. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(01)00358-5 [37] ST-ONGE L, SABSABI M, CIELO P. Analysis of solids using laser-induced plasma spectroscopy in double-pulse mode[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 1998, 53(3): 407-415. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(98)00080-9 [38] STRATIS D N, ELAND K L, ANGEL S M. Dual-pulse LIBS using a pre-ablation spark for enhanced ablation and emission[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2000, 54(9): 1270-1274. doi: 10.1366/0003702001951174 [39] STRATIS D N, ELAND K L, ANGEL S M. Effect of pulse delay time on a pre-ablation dual-pulse LIBS plasma[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2001, 55(10): 1297-1303. doi: 10.1366/0003702011953649 [40] STRATIS D N, ELAND K L, ANGEL S M. Enhancement of aluminum, titanium, and iron in glass using pre-ablation spark dual-pulse LIBS[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2000, 54(12): 1719-1726. doi: 10.1366/0003702001948871 [41] ANGEL S M, STRATIS D N, ELAND K L, et al. LIBS using dual- and ultra-short laser pulses[J]. Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 369(3): 320-327. [42] MUKHERJEE P, CHEN SH D, WITANACHCHI S. Effect of initial plasma geometry and temperature on dynamic plume expansion in dual-laser ablation[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1999, 74(11): 1546-1548. doi: 10.1063/1.123611 [43] AHMED R, BAIG M A. A comparative study of enhanced emission in double pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2015, 65: 113-118. [44] SEDOV L I. Similarity and Dimensional Methods in Mechanics[M]. 10th ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1993. [45] CRISTOFORETTI G, LEGNAIOLI S, PARDINI L, et al. Spectroscopic and shadowgraphic analysis of laser induced plasmas in the orthogonal double pulse pre-ablation configuration[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2006, 61(3): 340-350. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2006.03.004 [46] VISKUP R, PRAHER B, LINSMEYER T, et al. Influence of pulse-to-pulse delay for 532nm double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of technical polymers[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2010, 65(11): 935-942. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2010.09.003 [47] BHATT C R, HARTZLER D, JAIN J C, et al. Evaluation of analytical performance of double pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for the detection of rare earth elements[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2020, 126: 106110. [48] NOLL R, SATTMANN R, STURM V, et al. Space- and time-resolved dynamics of plasmas generated by laser double pulses interacting with metallic samples[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2004, 19(4): 419-428. doi: 10.1039/b315718k [49] SATTMANN R, STURM V, NOLL R. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of steel samples using multiple Q-switch Nd: YAG laser pulses[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 1995, 28(10): 2181-2187. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/28/10/030 [50] CRISTOFORETTI G, LEGNAIOLI S, PALLESCHI V, et al. Influence of ambient gas pressure on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technique in the parallel double-pulse configuration[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2004, 59(12): 1907-1917. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2004.09.003 [51] GAUTIER C, FICHET P, MENUT D, et al. Main parameters influencing the double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in the collinear beam geometry[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2005, 60(6): 792-804. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2005.05.006 [52] HEILBRUNNER H, HUBER N, WOLFMEIR H, et al. Double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for trace element analysis in sintered iron oxide ceramics[J]. Applied Physics A, 2012, 106(1): 15-23. doi: 10.1007/s00339-011-6669-5 [53] BABUSHOK V I, DELUCIA JR F C, GOTTFRIED J L, et al. Double pulse laser ablation and plasma: laser induced breakdown spectroscopy signal enhancement[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2006, 61(9): 999-1014. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2006.09.003 [54] WANG Y, CHEN A M, WANG Q Y, et al. Study of signal enhancement in collinear femtosecond-nanosecond double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2020, 122: 105887. [55] CRISTOFORETTI G. Orthogonal Double-pulse versus Single-pulse laser ablation at different air pressures: a comparison of the mass removal mechanisms[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2009, 64(1): 26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2008.10.028 [56] PROCHAZKA D, POŘÍZKA P, NOVOTNÝ J, et al. Triple-pulse LIBS: laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy signal enhancement by combination of pre-ablation and re-heating laser pulses[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2020, 35(2): 293-300. doi: 10.1039/C9JA00323A [57] CHOI I, MAO X L, GONZALEZ J J, et al. Plasma property effects on spectral line broadening in double-pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Applied Physics A, 2013, 110(4): 785-792. doi: 10.1007/s00339-012-7153-6 [58] RAI V N, YUEH F Y, SINGH J P. Time-dependent single and double pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of chromium in liquid[J]. Applied Optics, 2008, 47(31): G21-G29. doi: 10.1364/AO.47.000G21 [59] ZENG X ZH, MAO S S, LIU CH Y, et al. Plasma diagnostics during laser ablation in a cavity[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2003, 58(5): 867-877. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(03)00021-1 [60] DE GIACOMO A, DELL'AGLIO M, BRUNO D, et al. Experimental and theoretical comparison of single-pulse and double-pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy on metallic samples[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2008, 63(7): 805-816. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2008.05.002 [61] CHICHKOV B N, MOMMA C, NOLTE S, et al. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids[J]. Applied physics A, 1996, 63(2): 109-115. doi: 10.1007/BF01567637 [62] ELHASSAN A, GIAKOUMAKI A, ANGLOS D, et al. Nanosecond and femtosecond Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopic analysis of bronze alloys[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2008, 63(4): 504-511. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2008.02.003 [63] LE DROGOFF B, MARGOT J, VIDAL F, et al. Influence of the laser pulse duration on laser-produced plasma properties[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2004, 13(2): 223-230. doi: 10.1088/0963-0252/13/2/005 [64] LE DROGOFF B, MARGOT J, CHAKER M, et al. Temporal characterization of femtosecond laser pulses induced plasma for spectrochemical analysis of aluminum alloys[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2001, 56(6): 987-1002. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(01)00187-2 [65] EMMERT L A, CHINNI R C, CREMERS D A, et al. Comparative study of femtosecond and nanosecond laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of depleted uranium[J]. Applied Optics, 2011, 50(3): 313-317. doi: 10.1364/AO.50.000313 [66] MILOSHEVSKY A, HARILAL S S, MILOSHEVSKY G, et al. Dynamics of plasma expansion and shockwave formation in femtosecond laser-ablated aluminum plumes in argon gas at atmospheric pressures[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2014, 21(4): 043111. doi: 10.1063/1.4873701 [67] HARILAL S S, MILOSHEVSKY G V, DIWAKAR P K, et al. Experimental and computational study of complex shockwave dynamics in laser ablation plumes in argon atmosphere[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2012, 19(8): 083504. doi: 10.1063/1.4745867 [68] RAO E N, MATHI P, KALAM S A, et al. Femtosecond and nanosecond LIBS studies of nitroimidazoles: correlation between molecular structure and LIBS data[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2016, 31(3): 737-750. doi: 10.1039/C5JA00445D [69] KALAM S A, MURTHY N L, MATHI P, et al. Correlation of molecular, atomic emissions with detonation parameters in femtosecond and nanosecond LIBS plasma of high energy materials[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32(8): 1535-1546. doi: 10.1039/C7JA00136C [70] SERRANO J, MOROS J, LASERNA J J. Molecular signatures in femtosecond laser-induced organic plasmas: comparison with nanosecond laser ablation[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18(4): 2398-2408. doi: 10.1039/C5CP06456B [71] SULIYANTI M M, ISNAENI, PARDEDE M, et al. Comparison of excitation mechanisms and the corresponding emission spectra in femto second and nano second laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in reduced ambient air and their performances in surface analysis[J]. Journal of Laser Applications, 2020, 32(1): 012014. doi: 10.2351/1.5119182 [72] SARKAR A, SHAH R V, ALAMELU D, et al. Studies on the ns-IR-laser-induced plasma parameters in the vanadium Oxide[J]. Journal of Atomic and Molecular Physics, 2011, 2011: 504764. [73] ABDELHAMID M, GRASSINI S, ANGELINI E, et al. Effect of changing laser irradiance on the laser induced plasma parameters for Au/Cu layered target[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2009, 1172(1): 70-75. [74] LUO W F, ZHAO X X, SUN Q B, et al. Characteristics of the aluminum alloy plasma produced by a 1064 nm Nd: YAG laser with different irradiances[J]. Pramana, 2010, 74(6): 945-959. doi: 10.1007/s12043-010-0086-8 [75] VADILLO J M, ROMERO J M F, RODRÍGUEZ C, et al. Effect of plasma shielding on laser ablation rate of pure metals at reduced pressure[J]. Surface and Interface Analysis, 1999, 27(11): 1009-1015. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9918(199911)27:11<1009::AID-SIA670>3.0.CO;2-2 [76] HARILAL S S, BINDHU C V, ISSAC R C, et al. Electron density and temperature measurements in a laser produced carbon plasma[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1997, 82(5): 2140-2146. doi: 10.1063/1.366276 [77] CRISTOFORETTI G, LEGNAIOLI S, PALLESCHI V, et al. Observation of different mass removal regimes during the laser ablation of an aluminium target in air[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2008, 23(11): 1518-1528. doi: 10.1039/b800517f [78] PIRRI A N. Theory for momentum transfer to a surface with a high-power laser[J]. Physics of Fluids, 1973, 16(9): 1435-1440. doi: 10.1063/1.1694538 [79] AGUILERA J A, ARAGÓN C, PEÑALBA F. Plasma shielding effect in laser ablation of metallic samples and its influence on LIBS analysis[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1998, 127-129: 309-314. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(97)00648-X [80] CIRISAN M, JOUVARD J M, LAVISSE L, et al. Laser plasma plume structure and dynamics in the ambient air: The early stage of expansion[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109(10): 103301. doi: 10.1063/1.3581076 [81] ZENG Q D, GUO L B, LI X Y, et al. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using laser pulses delivered by optical fibers for analyzing Mn and Ti elements in pig iron[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2015, 30(2): 403-409. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00462K [82] HANIF M, SALIK M, BAIG M A. Quantitative studies of copper plasma using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2011, 49(12): 1456-1461. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2011.06.013 [83] DITTRICH K, WENNRICH R. Laser vaporization in atomic spectrometry[J]. Analytical Spectroscopy Library, 1990, 4: 107-146. [84] RUSSO R E, MAO X L, LIU H CH, et al. Laser ablation in analytical chemistry-a review[J]. Talanta, 2002, 57(3): 425-451. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00053-X [85] DUCREUX-ZAPPA M, MERMET J M. Analysis of glass by UV laser ablation inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Part 2. Analytical figures of merit[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 1996, 51(3): 333-341. doi: 10.1016/0584-8547(95)01427-6 [86] DURRANT S F. Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: achievements, problems, prospects[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1999, 14(9): 1385-1403. doi: 10.1039/a901765h [87] LAZIC V, COLAO F, FANTONI R, et al. Laser-induced plasma spectroscopy: principles, methods and applications[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2006, 876(1): 309-316. [88] CABALÍN L M, LASERNA J J. Experimental determination of laser induced breakdown thresholds of metals under nanosecond Q-switched laser operation[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 1998, 53(5): 723-730. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(98)00107-4 [89] CABALÍN L, ROMERO D, GARCÍA C C, et al. Time-resolved laser-induced plasma spectrometry for determination of minor elements in steelmaking process samples[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2002, 372(2): 352-359. doi: 10.1007/s00216-001-1121-x [90] MENUT D, FICHET P, LACOUR J L, et al. Micro-laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technique: a powerful method for performing quantitative surface mapping on conductive and nonconductive samples[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(30): 6063-6071. doi: 10.1364/AO.42.006063 [91] MAO X L, CIOCAN A C, RUSSO R E. Preferential vaporization during laser ablation inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 1998, 52(7): 913-918. doi: 10.1366/0003702981944706 [92] FANTONI R, CANEVE L, COLAO F, et al. Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS)[M]//BARTOLO B, FORTE O. Advances in Spectroscopy for Lasers and Sensing. Dordrecht: Springer, 2006: 229-254. [93] LEIS F, SDORRA W, KO J B, et al. Basic investigations for laser microanalysis: I. Optical emission spectrometry of laser-produced sample plumes[J]. Microchimica Acta, 1989, 98(4): 185-199. [94] SDORRA W, NIEMAX K. Basic investigations for laser microanalysis: III. Application of different buffer gases for laser-produced sample plumes[J]. Microchimica Acta, 1992, 107(3): 319-327. [95] LEE Y I, SONG K, CHA H K, et al. Influence of atmosphere and irradiation wavelength on copper plasma emission induced by excimer and Q-switched Nd: YAG laser ablation[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 1997, 51(7): 959-964. doi: 10.1366/0003702971941610 [96] LEE Y I, THIEM T L, KIM G H, et al. Interaction of an excimer-laser beam with metals. Part III: The effect of a controlled atmosphere in laser-ablated plasma emission[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 1992, 46(11): 1597-1604. doi: 10.1366/0003702924926871 [97] AGUILERA J A, ARAGÓN C. A comparison of the temperatures and electron densities of laser-produced plasmas obtained in air, argon, and helium at atmospheric pressure[J]. Applied Physics A, 1999, 69(1): S475-S478. [98] BASHIR S, FARID N, MAHMOOD K, et al. Influence of ambient gas and its pressure on the laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and the surface morphology of laser-ablated Cd[J]. Applied Physics A, 2012, 107(1): 203-212. doi: 10.1007/s00339-011-6730-4 [99] MARGETIC V, PAKULEV A, STOCKHAUS A, et al. A Comparison of nanosecond and femtosecond laser-induced plasma spectroscopy of brass samples[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2000, 55(11): 1771-1785. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(00)00275-5 [100] HERMANN J, GERHARD C, AXENTE E, et al. Comparative investigation of laser ablation plumes in air and argon by analysis of spectral line shapes: Insights on calibration-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2014, 100: 189-196. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2014.08.014 [101] WANG S, ZHANG D, CHNE N, et al. Self-absorption effects of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy under different gases and gas pressures[J]. Plasma Science and Technology: English Version, 2023, 25(2): 8. [102] GRAVEL J F Y, BOUDREAU D. Study by focused shadowgraphy of the effect of laser irradiance on laser-induced plasma formation and ablation rate in various gases[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2009, 64(1): 56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2008.10.037 [103] AGUILERA J A, ARAGÓN C, MADURGA V, et al. Study of matrix effects in laser induced breakdown spectroscopy on metallic samples using plasma characterization by emission spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2009, 64(10): 993-998. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2009.07.007 [104] YAO SH CH, ZHAO J B, XU J L, et al. Optimizing the binder percentage to reduce matrix effects for the LIBS analysis of carbon in coal[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32(4): 766-772. doi: 10.1039/C6JA00458J [105] VISKUP R, PRAHER B, STEHRER T, et al. Plasma plume photography and spectroscopy of Fe-Oxide materials[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255(10): 5215-5219. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.08.092 [106] ANZANO J M, VILLORIA M A, RUÍZ-MEDINA A, et al. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for quantitative spectrochemical analysis of geological materials: effects of the matrix and simultaneous determination[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2006, 575(2): 230-235. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2006.05.077 [107] LABUTIN T A, POPOV A M, LEDNEV V N, et al. Correlation between properties of a solid sample and laser-induced plasma parameters[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2009, 64(10): 938-949. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2009.07.033 [108] SHAO J F, GUO J, WANG Q Y, et al. Influence of target temperature on femtosecond laser-ablated brass plasma spectroscopy[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2020, 22(7): 074001. doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/ab7901 [109] GUO J, WANG T F, SHAO J F, et al. Emission enhancement of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy by increasing sample temperature combined with spatial confinement[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2018, 33(12): 2116-2123. doi: 10.1039/C8JA00246K [110] SABSABI M, CIELO P. Quantitative analysis of aluminum alloys by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and plasma characterization[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 1995, 49(4): 499-507. doi: 10.1366/0003702953964408 [111] ZHANG D, CHEN A M, WANG X W, et al. Enhancement mechanism of femtosecond double-pulse laser-induced Cu plasma spectroscopy[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2017, 96: 117-122. [112] KUZUYA M, MATSUMOTO H, TAKECHI H, et al. Effect of laser energy and atmosphere on the emission characteristics of laser-induced plasmas[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 1993, 47(10): 1659-1664. doi: 10.1366/0003702934334804 [113] UJIHARA K. Reflectivity of metals at high temperatures[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1972, 43(5): 2376-2383. doi: 10.1063/1.1661506 [114] LIU Y, TONG Y, WANG Y, et al. Influence of sample temperature on the expansion dynamics of laser-induced germanium plasma[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2017, 19(12): 125501. doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/aa8acc [115] ESCHLBÖCK-FUCHS S, HASLINGER E S, HINTERREITER M J, et al. Influence of sample temperature on the expansion dynamics and the optical emission of laser-induced plasma[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2013, 87: 36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2013.05.023 [116] ZHANG D, CHEN A M, WANG Q Y, et al. Influence of target temperature on H alpha line of laser-induced silicon plasma in air[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2018, 25(8): 083305. doi: 10.1063/1.5040895 [117] 李捷, 陆继东, 林兆祥, 等. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿固体样品中金属元素光谱的实验研究[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2009,36(11):2882-2887. doi: 10.3788/CJL20093611.2882LI J, LU J D, LIN ZH X, et al. Experimental analysis of spectra of metallic elements in solid samples by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2009, 36(11): 2882-2887. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL20093611.2882 [118] CHOI S J, YOH J J. Laser-induced plasma peculiarity at low pressures from the elemental lifetime perspective[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(23): 23097-23103. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.023097 [119] FU Y T, HOU Z Y, LI T Q, et al. Investigation of intrinsic origins of the signal uncertainty for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2019, 155: 67-78. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2019.03.007 [120] FU Y T, GU W L, HOU Z Y, et al. Mechanism of signal uncertainty generation for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Frontiers of Physics, 2020, 16(2): 22502. [121] 王阳恩. 延迟时间对灰岩中镍元素金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱强度的影响[J]. 冶金分析,2013,33(11):1-5. doi: 10.13228/j.issn.1000-7571.2013.11.001WANG Y E. Influence of delay time on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy intensity of nickel in limestone[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2013, 33(11): 1-5. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13228/j.issn.1000-7571.2013.11.001 [122] 郑培超, 刘红弟, 王金梅, 等. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导铝合金等离子体的时间演化过程研究[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2014,41(10):1015001. doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.1015001ZHENG P CH, LIU H D, WANG J M, et al. Study on time evolution process of laser-induced aluminum alloy plasma[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(10): 1015001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.1015001 [123] SONG K, CHA H, LEE J, et al. Investigation of the line-broadening mechanism for laser-induced copper plasma by time-resolved laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Microchemical Journal, 1999, 63(1): 53-60. doi: 10.1006/mchj.1999.1767 -






 下载:
下载: