-
摘要:
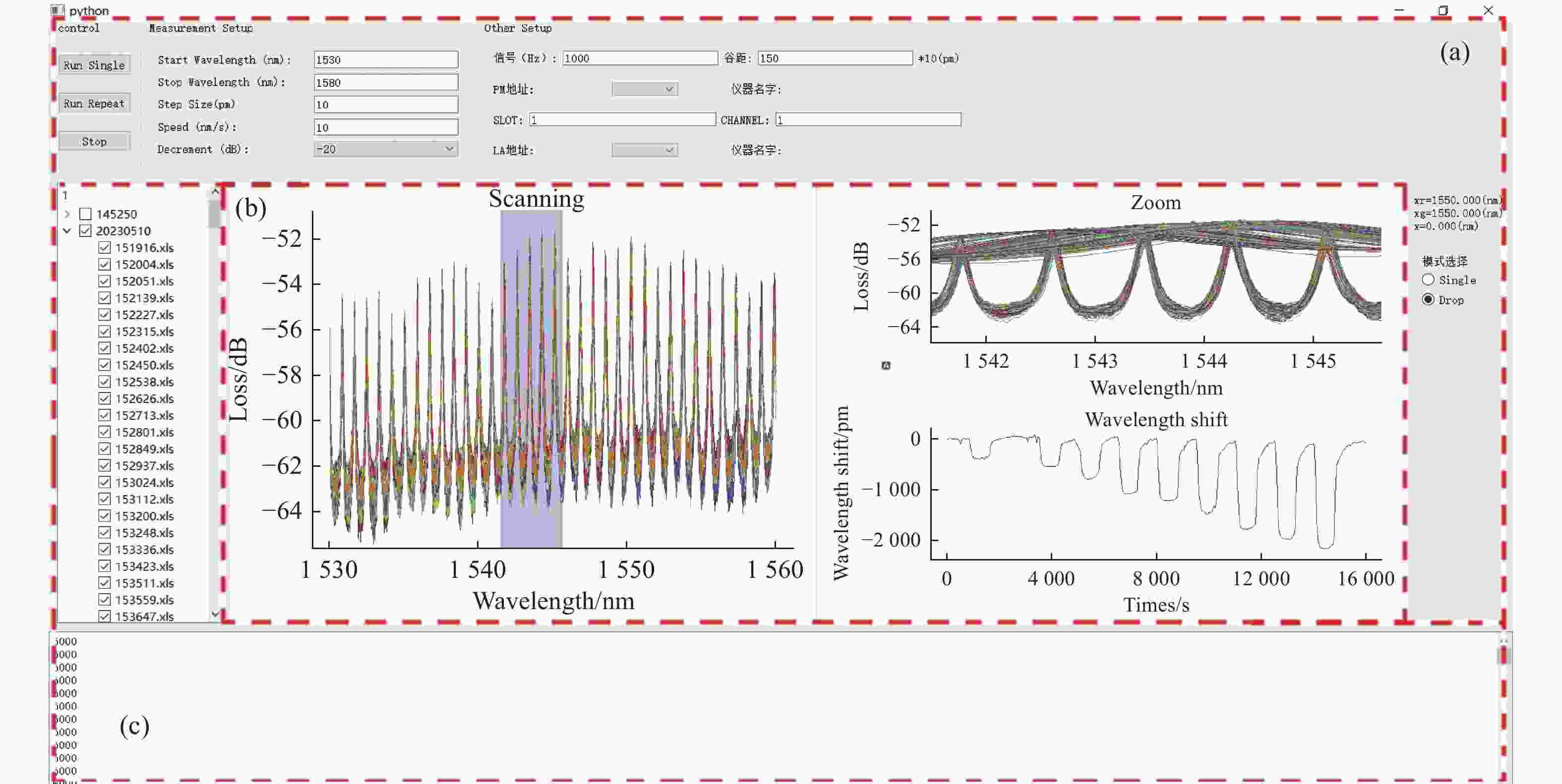
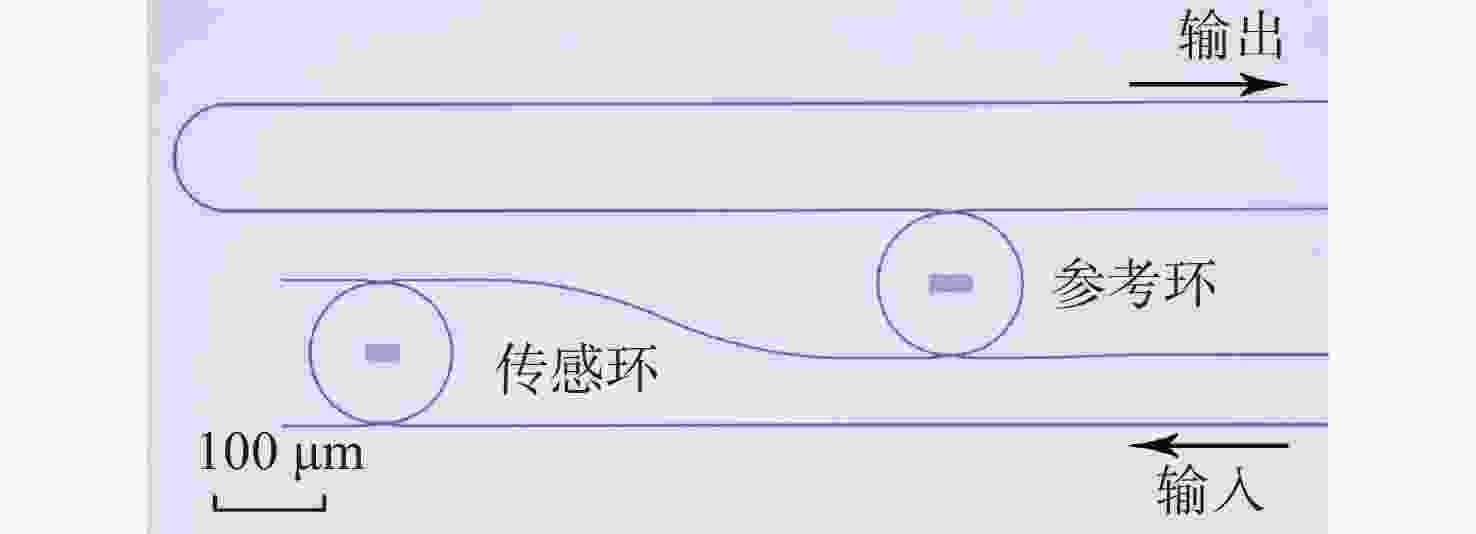
双环级联谐振腔(Cascaded Microring Resonators, CMRR)传感器作为一种新型的光学传感器,因具有高灵敏度、易于集成、功耗小等优点被广泛应用于生物、医学等领域。为了实现CMRR传感器输出光谱的实时数据分析处理,提出了一种基于Python的实时CMRR传感器输出光谱包络拟合方法。首先,利用不同的拟合模型对CMRR传感器输出光谱进行拟合;然后,通过灵敏度误差百分比对不同拟合模型的拟合误差进行比较,结果显示平滑样条拟合法在实时处理CMRR传感器输出光谱过程中表现最佳;最后对不同浓度的NaCl溶液进行实时输出光谱采集处理,验证了CMRR传感器输出光谱实时采集处理程序的可靠性。实验结果表明CMRR传感器的波长漂移量与溶液浓度呈线性关系。通过计算可知CMRR传感器对于盐水的灵敏度约为671.03529 nm/RIU。
Abstract:Cascaded Microring Resonators (CMRR), a new type of optical sensor, are widely used in biology, medicine, and other fields because of their high sensitivity, easy integration, and low power consumption. In this paper, we propose a Python-based envelope fitting method for real-time CMRR sensor’s output spectrum to achieve real-time data analysis and processing of the CMRR sensor’s output spectrum. First, different fitting models were used to fit the output spectrum of the CMRR sensor. Then, the fitting errors of different fitting models were compared by sensitivity error percentage, and it was concluded that the smooth spline fitting method performed best in real-time processing of the output spectrum of the CMRR sensor. Finally, NaCl solution with different concentrations was used for real-time acquisition and processing of the output spectrum. The reliability of the real-time acquisition and processing program for the CMRR sensor’s output spectrum is verified. The experimental results show that the wavelength drift of the CMRR sensor is linearly related to the concentration of the solution. It can be seen from the calculation that the sensitivity of the CMRR sensor for brine is about 671.03529 nm/RIU.
-
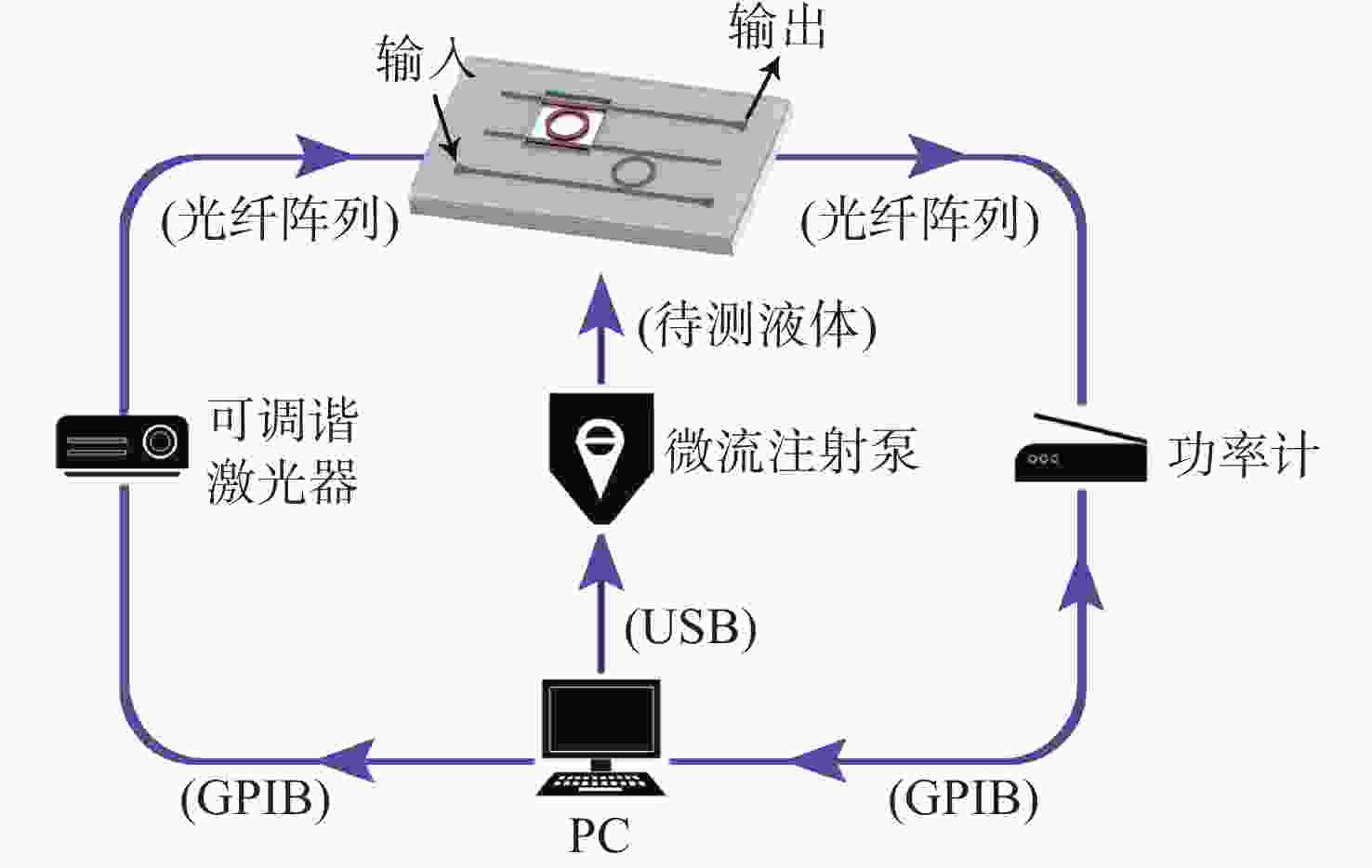
表 1 实验仪器与设备型号
Table 1. Experimental instruments and equipment models
仪器名称 实验用途 设备型号 生产公司 微流注射泵 定速进样 ZSB-SY03-60-M03-1 南京润泽流体 可调谐金宝搏188软件怎么用 器 光源 81600B( DE43501059) Agilent 功率计 探测输出光谱 N7748A Agilent 表 2 不同拟合法性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison of different fitting methods
拟合方法 R-squared 灵敏度( nm/RIU) 误差百分比(%) 理想状态 674.205 平滑拟合法 0.998132234 685.523 1.67 高斯拟合法 0.994447952 625.246 7.29 洛伦兹拟合法 0.991580189 634.419 5.91 傅立叶拟合法 0.969335425 663.864 1.53 -
[1] BOGAERTS W, DE HEYN P, VAN VAERENBERGH T, et al. Silicon microring resonators[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2012, 6(1): 47-73. [2] 谢佳一, 苏国帅, 李明宇, 等. 反射型法布里-珀罗腔和微环谐振腔级联的温度传感器[J]. 光学学报,2022,42(23):2328002. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.2328002XIE J Y, SU G SH, LI M Y, et al. Temperature sensor cascading reflective Fabry-Perot cavity with microring resonator[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(23): 2328002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.2328002 [3] 刘春娟, 王嘉伟, 吴小所, 等. 一种光栅辅助狭缝微环谐振器的传感特性[J]. 光学学报,2022,42(16):1613001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.1613001LIU CH J, WANG J W, WU X S, et al. Sensing characteristics of grating-assisted slot microring resonator[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(16): 1613001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.1613001 [4] ZHUANG SH Q, FENG J J, LIU H P, et al. Optical multistability in a cross-coupled double-ring resonator system[J]. Optics Communications, 2022, 507: 127637. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2021.127637 [5] 吴蓉, 张皓辰. 耦合区数量对鼎形微环谐振器输出的影响[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(6):1493-1500. doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2023-0009WU R, ZHANG H CH. The influence of the number of coupling regions on the output of the ding-shaped microring resonator[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(6): 1493-1500. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2023-0009 [6] 赵荣宇, 崔建功, 余亚鑫, 等. 面向倏逝波传感的光纤谐振腔设计与封装研究[J]. 传感器与微系统,2022,41(6):21-24.ZHAO R Y, CUI J G, YU Y X, et al. Design and packaging of optical fiber resonators for evanescent wave sensing[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2022, 41(6): 21-24. (in Chinese). [7] 晏崇宇, 高劭宏, 宋东雨, 等. 单环和双环微环谐振腔应用于马赫-曾德尔干涉仪滤波器的特性分析[J]. 光子学报,2015,44(7):0713003. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154407.0713003YAN CH Y, GAO SH H, SONG D Y, et al. Characteristic analysis of single and double Micro ring resonant cavity used in Mach-Zehnder interferometer filter[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2015, 44(7): 0713003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154407.0713003 [8] 朱庆明. 基于波长控制的谐振型硅基光开关及光滤波器研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2020.ZHU Q M. Research on resonant silicon photonic switch and filter based on wavelength locking[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2020. (in Chinese). [9] 肖泽华, 李明宇, 苏国帅, 等. 基于扫描反射镜结构的多路光开关[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(1):136-143. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0020XIAO Z H, LI M Y, SU G SH, et al. Multi-channel optical switching based on scanning mirror instrumentation[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(1): 136-143. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0020 [10] DE VOS K, BARTOLOZZI I, SCHACHT E, et al. Silicon-on-Insulator microring resonator for sensitive and label-free biosensing[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(12): 7610-7615. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.007610 [11] LIU W L, LI M, GUZZON R S, et al. An integrated parity-time symmetric wavelength-tunable single-mode microring laser[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15389. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15389 [12] 史冰耀. 面向免标记型光学生物传感的微环谐振器的研究[D]. 北京: 中央民族大学, 2023.SHI B Y. Research on Microring resonators for Label Free optical biosensing[D]. Beijing: Minzu University of China, 2023. (in Chinese) [13] AMBIKA S, VANJERKHEDE K. Modeling and analysis of photonic sensor based on ring resonator for glucose detection[J]. Journal of Optics, 2023, 52(4): 1837-1844. doi: 10.1007/s12596-022-01081-x [14] 韩源. 基于光波导环形谐振腔凹槽结构的声传感特性研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2023.HAN Y. Acoustic sensing characteristics research based on the groove structure of optical waveguide resonator[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2023. (in Chinese). [15] PAN J SH, LI Q, FENG Y M, et al. Parallel interrogation of the chalcogenide-based micro-ring sensor array for photoacoustic tomography[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 3250. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39075-3 [16] 祝敏, 张文栋, 崔建功, 等. 面向声压传感的硅基槽式谐振腔设计及研究[J]. 仪表技术与传感器,2023(1):1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2023.01.001ZHU M, ZHANG W D, CUI J G, et al. Design and research of silicon-based resonator for sound pressure sensing[J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor, 2023(1): 1-6. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2023.01.001 [17] CHEN Y Q, YU F, YANG CH, et al. Label-free biosensing using cascaded double-microring resonators integrated with microfluidic channels[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 344: 129-133. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2015.01.028 [18] CARDENOSA-RUBIO M C, ROBISON H M, BAILEY R C. Recent advances in environmental and clinical analysis using microring resonator–based sensors[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 2019, 10: 38-46. [19] PIRZADA M, ALTINTAS Z. Recent progress in optical sensors for biomedical diagnostics[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11(4): 356. doi: 10.3390/mi11040356 [20] JIN L, LI M Y, HE J J. Optical waveguide double-ring sensor using intensity interrogation with a low-cost broadband source[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(7): 1128-1130. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.001128 [21] JIN L, LI M Y, HE J J. Analysis of wavelength and intensity interrogation methods in cascaded double-ring sensors[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2012, 30(12): 1994-2002. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2012.2187272 [22] CLAES T, BOGAERTS W, BIENSTMAN P. Experimental characterization of a silicon photonic biosensor consisting of two cascaded ring resonators based on the Vernier-effect and introduction of a curve fitting method for an improved detection limit[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(22): 22747-22761. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.022747 [23] 苏畅, 朱慧慧, 曹紫葳, 等. 双环级联谐振腔传感器透射谱线包络拟合方法[J]. 光子学报,2018,47(10):1023002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20184710.1023002SU CH, ZHU H H, CAO Z W, et al. Fitting methods of transmission spectrum envelope in cascaded double-ring resonator sensors[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2018, 47(10): 1023002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20184710.1023002 [24] POON J K S, SCHEUER J, MOOKHERJEA S, et al. Matrix analysis of microring coupled-resonator optical waveguides[J]. Optics Express, 2004, 12(1): 90-103. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.12.000090 [25] 刘勇. 基于SOI的环形谐振腔生物传感器研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017.LIU Y. Biosensor based on SOI microring resonators[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. (in Chinese). [26] 赵琪涵, 王永红, 高新亚, 等. 基于平滑样条拟合的相位图像滤波评价方法[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(8):0815020. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0815020ZHAO Q H, WANG Y H, GAO X Y, et al. Filtering evaluation method of phase images based on smooth spline fitting[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(8): 0815020. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0815020 [27] 姚泽楷, 蔡耀仪, 李诗文, 等. 基于平滑样条曲线结合离散状态转移算法的拉曼光谱基线校正方法[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2022,49(18):1811001. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1811001YAO Z K, CAI Y Y, LI SH W, et al. Baseline correction for Raman spectroscopy using cubic spline smoothing combined with discrete state transformation algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(18): 1811001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1811001 [28] 李立. 基于贝叶斯框架的光滑样条模型研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2023.LI L. Advances on smoothing spline model based on Bayesian framework[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2023. (in Chinese). [29] 高楠, 于永波, 杜振辉, 等. 基于高斯/洛伦兹线型拟合比的谐波检测压强反演研究[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2023,52(8):20230428. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230428GAO N, YU Y B, DU ZH H, et al. Research on harmonic detection pressure inversion based on Gauss/Lorentz line fitting ratio[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(8): 20230428. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230428 [30] 张景源, 陈北北, 杨永兴, 等. 融合遗传算法和BP神经网络的光斑定位方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(2):407-414. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0084ZHANG J Y, CHEN B B, YANG Y X, et al. Positioning algorithm for laser spot center based on BP neural network and genetic algorithm[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(2): 407-414. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0084 [31] 谭诗斌. Beta模型的柔性扩展与洛伦兹曲线拟合优化[J]. 数学的实践与认识,2023,53(7):154-168.TAN SH B. Flexible expansion of beta model and Lorentz curve fitting optimization[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2023, 53(7): 154-168. (in Chinese). [32] 张凯, 门昌骞, 王文剑. 基于随机傅里叶特征空间的高斯核近似模型选择算法[J]. 数据采集与处理,2023,38(3):616-628.ZHANG K, MENG CH Q, WANG W J. Gaussian kernel approximation model selection algorithm based on random fourier feature space[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2023, 38(3): 616-628. (in Chinese). [33] 屈文星, 刘浩, 秦楚, 等. 基于MATLAB傅里叶曲线拟合的天线跟踪精度评估方法[J]. 电子测量技术,2020,43(12):91-95.QU W X, LIU H, QIN CH, et al. Antenna tracking accuracy evaluation method based on MATLAB Fourier curve fitting[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2020, 43(12): 91-95. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: