Simulation and experiment of weak multi-target laser detection in complex hydrology
-
摘要:
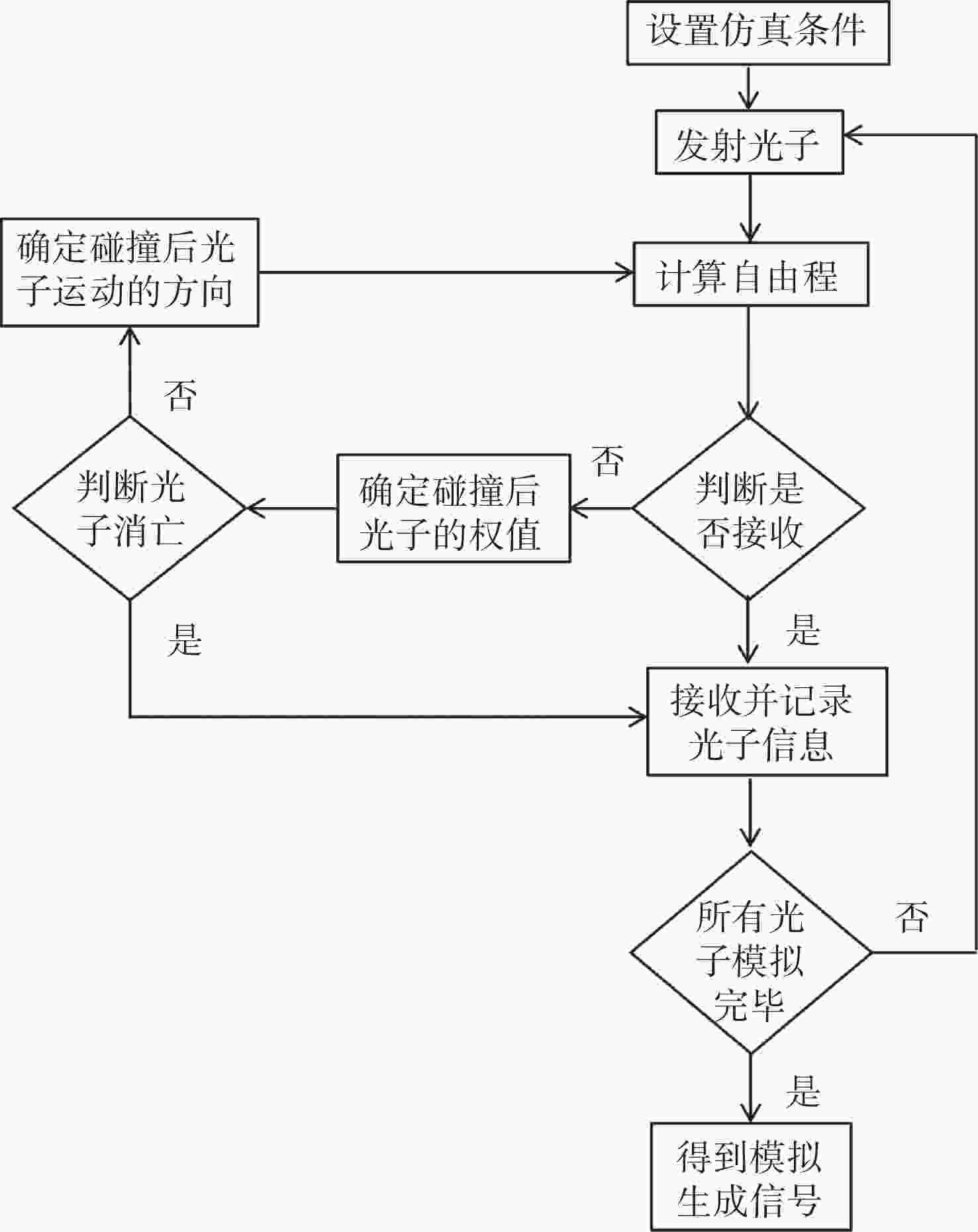
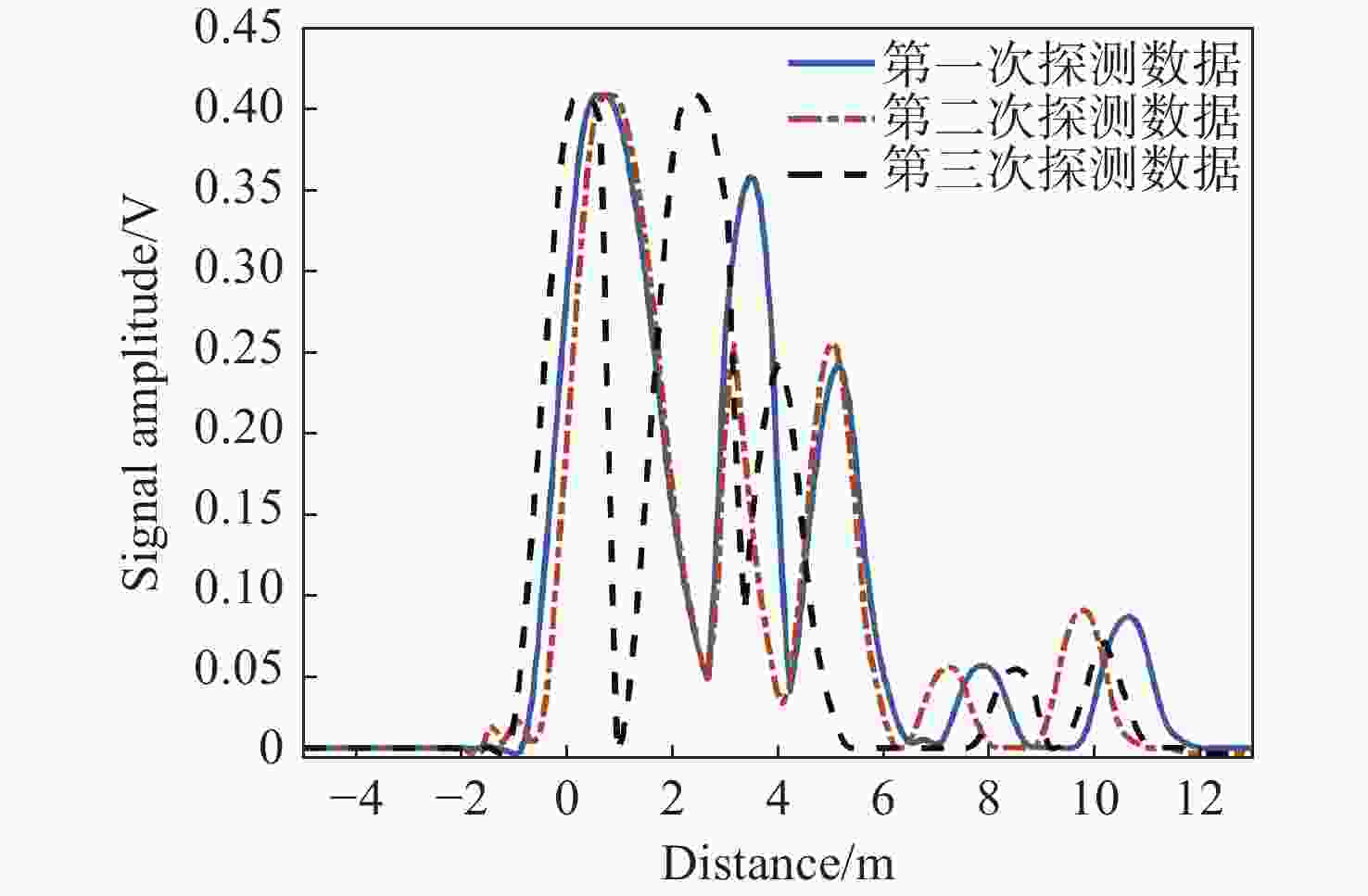
为了探究在近岸复杂水体中金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测对微弱目标的探测能力,研究水质、目标特征、目标距离对水下金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测的影响具有重要理论和应用价值。论文建立了水下微弱目标金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测模型,采用蒙特卡洛仿真验证了不同浊度微弱多目标金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测性能,模拟了不同距离下微弱目标的金宝搏188软件怎么用 后向散射回波信号,对多个不同反射系数的目标后向散射回波特性进行了分析。同时设计并研制了灵巧便携式水下微弱目标金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测系统,进行了实验室及外场湖泊环境下的多目标探测、测距测试验证。在浊度为12.87 NTU的近岸湖泊水域,该系统可在10 m范围内对3~4个直径为80~400 μm的不同低反射系数的混合小目标进行有效探测,平均测量误差为±0.11 m,与理论仿真结果一致。本文研究结果可为蓝绿金宝搏188软件怎么用 水下多微弱目标探测链路计算、系统设计及参数优化提供参考,可以支撑近海浑浊水体下水下障碍物金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测工程实践。
-
关键词:
- 金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测与测距 /
- 微弱多目标 /
- 复杂水文 /
- 蒙特卡洛
Abstract:Investigating the impact of water quality, target characteristics, and target distance on underwater laser detection is crucial to assessing the effectiveness of laser detection for weak targets in complex coastal water bodies. We examine the theoretical and practical significance of understanding these factors in underwater laser detection. In this study, a laser detection model for detecting weak underwater targets is established. Monte Carlo simulation is used to verify the detection performance of weak multi-target laser ranging under different turbidities. The laser backscattering echo signals of weak targets at different distances are simulated, and the backscattering echo characteristics of multiple targets with various reflection coefficients are analyzed. Additionally, a smart and portable laser detection system for detecting weak underwater targets has been designed and developed. Laboratory and field lake environment tests were conducted to detect and range for multi-target. In a near-shore lake with a turbidity of 12.87 NTU, the system can effectively detect 3−4 mixed small target groups. These groups have different low reflection coefficients and diameters varying from 80 to 400 μm, all within a range of 10 meters. The average measurement error is ±0.11 m, which is consistent with the theoretical simulation results. The research results serve as a guide for computing links, designing systems, and optimizing parameters for detecting weak underwater multi-targets using blue and green lasers. Furthermore, the results assist in the engineering practice of detecting underwater obstacles in offshore turbid waters.
-
Key words:
- laser detection and ranging /
- weak multi-target /
- complex hydrology /
- Monte Carlo
-
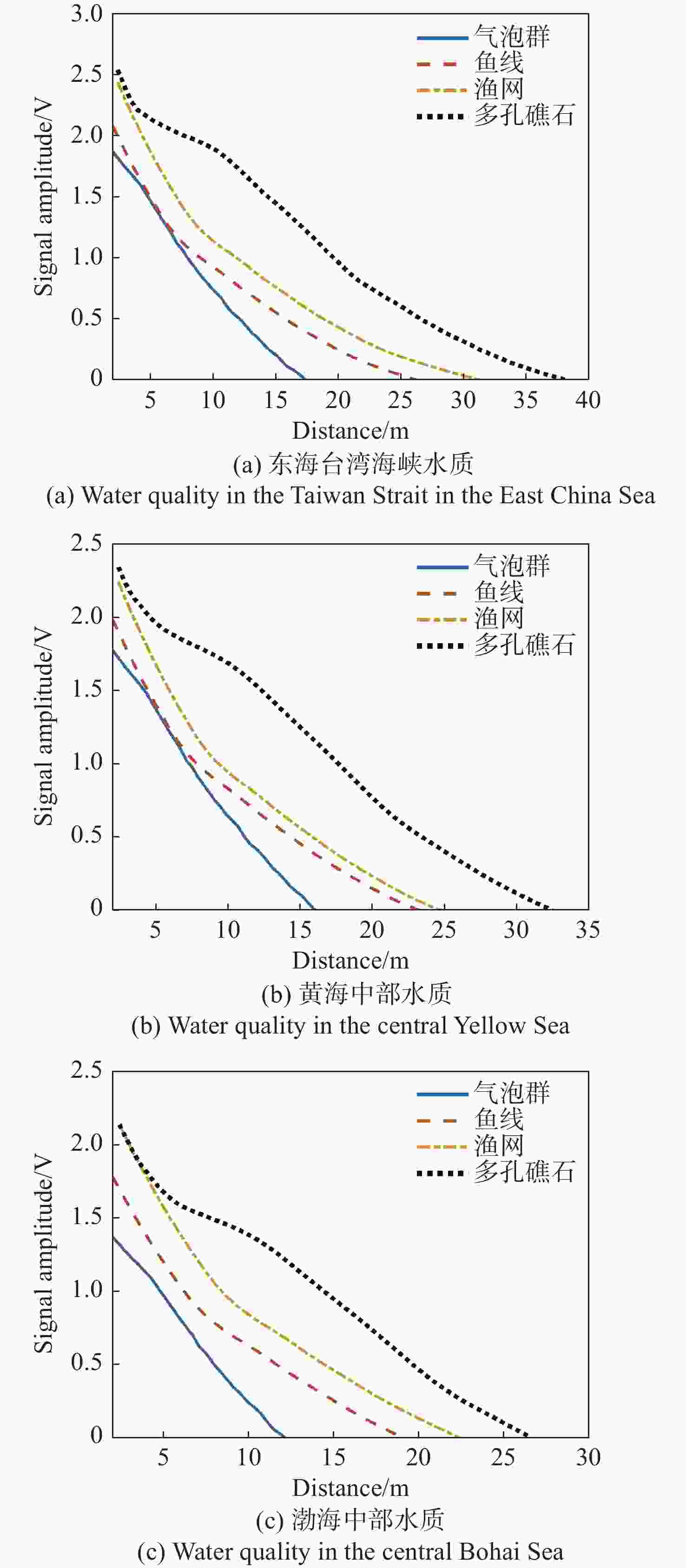
目标类型 反射系数 气泡群 0.05 鱼线 0.1 渔网 0.23 多孔礁石 0.36 表 2 不同水质下4种探测目标最远距离统计
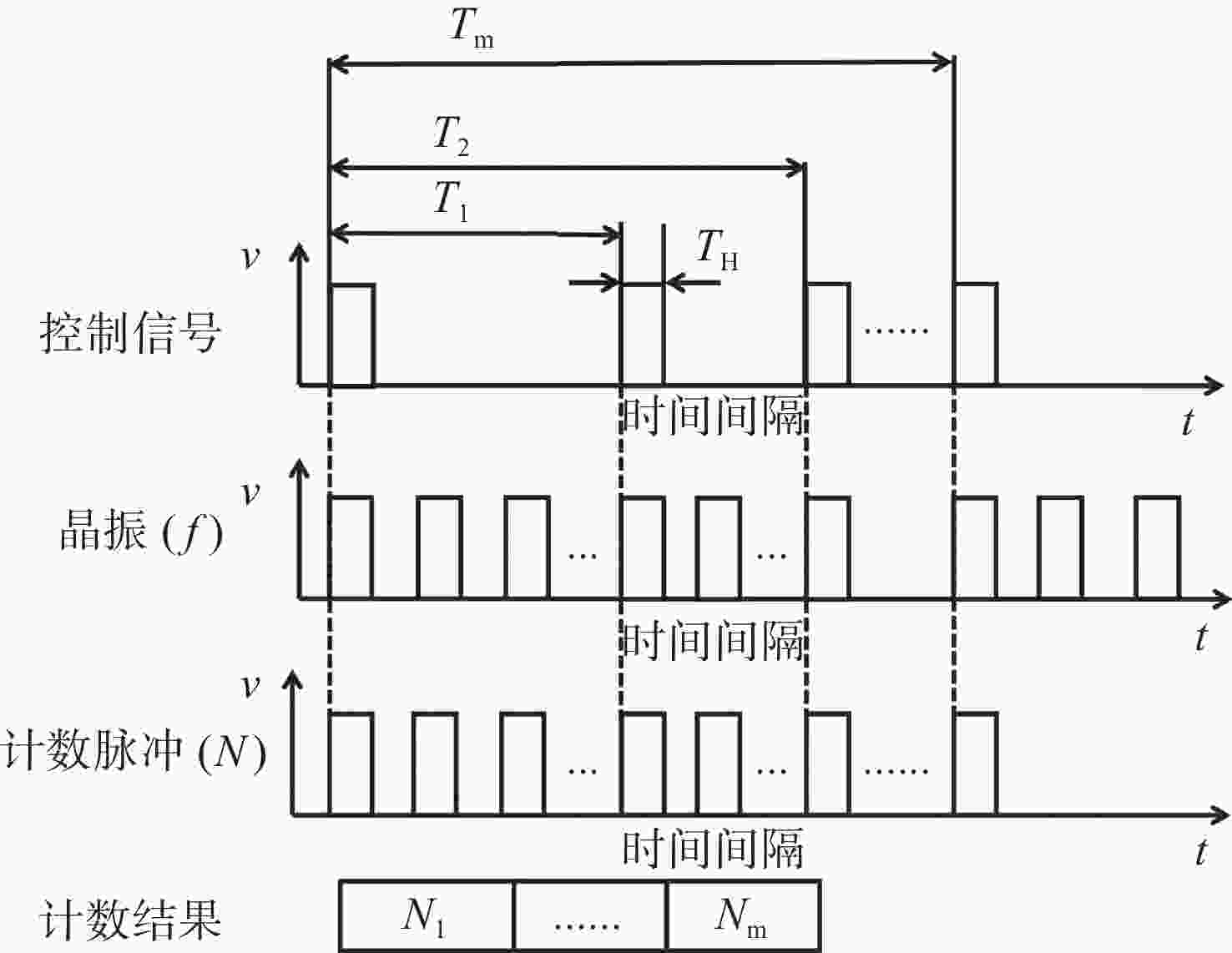
Table 2. Statistics of the farthest distances of four detection targets under different water quality conditions
(m) 水质 目标类型 气泡群 鱼线 渔网 多孔礁石 东海台湾海峡 17.2 25.4 30.5 38.8 黄海中部 15.8 22.7 25 32 渤海中部 12.4 19.6 22 26 表 3 不同水质下3种目标探测距离
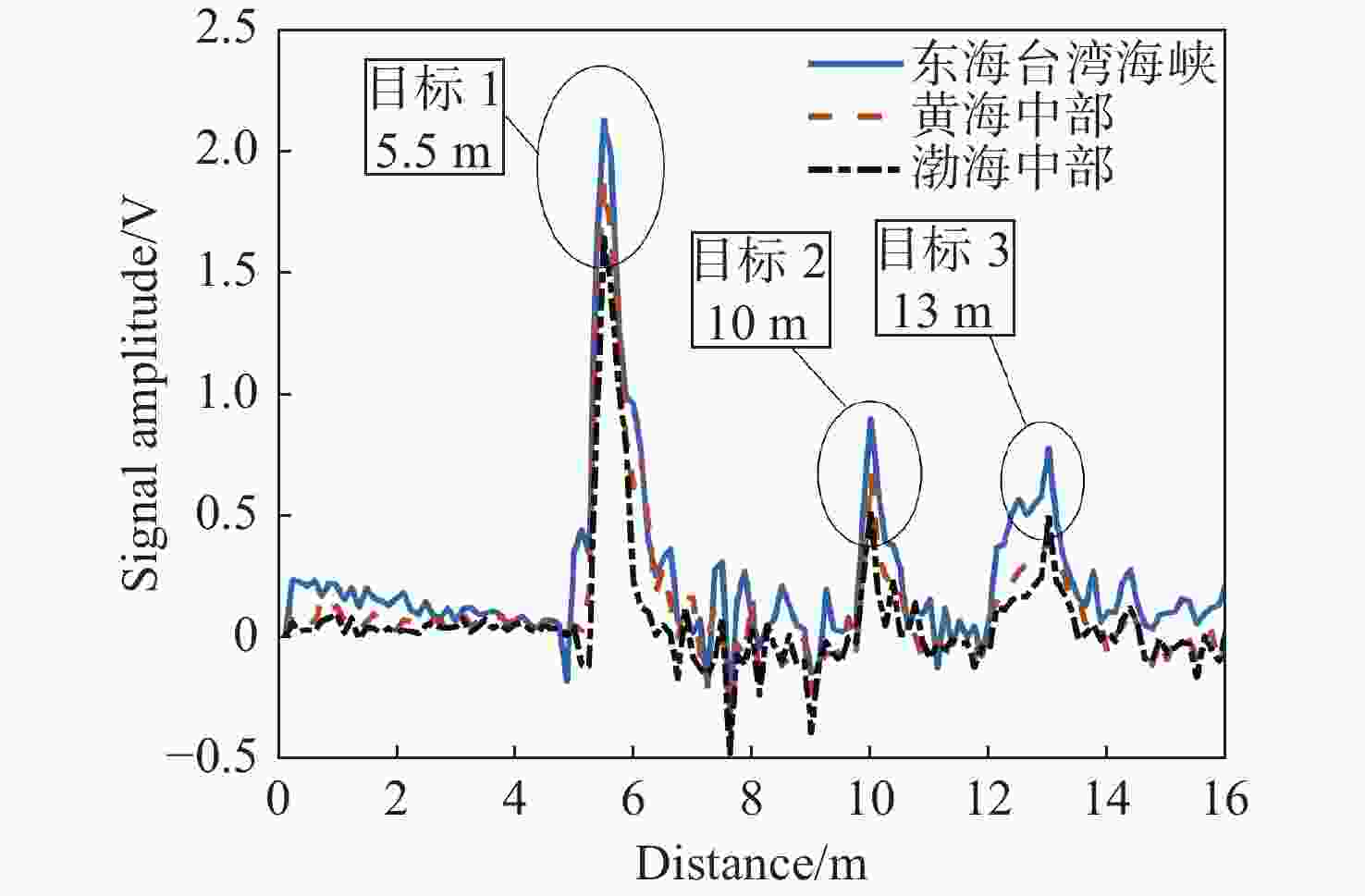
Table 3. Three target detection distances under different water quality conditions
目标类型 时间/ns 探测距离/m 渔网 47.8 5.5 气泡群 87.0 10 鱼线/多孔礁石 113.1 13 表 4 不同水质下4种目标探测距离
Table 4. Four target detection distances under different water quality conditions
目标类型 时间/ns 探测距离/m 渔网 17.4 2 气泡群 34.8 4 鱼线 69.6 8 多孔礁石 87.0 10 表 5 测试目标尺寸
Table 5. Size of test target
目标类型 尺寸 气泡群 D为70~90 μm 鱼线 D=210 μm 渔网 Φ=2.5 cm;D=280 μm;l=3 m 多孔礁石 L=15 cm;W=13 cm;H=20 cm 表 6 三目标探测距离与实际距离结果对比
Table 6. Comparison of detection distance and actual distance for three targets
目标类型 探测距离/m 时间/ns 实际探测距离/m 平均值/m 相对误差/m 标准差 渔网 5.5 51.2 46.5 48.6 5.894 5.345 5.582 5.607 0.107 0.1548 气泡群 10 91.9 87.85 84.05 10.366 9.909 9.475 9.916 0.084 0.210 鱼线 13 114.8 116.55 115.6 12.955 13.35 13.039 13.15 0.150 0.0538 表 7 四目标探测距离与实际距离结果对比
Table 7. Comparison of detection distance and actual distance for four targets
目标类型 探测距离/m 时间/ns 实际探测距离/m 平均值/m 相对误差/m 标准差 鱼线 2 18.5 18.3 18.05 2.128 2.105 2.075 2.102 0.102 0.03 气泡群 4 34.5 36.2 37.7 3.968 4.163 4.334 4.155 0.155 0.259 渔网 8 70.1 69.3 68.3 8.05 7.970 7.855 7.958 0.042 0.133 多孔礁石 10 91.1 86.5 87.15 10.477 9.940 10.010 10.142 0.142 0.413 -
[1] JANTZI A, JEMISON W, LAUX A, et al. Enhanced underwater ranging using an optical vortex[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(3): 2668-2674. [2] WANG Y Q, ZHANG J H, ZHENG Y CH, et al. Brillouin scattering spectrum for liquid detection and applications in oceanography[J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2023, 6(1): 220016. doi: 10.29026/oea.2023.220016 [3] 王翀, 杨嘉皓, 朱炳利, 等. 距离选通成像系统中短脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用 驱动技术研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(3):567-577. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0142WANG CH, YANG J H, ZHU B L, et al. Short pulse laser drive technology in a distance-selective imaging system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(3): 567-577. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0142 [4] 宗思光, 张鑫, 梁善永, 等. 多尺度复杂水质尾流气泡的金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测仿真与实验[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2023,50(5):0504003. doi: 10.3788/CJL220853ZONG S G, ZHANG X, LIANG SH Y, et al. Laser detection simulation and experiment of multiscale complex water wake bubble[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(5): 0504003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL220853 [5] 刘东, 姚清睿, 张思诺, 等. 拉曼金宝搏188软件怎么用 雷达大气温湿压探测技术研究进展[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(2):243-257. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0145LIU D, YAO Q R, ZHANG S N, et al. Research progress of temperature, humidity and pressure detection technology using Raman Lidar[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(2): 243-257. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0145 [6] JIANG Z Q, LIU X M, CAI F H, et al. Imaging comparison experiment of an underwater imaging system with a semiconductor white laser, a monochromatic laser and an LED white light as the light source[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(2): 466-478. doi: 10.37188/CO.EN.2022-0012 [7] 彭波, 钟昆, 赵慧, 等. 水下目标金宝搏188软件怎么用 周向扫描探测模型与仿真分析[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2019,48(12):135-141.PENG B, ZHONG K, ZHAO H, et al. Laser circumferential scanning detection model and simulation analysis of underwater targets[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(12): 135-141. (in Chinese). [8] 郜魏柯, 杜小平, 王阳, 等. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 散斑目标探测技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1182-1193. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0049GAO W K, DU X P, WANG Y, et al. Review of laser speckle target detection technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1182-1193. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0049 [9] 胡波, 张云菲, 吴超鹏, 等. 基于图像的水下三点金宝搏188软件怎么用 测距方法研究[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2019,48(10):1005011. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.1005011HU B, ZHANG Y F, WU CH P, et al. Image-based three-beam underwater laser ranging method[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(10): 1005011. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.1005011 [10] 刘欣宇, 杨苏辉, 廖英琦, 等. 基于小波变换的金宝搏188软件怎么用 水下测距[J]. 物理学报,2021,70(18):184205. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20210569LIU X Y, YANG S H, LIAO Y Q, et al. Laser underwater ranging based on wavelet transform[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(18): 184205. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20210569 [11] 李坤, 杨苏辉, 廖英琦, 等. 强度调制532 nm金宝搏188软件怎么用 水下测距[J]. 物理学报,2021,70(8):084203. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20201612LI K, YANG S H, LIAO Y Q, et al. Underwater ranging with intensity modulated 532 nm laser source[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(8): 084203. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20201612 [12] 申玲菲, 范婷威, 胡谷雨, 等. 基于蒙特卡洛仿真的水下四点单目测距研究[J]. 光通信研究,2023(4):60-67.SHEN L F, FAN T W, HU G Y, et al. Research on underwater four-point monocular ranging based on Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Study on Optical Communications, 2023(4): 60-67. (in Chinese). [13] 张鑫, 宗思光, 余扬, 等. 近岸渔网金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测特性与实验研究[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 杂志,2023,44(3):105-110. doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2023.03.105ZHANG X, ZONG S G, YU Y, et al. Laser detection characteristics and experimental study of inshore fishing net[J]. Laser Journal, 2023, 44(3): 105-110. (in Chinese). doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2023.03.105 [14] 孔琪. 相位式金宝搏188软件怎么用 测距技术研究与实现[D]. 成都: 四川师范大学, 2018.KONG Q. Research and implementation of phase laser ranging technology[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Normal University, 2018. (in Chinese). [15] 宗思光, 张鑫, 曹静, 等. 舰船尾流金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测跟踪方法与试验[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2023,52(3):20220507. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220507ZONG S G, ZHANG X, CAO J, et al. Method and experiment of laser detection and tracking of ship wake[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(3): 20220507. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220507 [16] 钟昆, 苏伟, 彭波, 等. 水下脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测后向散射噪声自适应滤波算法[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报,2023,21(2):208-215,224. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2020461ZHONG K, SU W, PENG B, et al. An adaptive filter algorithm of underwater pulse laser detection based on backscattering correlative characters[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2023, 21(2): 208-215,224. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2020461 [17] 刘心溥, 元志安, 王玲, 等. 副载波调制水下金宝搏188软件怎么用 雷达测距性能仿真[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2020,49(S2):20200193.LIU X F, YUAN ZH A, WANG L, et al. Performance simulation of underwater lidar ranging system based on subcarrier modulation technology[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(S2): 20200193. (in Chinese) [18] 张鑫, 宗思光, 余扬, 等. 水下微弱目标双通道金宝搏188软件怎么用 探测方法研究[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与红外,2023,53(2):185-193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2023.02.004ZHANG X, ZONG S G, YU Y, et al. Research on dual-channel laser detection method for underwater weak target[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2023, 53(2): 185-193. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2023.02.004 [19] 邢刚, 许冬生, 夏云. 基于CPLD的多目标脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用 测距系统的设计与实现[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与红外,2010,40(2):152-154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2010.02.009XING G, XU D SH, XIA Y. Design and realization of multi-target pulsed laser range finder on CPLD[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2010, 40(2): 152-154. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2010.02.009 [20] 魏昊, 姜建芳, 施峰, 等. FPGA的多目标金宝搏188软件怎么用 测距系统的设计与实现[J]. 火力与指挥控制,2007,32(7):120-122,125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2007.07.034WEI H, JIANG J F, SHI F, et al. The design and realization of multi-target laser range finder on FPGA[J]. Fire Control and Command Control, 2007, 32(7): 120-122,125. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2007.07.034 [21] 董驰, 赵宇, 张翀, 等. 基于FPGA的相位式金宝搏188软件怎么用 测距系统[J]. 国外电子测量技术,2021,40(8):36-40. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2002701DONG CH, ZHAO Y, ZHANG CH, et al. Phase laser ranging system based on FPGA[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 40(8): 36-40. (in Chinese). doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2002701 [22] 纪荣祎, 赵长明, 任学成, 等. 脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用 测距高精度计时系统的设计[J]. 工矿自动化,2010,36(8):18-22.JI R Y, ZHAO CH M, REN X CH, et al. Design of timing system with high precision of pulse laser ranging[J]. Industry and Mine Automation, 2010, 36(8): 18-22. (in Chinese). [23] 谭亚运. 水下脉冲金宝搏188软件怎么用 近程周向扫描探测技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2017.TAN Y Y. Research on underwater laser proximity circumferential scanning detection technology[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2017. (in Chinese). [24] 李铜基, 林明森, 何贤强, 等. 中国近海海洋——海洋光学特性与遥感[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2012.LI T J, LIN M S, HE X Q, et al. Offshore China - Marine Optical Properties and Remote Sensing[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2012. (in Chinese) . [25] 胡江华, 贾其, 李凌, 等. 伪装技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 兵器工业出版社, 2022.HU J H, JIA Q, LI L, et al. Camouflage Technology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Weapon Industry Press, 2022. (in Chinese) . -





 下载:
下载: