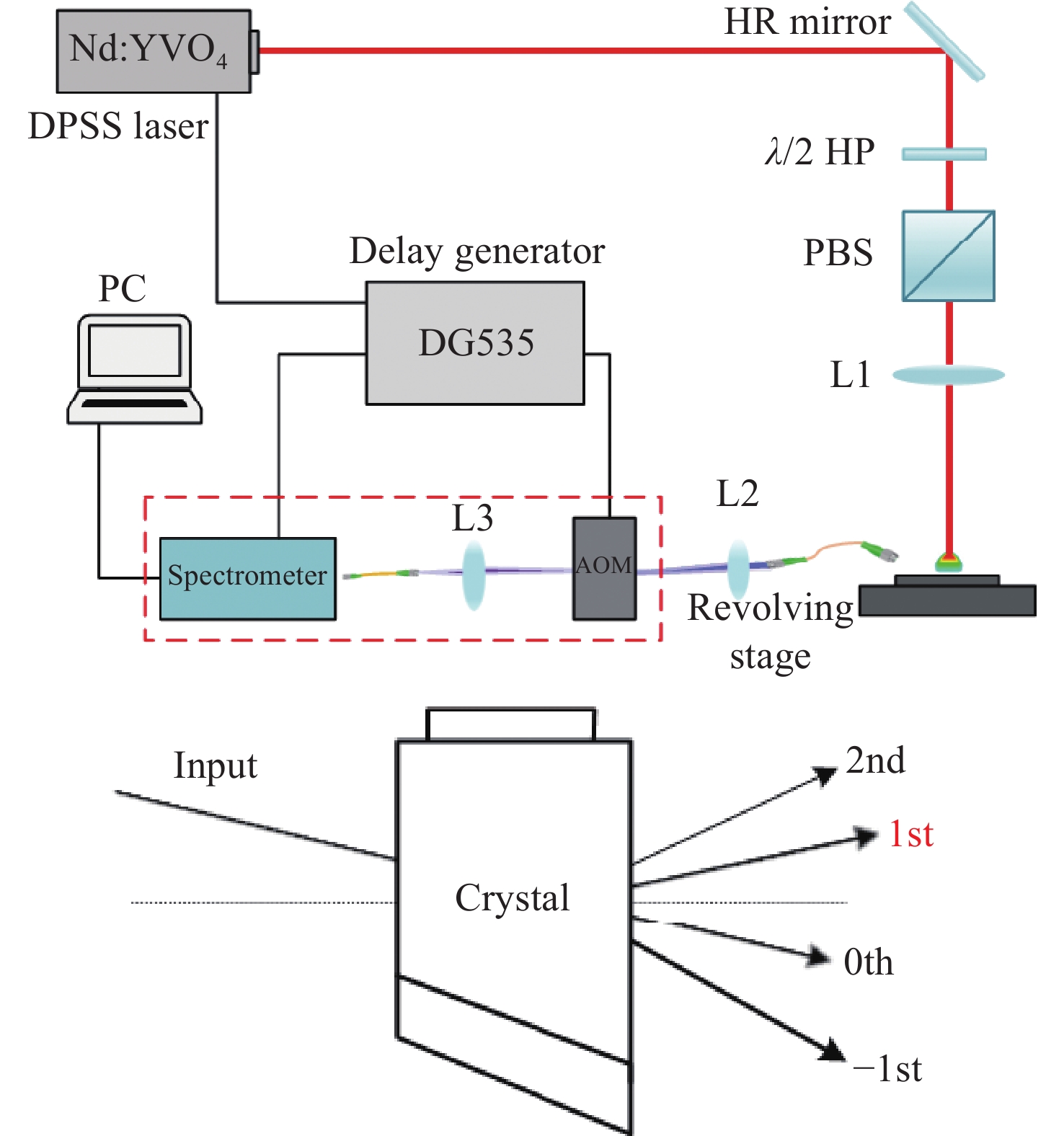
Study and analysis of self-absorption-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with high-repetition rate acousto-optic gating
-
摘要:
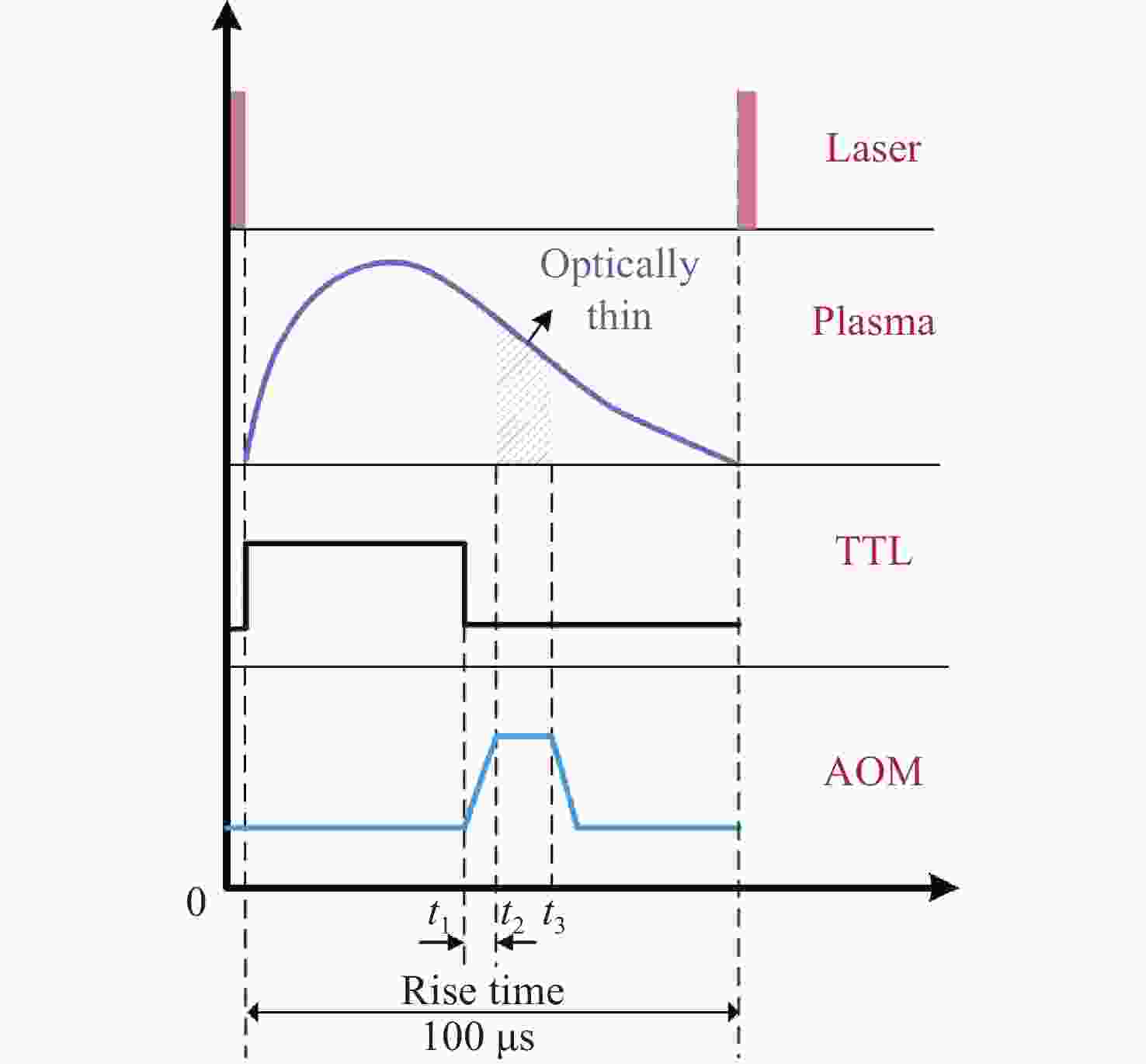
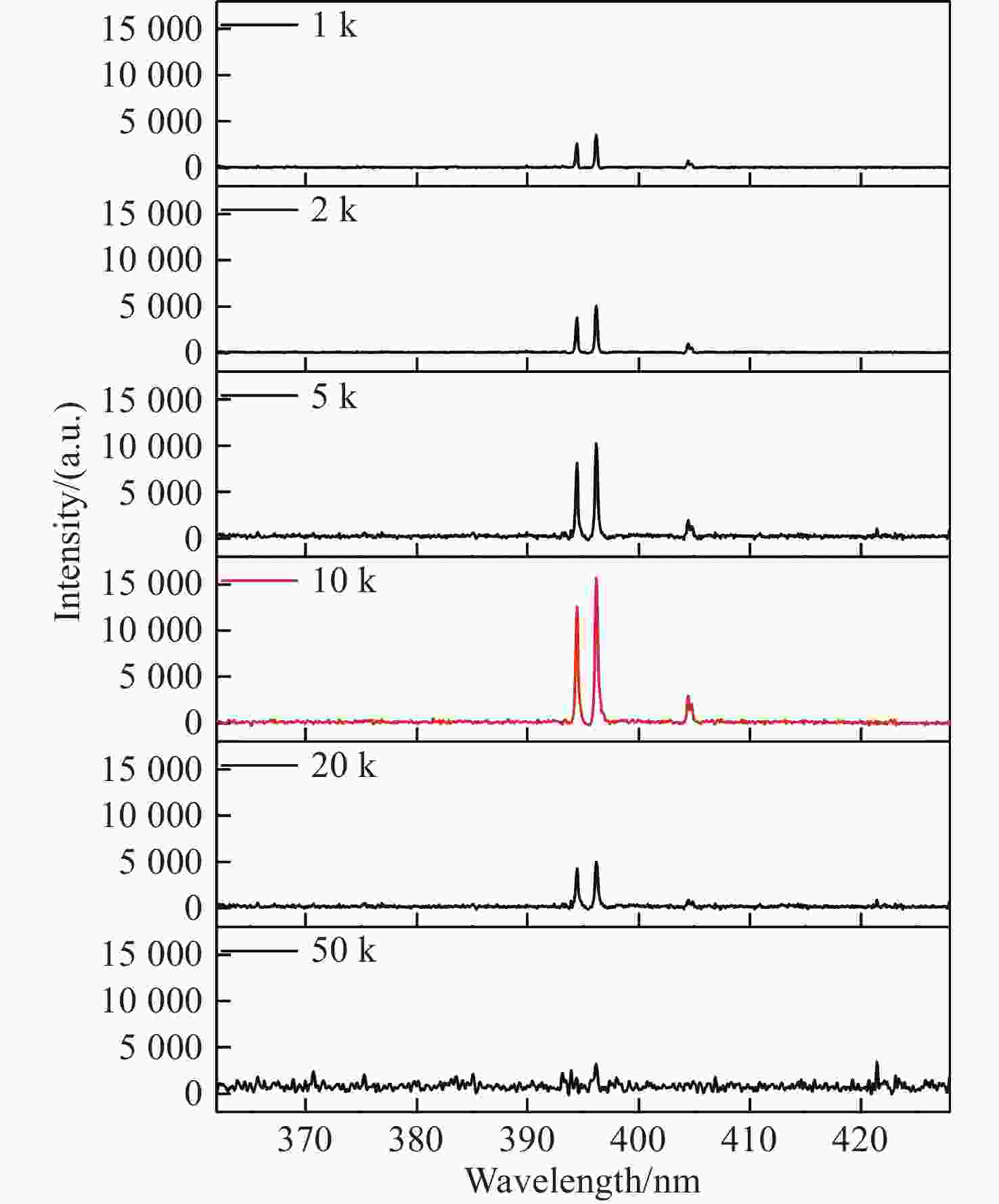
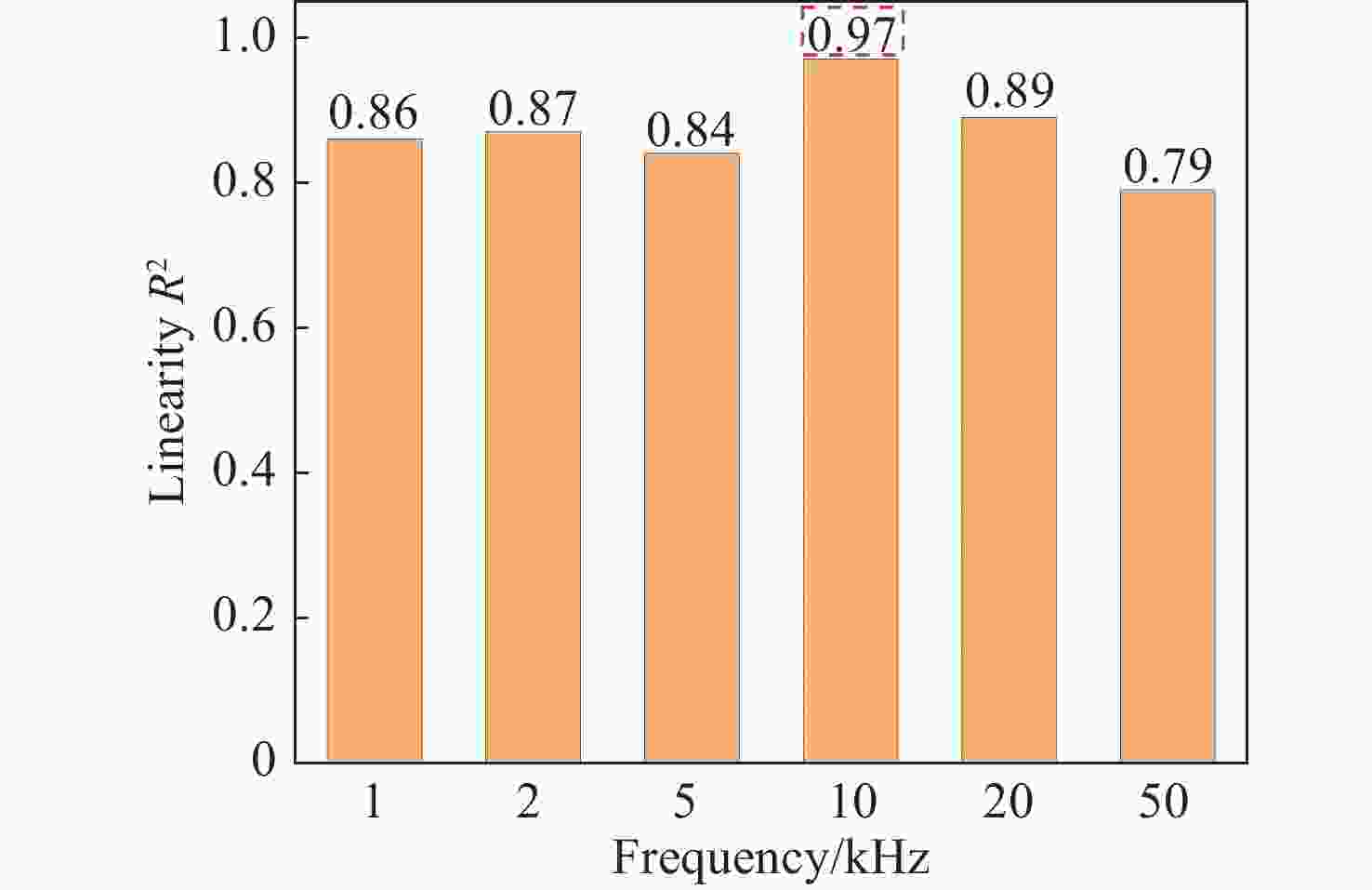
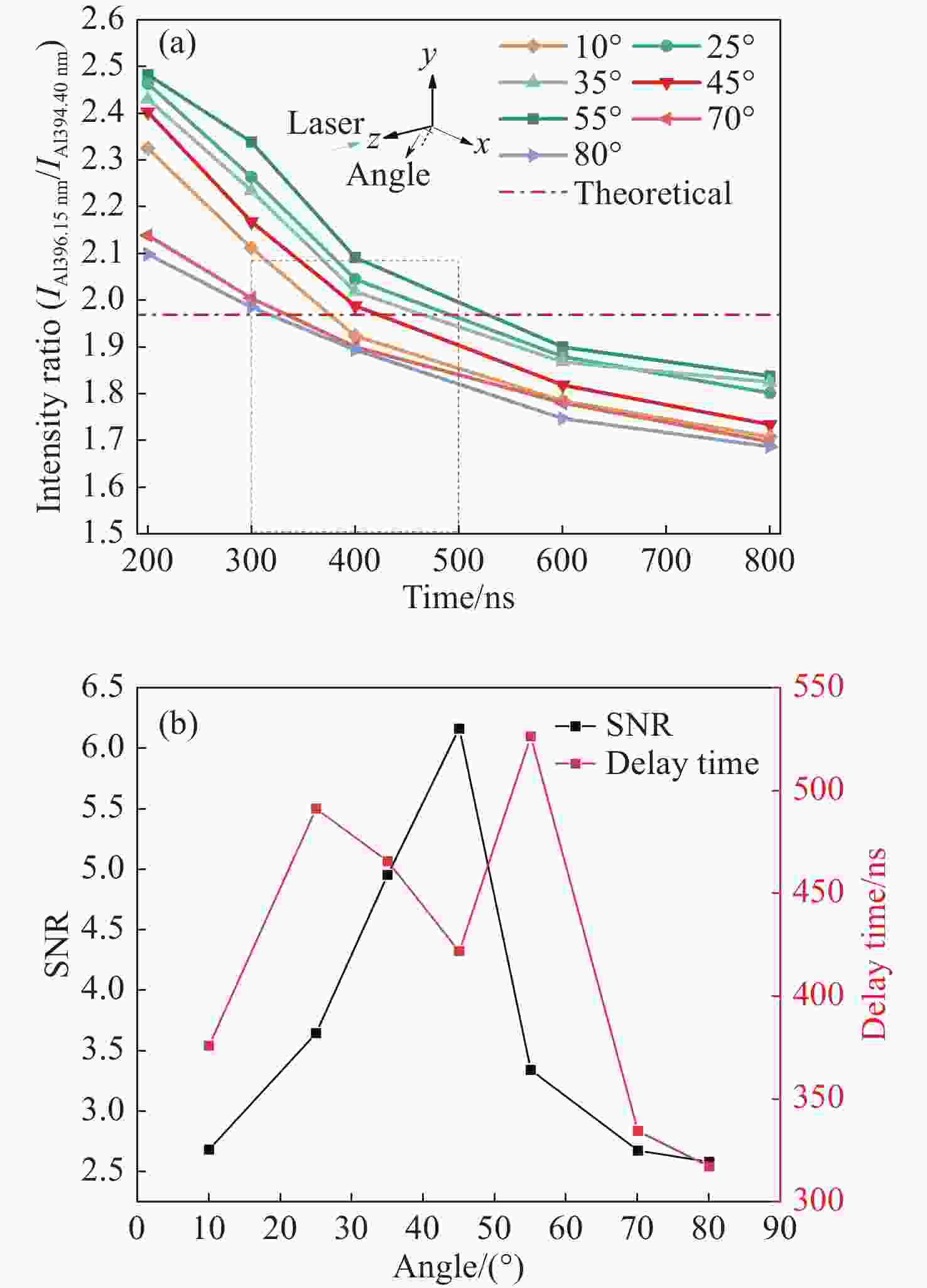
为了消除金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱技术(laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy,LIBS)中的自吸收效应,提高元素定量分析的精确度,同时满足工业中便捷分析元素的要求,需将自吸收免疫金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱技术(self-absorption free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy,SAF-LIBS)的装置小型化。本文提出了一项新型的高重频声光门控SAF-LIBS定量分析技术,使用高重频金宝搏188软件怎么用 器产生准连续的等离子体以增强光谱强度,并将声光调制器(acousto-optic modulator,AOM)作为门控开关,从而使微型CCD光谱仪和AOM能够代替传统大型SAF-LIBS装置中的像增强探测器(intensified charge coupled device,ICCD)和中阶梯型光栅光谱仪,实现自吸收免疫的同时缩小了装置的体积,降低了装置的成本。将该系统参数进行优化选择后,对样品中的Al元素进行了定量分析和预测。实验结果表明,等离子体的特性受金宝搏188软件怎么用 重复频率的影响进而会影响光谱信号的强度。在1 ~ 50 kHz金宝搏188软件怎么用 重复频率范围内,Al I 394.4 nm和Al I 396.15 nm的双线强度先增强后减弱,确定最佳的金宝搏188软件怎么用 重复频率为10 kHz。在不同的光纤采集角度下,Al的双线强度比随延迟时间的增加而减小,在45°处信噪比最高,且在一定的积分时间下,最佳光学薄时间
t ot为426 ns。在金宝搏188软件怎么用 重复频率为10 kHz、光纤采集角为45°、延迟时间为400 ns的条件下,对Al元素进行定量分析和预测结果表明,Al元素定标曲线的线性度R 2为0.982,平均绝对测量误差相对于单一LIBS的0.8%可以降低至0.18%。定量分析结果与传统大型SAF-LIBS装置的测量精度相持平。因此本高重频声光门控SAF-LIBS装置不仅有效地屏蔽了光学厚等离子体中的连续背景辐射和谱线加宽,同时具备小型化、低成本、高可靠性的优点,有助于推动SAF-LIBS技术由实验室走向工业应用。-
关键词:
- 金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱 /
- 自吸收免疫 /
- 光学薄 /
- 高重频金宝搏188软件怎么用 器 /
- 声光门控
Abstract:To eliminate the self-absorption effect in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and improve the accuracy of elemental quantitative analysis, the device of self-absorption free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (SAF-LIBS) technology needs to be miniaturized to meet the requirement of convenient elemental analysis in industry. This paper presents a novel quantitative analysis technique, the high repetition rate acousto-optic gated SAF-LIBS method. To enhance integral spectral intensity, a high repetition rate laser is used to produce quasi-continuous plasmas. In addition, an AOM (acousto-optic modulator) serves as an optical gating switch, enabling the use of a compact charge-coupled device (CCD) spectrometer and AOM instead of the intensified charge coupled device (ICCD) and medium step grating spectrometer in conventional large-scale SAF-LIBS devices. The results in a self-absorption-free system that is less bulky and less expensive. After optimizing the system parameters, the quantitative analysis and prediction of the Al element in the sample was achieved. Experimental results show that plasma characteristics are impacted by the laser repetition rate, which affects the intensity of spectral signal. The doublet intensity of Al I 394.4 nm and Al I 396.15 nm is enhanced and then diminished at a laser repetition rate ranging from 1 kHz to 50 kHz, with the optimal repetition rate identified as being 10 kHz. The doublet line intensity ratios of Al decrease with delay time under different fiber collection angles. The highest signal-to-noise ratio is achieved at an angle of 45°, while the optimal optically thin time
t ot is 426 ns at a certain integration time. Al is quantitatively analyzed and predicted at a laser repetition rate of 10 kHz, fiber collection angle of 45°, and delay time of 400 ns. The experimental results show that the calibration curve linearity ofR 2 is 0.982 and an average absolute prediction error of aluminum is reduced from 0.8% of single LIBS to 0.18%, which is equivalent to that of traditional SAF-LIBS. Additionally, the high repetition rate acousto-optic gating SAF-LIBS not only effectively eliminates continuous background radiation and broadens spectral lines in optically thick plasma, but also offers the advantages of miniaturization, low cost, convenience, and reliability. Therefore, this study plays a significant role in advancing SAF-LIBS technology from laboratory testing to industrial applications. -
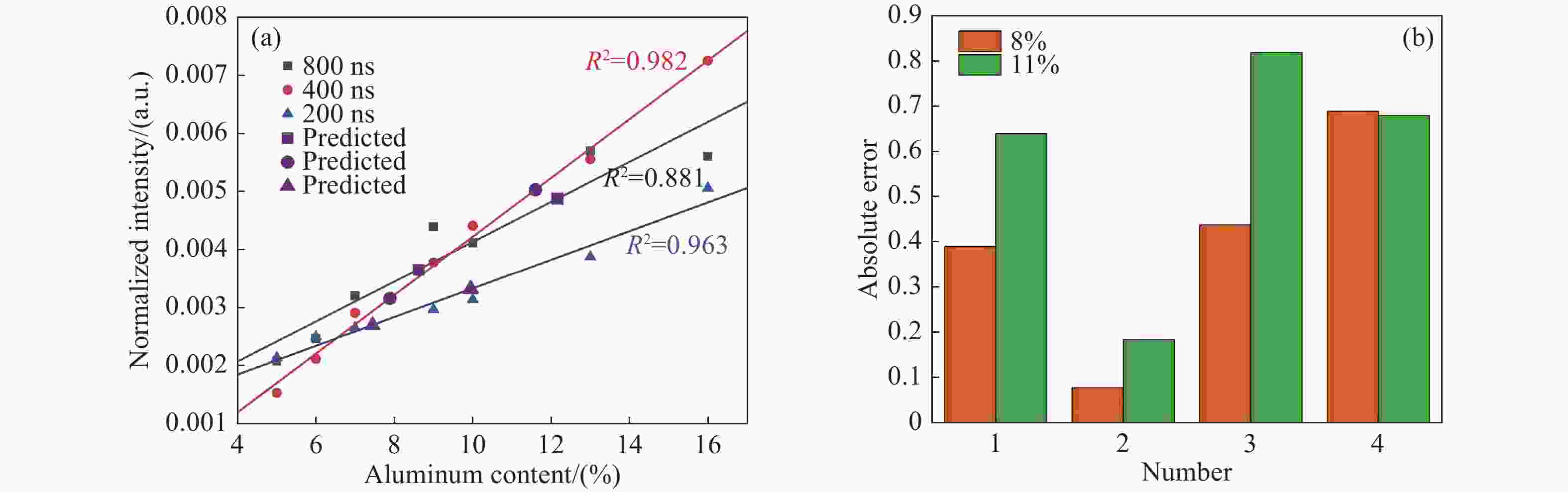
图 8 (a)延迟时间分别为200 ns、400 ns、800 ns时的Al定标曲线及预测值;(b)不同实验条件下对Al含量预测误差比较,序号1~4分别对应200 ns、400 ns、800 ns和无AOM
Figure 8. (a) Calibration curves and predicted results of Al at delay times of 200 ns, 400 ns and 800 ns; (b) comparison of prediction errors of Al under different experimental conditions, the numbers 1-4 here correspond to delay of 200 ns, 400 ns, 800 ns and without AOM, respectively
表 1 不同压片样品中的Al含量
Table 1. Aluminum content in different press tablet samples
样品编号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 占比(%) 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 16 19 -
[1] ZHOU ZH Y, GE Y F, LIU Y ZH. Real-time monitoring of carbon concentration using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and machine learning[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(24): 39811-39823. doi: 10.1364/OE.443732 [2] 甄佳, 乌日娜, 付林, 等. 基于金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱的塑料鉴别研究[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与红外,2022,52(11):1587-1591. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.11.001ZHEN J, WU R N, FU L, et al. Identification of plastics based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2022, 52(11): 1587-1591 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.11.001 [3] LANGROUDI P P, KAPTEINA G, ILLGUTH M. Automated distinction between cement paste and aggregates of concrete using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(16): 4624. doi: 10.3390/ma14164624 [4] PENG J Y, LIU Y F, YE L F, et al. Fast detection of minerals in rice leaves under chromium stress based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 860: 160545. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160545 [5] 舒开强, 陈友元, 彭郑英, 等. 铀矿中多目标元素的金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱定量分析方法研究[J]. 分析化学,2023,51(7):1195-1203.SHU K Q, CHEN Y Y, PENG ZH Y, et al. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for quantitative analysis of multi-target elements in uranium ore[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(7): 1195-1203. (in Chinese). [6] 程军杰, 曹智, 杨灿然, 等. 便携式远程金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导击穿光谱系统及其定量分析性能[J]. 应用化学,2022,39(9):1447-1452. doi: 10.19894/j.issn.1000-0518.210547CHENG J J, CAO ZH, YANG C R, et al. Quantitative analysis with a portable remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(9): 1447-1452. (in Chinese). doi: 10.19894/j.issn.1000-0518.210547 [7] KONJEVIĆ N. Plasma broadening and shifting of non-hydrogenic spectral lines: present status and applications[J]. Physics Reports, 1999, 316(6): 339-401. doi: 10.1016/S0370-1573(98)00132-X [8] HOU J J, ZHANG L, ZHAO Y, et al. Mechanisms and efficient elimination approaches of self-absorption in LIBS[J]. Plasma Science and Technology, 2019, 21(3): 034016. doi: 10.1088/2058-6272/aaf875 [9] PALLESCHI V. Avoiding Misunderstanding self-Absorption in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) analysis[J]. Spectroscopy, 2022, 37(8): 60-62. [10] EL SHERBINI A M, EL SHERBINI T M, HEGAZY H, et al. Evaluation of self-absorption coefficients of aluminum emission lines in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy measurements[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2005, 60(12): 1573-1579. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2005.10.011 [11] LI T Q, HOU Z Y, FU Y T, et al. Correction of self-absorption effect in calibration-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (CF-LIBS) with blackbody radiation reference[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019, 1058: 39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.01.016 [12] ALFARRAJ B A, BHATT C R, YUEH F Y, et al. Evaluation of optical depths and self-absorption of strontium and Aluminum emission lines in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2017, 71(4): 640-650. doi: 10.1177/0003702817693231 [13] MOON H Y, HERRERA K K, OMENETTO N, et al. On the usefulness of a duplicating mirror to evaluate self-absorption effects in laser induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2009, 64(7): 702-713. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2009.06.011 [14] CAI S, TANG Y, WANG F, et al. Investigation of the multi-elemental self-absorption mechanism and experimental optimization in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2020, 35(5): 912-926. doi: 10.1039/D0JA00048E [15] HU ZH L, NIE J F, OUYANG ZH Y, et al. Self-absorption correction method for one-point calibration laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2023, 48(1): 1-4. doi: 10.1364/OL.472224 [16] 侯华明, 李颖, 卢渊, 等. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导镍等离子体的自吸收时间分辨特性研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2011,31(3):595-599.HOU H M, LI Y, LU Y, et al. Time-resolved evaluation of self-absorption in laser induced plasma from nickel sample[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2011, 31(3): 595-599. (in Chinese). [17] SABRI N M, HAIDER Z, TUFAIL K, et al. Spectroscopic diagnostics of laser induced plasma and self-absorption effects in Al lines[J]. Physics of Plasmas, 2018, 25(7): 073303. doi: 10.1063/1.5023666 [18] 马云云, 刘国荣, 魏秀芳, 等. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 诱导锌等离子体的自吸收效应研究[J]. 西北师范大学学报(自然科学版),2022,58(4):45-49, 57. doi: 10.16783/j.cnki.nwnuz.2022.04.007MA Y Y, LIU G R, WEI X F, et al. Study on self-absorption effect of laser induced zinc plasmas[J]. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science), 2022, 58(4): 45-49, 57. (in Chinese). doi: 10.16783/j.cnki.nwnuz.2022.04.007 [19] HOU J J, ZHANG L, YIN W B, et al. Development and performance evaluation of self-absorption-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for directly capturing optically thin spectral line and realizing accurate chemical composition measurements[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(19): 23024-23034. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.023024 [20] HOU J J, ZHANG L, ZHAO Y, et al. Rapid selection of analytical lines for SAF-LIBS based on the doublet intensity ratios at the initial and final stages of plasma[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(22): 32184-32192. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.032184 [21] SAKKA T, IRIE K, FUKAMI K, et al. Emission spectroscopy of laser ablation plasma with time gating by acousto-optic modulator[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2011, 82(2): 023112. doi: 10.1063/1.3544021 [22] POřÍZKA P, KLESSEN B, KAISER J, et al. High repetition rate laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using acousto-optically gated detection[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2014, 85(7): 073104. doi: 10.1063/1.4890337 -






 下载:
下载: