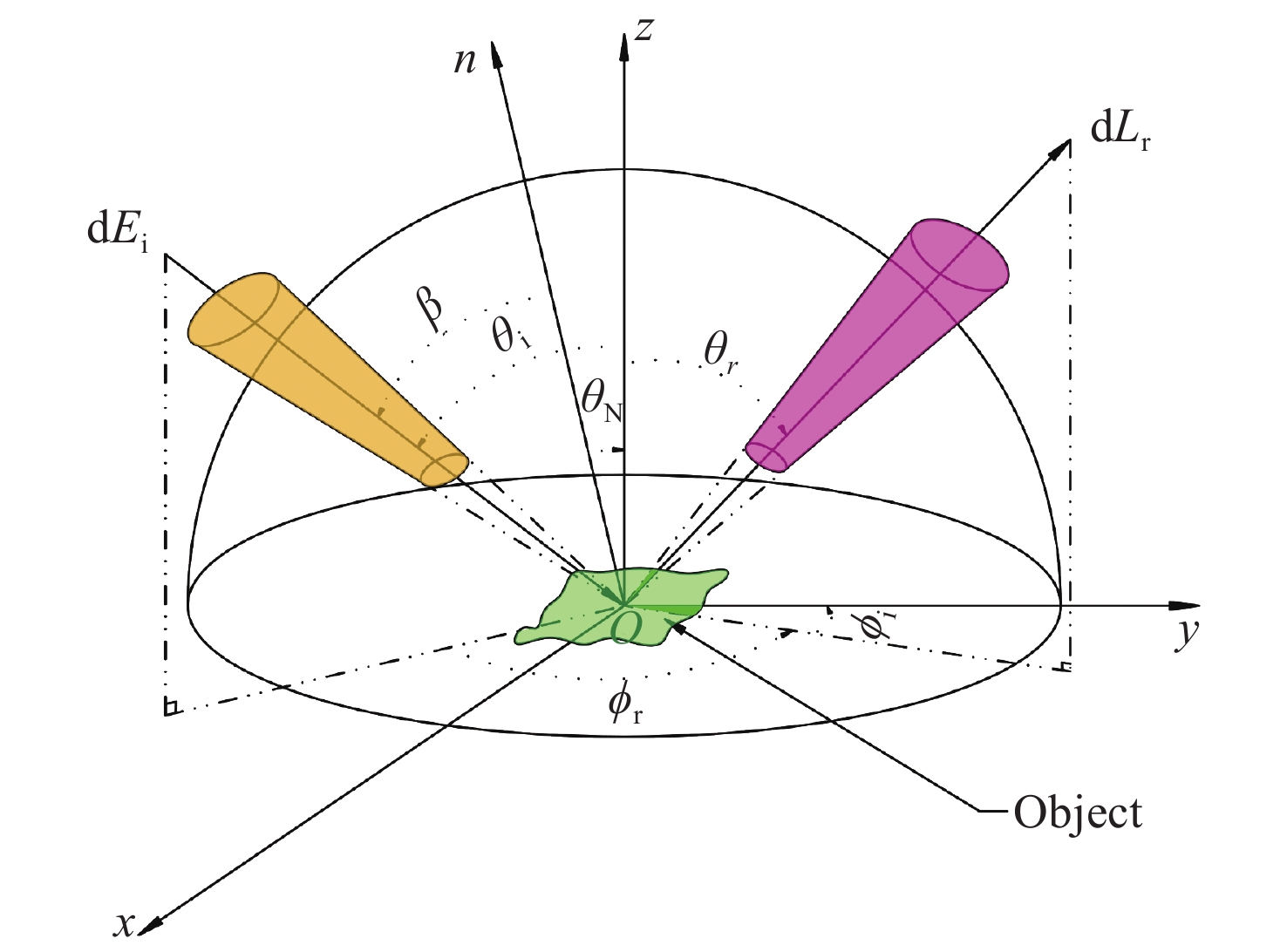
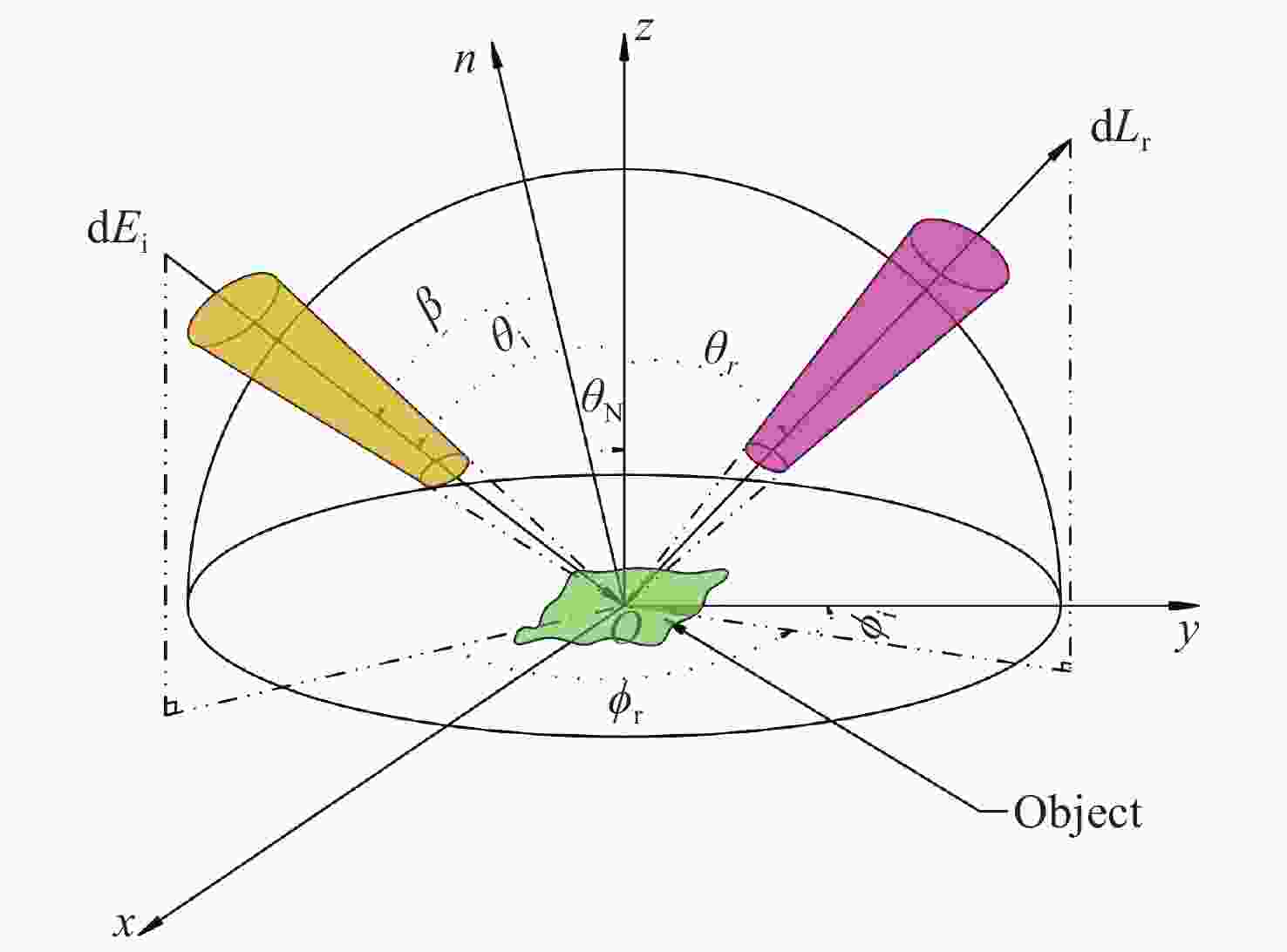
Visible polarized reflection of target material surface based on improved Blinn masking function
-
摘要:
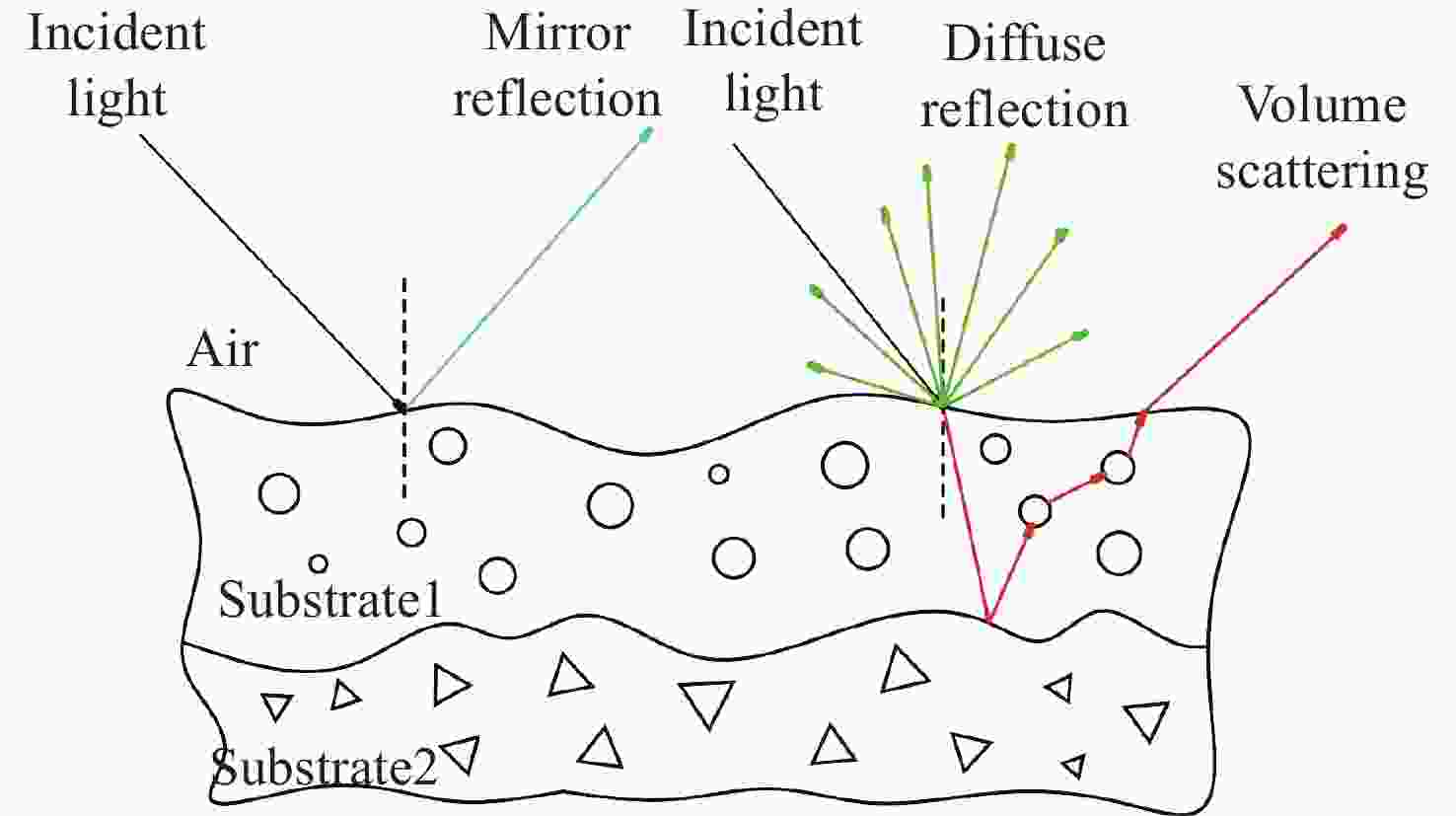
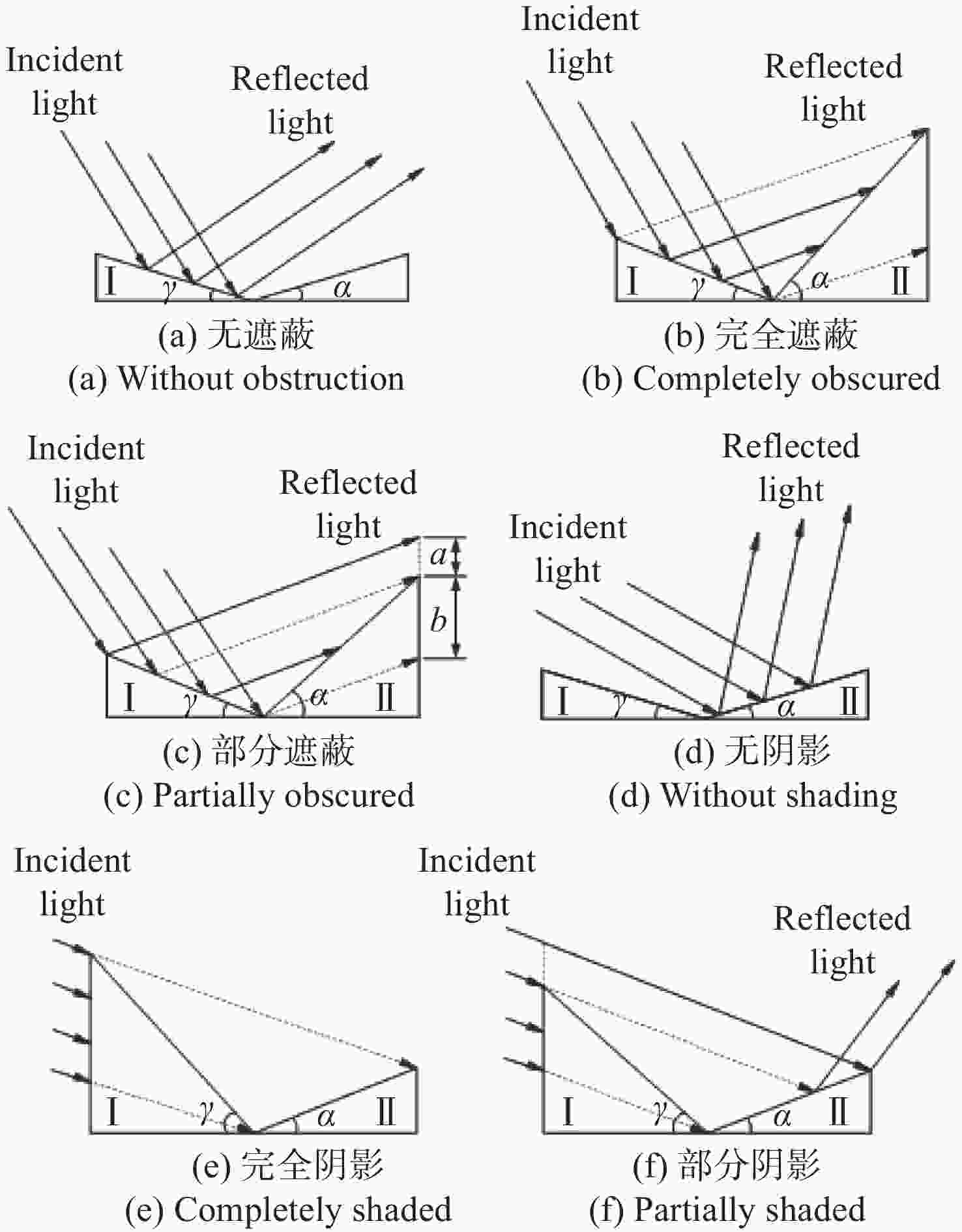
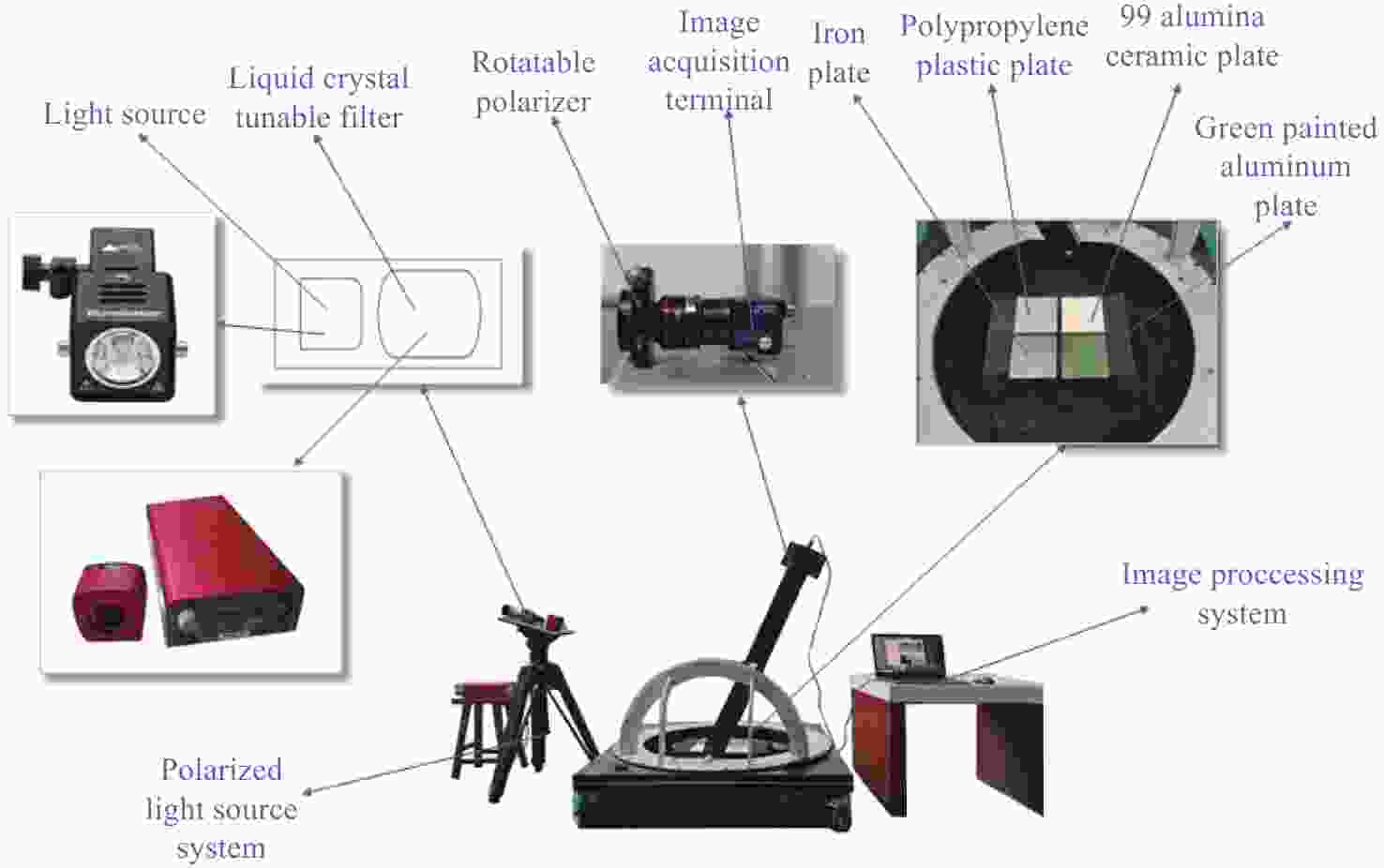
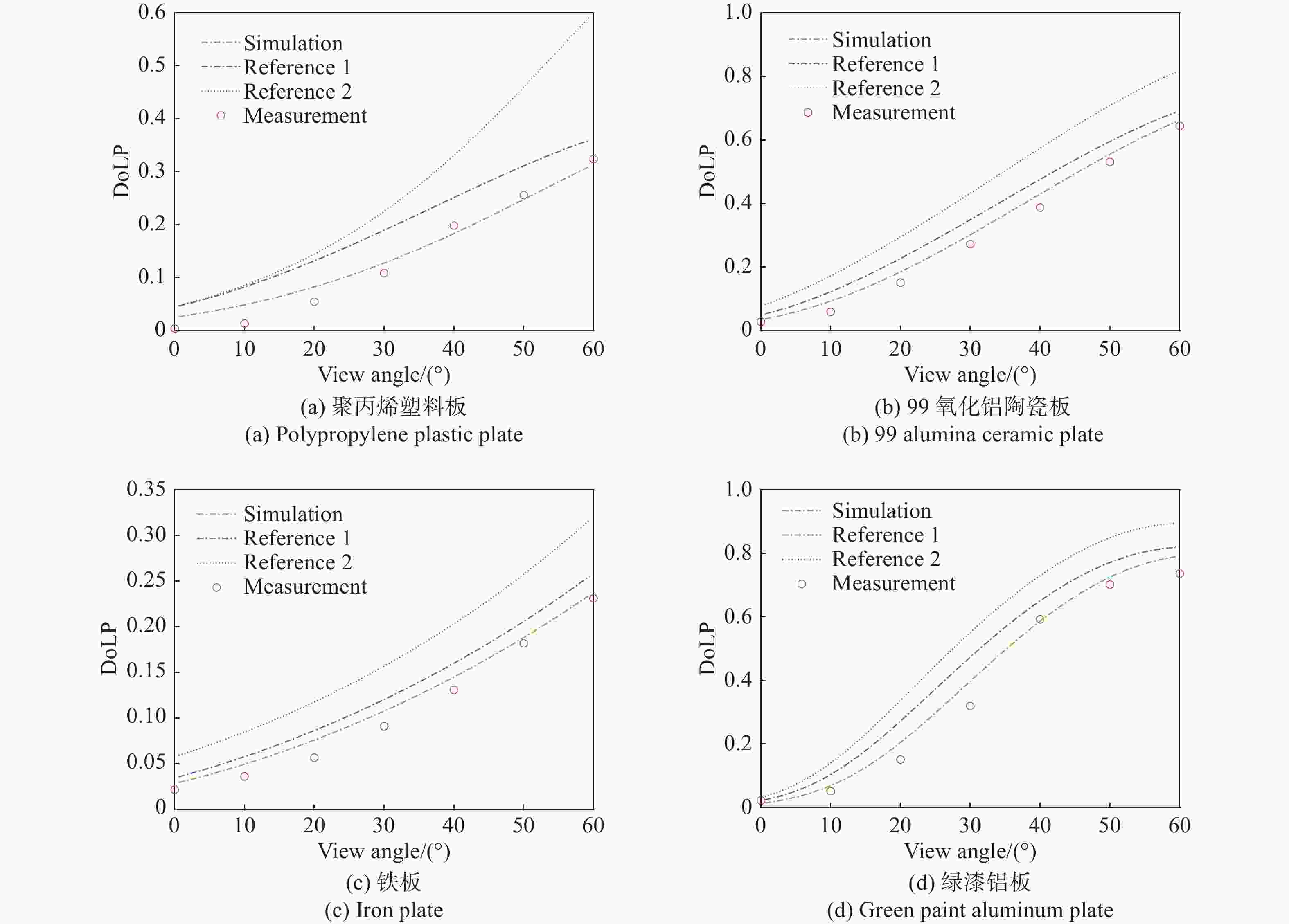
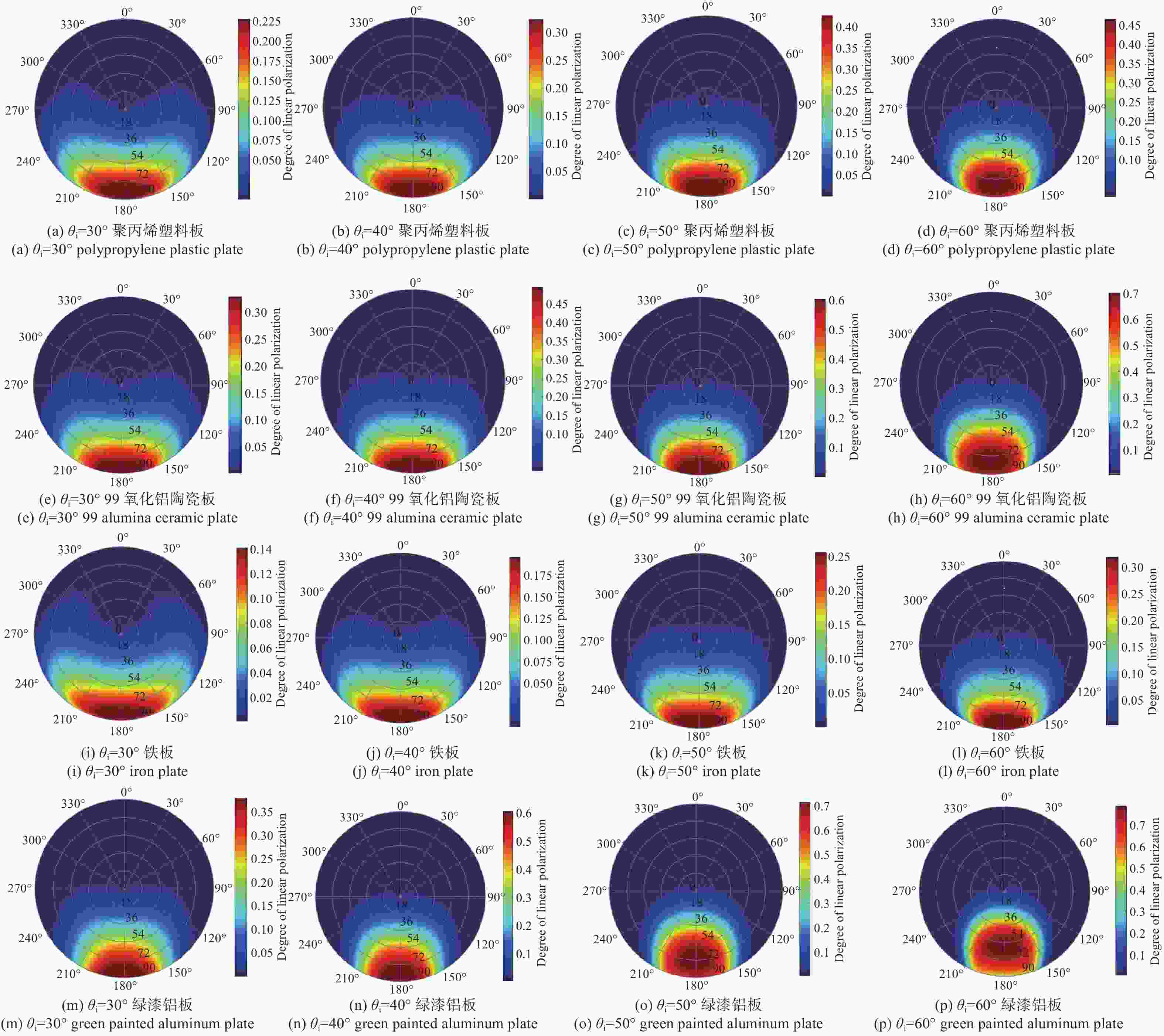
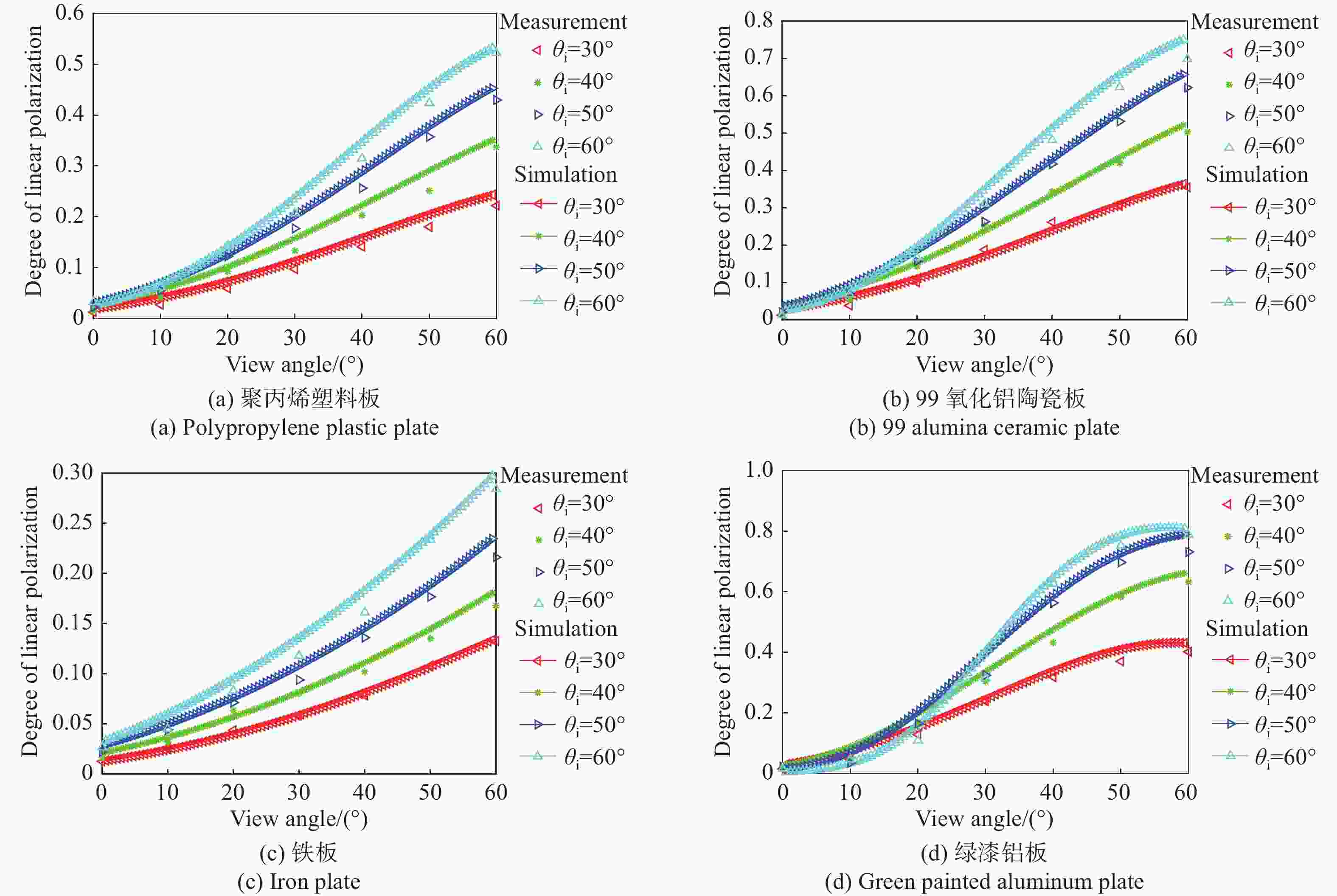
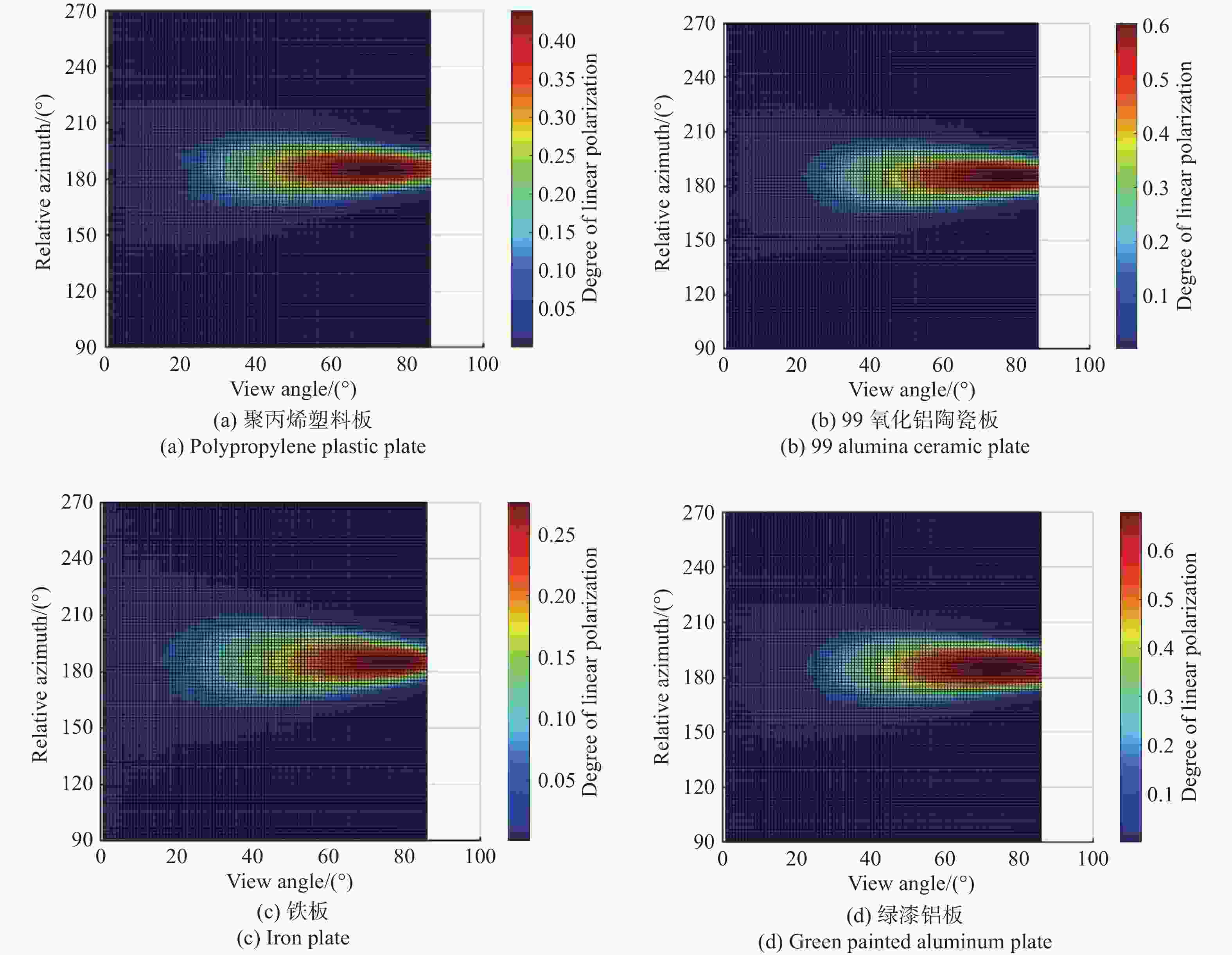
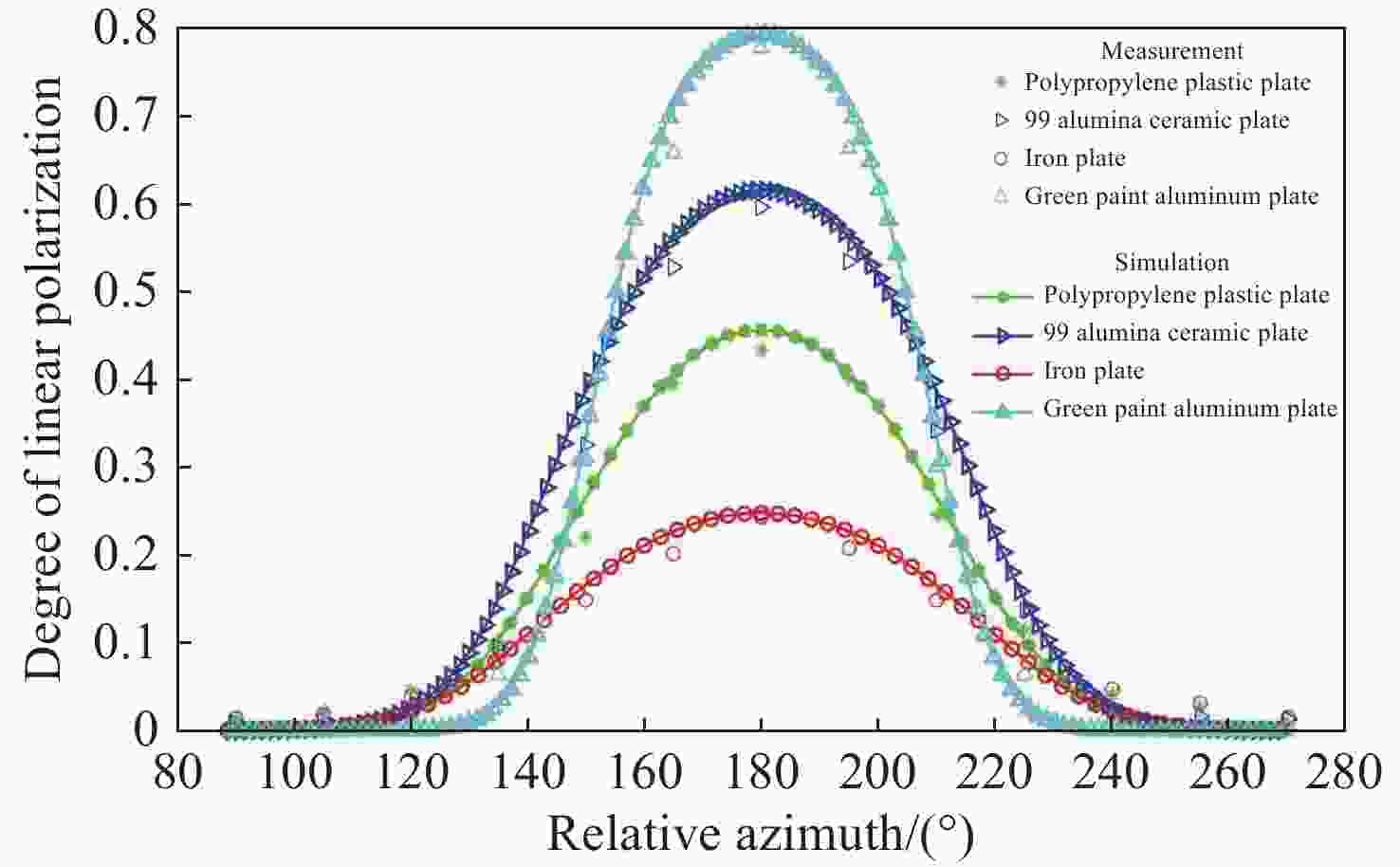
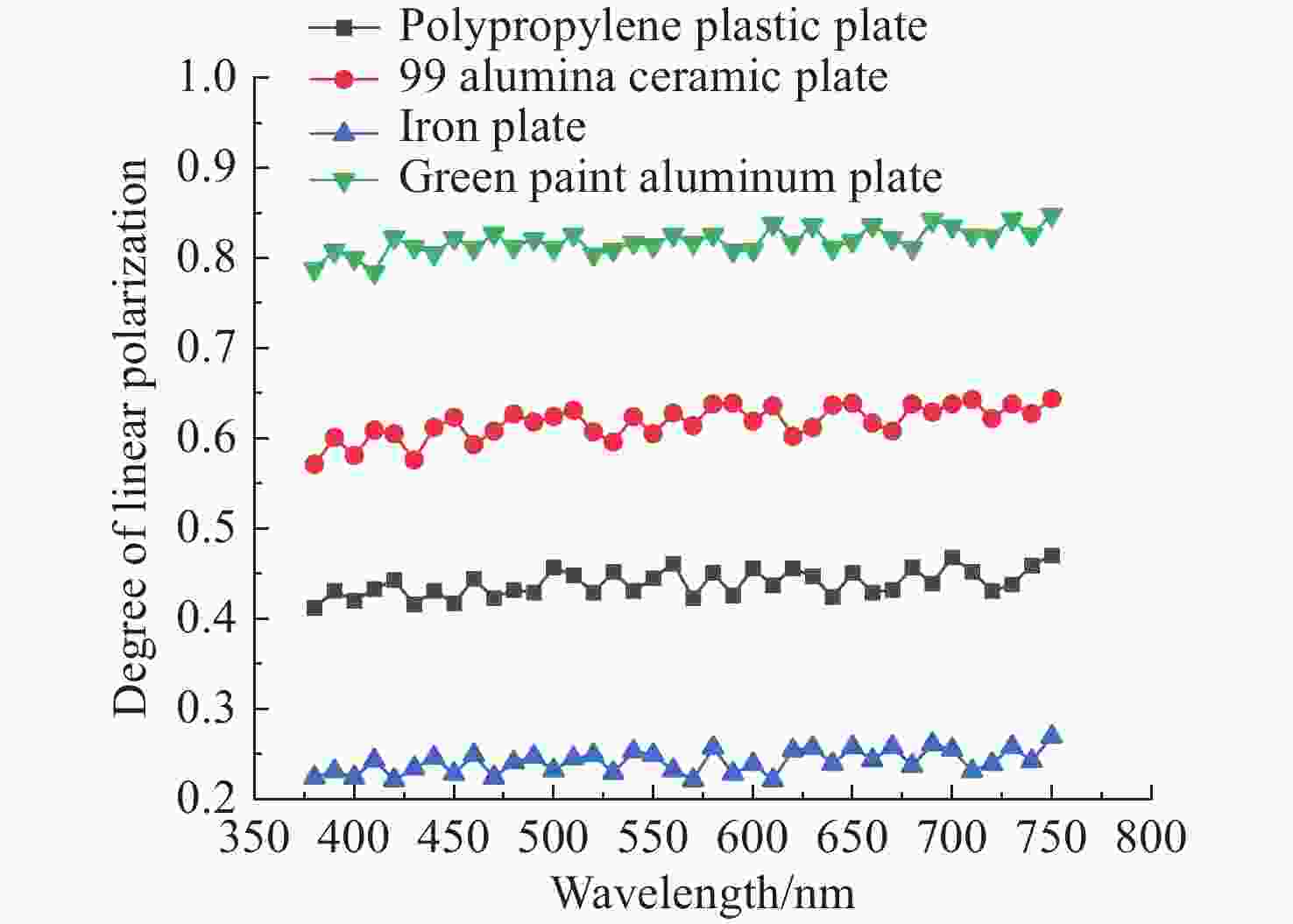
为了研究典型目标材料表面的可见光偏振反射特性,本文针对传统“V”型表面结构缺陷,引入改进Blinn型阴影遮蔽函数,综合考虑镜面反射、漫反射和体散射的影响,建立了典型目标材料表面偏振六参量双向反射分布函数模型。对不同材料(聚丙烯塑料板、99氧化铝陶瓷板、铁板、绿漆铝板)目标样板进行可见光600 nm波段的偏振特性测试实验,并采用遗传算法进行参数反演。实验与仿真结果表明:与传统“V”型遮蔽模型相比,在入射角为50°,相对方位角为180°,0°~60°观测角对目标材料表面偏振特性的影响中,聚丙烯塑料板模型精度提升最大,RMSE百分比提升了70.61%;在入射角为50°,观测角为50°,DoLP随90°~270°相对方位角变化的过程中,与另两种参考模型相比,本模型精度至少提升了24.73%,线偏振度最小均方根误差值仅为1.29%。对于本文使用材料而言,偏振特性取决于其复折射率的值,当入射角确定,观测角为0°~60°,相对方位角在0°~360°内时,
n /k 的比值越大,线偏振度峰值越大。在可见光波段,波长对线偏振度的影响不大。-
关键词:
- 偏振特性 /
- 材料表面 /
- 可见光波段 /
- 遮蔽函数 /
- 偏振双向反射分布函数
Abstract:Focusing on the visible polarization reflection characteristics of typical target materials surfaces, the polarization bidirectional reflection distribution function model based on the improved Blinn masking function was established considering the effects of specular reflection, diffuse reflection and volume scattering, which maked up for the defect of traditional "V" masking function. The physical parameters of the target materials were inverted by genetic algorithm, and the visible light polarization characteristics of four target materials, namely polypropylene, 99 alumina ceramic, iron and green painted aluminum, were simulated. Experimental tests validate the model’s accuracy. Results indicate that at an incidence angle of 50°, relative azimuth angles of 90°−270°, and detection angles of 0°−60°, the improved model reduces the root mean square error (RMSE) by 70.61% to 24.73%, with a minimum RMSE of 0.0129. Significant polarization is observed at relative azimuth angles of 120°−240°. The larger the ratio of the real part to the imaginary part of the complex refractive index of the four materials, the greater the peak value of the degree of polarization. In the visible light band, the wavelength has little effect on the degree of polarization. These findings provide theoretical data supporting the understanding of polarization characteristics in typical target materials.
-
Key words:
- polarization property /
- surface of material /
- visible wavelength /
- masking function /
- PBRDF
-
表 1 不同目标材料参数的反演结果
Table 1. Inversion results of different target material parameters
样品 参数 $n$ $ n' $ $ \sigma $ $ c $ ${\rho _0}$ ${R_\infty }$ 聚丙烯塑料板 1.471 0.698 0.325 0.552 0.517 0.6643 99氧化铝陶瓷板 1.713 0.596 0.283 0.732 0.4885 0.467 铁板 2.836 3.277 0.3612 0.485 0.568 0.6942 绿漆铝板 1.318 0.335 0.227 0.906 0.3715 0.359 表 2 在入射角为50°,相对方位角为180°时,三种模型DoLP仿真值与实测值的均方根误差
Table 2. Root mean square error of DoLP simulation values and actual measurements for three models at an incident angle of 50° and a relative azimuth angle of 180°
样品 RMSE1 RMSE2 RMSE3 百分比/% 聚丙烯塑料板 0.0936 0.0486 0.0275 70.61%43.41% 99氧化铝陶瓷板 0.0426 0.0274 0.0187 56.1%31.75% 铁板 0.0504 0.0316 0.0223 55.75%29.43% 绿漆铝板 0.0285 0.0188 0.0129 54.73%31.38% 表 3 在入射角60°,相对方位角180°时,三种模型DoLP仿真值与实测值的均方根误差
Table 3. Root mean square error of DoLP simulation values and actual measurements for three models at an incident angle of 60° and a relative azimuth angle of 180°
样品 RMSE1 RMSE2 RMSE3 百分比/% 聚丙烯
塑料板0.0831 0.0548 0.0312 62.45%
43.07%99氧化铝
陶瓷板0.0573 0.0388 0.0228 60.21%
41.23%铁板 0.0642 0.0402 0.0246 53.89%
38.81%绿漆铝板 0.0368 0.0249 0.0178 51.63%
28.51%表 4 在入射角50°,观测角50°时,三种模型DoLP仿真值与实测值的均方根误差
Table 4. Root mean square error of DoLP simulation and measurement values for three models at an incident angle of 50° and an observation angle of 50°
样品 RMSE1 RMSE2 RMSE3 百分比/% 聚丙烯
塑料板0.0613 0.0484 0.0289 52.85%
40.29%99氧化铝
陶瓷板0.0419 0.0295 0.0215 48.69%
27.12%铁板 0.0377 0.0281 0.0196 48.01%
30.24%绿漆铝板 0.0254 0.0182 0.0137 46.06%
24.73% -
[1] 丰玉强, 杜泽旭, 胡正飞. 镍含量对 熔覆镍钛合金涂层组织与性能的影响[J]. 中国 ,2022,49(8):0802022. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.0802022FENG Y Q, DU Z X, HU ZH F. Influence of Ni content on microstructure and properties of NiTi alloy coatings fabricated by laser cladding[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(8): 0802022. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.0802022 [2] 李昊, 胡德骄, 秦飞, 等. 原子层厚度超表面光场调控原理及应用[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(4):851-866. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0069LI H, HU D J, QIN F, et al. Principle and application of metasurface optical field modulation of atomic layer thickness[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(4): 851-866. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0069 [3] 刘博韬, 陈勇, 帅斌财. 锆基合金包壳管保护涂层的材料、制备及特性[J]. 机电工程技术,2023,52(1):126-128,137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9492.2023.01.030LIU B T, CHEN Y, SHUAI B C. Materials, preparation and properties of zirconium based alloy protective coatings for nuclear fuels[J]. Mechanical & Electrical Engineering Technology, 2023, 52(1): 126-128,137. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9492.2023.01.030 [4] 靳佩昕, 张兆栋, 马紫成, 等. 沉积路径对 诱导MIG增材2319铝合金的影响[J]. 中国 ,2022,49(14):1402205. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1402205JIN P X, ZHANG ZH D, MA Z CH, et al. Effect of stacking path on laser induced MIG additive 2319 aluminum alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(14): 1402205. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1402205 [5] 付强, 闫磊, 谭双龙, 等. 轻小型金属基增材制造光学系统[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(5):1019-1028. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0128FU Q, YAN L, TAN SH L, et al. Light-and-small optical systems by metal-based additive manufacturing[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(5): 1019-1028. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0128 [6] 邓光晟, 陈文卿, 余振春, 等. 基于导电塑料膜的角度不敏感宽带超材料吸波体设计及制备[J]. 光学学报,2022,42(22):2216001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.2216001DENG G SH, CHEN W Q, YU ZH CH, et al. Design and preparation of angle-insensitive broadband metamaterial absorber based on conductive plastic film[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(22): 2216001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.2216001 [7] TOBIN R, HALIMI A, MCCARTHY A, et al. Long-range depth profiling of camouflaged targets using single-photon detection[J]. Optical Engineering, 2018, 57(3): 031303. [8] 段锦, 付强, 莫春和, 等. 国外偏振成像军事应用的研究进展(上)[J]. 红外技术,2014,36(3):190-195. doi: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201403003DUAN J, FU Q, MO CH H, et al. Review of polarization imaging technology for international military application I[J]. Infrared Technology, 2014, 36(3): 190-195. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201403003 [9] 莫春和, 段锦, 付强, 等. 国外偏振成像军事应用的研究进展(下)[J]. 红外技术,2014,36(4):265-270. doi: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201404002MO CH H, DUAN J, FU Q, et al. Review of polarization imaging technology for international military application (II)[J]. Infrared Technology, 2014, 36(4): 265-270. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201404002 [10] PATTY C H L, TEN KATE I L, BUMA W J, et al. Circular spectropolarimetric sensing of vegetation in the field: possibilities for the remote detection of extraterrestrial life[J]. Astrobiology, 2019, 19(10): 1221-1229. doi: 10.1089/ast.2019.2050 [11] 王炫力, 刘爽, 谢敏, 等. 铈掺杂Y3Al5O12热障涂层陶瓷材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 中国稀土学报,2023,41(6):1119-1125.WANG X L, LIU SH, XIE M, et al. Preparation and properties of cerium doped Y3Al5O12 thermal barrier coating ceramic materials[J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2023, 41(6): 1119-1125. (in Chinese). [12] 吴玉茵, 卜铁伟, 王真. 多波段伪装隐身涂层织物的制备研究与应用[J]. 化工新型材料,2021,49(3):248-251.WU Y Y, BU T W, WANG ZH. Research on preparation and application of multi band camouflage coating fabric[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2021, 49(3): 248-251. (in Chinese). [13] 马王杰慧, 刘彦磊, 陈志影, 等. 变温下材料表面近红外双向反射分布函数的测量研究[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(5):1115-1123. doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0256MA W J H, LIU Y L, CHEN ZH Y, et al. Near-infrared BRDF of material surfaces at varying temperatures[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(5): 1115-1123. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0256 [14] VOSCHULA I V, DLUGUNOVICH V A, ZHUMAR A Y. Bidirectional reflectance distribution function of thermal control coatings and heat-shielding materials illuminated by polarized light[J]. Journal of Applied Spectroscopy, 2013, 80(2): 197-204. doi: 10.1007/s10812-013-9745-0 [15] RENHORN I G E, HALLBERG T, BOREMAN G D. Efficient polarimetric BRDF model[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(24): 31253-31273. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.031253 [16] 高明, 宋冲, 巩蕾. 基于偏振双向反射分布函数的粗糙面光散射偏振特性研究[J]. 中国 ,2013,40(12):1213002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.1213002GAO M, SONG CH, GONG L. Analysis of polarization characteristics about rough surface light scattering based on polarized bidirectional reflectance distribution function[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2013, 40(12): 1213002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.1213002 [17] 杨敏, 方勇华, 吴军, 等. 基于Kubelka-Munk理论的涂层表面多参量偏振双向反射分布函数模型[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(1):0126002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0126002YANG M, FANG Y H, WU J, et al. Multiple-component polarized bidirectional reflectance distribution function model for painted surfaces based on Kubelka-Munk theory[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(1): 0126002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0126002 [18] NICODEMUS F E, RICHMOND J C, HSIA J J, et al. Geometrical Considerations and Nomenclature for Reflectance[M]. Washington: U. S. Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards, 1977: 1-7. [19] PRIEST R G, GERMER T A. Polarimetric BRDF in the microfacet model: theory and measurements[C]. Proceedings of the 2000 Meeting of the Military Sensing Symposia Specialty Group on Passive Sensors, Infrared Information Analysis Center, 2000, 1: 169-181. [20] 刘宏, 朱京平, 王凯. 基于随机表面微面元理论的二向反射分布函数几何衰减因子修正[J]. 物理学报,2015,64(18):184213. doi: 10.7498/aps.64.184213LIU H, ZHU J P, WANG K. Modification of geometrical attenuation factor of bidirectional reflection distribution function based on random surface microfacet theory[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(18): 184213. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.64.184213 [21] MINNAERT M. The reciprocity principle in lunar photometry[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 1941, 93: 403-410. doi: 10.1086/144279 [22] LE HORS L, HARTEMANN P, DOLFI D, et al. Phenomenological model of paints for multispectral polarimetric imaging[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2001, 4370: 94-105. doi: 10.1117/12.440065 [23] 于婷, 战俊彤, 马莉莉, 等. 椭球形粒子浓度对 偏振传输特性的影响[J]. 中国 ,2019,46(2):0208002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0208002YU T, ZHAN J T, MA L L, et al. Effect of ellipsoidal particle concentration on laser polarization transmission characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2019, 46(2): 0208002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0208002 [24] 韦顺. 红外偏振成像特性分析[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2020.WEI SH. Analysis of infrared polarization imaging characteristics[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2020. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: