-
摘要:
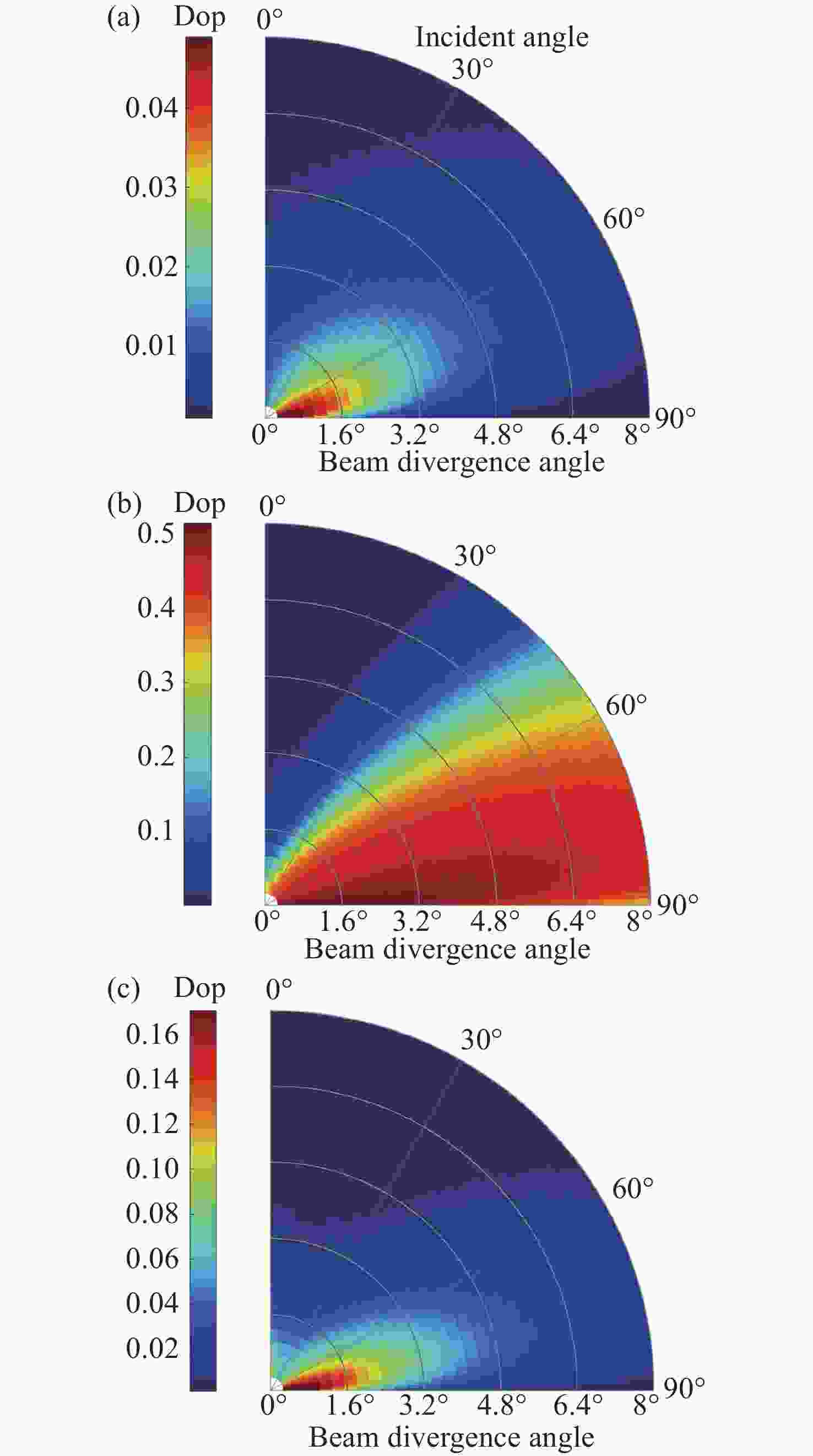
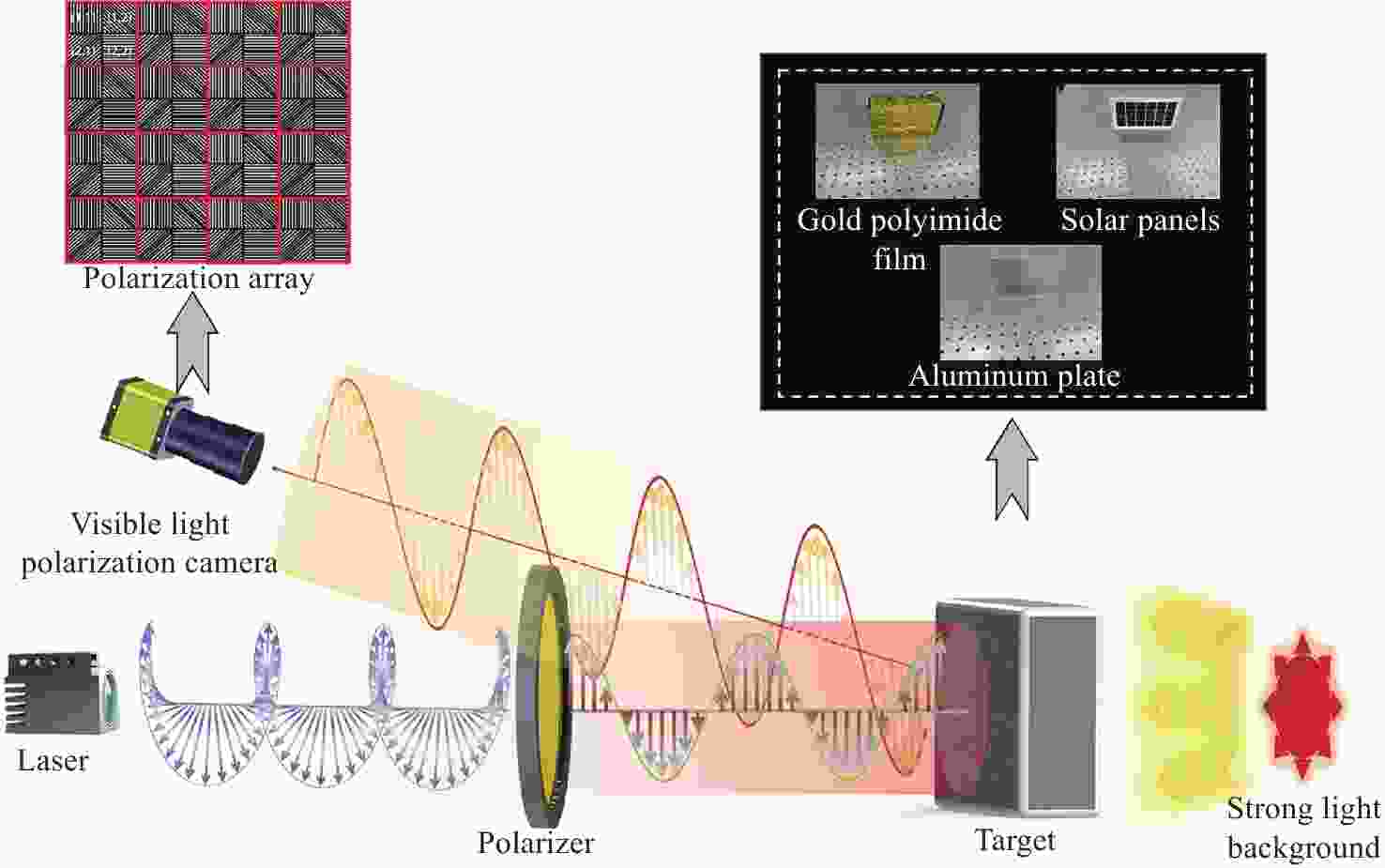
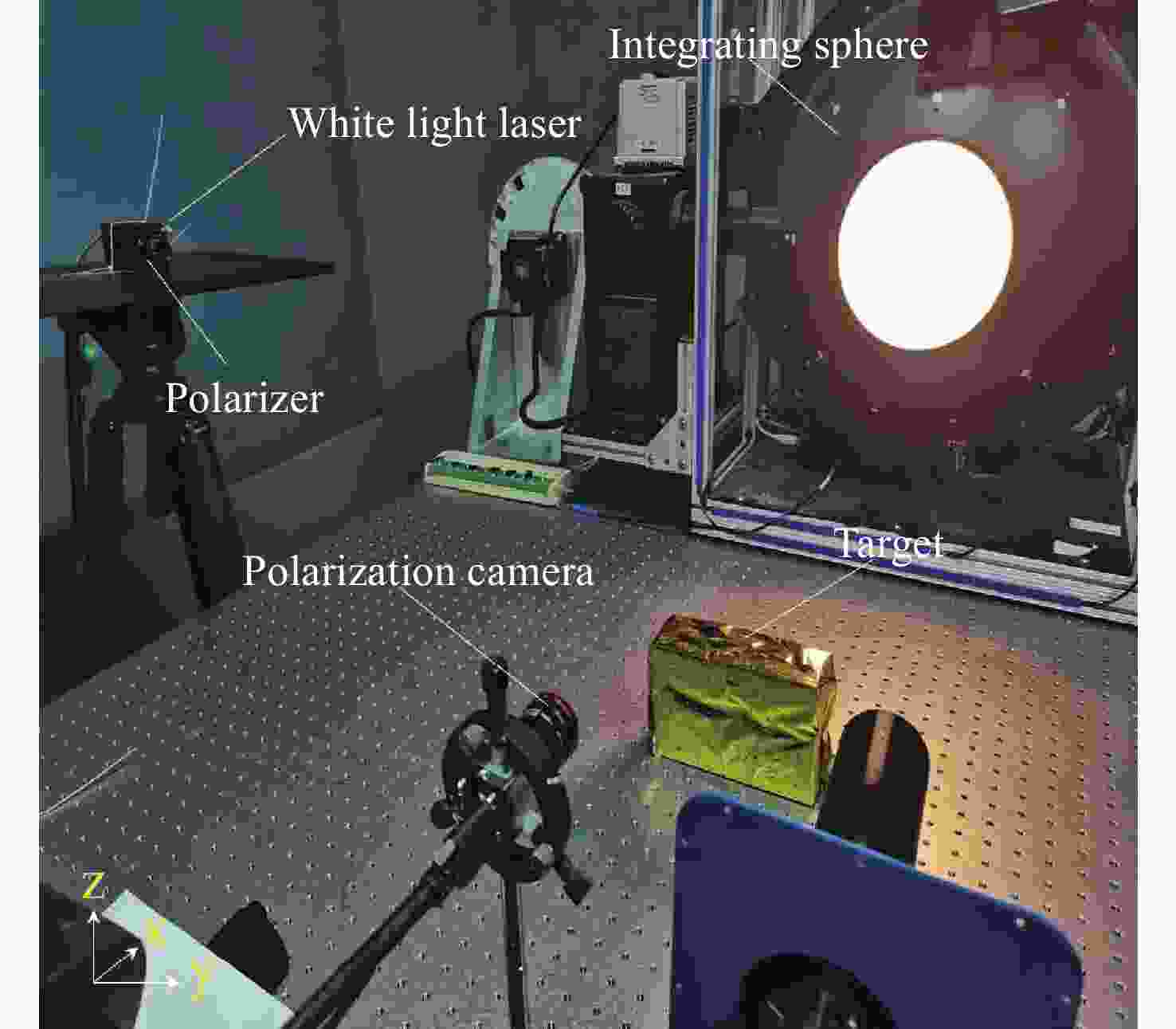
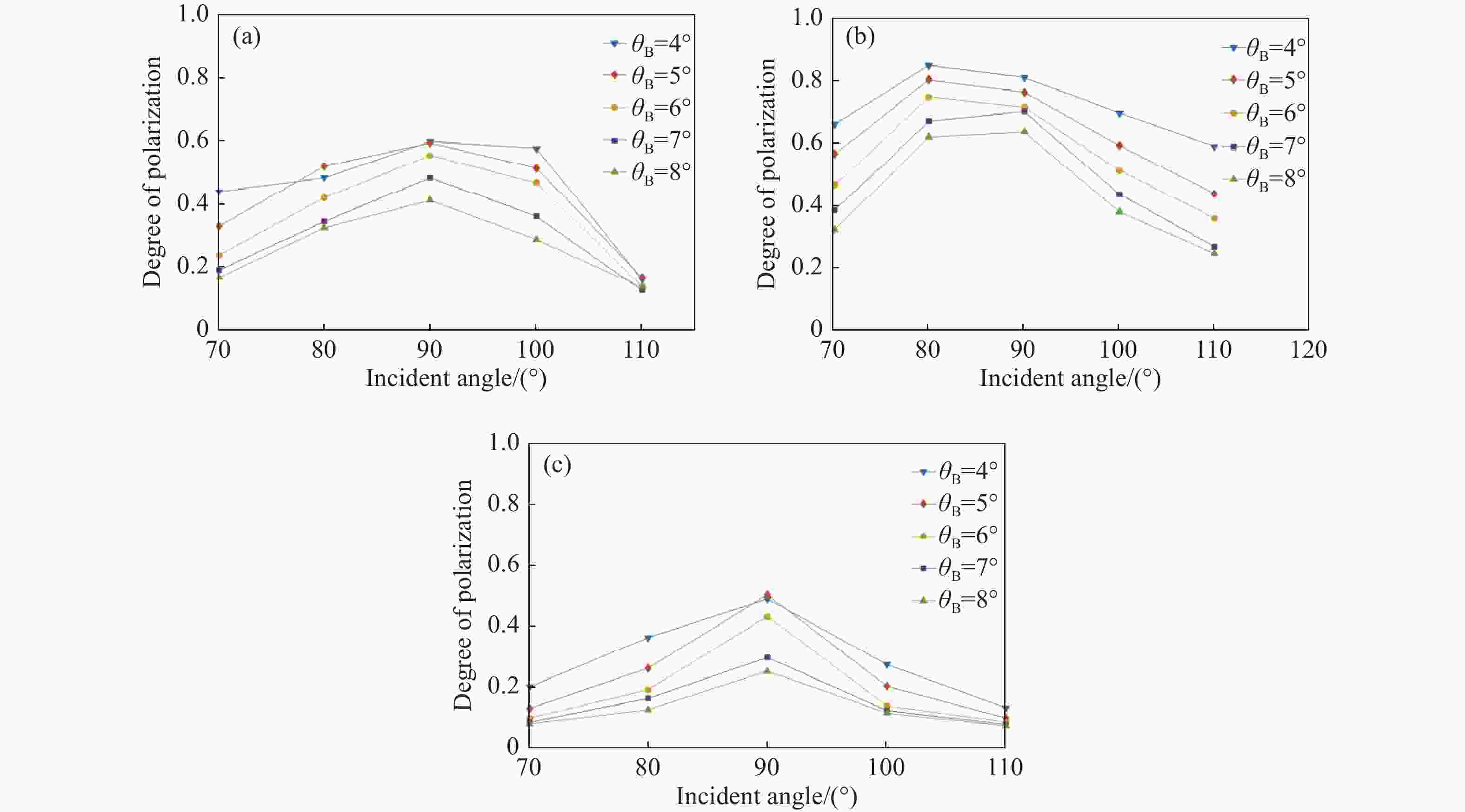
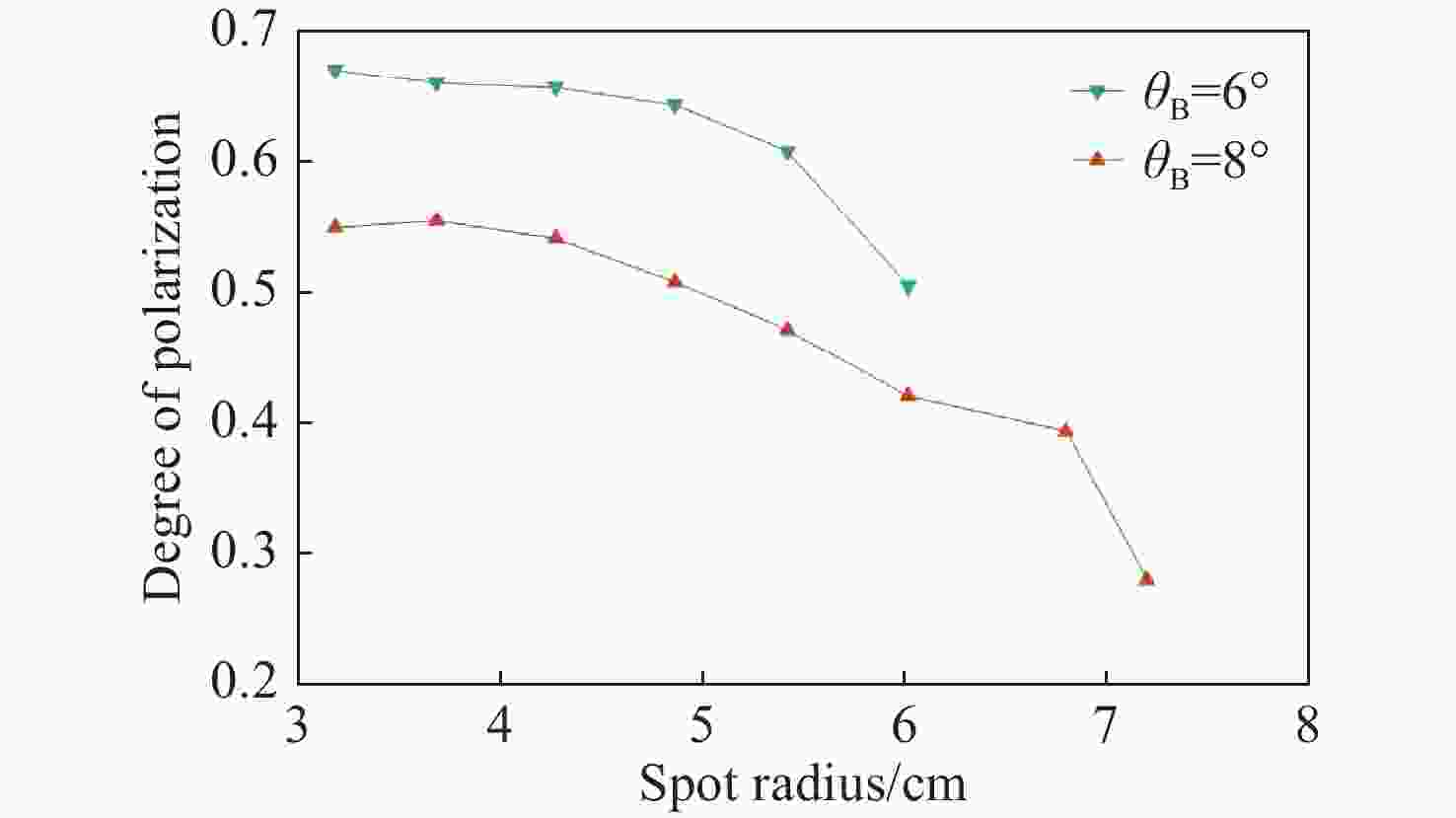
针对传统光电探测方法在强光背景下目标探测对比度低的问题,本文提出一种基于金宝搏188软件怎么用 照明的主动偏振成像方法。首先构建金宝搏188软件怎么用 入射双向反射分布模型、金宝搏188软件怎么用 入射偏振双向反射分布模型以及金宝搏188软件怎么用 照明的目标表面偏振度模型,并分析3种典型目标材料偏振特性与束散角之间的耦合关系。然后在暗室可控条件下开展逆光观测实验,验证目标偏振特性受金宝搏188软件怎么用 束散角的影响。实验结果表明:强光背景下主动偏振成像目标对比度与传统被动强度成像相比提升了86.11%,不同束散角下不同目标材料的可见光偏振特性间存在差异,金属材质相对于非金属材质的线偏振度提升更高,实验结果与理论分析具有较好的一致性。最后,在室外开展太阳逆光观测实验,验证了研究方法在室外高强光、远距离下依旧具有适用性。本研究为提升强光背景下的目标精准感知能力奠定了理论基础。
-
关键词:
- 金宝搏188软件怎么用 束散角 /
- 强背景光 /
- 可见光偏振特性 /
- 偏振双向反射分布函数 /
- 偏振度
Abstract:In this study, we propose an active polarization imaging method based on laser illumination to tackle the issue of low target detection contrast in strong light backgrounds, which is a challenge in conventional photoelectric detection. Through constructing a laser incident bidirectional reflection distribution model, a laser incident polarization bidirectional reflection distribution model and a target surface polarization model of laser illumination, the coupling relationship between the polarization characteristics of three typical target materials and the divergence angle of a laser beam is analyzed. Backlight observation experiments are conducted in a controlled darkroom to verify the impact of the scattering angle of the laser beam on the polarization characteristics of the target. The experimental results show an 86.11% increase in target contrast for active polarization imaging under strong light background compared to traditional passive intensity imaging. Additionally, the visible polarization characteristics of different target materials vary with different divergence angles, and the line polarization of metallic materials is higher than that of non-metallic materials. The experimental results are in good agreement with the theoretical analysis. The outdoor solar backlight observation experiment verifies the applicability of the research method in high-intensity light and long-distance settings. This study can lay a theoretical foundation for improving accurate target perception under a strong light background.
-
图 5 逆光状态下金色聚酰亚胺薄膜、铝板、太阳能电池板(从左到右)非偏与偏振图像对比图。(a)、(b)、(c)非偏图像(d)、(e)、(f)偏振图像
Figure 5. Comparison of unpolarized and polarized images of gold polyimide film, aluminum plate, and solar panel (from left to right) under backlight state. (a), (b) and (c) are unpolarized images and (d), (e) and (f) are polarized images
表 1 定标实验结果
Table 1. Results of calibration experiments
定标参数 参数数值 积分球输出功率/mW 20.920 金宝搏188软件怎么用 输出功率/W 2.080 偏振片消光比 0.517 黑布吸收率 0.996 表 2 成像、照明系统的主要技术参数
Table 2. Main technical parameters of imaging and lighting systems
系统 指标 参数 可见光偏振相机 响应波段/μm $0.3 \sim 0.7 $ 镜头焦距/mm 15 光圈数 2.8 靶面分辨率 $2\;464 \times 2\;056$ 像元尺寸/μm 3.45 灵敏度/lx 0.01 白光金宝搏188软件怎么用 器 输出波段/μm $0.3 \sim 0.7$ 电功率/W $\geqslant10$ 束散角/(°) $ 3 \sim 11$ 输出流明值/lm $ \geqslant 230$ 输出光功率/W 2 表 3 强光背景下不同目标的实验结果
Table 3. Experimental results of different targets under strong background light
目标 图像对比度 非偏图像 线偏振度图像 金色聚酰亚胺薄膜 0.36 0.65 铝板 0.45 0.80 太阳能电池板 0.24 0.48 表 5 室外强光背景下不同探测模式的实验结果
Table 5. Experimental results of different detection modes under strong outdoor light background
目标 图像对比度 非偏图像 偏振图像 无人机 0.03 0.24 表 4 成像系统主要技术参数
Table 4. Main technical parameters of imaging system
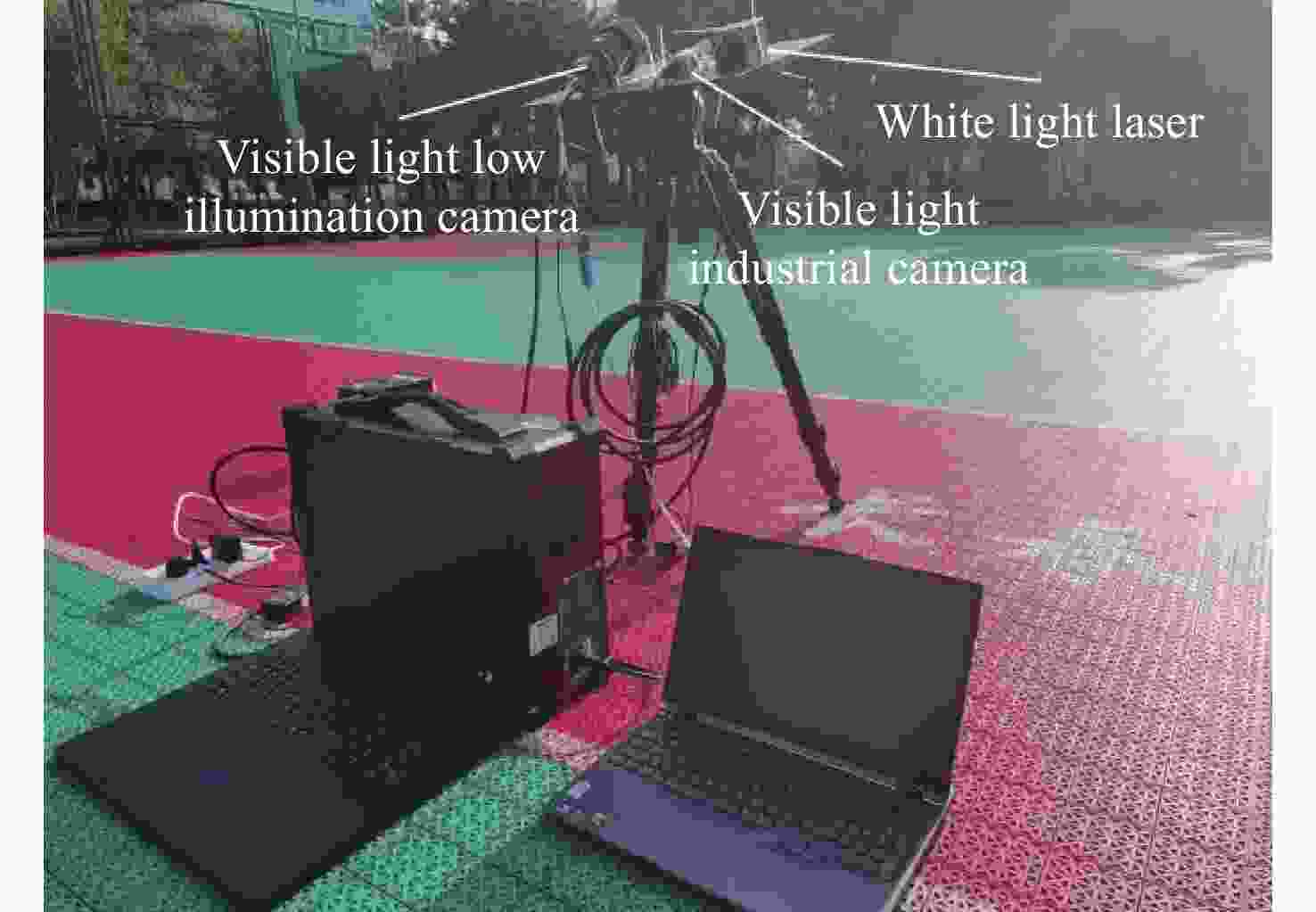
相机类型 指标 参数 可见光工业相机 响应波段/μm $0.3 \sim 0.7$ 镜头焦距/mm 25 光圈数 16 靶面分辨率 $2\;046 \times 2\;046 $ 像元尺寸/μm 5.5 灵敏度/lx 0.01 低照度相机 响应波段/μm $0.3 \sim 0.7$ 镜头焦距/mm 25 光圈数 16 靶面分辨率 $1\;920 \times 1\;080$ 像元尺寸/μm 12 灵敏度/lx 10−4 -
[1] 徐淼, 史浩东, 王超, 等. 空间目标多维度探测与金宝搏188软件怎么用 通信一体化技术研究[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2021,48(12):1206002. doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.1206002XU M, SHI H D, WANG CH, et al. Technology for integrating space object multidimensional detection and laser communication[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48(12): 1206002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.1206002 [2] 付强, 史浩东, 王超, 等. 天基空间碎片光电探测新技术研究[J]. 空间碎片研究,2020,20(4):49-55.FU Q, SHI H D, WANG CH, et al. Research on new technology of photoelectric detection for space-based space debris[J]. Space Debris Research, 2020, 20(4): 49-55. (in Chinese). [3] 张海峰, 张忠萍, 秦思, 等. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 主动照亮地影中空间目标实验研究[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2014,41(S1):s108003.ZHANG H F, ZHANG ZH P, QIN S, et al. Experimental study on laser active illumination to space targets within the shadow of earth[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(S1): s108003. (in Chinese). [4] LI H SH. Research on space target detection ability calculation method and spectral filtering technology in sky-screen's photoelectric system[J]. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 2016, 58(5): 1035-1041. doi: 10.1002/mop.29723 [5] 鲁梅, 陈忠碧. 基于梯度特征的弱小目标检测[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与红外,2022,52(1):129-135.LU M, CHEN ZH B. Dim target detection based on gradient feature[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2022, 52(1): 129-135. (in Chinese). [6] 李岩松, 赵慧洁, 李娜, 等. 基于中红外偏振的海面太阳耀光背景下的目标探测[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2022,49(19):1910004. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1910004LI Y S, ZHAO H J, LI N, et al. Detection of marine targets covered in sun glint based on mid-infrared polarization[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(19): 1910004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1910004 [7] 郭庭, 张彬, 顾乃庭, 等. 偏振哈特曼波前探测技术研究[J]. 光电工程,2021,48(7):210076.GUO T, ZHANG B, GU N T, et al. Research on polarization hartmann wavefront detection technology[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2021, 48(7): 210076. (in Chinese). [8] 于洁, 巩蕾, 王海斌, 等. 伪装涂层红外偏振模型优化及辐射特性研究[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2023,50(13):1304007. doi: 10.3788/CJL221016YU J, GONG L, WANG H B, et al. Optimization of infrared polarization model and study of radiation characteristics of camouflaged coatings[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(13): 1304007. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL221016 [9] 柳祎, 史浩东, 姜会林, 等. 粗糙目标表面红外偏振特性研究[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(3):459-471.LIU Y, SHI H D, JIANG H L, et al. Infrared polarization properties of targets with rough surface[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(3): 459-471. (in Chinese). [10] 高明, 宋冲, 巩蕾. 基于偏振双向反射分布函数的粗糙面光散射偏振特性研究[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2013,40(12):1213002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.1213002GAO M, SONG CH, GONG L. Analysis of polarization characteristics about rough surface light scattering based on polarized bidirectional reflectance distribution function[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2013, 40(12): 1213002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.1213002 [11] 凌军, 张拴勤, 吴坚业, 等. 伪装涂层金宝搏188软件怎么用 反射特性检测与实验研究[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2012,39(3):0308005. doi: 10.3788/CJL201239.0308005LING J, ZHANG SH Q, WU J Y, et al. Measurement and experimental study of laser reflectance characteristics of camouflage coat[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2012, 39(3): 0308005. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201239.0308005 [12] 陆君, 李季波. 常见自然地物对1.06 μm金宝搏188软件怎么用 反射特性研究[J]. 光电技术应用,2015,30(5):71-73.LU J, LI J B. Research on 1.06 μm laser reflectance characteristic for common natural features[J]. Electro-Optic Technology Application, 2015, 30(5): 71-73. (in Chinese). [13] 赵若曼, 陈少捷, 张川. 空间目标金宝搏188软件怎么用 雷达散射波实验室模拟技术[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 杂志,2021,42(3):91-95.ZHAO R M, CHEN SH J, ZHANG CH. Laboratory simulation technology of Lidar scattering wave of space target[J]. Laser Journal, 2021, 42(3): 91-95. (in Chinese). [14] 汪杰君, 王鹏, 王方原, 等. 材料表面偏振双向反射分布函数模型修正[J]. 光子学报,2019,48(1):0126001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194801.0126001WANG J J, WANG P, WANG F Y, et al. Modified model of polarized bidirectional reflectance distribution function on material surface[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2019, 48(1): 0126001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194801.0126001 [15] 张卫国. 海面太阳耀光背景下的偏振探测技术[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(2):231-236. doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0231ZHANG W G. Application of polarization detection technology under the background of sun flare on sea surface[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(2): 231-236. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0231 [16] 王新涛, 郑建华, 李明涛. 小行星天基光学监测信噪比分析[J]. 光学 精密工程,2021,29(12):2763-2773. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212912.2763WANG X T, ZHENG J H, LI M T. Analysis of signal-to-noise ratio for space-based optical surveillance of asteroids[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(12): 2763-2773. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212912.2763 -






 下载:
下载: