-
摘要:
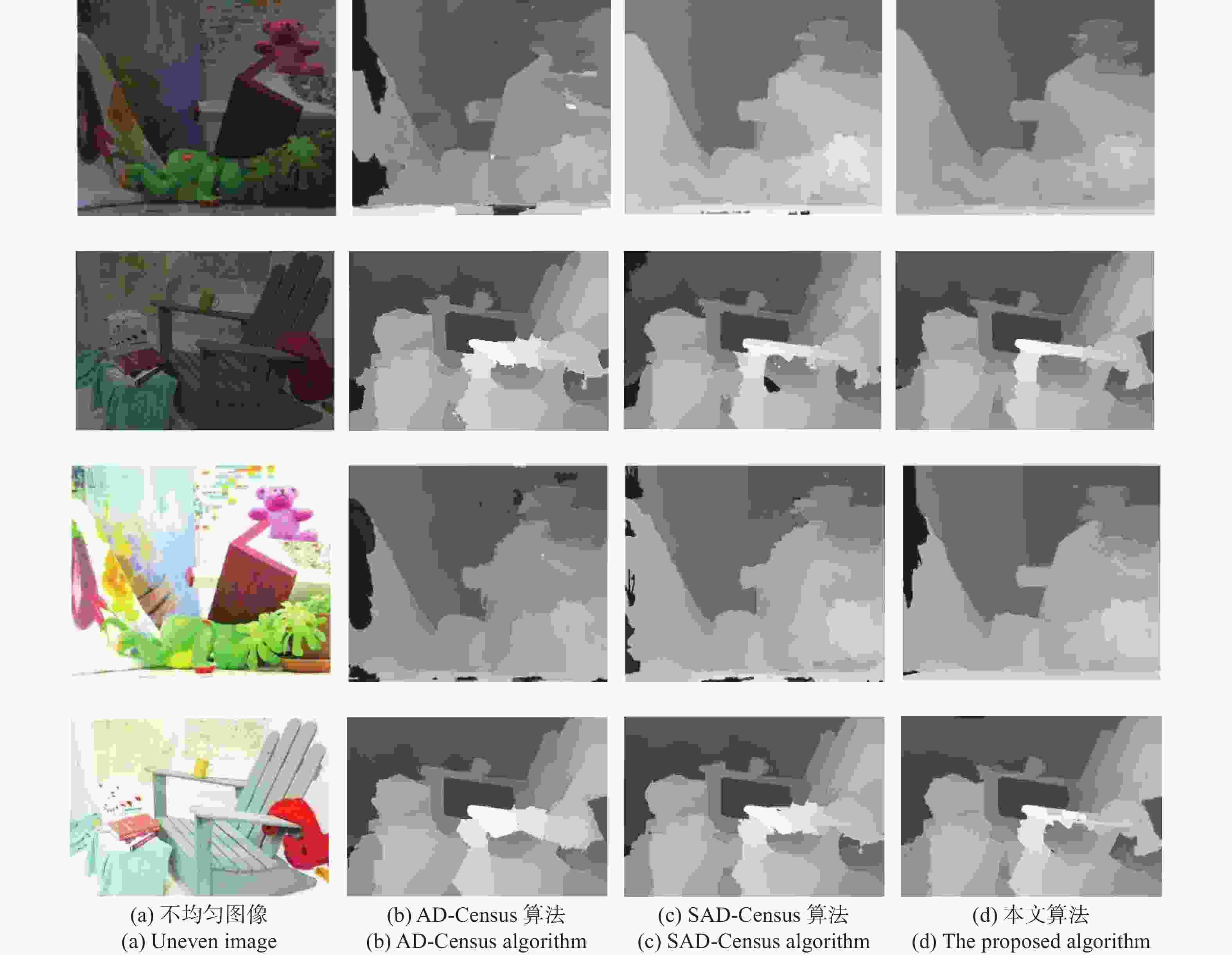
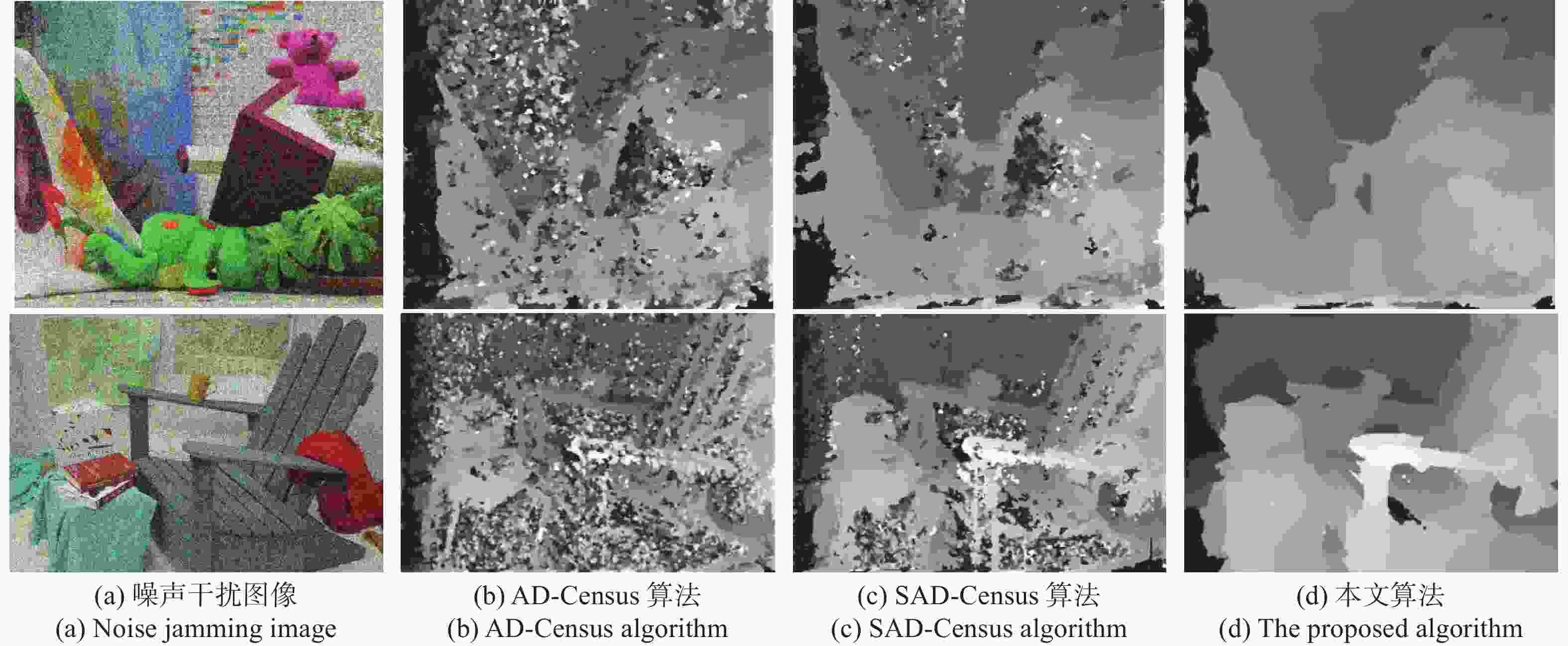
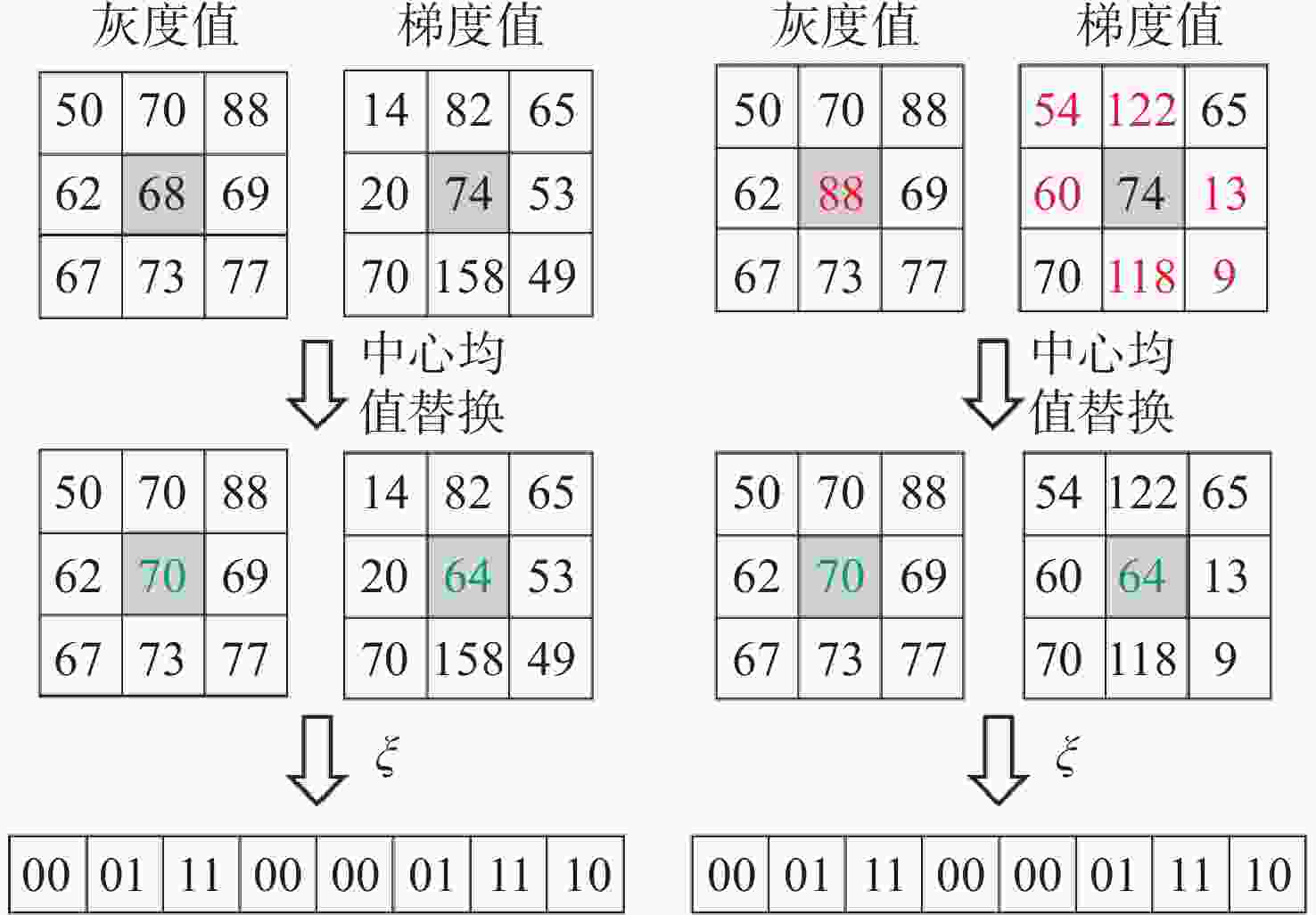
视差不连续区域和重复纹理区域的误匹配率高一直是影响双目立体匹配测量精度的主要问题,为此,本文提出一种基于多特征融合的立体匹配算法。首先,在代价计算阶段,通过高斯加权法赋予邻域像素点的权值,从而优化绝对差之和(Sum of Absolute Differences,SAD)算法的计算精度。接着,基于Census变换改进二进制链码方式,将邻域内像素的平均灰度值与梯度图像的灰度均值相融合,进而建立左右图像对应点的判断依据并优化其编码长度。然后,构建基于十字交叉法与改进的引导滤波器相融合的聚合方法,从而实现视差值再分配,以降低误匹配率。最后,通过赢家通吃(Winner Take All,WTA)算法获取初始视差,并采用左右一致性检测方法及亚像素法提高匹配精度,从而获取最终的视差结果。实验结果表明,在Middlebury数据集的测试中,所提SAD-Census算法的平均非遮挡区域和全部区域的误匹配率为分别为2.67%和5.69%,测量200~900 mm距离的平均误差小于2%;而实际三维测量的最大误差为1.5%。实验结果检验了所提算法的有效性和可靠性。
-
关键词:
- 机器视觉 /
- 立体匹配 /
- SAD-Census变换 /
- 十字交叉法 /
- 引导滤波
Abstract:The high mismatching rate of the parallax discontinuity region and the repeated texture region has been a major issue affecting the measurement accuracy of binocular stereo matching. For these reasons, we propose a stereo matching algorithm based on multi-feature fusion. Firstly, the weight of neighboring pixels is given using Gaussian weighting method, which optimizes the calculation accuracy of the Sum of Absolute Differences (SAD) algorithm. Based on the Census transformation, the binary chain code technique has been enhanced to fuse the average gray value of neighborhood pixels with the average gray value of gradient image, and then the judgment basis of the left and right image corresponding points is established, and the coding length is optimized. Secondly, an aggregation technique has been developed that combines the cross method and the improved guide filter to redistribute disparity values with the aim of minimizing false matching rate. Finally, the initial disparity is obtained by the Winner Take All (WTA) algorithm, and the final disparity results are obtained by the left-right consistency detection method, sub-pixel method, and then a stereo matching algorithm based on the multi-feature SAD Census transform is established. The experimental results show that in the testing of the Middlebury dataset, the average mismatch rates of the proposed algorithm for non-occluded regions and all regions are 2.67% and 5.69%, the average error of the 200−900 mm distance is less than 2%, and the maximum error of the actual 3D data measurement is 1.5%. Experimental results verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
Key words:
- machine vision /
- stereo matching /
- SAD-Census transform /
- cross method /
- guided filtering
-
表 1 实验参数设置
Table 1. Experimental parameter setting
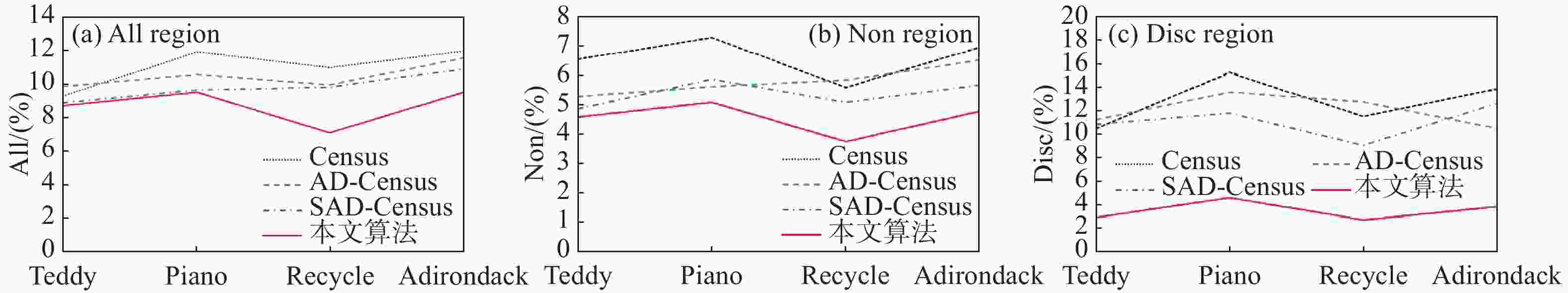
Parameter Value Parameter Value б 2 λ 0.003 τ1 16 ε 0.001 τ2 4 ω 9×7 L1 30 β1 0.6 L2 15 β2 0.4 δ0 1 表 2 不同算法在非遮挡区域和全部区域的误匹配率
Table 2. Mismatch rate of different algorithms in the non-occluded region and all regions
(%) Algorithm
Tsukuba
Venus
Teddy
ConesAvg Non all Disc Non all Disc Non all Disc Non all Disc Non all Disc GC-occ 1.19 2.01 6.24 1.64 2.19 6.75 11.20 17.40 19.80 5.36 12.40 13.00 4.84 8.50 11.45 SemiGlob 3.26 3.96 12.80 1.00 1.57 11.30 6.02 12.20 16.30 3.06 9.75 8.90 3.34 6.87 12.32 RTCensus 5.08 6.25 19.20 1.58 2.42 14.20 7.96 13.8 20.30 4.10 9.54 12.20 4.68 8.01 16.48 HCA 1.31 2.47 0.94 0.11 0.23 0.24 4.23 9.45 3.67 5.64 11.59 4.30 2.83 5.94 2.29 Cross-ScaleGF 2.38 2.85 8.40 1.13 1.98 9.26 7.05 14.9 16.80 3.32 11.00 7.99 3.47 7.68 10.61 GradAdaptWgt 2.26 2.63 8.99 0.99 1.39 4.92 8.00 13.10 18.60 2.61 7.67 7.43 3.46 6.19 9.99 Proposed algorithm 1.25 2.73 0.90 0.15 0.31 0.31 4.62 8.73 2.98 4.69 10.98 4.11 2.67 5.69 2.08 表 3 三维测距实验结果
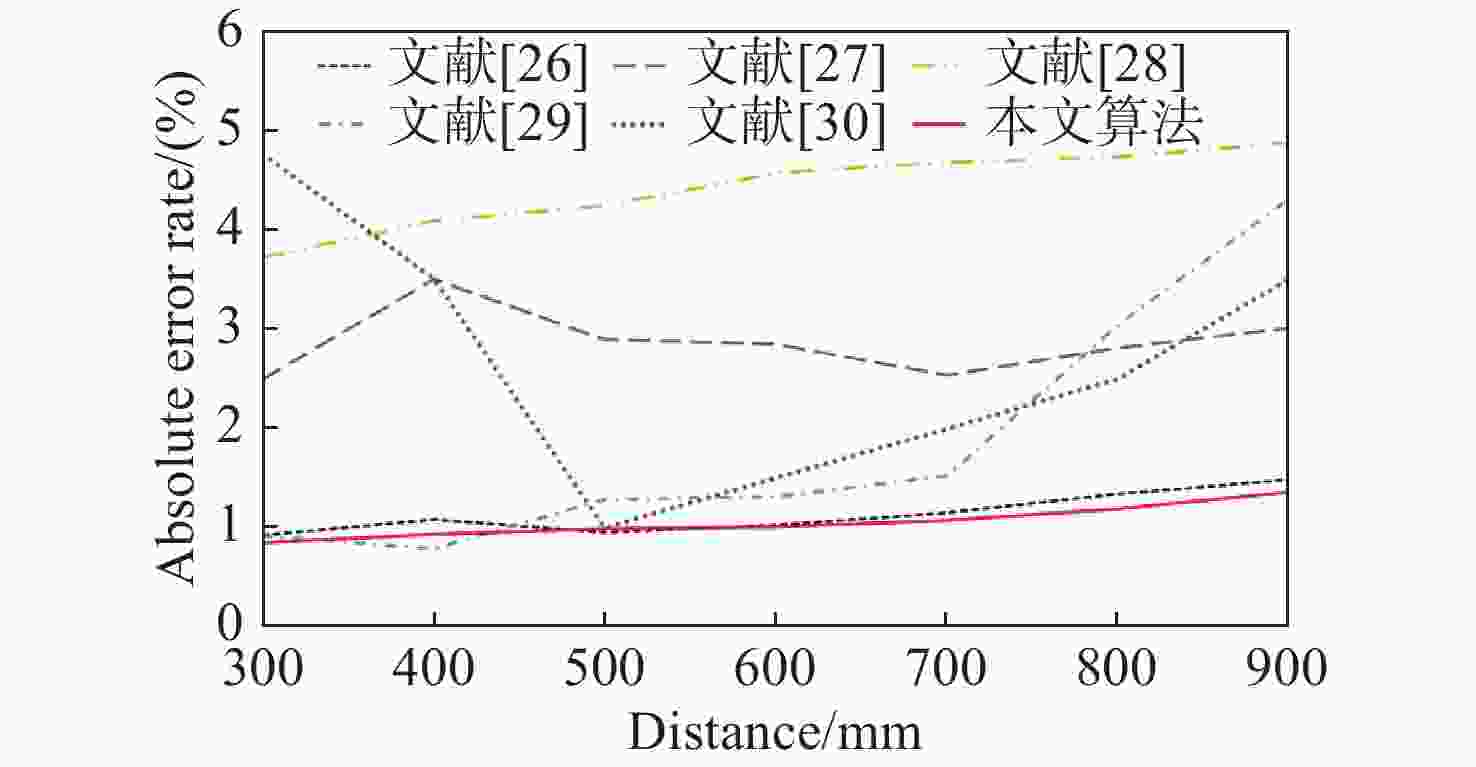
Table 3. Experimental results of three-dimensional distance measurement
序号 实际距离/mm 测量距离/mm 距离误差/mm 距离误差率/% 1 200 198.42 −1.58 0.79 2 300 302.55 2.55 0.85 3 400 403.76 3.76 0.94 4 500 495.05 −4.95 0.99 5 600 606.06 6.06 1.01 6 700 707.56 7.56 1.08 7 800 809.52 9.52 1.19 8 900 912.24 12.24 1.36 表 4 测量样本实验结果
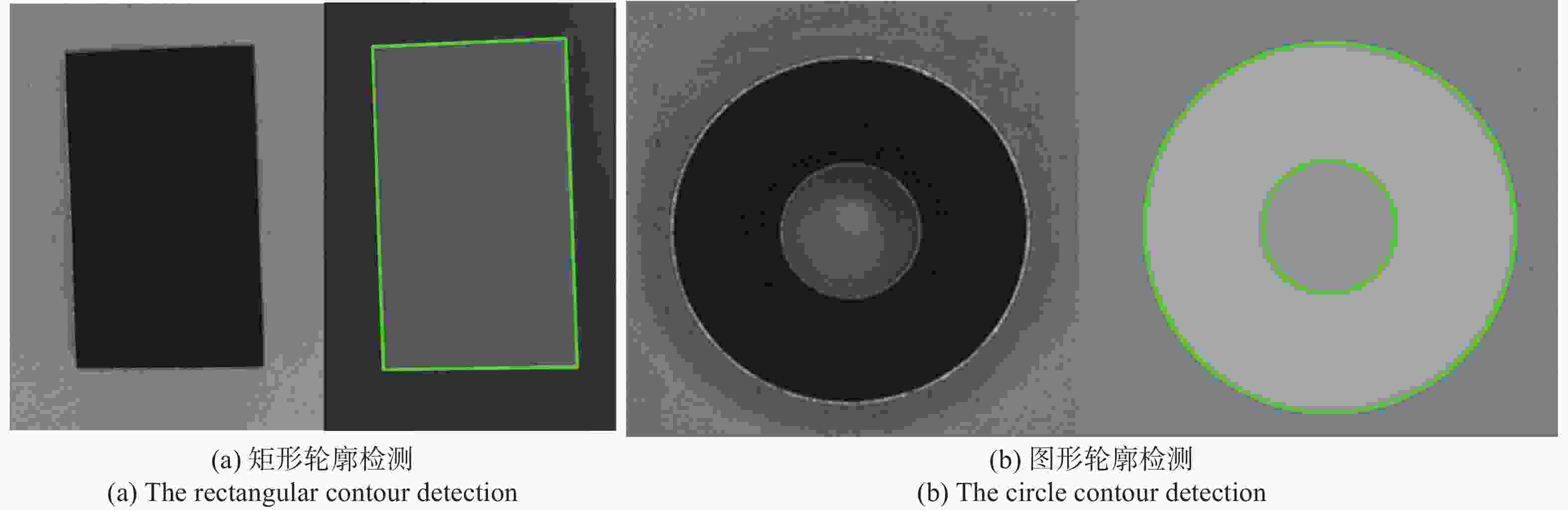
Table 4. Sample experimental results
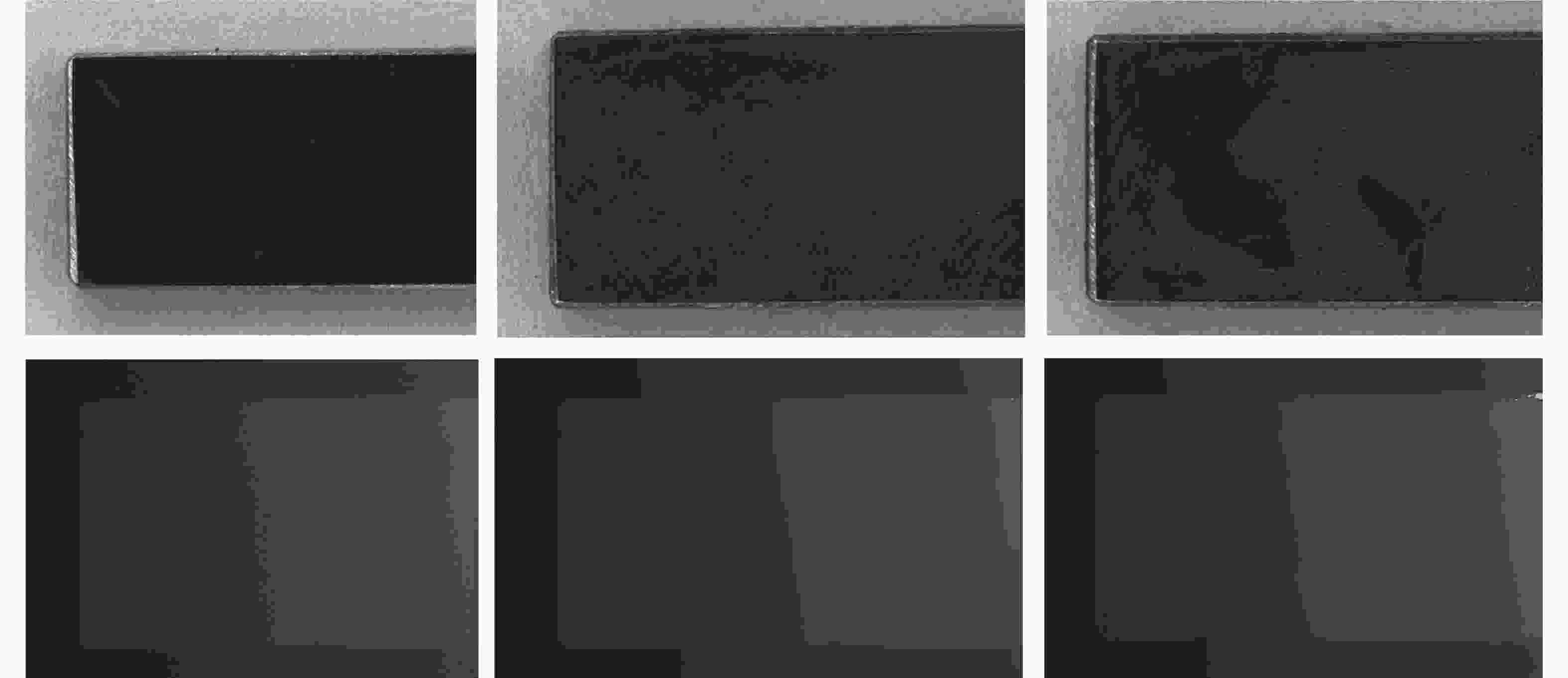
样本序号 实际长度/mm 测量长度/mm 误差/mm 误差率/% 1 20 19.9575 −0.0425 −0.21 35 34.6144 −0.3856 −1.1 2 35 35.1649 0.1649 −0.47 50 49.9672 −0.0328 −0.06 3 5 4.9439 −0.0561 −1.12 15 14.7565 −0.2435 −1.62 4 20 20.3541 0.3541 0.71 30 29.5784 −0.4216 −1.41 表 5 厚度测量结果
Table 5. Thickness measurement results
序号 实际厚度/mm 测量厚度/mm 测量误差/mm 绝对误差率/% 1 1.00 1.0105 0.0105 1.05 2 1.10 1.1235 0.0235 2.13 3 1.20 1.2335 0.0335 2.79 4 1.50 1.5563 0.0563 3.75 5 2.00 1.9346 −0.0654 3.27 -
[1] 陈仁虹, 梁晋, 叶美图, 等. 柔性复合薄膜成形极限曲线的视觉测定方法[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(1):22-33. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0101CHEN R H, LIANG J, YE M T, et al. Visual method for measuring forming limit curve of pliable composite film[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(1): 22-33. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0101 [2] 任晓奎, 关钧渤, 殷新勇, 等. 基于改进局部一致性约束的立体匹配算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2023,38(4):543-553. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0226REN X K, GUAN J B, YIN X Y, et al. Stereo matching algorithm based on improved local consistency constraint[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2023, 38(4): 543-553. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0226 [3] 张强, 刘婷婷, 李海滨, 等. 基于最佳搜索域的水下图像区域匹配算法研究[J]. 光学学报,2014,34(6):0615001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201434.0615001ZHANG Q, LIU T T, LI H B, et al. Research on region matching for underwater images based on optimum searching area[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2014, 34(6): 0615001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201434.0615001 [4] LEE J, JUN D, EEM C, et al. Improved census transform for noise robust stereo matching[J]. Optical Engineering, 2016, 55(6): 063107. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.55.6.063107 [5] 彭新俊, 韩军, 汤踊, 等. 基于改进Census变换和异常值剔除的抗噪立体匹配算法[J]. 光学学报,2017,37(11):1115004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.1115004PENG X J, HAN J, TANG Y, et al. Anti-noise stereo matching algorithm based on improved census transform and outlier elimination[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(11): 1115004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.1115004 [6] 刘建国, 俞力, 柳思健, 等. 基于改进Census变换和多尺度空间的立体匹配算法[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2017,45(12):43-49.LIU J G, YU L, LIU S J, et al. Stereo matching algorithm based on improved census transform and multi-scale space[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(12): 43-49. (in Chinese) [7] 杨春雨, 顾振, 张鑫, 等. 基于深度学习的带式输送机煤流量双目视觉测量[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2021,42(8):164-174.YANG CH Y, GU ZH, ZHANG X, et al. Binocular vision measurement of coal flow of belt conveyors based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2021, 42(8): 164-174. (in Chinese) [8] HOSNI A, BLEYER M, GELAUTZ M. Secrets of adaptive support weight techniques for local stereo matching[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2013, 117(6): 620-632. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2013.01.007 [9] 孔令寅, 朱江平, 应三丛. 基于引导图像和自适应支持域的立体匹配[J]. 光学学报,2020,40(9):0915001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0915001KONG L Y, ZHU J P, YING S C. Stereo matching based on guidance image and adaptive support region[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(9): 0915001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0915001 [10] CHANG N Y C, TSAI T H, HSU B H, et al. Algorithm and architecture of disparity estimation with mini-census adaptive support weight[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2010, 20(6): 792-805. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2010.2045814 [11] 王森, 危辉, 孟令江. 基于控制点和RGB向量差联合梯度Census变换的立体匹配算法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能,2022,35(1):37-50.WANG S, WEI H, MENG L J. Stereo matching algorithm based on control points, RGB vector difference and gradient census transform[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 35(1): 37-50. (in Chinese) [12] ZHANG K, LU J B, LAFRUIT G. Cross-based local stereo matching using orthogonal integral images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2009, 19(7): 1073-1079. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2009.2020478 [13] WANG W Q, YAN J, XU N Y, et al. Real-time high-quality stereo vision system in FPGA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2015, 25(10): 1696-1708. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2015.2397196 [14] CHENG F Y, ZHANG H, SUN M G, et al. Cross-trees, edge and superpixel priors-based cost aggregation for stereo matching[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2015, 48(7): 2269-2278. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2015.01.002 [15] 洪梓嘉, 李彦明, 林洪振, 等. 基于双目视觉的种植前期农田边界距离检测方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2022,53(5):27-33,56.HONG Z J, LI Y M, LIN H ZH, et al. Field boundary distance detection method in early stage of planting based on binocular vision[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(5): 27-33,56. (in Chinese) [16] ZHAN Y L, GU Y Z, ZHANG X L, et al. Stereo matching based on efficient image-guided cost aggregation[J]. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2016, E99.D(3): 781-784. doi: 10.1587/transinf.2015EDL8223 [17] YAO M, OUYANG W B, XU B G. Hybrid cost aggregation for dense stereo matching[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(31): 23189-23202. [18] YANG Q X. Stereo matching using tree filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(4): 834-846. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2353642 [19] HIRSCHMÜLLER H. Accurate and efficient stereo processing by semi-global matching and mutual information[C]. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2005: 807-814. [20] 张建业, 朴燕. 基于改进稳态匹配概率的立体匹配算法研究[J]. 液晶与显示,2018,33(4):357-364. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20183304.0357ZHANG J Y, PIAO Y. Stereo matching algorithm based on improved steady-state matching probability[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2018, 33(4): 357-364. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20183304.0357 [21] LI ZH G, ZHENG J H, ZHU Z J, et al. Weighted guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(1): 120-129. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2371234 [22] HUMENBERGER M, ZINNER C, WEBER M, et al. A fast stereo matching algorithm suitable for embedded real-time systems[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2010, 114(11): 1180-1202. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2010.03.012 [23] 刘杰, 张建勋, 代煜, 等. 基于跨尺度引导图像滤波的稠密立体匹配[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(1):0115004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0115004LIU J, ZHANG J X, DAI Y, et al. Dense stereo matching based on cross-scale guided image filtering[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(1): 0115004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0115004 [24] KOLMOGOROV V, ZABIH R. Computing visual correspondence with occlusions using graph cuts[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2001: 508-515. [25] DE-MAEZTU L, VILLANUEVA A, CABEZA R. Stereo matching using gradient similarity and locally adaptive support-weight[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2011, 32(13): 1643-1651. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2011.06.027 [26] 任久斌. 基于双目立体视觉的三维重建技术研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2020.REN J B. Research on 3D reconstruction technology based on binocular stereo vision[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2020. (in Chinese) [27] 符强, 孔健明, 纪元法, 等. 基于双目视觉的无人机实时测距算法[J]. 电光与控制,2023,30(4):94-99.FU Q, KONG J M, JI Y F, et al. A method of UAV real-time ranging based on binocular vision[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2023, 30(4): 94-99. (in Chinese) [28] 仲伟波, 姚旭洋, 冯友兵, 等. 双目区域视差快速计算及测距算法[J]. 中国图象图形学报,2019,24(9):1537-1545.ZHONG W B, YAO X Y, FENG Y B, et al. Rapid calculation and ranging algorithm based on binocular region parallax[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2019, 24(9): 1537-1545. (in Chinese) [29] 肖纯, 林嘉欣, 王玮. 基于双目测距的晶英石板自动打磨系统研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报,2018,40(3):78-83.XIAO CH, LIN J X, WANG W. Research on automatic jing ying stone grinding system based on binocular distance measurement[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2018, 40(3): 78-83. (in Chinese) [30] HUANG L, WU G P, LIU J Y, et al. Obstacle distance measurement based on binocular vision for high-voltage transmission lines using a cable inspection robot[J]. Science Progress, 2020, 103(3): 003685042093691. -





 下载:
下载: