Optimal position for suger content detection of Yongquan honey oranges based on hyperspectral imaging technology
-
摘要:
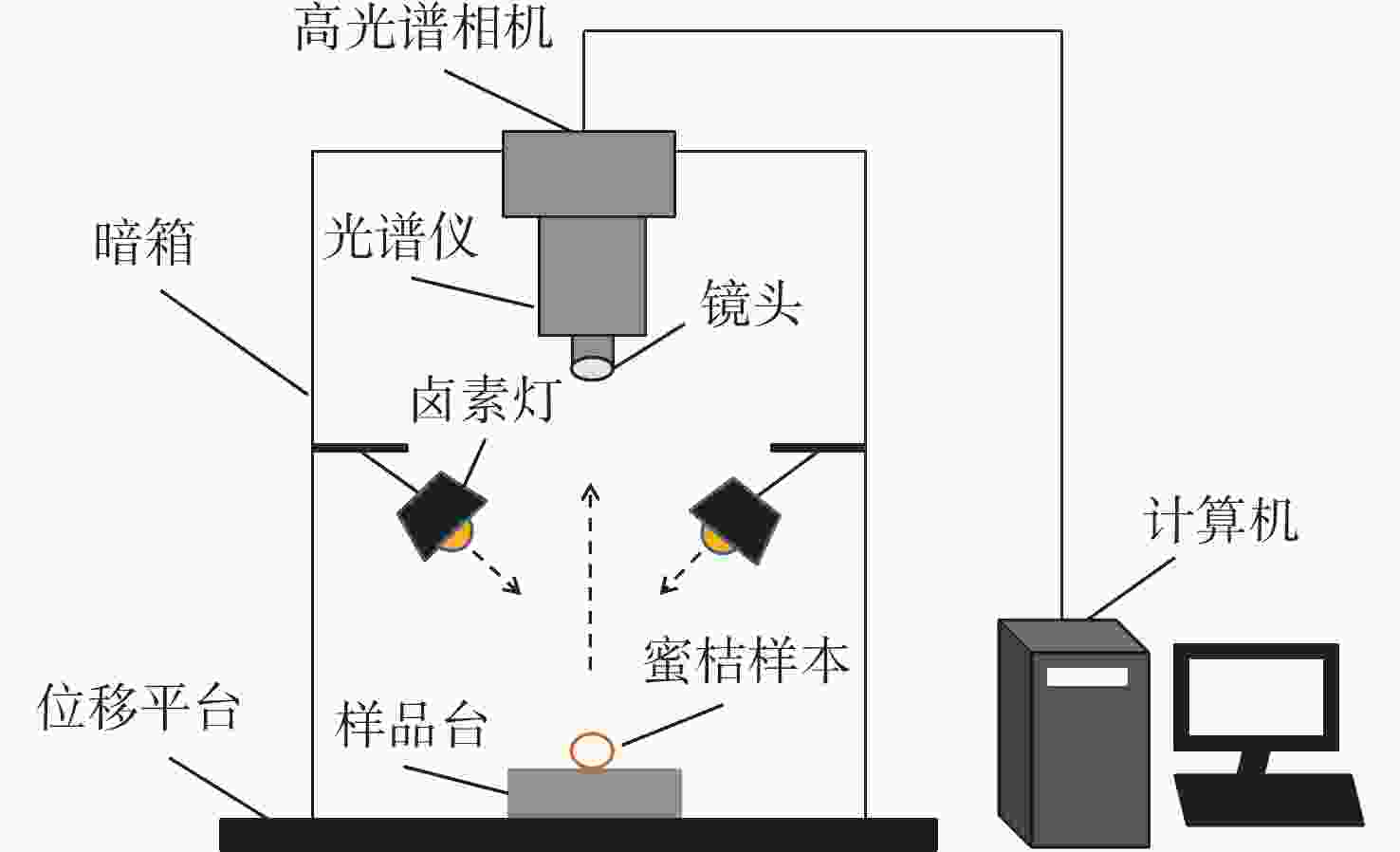
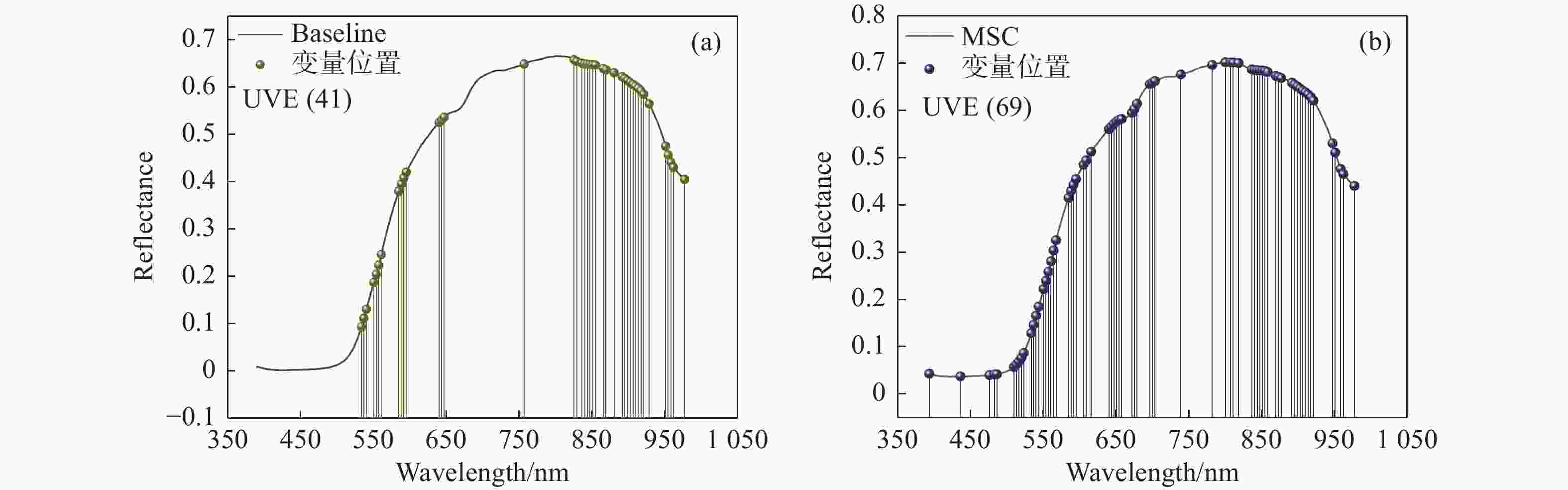
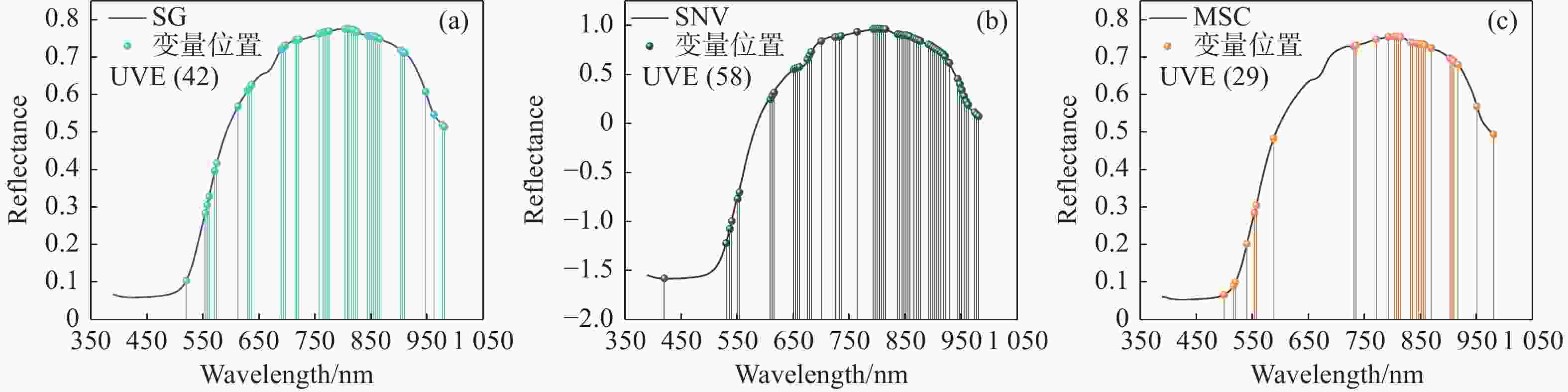
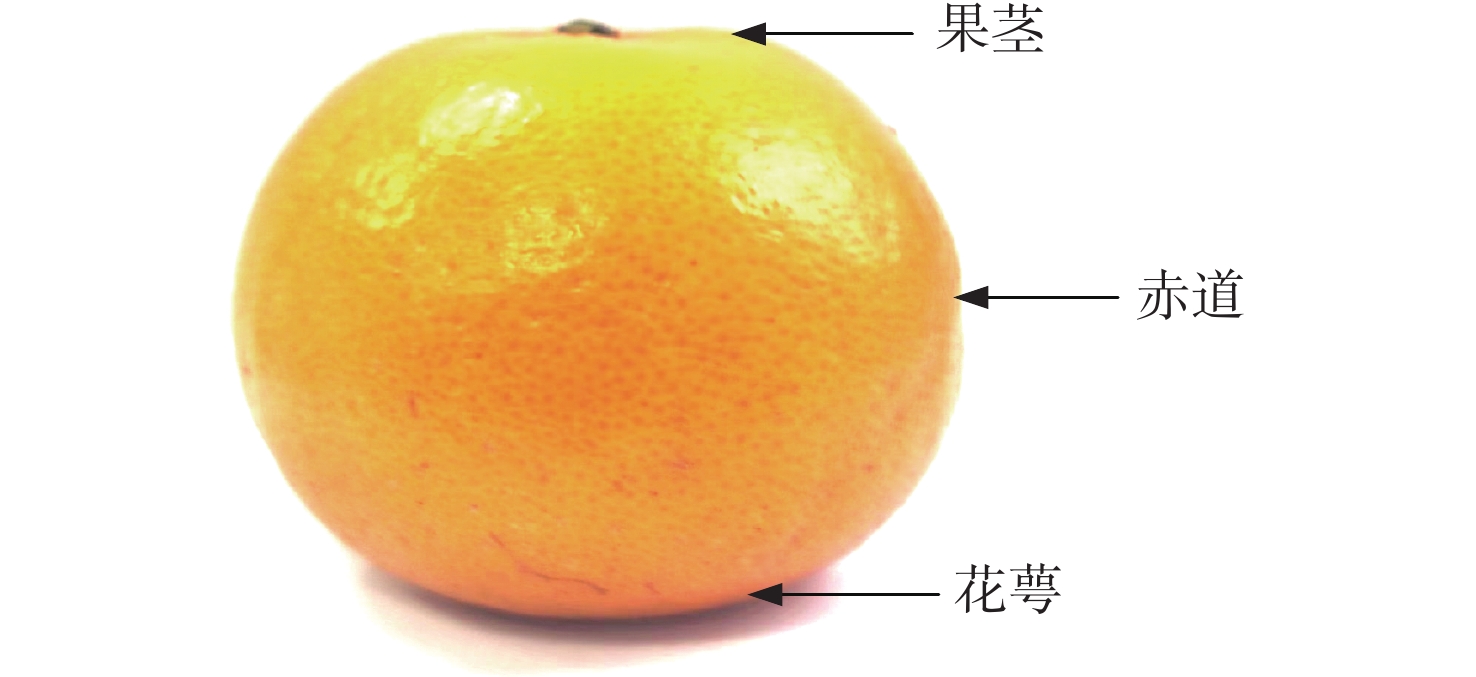
本文旨在探索涌泉蜜桔糖度的最优检测位置和最佳预测模型,以便为蜜桔糖度检测分级提供理论依据。本文利用波长为390.2~981.3 nm的高光谱成像系统对涌泉蜜桔糖度最佳检测位置进行研究,将涌泉蜜桔的花萼、果茎、赤道和全局的光谱信息与其对应部位的糖度结合,建立其预测模型。使用标准正态变量变换(SNV)、多元散射校正(MSC)、基线校准(Baseline)和SG平滑(Savitzkv-Golay)4种预处理方法对不同部位的原始光谱进行预处理,用预处理后的光谱数据建立偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)和最小二乘支持向量机(LSSVM)模型。找出蜜桔不同部位的最佳预处理方式,对经过最佳预处理后的光谱数据采用竞争性自适应重加权算法(CARS)和无信息变量消除法(UVE)进行特征波长筛选。最后,用筛选后的光谱数据建立PLSR和LSSVM模型并进行分析比较。研究结果表明,全局的MSC-CARS-LSSVM模型预测效果最佳,其预测集相关系数
Rp =0.955,均方根误差RMSEP=0.395,其次是蜜桔赤道部位的SNV-PLSR模型,其预测集相关系数Rp =0.936,均方根误差RMSEP=0.37。两者预测集相关系数相近,因此可将赤道位置作为蜜桔糖度的最优检测位置。本研究表明根据蜜桔不同部位建立的糖度预测模型的预测效果有所差异,研究最优检测位置和最佳预测模型可以为蜜桔进行糖度检测分级提供理论依据。Abstract:The objective of this study is to explore the optimal detection location and the best prediction model of the suger level of Yongquan honey oranges, which can provide a theoretical basis for the brix measurement and classification of honey oranges. With the wavelength range of 390.2−981.3 nm hyperspectral imaging system was used to study the best position for detecting the sugar content of Yongquan honey oranges, and the spectral information of the calyx, fruit stem, equator and global of Yongquan honey oranges were combined with their sugar content of corresponding parts to establish its prediction model. The original spectra from the different locations were pre-processed by Standard Normal Variance (SNV) transformation, Multiple Scattering Correction (MSC), baseline calibration (Baseline) and SG smoothing, respectively, and the Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR) and Least Squares Support Vector Machine (LSSVM) models were established based on the pre-processed spectral data. The best pre-processing methods for different parts of the honey oranges were found, and the optimal spectral data obtained by the best pre-processing methods were conducted to identify characteristic wavelengths using the Competitive Adaptive Re-weighting Sampling algorithm (CARS) and Uninformative Variable Elimination (UVE). Finally, the PLSR and LSSVM models were established and compared based on the selected spectral data. The results show that the global MSC-CARS-LSSVM model demonstrates the most accurate prediction performance, with a correlation coefficient of
Rp =0.955 and an RMSEP value of 0.395. Alternatively, the SNV-PLSR model of the equatorial location of honey oranges was found to be the next more effective, with a correlation coefficient ofRp =0.936, and an RMSEP value of 0.37. The correlation coefficients of the two prediction models are similar, the equatorial location can be used as the optimal position for measuring the sugar content of honey oranges. This study demonstrates that the prediction models based on different parts of the orange have different effects. Identifying the optimal position and prediction model can provide a theoretical basis for classifying oranges for sugar content testing. -
表 1 涌泉蜜桔不同部位的糖度统计分析结果
Table 1. Statistical analysis of the sugar content of different parts of Yongquan honey orange
蜜桔部位 样本数 最大值
/ OBrix最小值
/ OBrix平均值
/ OBrix标准差
/ OBrix花萼 120 19.8 10.8 15.2 1.39 果茎 120 17.9 10.1 14.2 1.52 赤道 120 18.2 11.3 14.5 1.37 全局 120 17.8 11.2 14.6 1.34 表 2 基于不同预处理方法的涌泉蜜桔糖度检测PLSR模型比较
Table 2. Comparison of PLSR models for detecting the sugar content of Yongquan honey orange based on different pretreatments
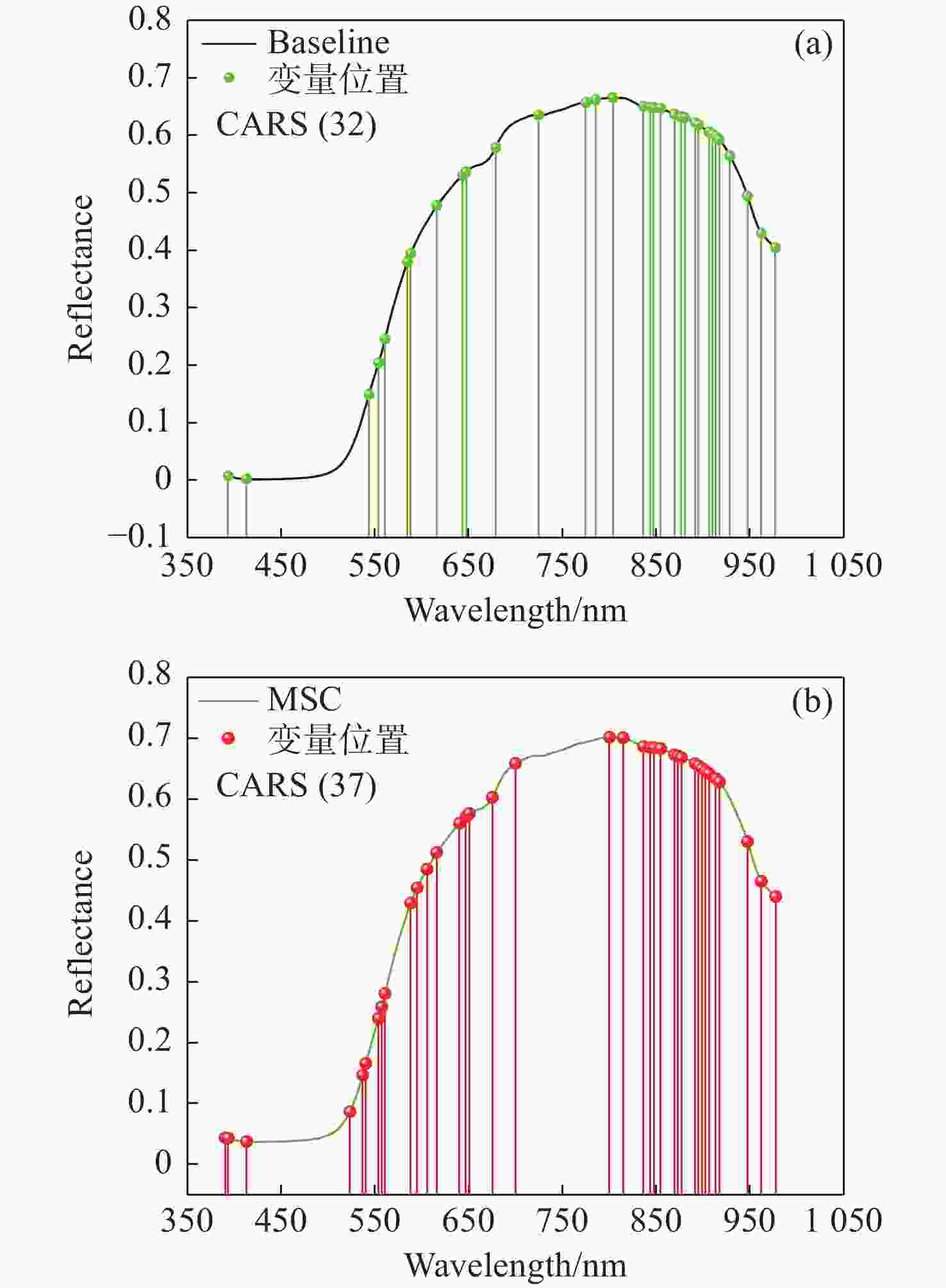
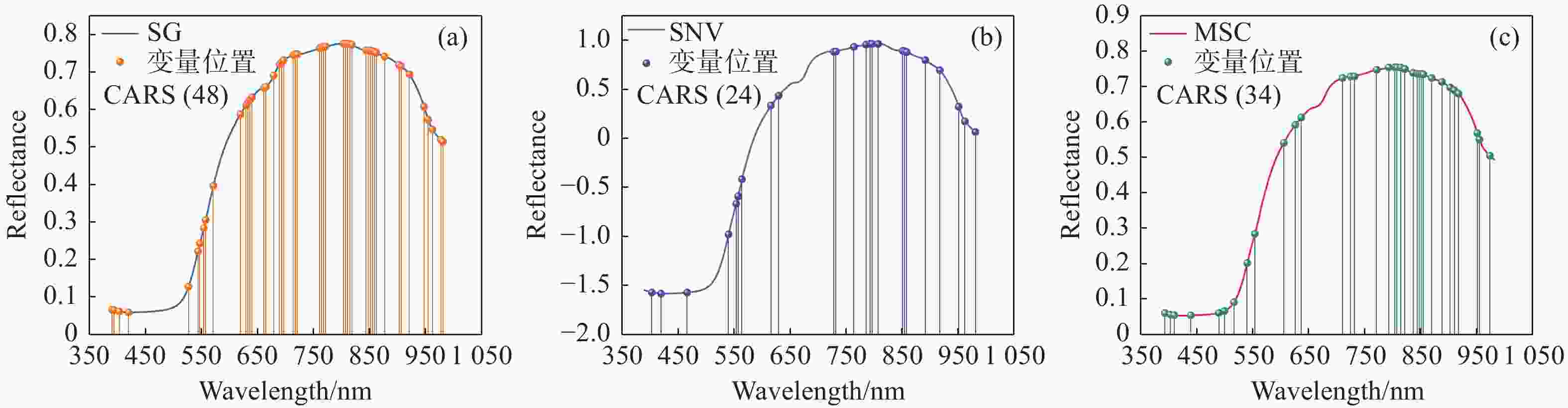
预测模型 预处理方法 建模集 预测集 RC RMSEC/OBrix RP RMSEP/OBrix 花萼模型 Raw 0.946 0.384 0.893 0.457 SNV 0.847 0.58 0.806 0.688 MSC 0.832 0.622 0.766 0.564 Baseline 0.921 0.409 0.890 0.518 SG 0.932 0.427 0.898 0.436 果茎模型 Raw 0.949 0.428 0.859 0.587 SNV 0.902 0.593 0.882 0.669 MSC 0.889 0.599 0.864 0.587 Baseline 0.931 0.498 0.913 0.468 SG 0.943 0.455 0.868 0.569 赤道模型 Raw 0.932 0.471 0.861 0.553 SNV 0.946 0.408 0.936 0.370 MSC 0.960 0.365 0.878 0.458 Baseline 0.964 0.349 0.933 0.384 SG 0.924 0.497 0.861 0.555 全局模型 Raw 0.971 0.305 0.920 0.388 SNV 0.945 0.403 0.901 0.435 MSC 0.953 0.374 0.934 0.435 Baseline 0.926 0.469 0.855 0.495 SG 0.927 0.476 0.923 0.384 表 3 基于不同预处理的涌泉蜜桔糖度LSSVM模型比较
Table 3. Comparison of LSSVM models for detecting the sugar content of Yongquan honey orange basedon different pretreatments
预测模型 预处理
方法建模集 预测集 RC RMSEC/OBrix RP RMSEP/ OBrix 花萼模型 Raw 0.921 0.470 0.860 0.513 SNV 0.938 0.383 0.789 0.700 MSC 0.959 0.323 0.788 0.539 Baseline 0.942 0.360 0.869 0.585 SG 0.923 0.459 0.876 0.477 果茎模型 Raw 0.979 0.286 0.782 0.750 SNV 0.908 0.594 0.834 0.710 MSC 0.955 0.404 0.884 0.596 Baseline 0.924 0.527 0.642 0.854 SG 0.953 0.419 0.827 0.650 赤道模型 Raw 0.965 0.355 0.829 0.594 SNV 0.954 0.388 0.906 0.405 MSC 0.973 0.315 0.827 0.530 Baseline 0.979 0.281 0.867 0.544 SG 0.956 0.388 0.845 0.575 全局模型 Raw 0.962 0.355 0.892 0.443 SNV 0.972 0.296 0.897 0.456 MSC 0.980 0.253 0.946 0.400 Baseline 0.973 0.293 0.811 0.590 SG 0.961 0.356 0.909 0.414 表 4 基于CARS特征波长筛选后蜜桔不同部位的PLSR和LSSVM模型比较
Table 4. Comparison of PLSR and LSSVM models for different parts of honey oranges after CARS characteristic wavelengths screening
预测模型 不同部位 建模集 预测集 RC RMSEC/ OBrix RP RMSEP/ OBrix PLSR 花萼 0.926 0.447 0.918 0.400 果茎 0.928 0.507 0.922 0.424 赤道 0.933 0.452 0.914 0.400 全局 0.948 0.394 0.942 0.399 LSSVM 花萼 0.927 0.445 0.914 0.408 果茎 0.951 0.412 0.904 0.546 赤道 0.960 0.352 0.901 0.423 全局 0.975 0.274 0.955 0.395 表 5 基于UVE特征波长筛选后蜜桔不同部位的PLSR和LSSVM模型比较
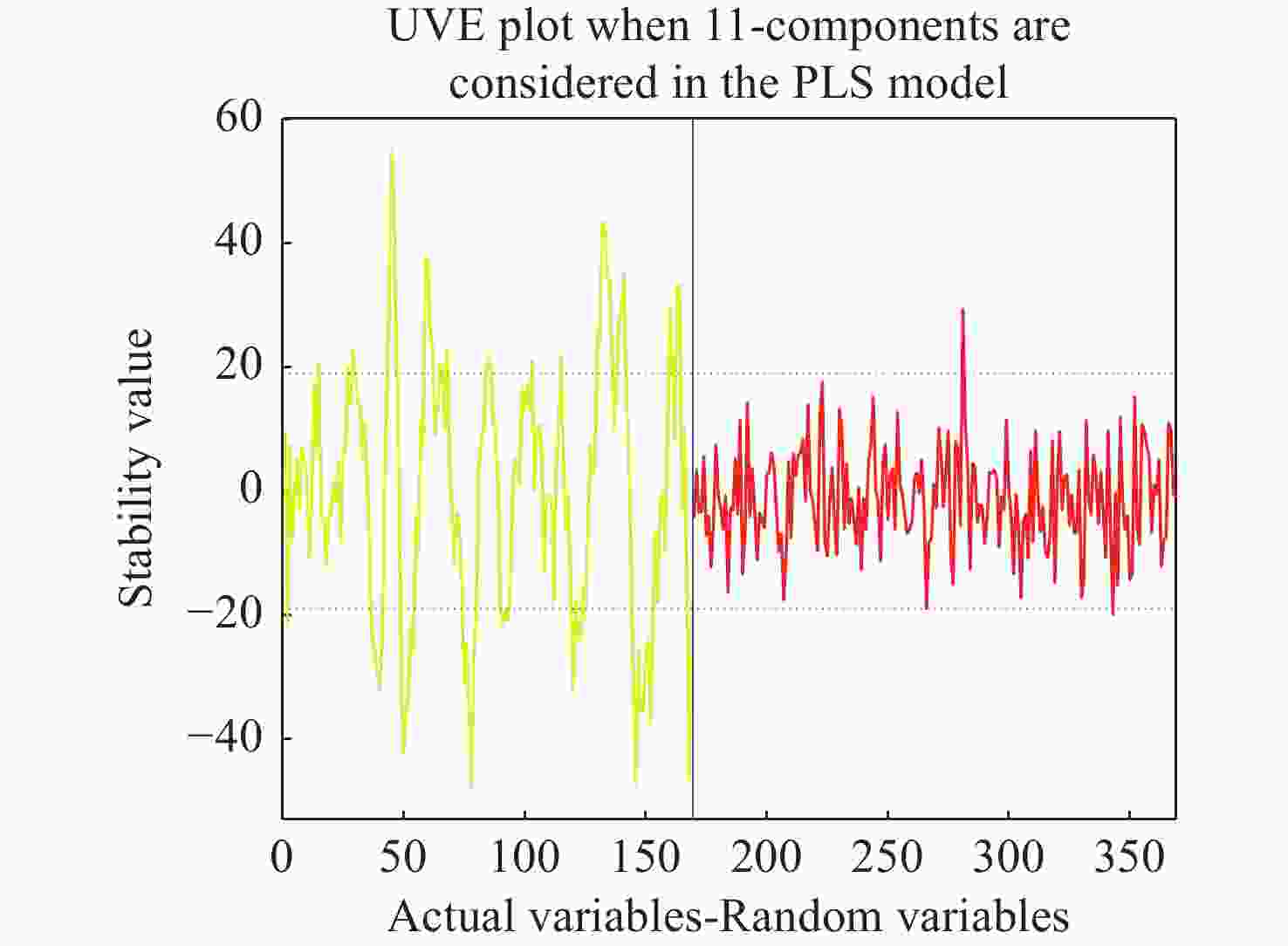
Table 5. Comparison of PLSR and LSSVM models for different parts of honey oranges after UVE characteristic wavelengths screening
预测模型 不同部位 建模集 预测集 RC RMSEC/ OBrix RP RMSEP/ OBrix PLSR 花萼 0.890 0.538 0.850 0.519 果茎 0.885 0.633 0.812 0.655 赤道 0.943 0.419 0.933 0.364 全局 0.949 0.393 0.937 0.434 LSSVM 花萼 0.901 0.514 0.838 0.537 果茎 0.950 0.416 0.896 0.575 赤道 0.950 0.400 0.900 0.423 全局 0.956 0.368 0.943 0.414 -
[1] 王玲娇, 蒋守渭. 临海涌泉蜜桔网络营销策略研究[J]. 现代商业,2015(35):36-37.WANG L J, JIANG SH W. Research on network marketing strategy of Linhai Yongquan honey tangerine[J]. Modern Business, 2015(35): 36-37. (in Chinese) [2] 介邓飞, 杨杰, 彭雅欣, 等. 基于高光谱技术的柑橘不同部位糖度预测模型研究[J]. 食品与机械,2017,33(3):51-54.JIE D F, YANG J, PENG Y X, et al. Research on the detection model of sugar content in different position of citrus based on the hyperspectral technology[J]. Food &Machinery, 2017, 33(3): 51-54. (in Chinese) [3] 王玥, 樊柳荫. 猪肉可视化新鲜度智能指示薄膜研究[J]. 分析化学,2023,51(1):139-145.WANG Y, FAN L Y. Intelligent indicator film for visual meat freshness monitoring[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(1): 139-145. (in Chinese) [4] 田喜, 陈立平, 王庆艳, 等. 全透射近红外光谱的苹果整果糖度在线检测模型优化[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2022,42(6):1907-1914.TIAN X, CHEN L P, WANG Q Y, et al. Optimization of online determination model for sugar in a whole apple using full transmittance spectrum[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2022, 42(6): 1907-1914. (in Chinese) [5] 陈玥瑶, 夏静静, 韦芸, 等. 近红外光谱法无损检测平谷产大桃品质方法研究[J]. 分析化学,2023,51(3):454-462.CHEN Y Y, XIA J J, WEI Y, et al. Research on nondestructive quality test of Pinggu peach by near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(3): 454-462. (in Chinese) [6] LU Y ZH, HUANG Y P, LU R F. Innovative hyperspectral imaging-based techniques for quality evaluation of fruits and vegetables: A review[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(2): 189. doi: 10.3390/app7020189 [7] MESA A R, CHIANG J Y. Multi-input deep learning model with RGB and hyperspectral imaging for banana grading[J]. Agriculture, 2021, 11(8): 687. doi: 10.3390/agriculture11080687 [8] 徐婧, 郑红, 谢丽芳, 等. 鸡肉样品中痕量喹诺酮类抗生素的表面增强拉曼光谱检测研究[J]. 分析化学,2023,51(3):397-404.XU J, ZHENG H, XIE L F, et al. Fast detection of trace enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in chicken meat by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(3): 397-404. (in Chinese) [9] 沈彦龙, 程立业, 孟祥茹, 等. 人参连作土壤对不同生育期人参生长发育及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 应用化学,2023,40(1):109-115.SHEN Y L, CHENG L Y, MENG X R, et al. Effects of ginseng continuous soil crop on growth development and antioxidant system of ginseng at different fertility stages[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2023, 40(1): 109-115. (in Chinese) [10] 黄蕊, 叶长青, 李亚军, 等. 线粒体靶向的近红外HClO/ClO-荧光探针的研究进展[J]. 应用化学,2022,39(3):407-424.HUANG R, YE CH Q, LI Y J, et al. Progress of mitochondria-targeted near-infrared HClO/ClO- fluorescent probes[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(3): 407-424. (in Chinese) [11] 王瑞, 孟祥茹, 李琼, 等. 人参属中药腐解化感作用研究进展[J]. 应用化学,2023,40(1):1-8.WANG R, MENG X R, LI Q, et al. Research progress on the decomposed Allelopathy of Panax genus[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2023, 40(1): 1-8. (in Chinese) [12] KIM D, BURKS T F, RITENOUR M A, et al. Citrus black spot detection using hyperspectral imaging[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2014, 7(6): 20-27. [13] 孟田源, 王转卫, 迟茜, 等. 基于高光谱成像技术生长发育后期苹果糖度的无损检测[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(6):228-234.MENG T Y, WANG ZH W, CHI X, et al. Hyperspectral imaging based non-destructive prediction of soluble solids content in apples at late development period[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(6): 228-234. (in Chinese) [14] 许丽佳, 陈铭, 王玉超, 等. 高光谱成像的猕猴桃糖度无损检测方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2021,41(7):2188-2195.XU L J, CHEN M, WANG Y CH, et al. Study on non-destructive detection method of kiwifruit sugar content based on hyperspectral imaging technology[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2021, 41(7): 2188-2195. (in Chinese) [15] 杨杰, 马本学, 王运祥, 等. 葡萄可溶性固形物的高光谱无损检测技术[J]. 江苏农业科学,2016,44(6):401-403.YANG J, MA B X, WANG Y X, et al. Hyperspectral nondestructive detection technique of soluble solids in grapes[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2016, 44(6): 401-403. (in Chinese) [16] SUN X D, XU C, LUO CH G, et al. Non-destructive detection of tea stalk and insect foreign bodies based on THz-TDS combination of electromagnetic vibration feeder[J]. Food Quality and Safety, 2023, 7: fyad004. doi: 10.1093/fqsafe/fyad004 [17] LIU Y D, SUN X D, OUYANG A G. Nondestructive measurement of soluble solid content of navel orange fruit by visible-NIR spectrometric technique with PLSR and PCA-BPNN[J]. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 2010, 43(4): 602-607. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2009.10.008 [18] YANG Y, ZHAO CH J, HUANG W Q, et al. Optimization and compensation of models on tomato soluble solids content assessment with online Vis/NIRS diffuse transmission system[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2022, 121: 104050. [19] 袁琳, 徐怀德, 李钰金. 近红外漫反射光谱检测网纹瓜可溶性固形物含量的研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2010,10(4):272-277.YUAN L, XU H D, LI Y J. Studies on the rapid measurements of soluble solids content in nutmeg melon by near infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2010, 10(4): 272-277. (in Chinese) [20] ZHANG D Y, XU L, WANG Q Y, et al. The optimal local model selection for robust and fast evaluation of soluble solid content in melon with thick peel and large size by Vis-NIR spectroscopy[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2019, 12(1): 136-147. doi: 10.1007/s12161-018-1346-3 [21] 孙博康, 刘贵珊. 基于高光谱技术检测香水梨硬度的研究[J]. 食品安全导刊,2021(19):118-120.SUN B K, LIU G SH. Study on the detection of hardness of perfumed pears based on hyperspectral technology[J]. Journal of Food Safety, 2021(19): 118-120. (in Chinese) [22] ZHANG F, LI B, YIN H, et al. Study on the quantitative assessment of impact damage of yellow peaches using the combined hyperspectral technology and mechanical parameters[J]. Journal of Spectroscopy, 2022, 2022: 7526826. [23] WANG ZH L, CHEN J, FAN Y F, et al. Evaluating photosynthetic pigment contents of maize using UVE-PLS based on continuous wavelet transform[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 169: 105160. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2019.105160 [24] 廉小亲, 汤燊淼, 吴静珠, 等. 基于近红外的兰州百合品质定量建模方法研究[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(7):298-302.LIAN X Q, TANG S M, WU J ZH, et al. Research on quantitative model of Lilium Lanzhou quality by near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2020, 45(7): 298-302. (in Chinese) [25] YANG X Y, LIU G SH, HE J G, et al. Determination of sugar content in Lingwu jujube by NIR–hyperspectral imaging[J]. Journal of Food Science, 2021, 86(4): 1201-1214. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15674 [26] 李斌, 邹吉平, 张烽, 等. 基于高光谱成像技术和力学参数对贡梨冲击损伤的定量研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报,2023,28(2):186-197.LI B, ZOU J P, ZHANG F, et al. Quantitative study on impact damage of Gongli based on hyperspectral imaging technology and mechanical parameters[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2023, 28(2): 186-197. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: