Characteristics of a distributed feedback diode laser with feedback from a fiber-Bragg-grating-based long external cavity
-
摘要:
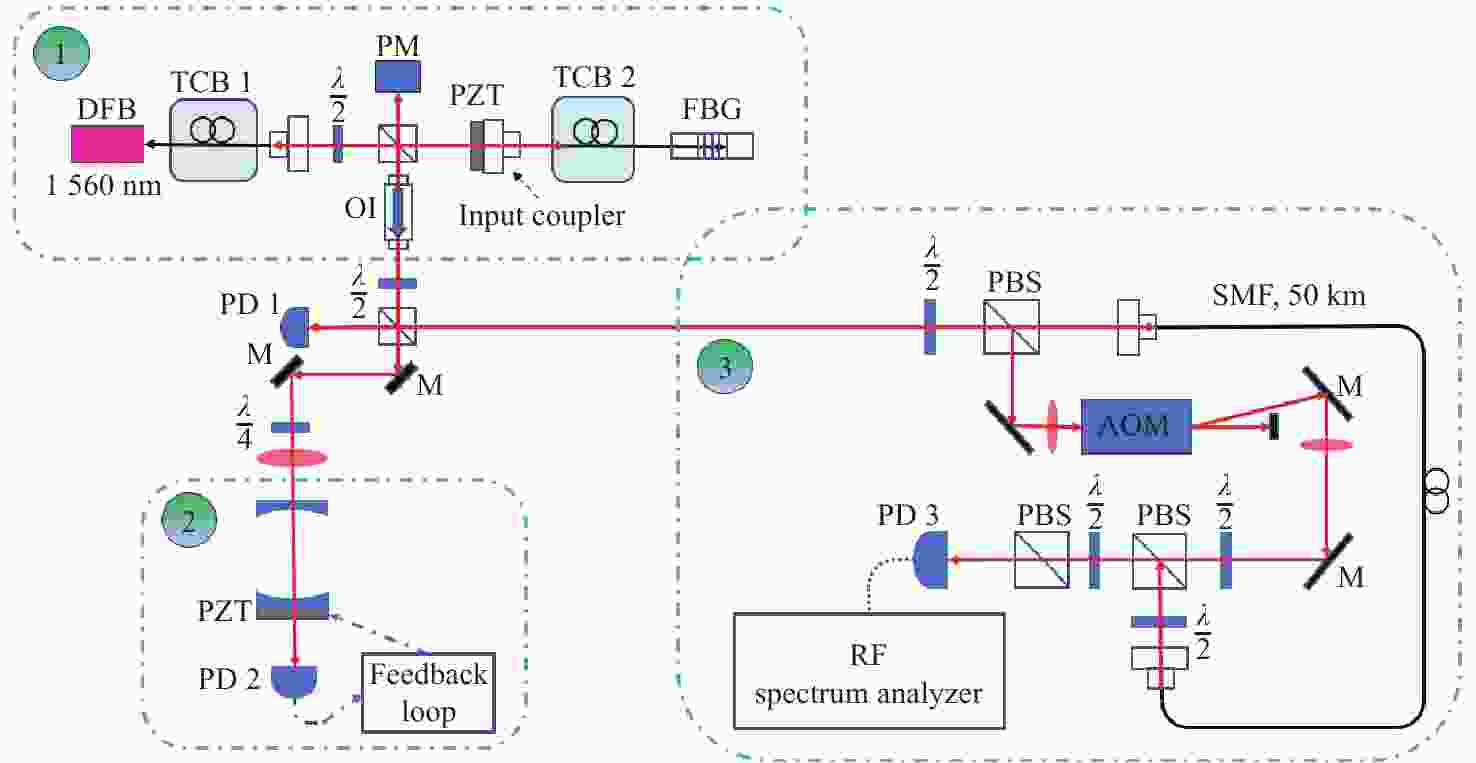
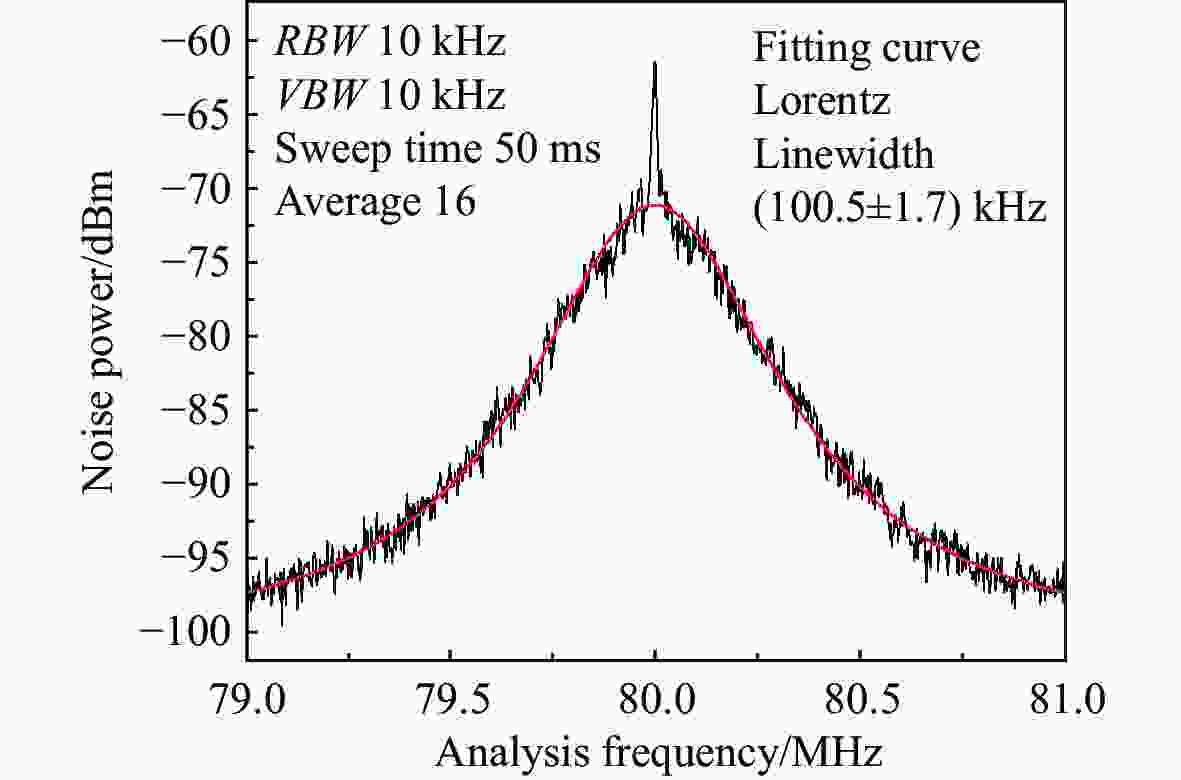
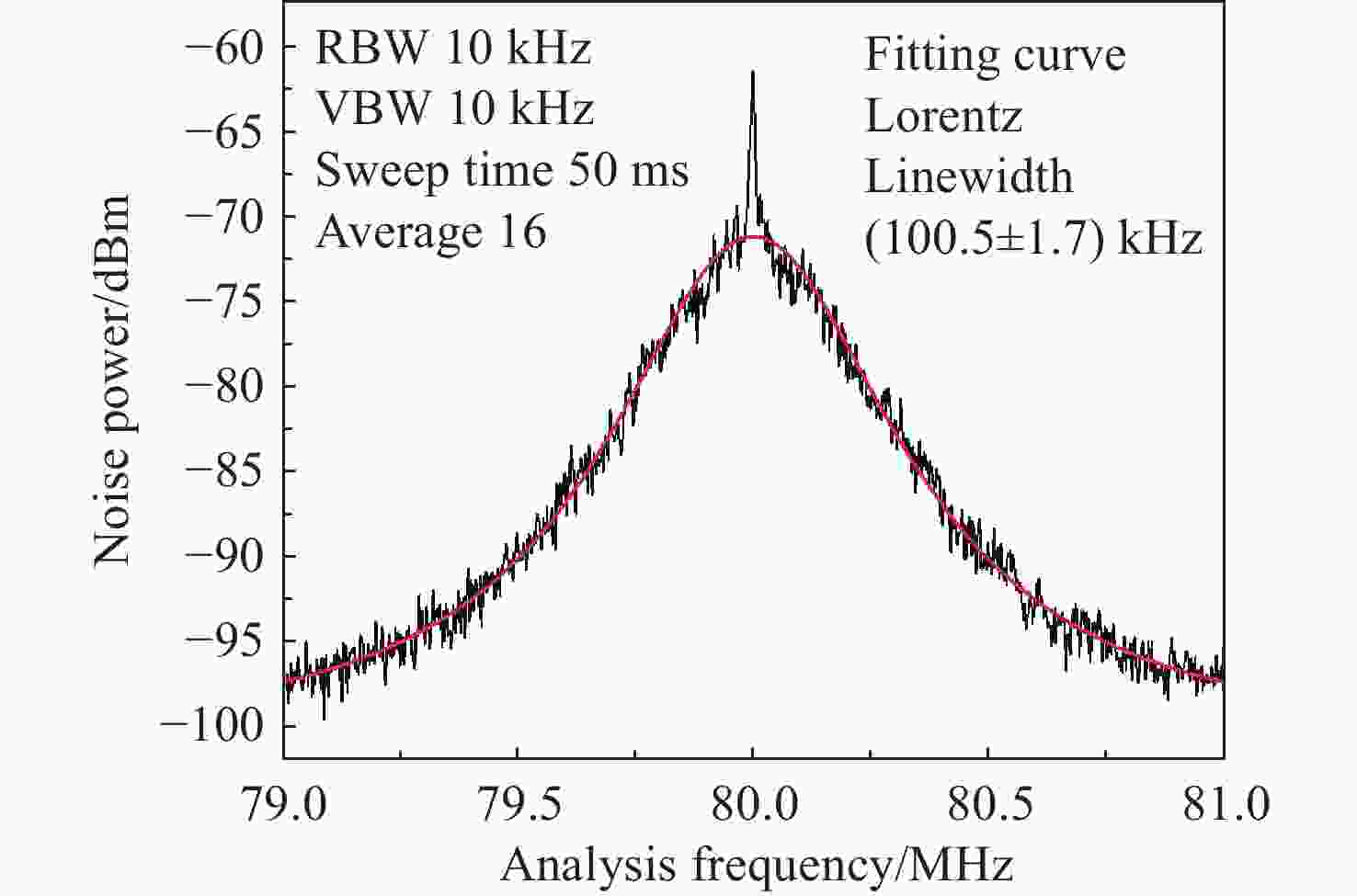
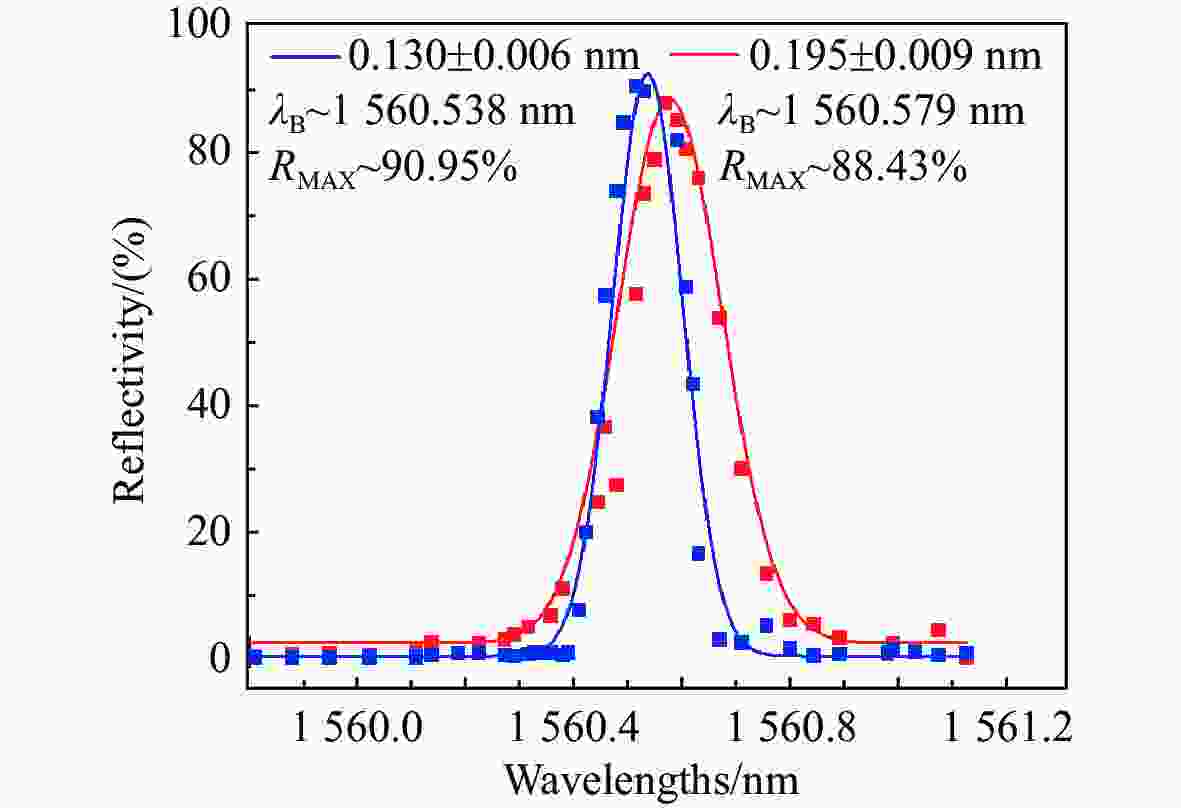
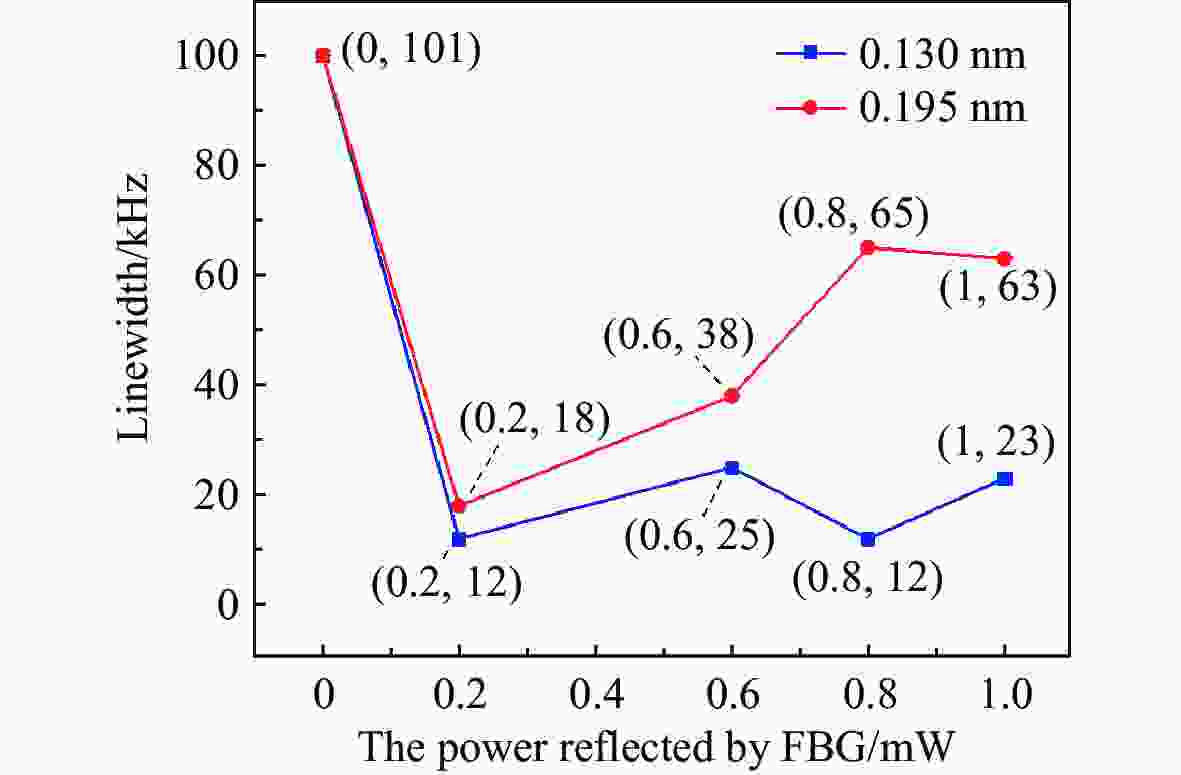
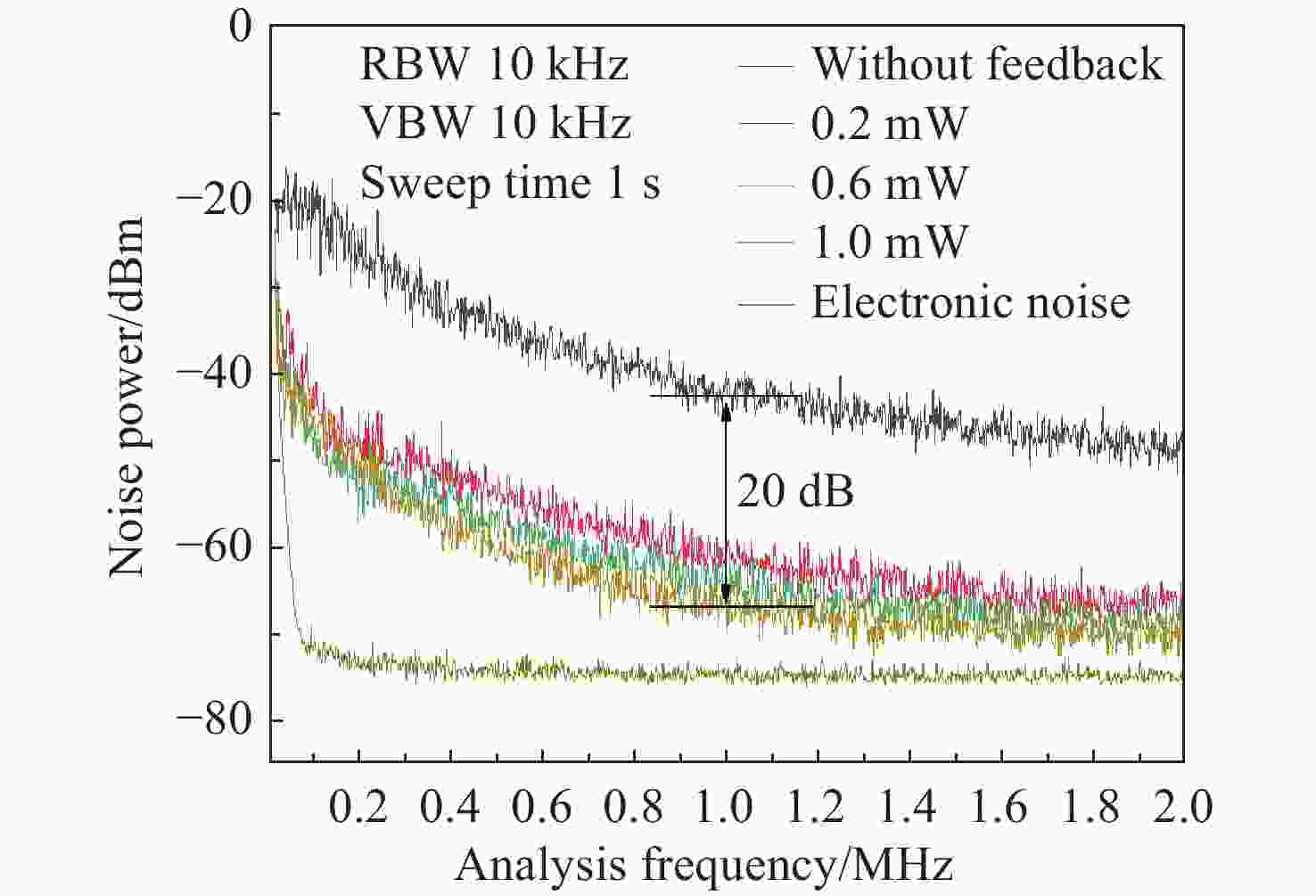
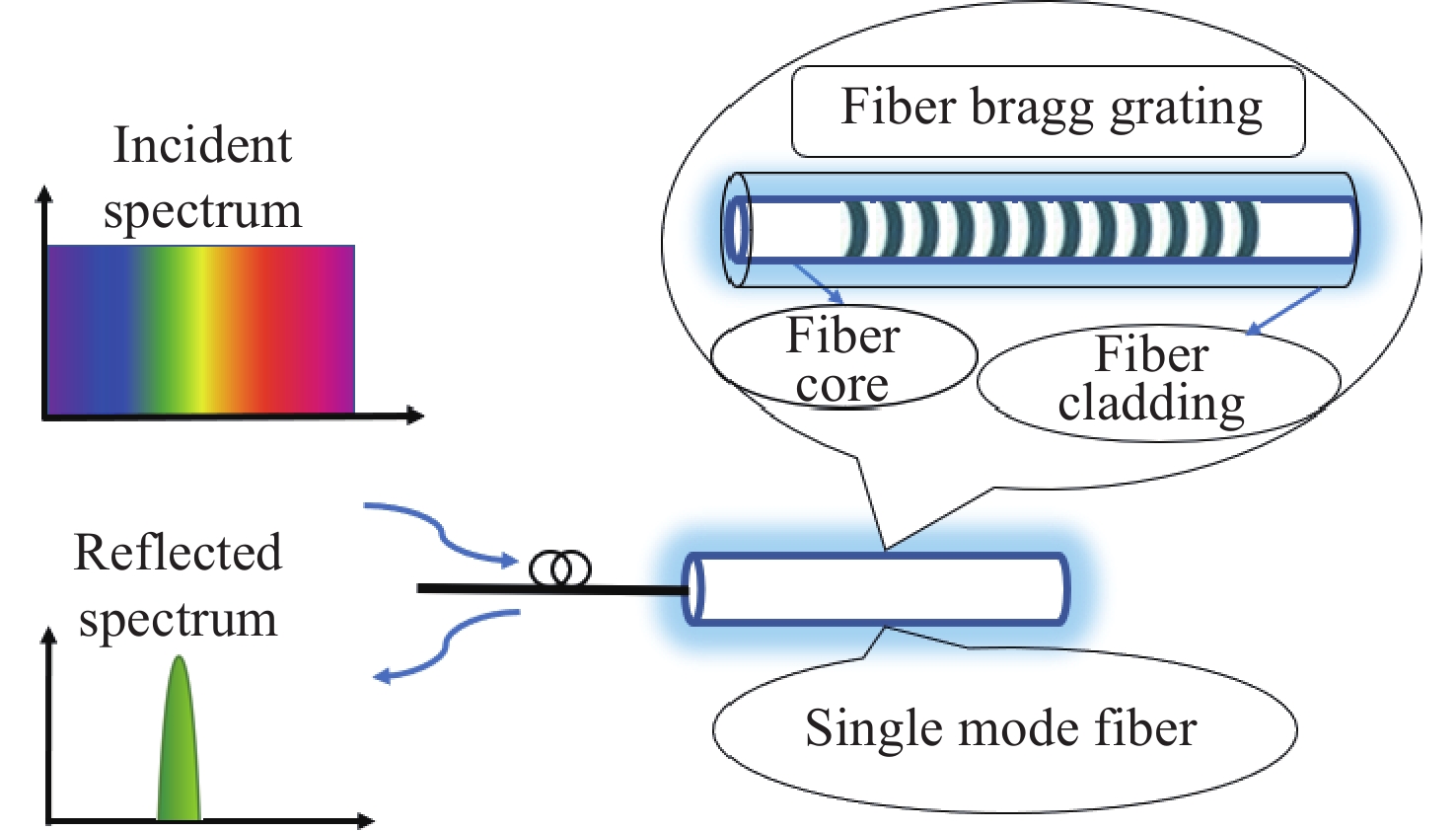
窄线宽 器是光谱学和精密计量学等实验的基本组成部分。由于半导体 器对外部光学反馈十分敏感,所以可以利用光反馈的高带宽抑制半导体 器的相位噪声,进而压窄线宽。本文采用光纤布拉格光栅作为反馈元件,搭建了长外腔反馈回路。为了降低外界环境温度起伏和气流扰动的影响,对反馈光路的光纤控温,使得1小时内最大温度起伏从0.039 °C降低到0.003 °C。此外,测试了反馈带宽对 线宽的影响,尽管实验所用光纤布拉格光栅的带宽远大于自由运转的 线宽,但仍然可以观察到 线宽被压窄,且光纤光栅的带宽越小, 线宽越窄。对于此现象,分析认为在反馈回路中应该存在一种负反馈机制,可以将 线宽稳定到反馈光谱的某个斜率处,所以光纤光栅的反馈带宽越窄,反馈光谱的斜率越大,反馈越灵敏。通过调整光纤光栅的反馈功率在0~1 mW范围内改变,观察到当反射功率为0.8 mW时,光反馈将 线宽从自由运转的100.5 kHz压窄到最窄的11.5 kHz,0.2 kHz~2 MHz范围内的相位噪声降低约20 dB。
Abstract:Narrow linewidth lasers are the basic components of spectroscopy, precision metrology, and other experiments. Because diode lasers are very sensitive to external optical feedback, the phase noise of diode lasers, can be suppressed by using a high optical feedback bandwidth, enabling the narrowing of the linewidth. In the paper, we use fiber Bragg grating (FBG) as a feedback element and builds a long external cavity feedback loop. In order to reduce the influence of temperature fluctuation of external environment and air flow disturbance, the temperature of the optical fiber is controlled. Then, the maximum temperature fluctuation within 1 hour is reduced from 0.039 °C to 0.003 °C. In addition, the effect of feedback bandwidth on laser linewidth is also tested. Although the bandwidth of the FBG used in the experiment is much larger than the free-running laser linewidth, a narrowing of the laser linewidth is still observed. The smaller the FBG bandwidth, the narrower the laser linewidth. For this phenomenon, we believe that there should be a negative feedback mechanism in the feedback loop, which can stabilize the laser linewidth to a certain slope of the feedback spectrum. Therefore the narrower the feedback bandwidth of the fiber grating, the larger the slope of the feedback spectrum, and the more sensitive the feedback. In addition, by changing the feedback power of FBG in the range of 0~1 mW, it is observed that at the reflected power of 0.8 mW, the optical feedback narrows the laser linewidth from the free-running 100.5 kHz to the narrowest 11.5 kHz, and phase noise in the range of 0.2 kHz to 2 MHz is reduced by about 20 dB.
-
-
[1] LIN Q, VAN CAMP M A, ZHANG H, et al. Long-external-cavity distributed Bragg reflector laser with subkilohertz intrinsic linewidth[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(11): 1989-1991. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.001989 [2] KAPASI D P, EICHHOLZ J, MCRAE T, et al. Tunable narrow-linewidth laser at 2 μm wavelength for gravitational wave detector research[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(3): 3280-3288. doi: 10.1364/OE.383685 [3] ZHAO Y, LI Y, WANG Q, et al. 100-Hz linewidth diode laser with external optical feedback[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2012, 24(20): 1795-1798. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2012.2214029 [4] 刘云凤, 梁伟. 自注入锁定外腔超窄线宽半导体 [J]. 中国 ,2021,48(17):1715001. doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.1715001LIU Y F, LIANG W. Compact narrow linewidth external cavity semiconductor laser realized by self-injection locking to Fabry-Perot cavity[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48(17): 1715001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.1715001 [5] RAUCH S, SACHER J. Compact Bragg grating stabilized ridge waveguide laser module with a power of 380 mW at 780 nm[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2015, 27(16): 1737-1740. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2015.2438545 [6] KONG J, LUCIVERO V G, JIMÉNEZ-MARTÍNEZ R, et al. Long-term laser frequency stabilization using fiber interferometers[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2015, 86(7): 073104. doi: 10.1063/1.4926345 [7] 潘碧玮, 余力强, 陆丹, 等. 20 kHz窄线宽光纤光栅外腔半导体 器[J]. 中国 ,2015,42(5):0502007. doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.0502007PAN B W, YU L Q, LU D, et al. 20 kHz narrow linewidth Fiber Bragg grating external cavity semiconductor laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(5): 0502007. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.0502007 [8] 孙广伟, 魏芳, 张丽, 等. 基于保偏光纤光栅的低噪声外腔半导体 器[J]. 中国 ,2018,45(6):0601004. doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.0601004SUN G W, WEI F, ZHANG L, et al. Low-noise external cavity semiconductor lasers based on polarization-maintaining fiber Bragg gratings[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(6): 0601004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.0601004 [9] SAMUTPRAPHOOT P, WEBER S, LIN Q, et al. Passive intrinsic-linewidth narrowing of ultraviolet extended-cavity diode laser by weak optical feedback[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(10): 11592-11599. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.011592 [10] HILL K O, FUJII Y, JOHNSON D C, et al. Photosensitivity in optical fiber waveguides: Application to reflection filter fabrication[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1978, 32(10): 647-649. doi: 10.1063/1.89881 [11] 白建东, 王杰英, 王军民. 基于光纤延时声光频移自差拍法快速测量 线宽[J]. 与光电子学进展,2016,53(6):061407.BAI J D, WANG J Y, WANG J M. Rapid measurement of laser linewidth based on Fiber-Delayed AOM-shifted self-heterodyne scheme[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2016, 53(6): 061407. (in Chinese). [12] 尹增谦, 武臣, 宫琬钰, 等. Voigt线型函数及其最大值的研究[J]. 物理学报,2013,62(12):123301. doi: 10.7498/aps.62.123301YIN Z Q, WU CH, GONG W Y, et al. Voigt profile function and its maximum[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(12): 123301. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.62.123301 [13] HENRY C. Phase noise in semiconductor lasers[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 1986, 4(3): 298-311. doi: 10.1109/JLT.1986.1074721 [14] AOYAMA K, YOKOTA N, YASAKA H. Strategy of optical negative feedback for narrow linewidth semiconductor lasers[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(16): 21159-21169. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.021159 [15] 齐翔羽. 窄线宽半导体 器相频噪声和线宽特性研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2019.QI X Y. Research on phase-frequency noise and linewidth characteristics of narrow linewidth semiconductor laser[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese). [16] 张云, 张天才, 李廷鱼, 等. 法布里-珀罗腔对相位噪声测量的影响[J]. 光学学报,2000,20(4):465-471.ZHANG Y, ZHANG T C, LI T Y, et al. Phase noise measurement by F-P cavity[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2000, 20(4): 465-471. (in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: