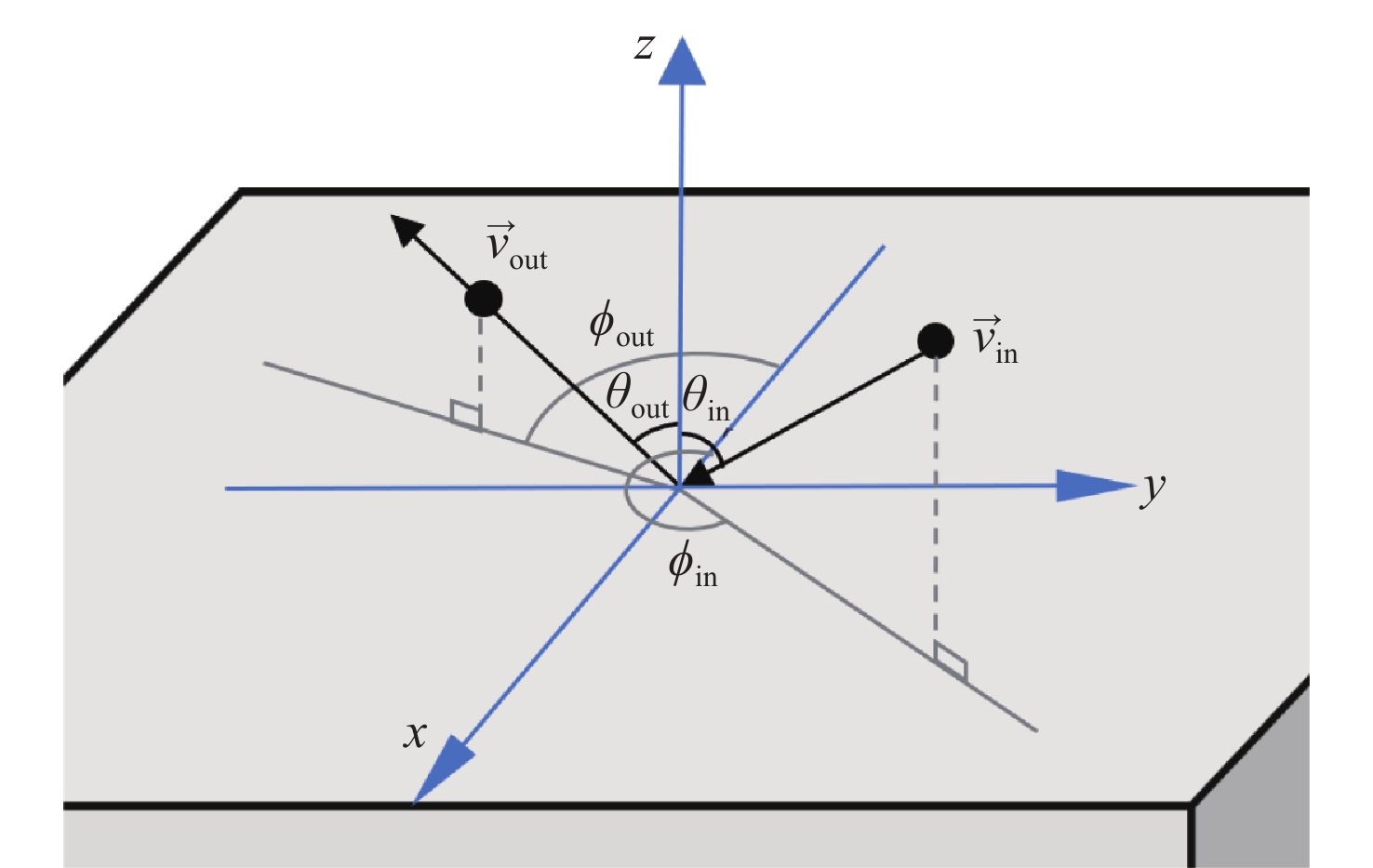
Simulation of residual gas noise in high-precision inertial sensors with optical readout
-
摘要:
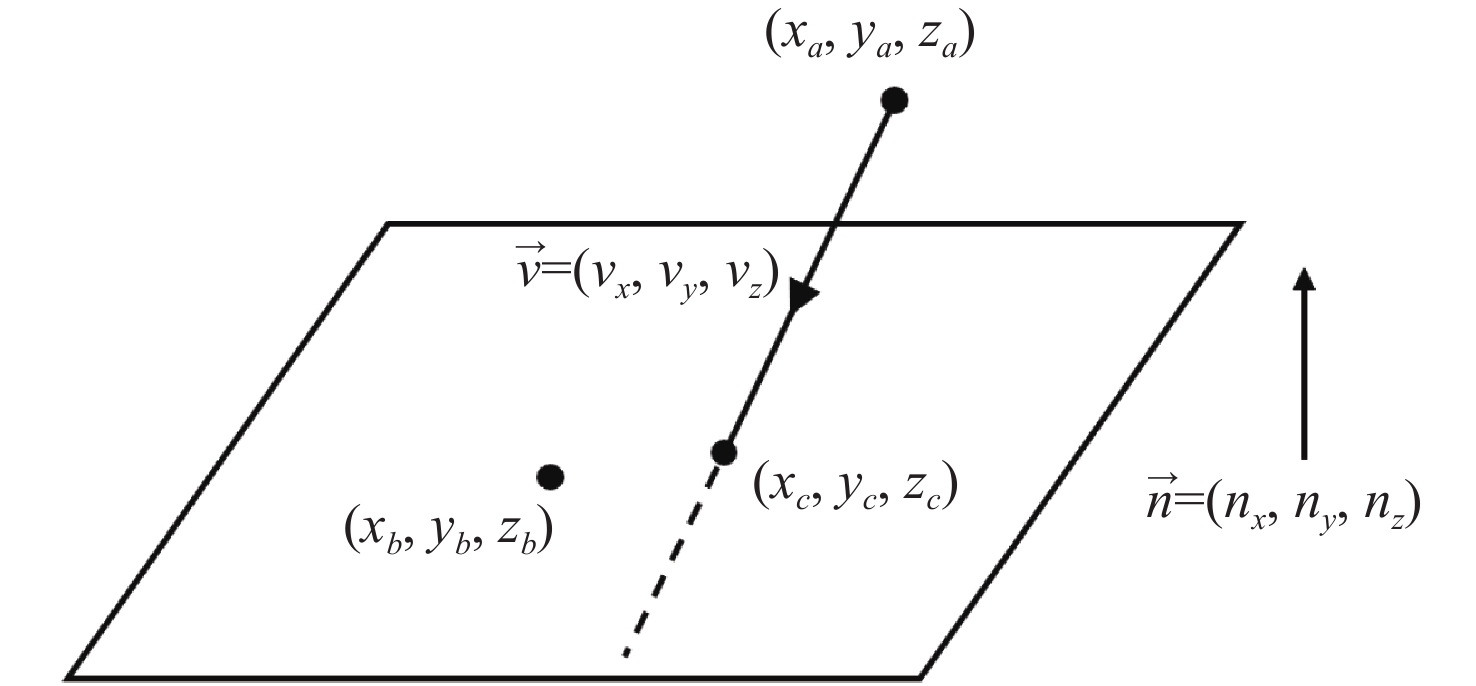
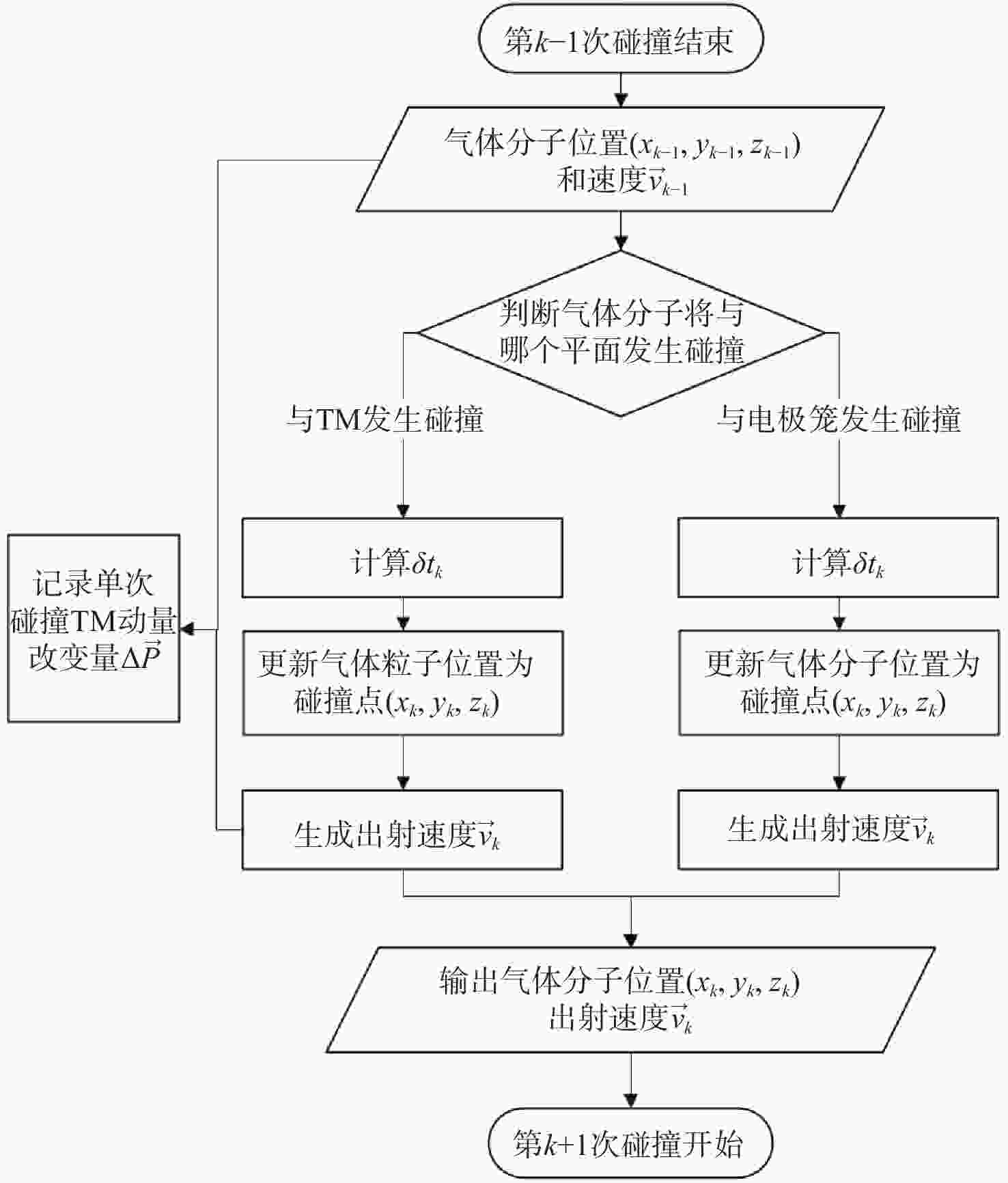
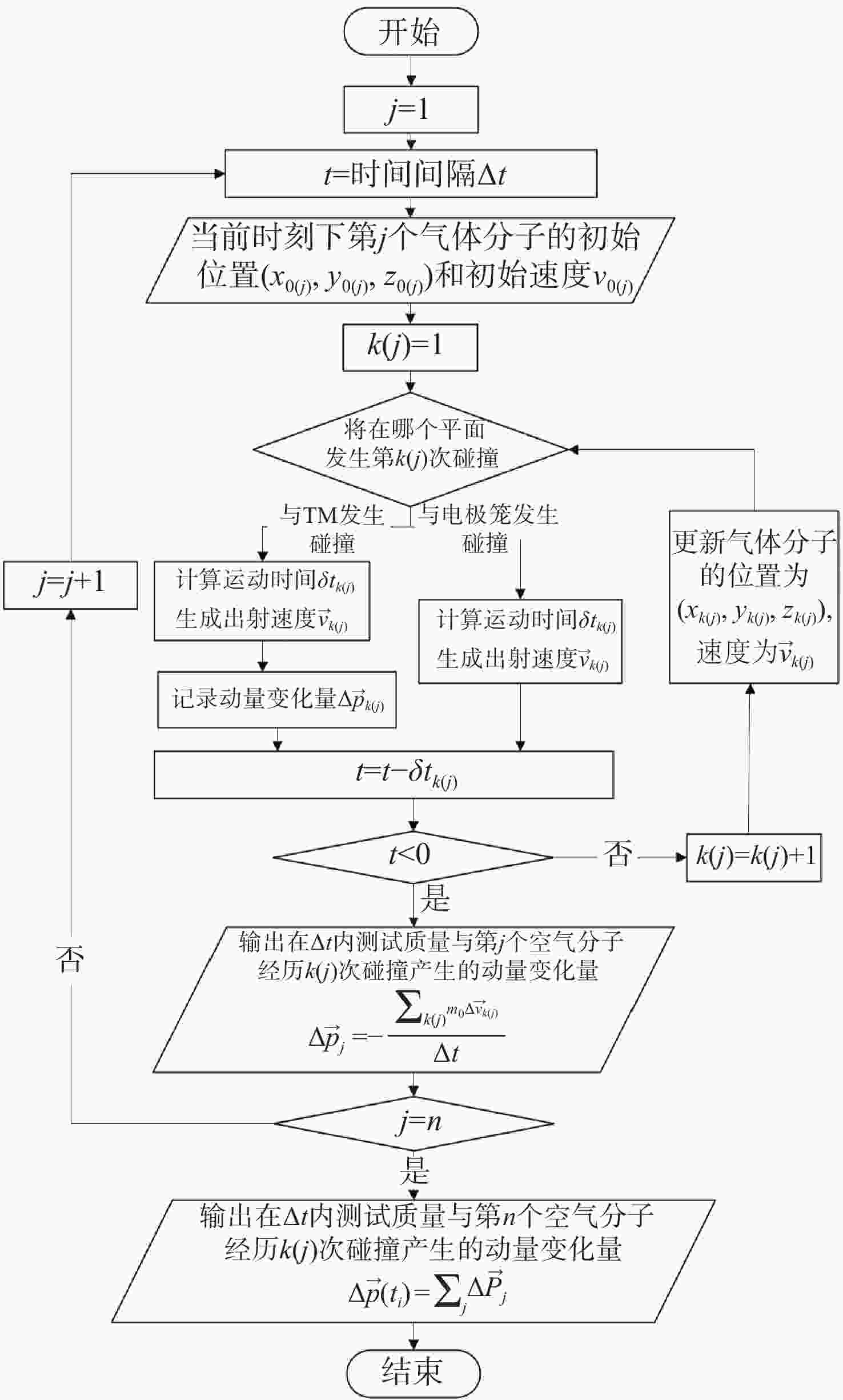
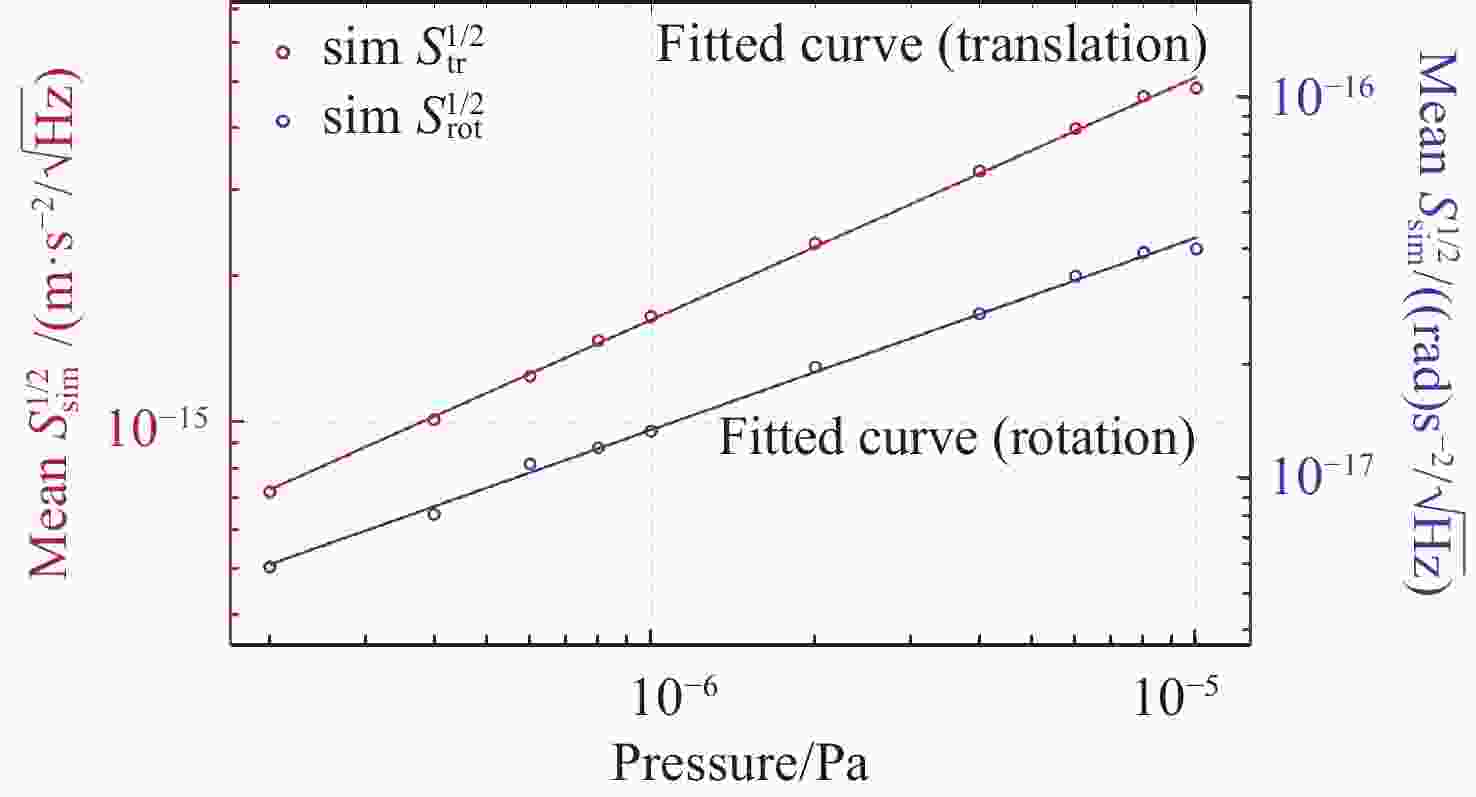
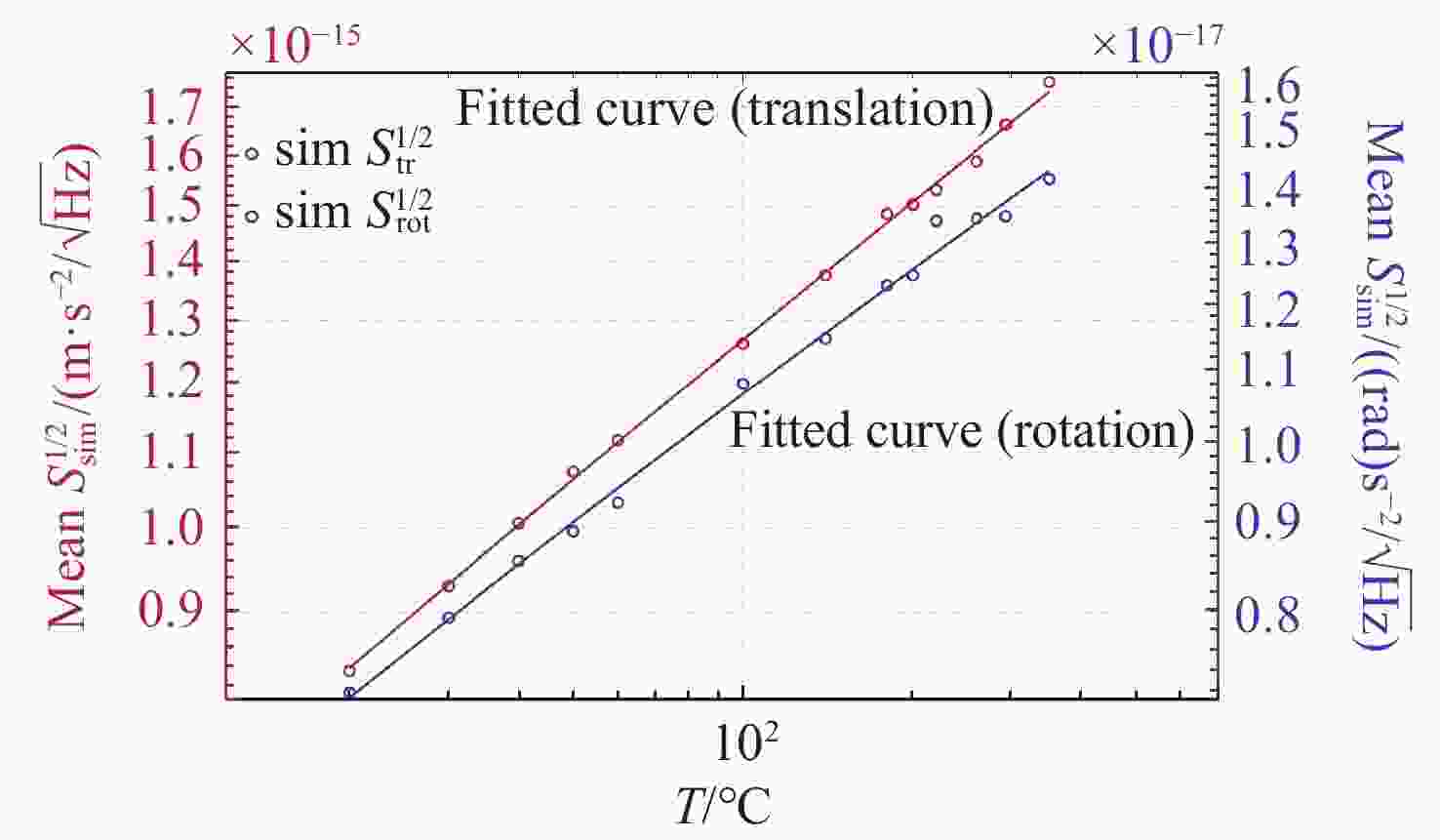
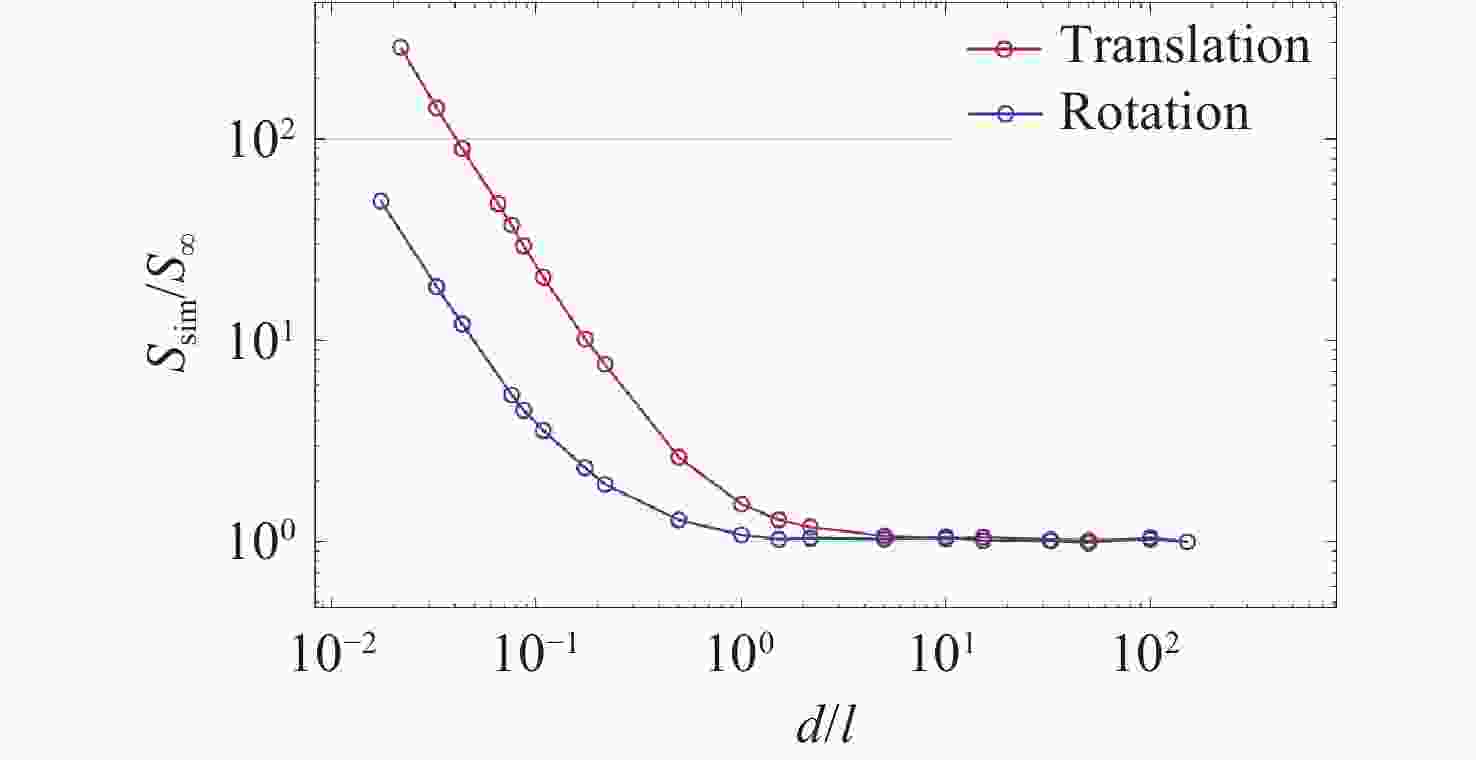
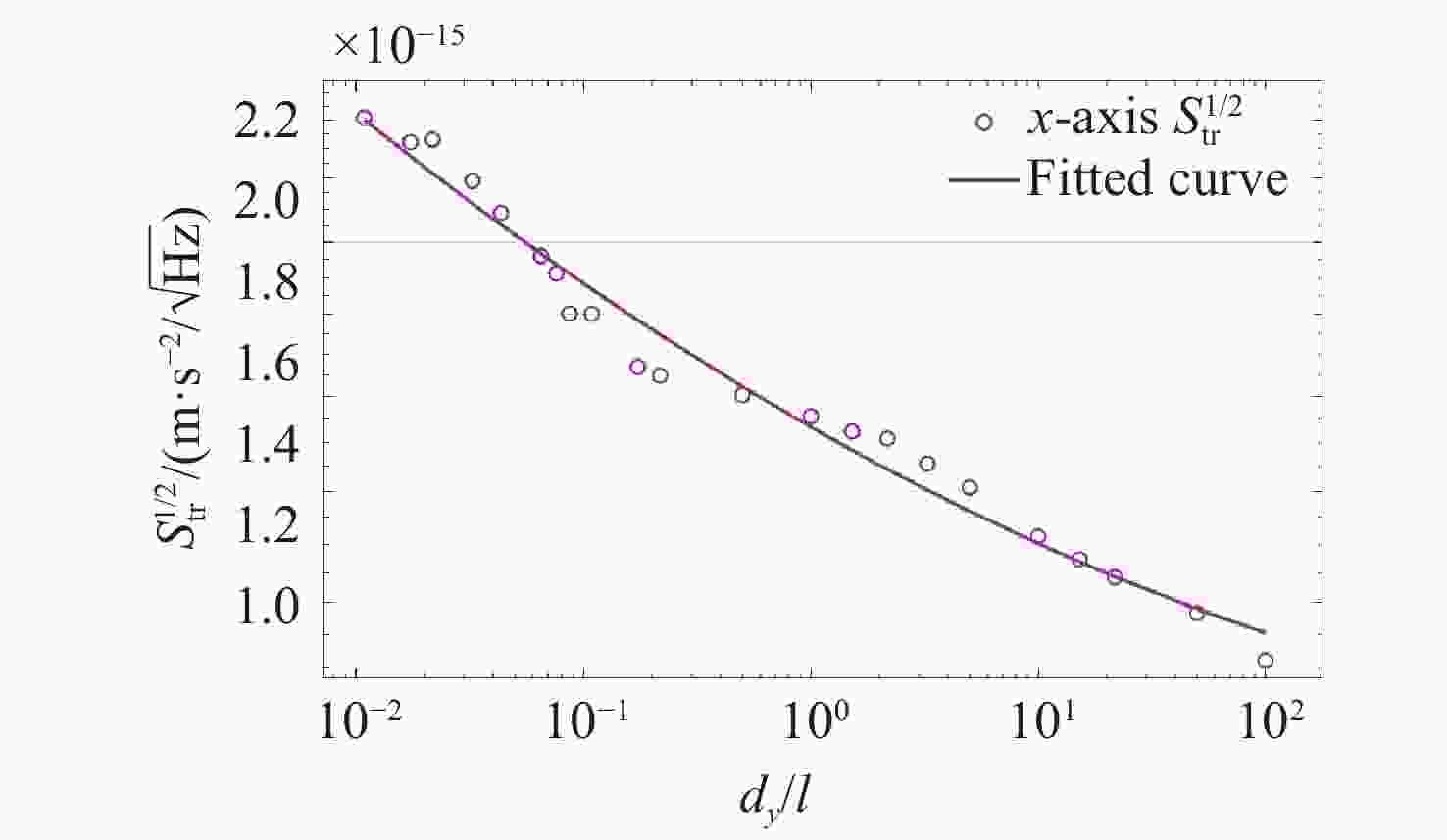
高精度惯性传感器在航天、导航和精密测量等领域具有广泛的应用前景,对其噪声进行高精度评估具有重要意义。本文提出了一种基于Ray Tracing技术的残气噪声仿真方法。首先,基于真实的惯性传感器模型,模拟在轨条件下残余气体在惯性传感器电极笼中的运动,获得残气加速度噪声的统计特性;其次,探究了不同压强和温度对残余气体噪声的影响;最后,分析了敏感轴的残余气体噪声对非敏感轴的间隙大小的依赖关系。仿真结果表明:利用Ray Tracing技术能够模拟追踪残余气体与敏感结构相互作用过程,实现残气加速度噪声在
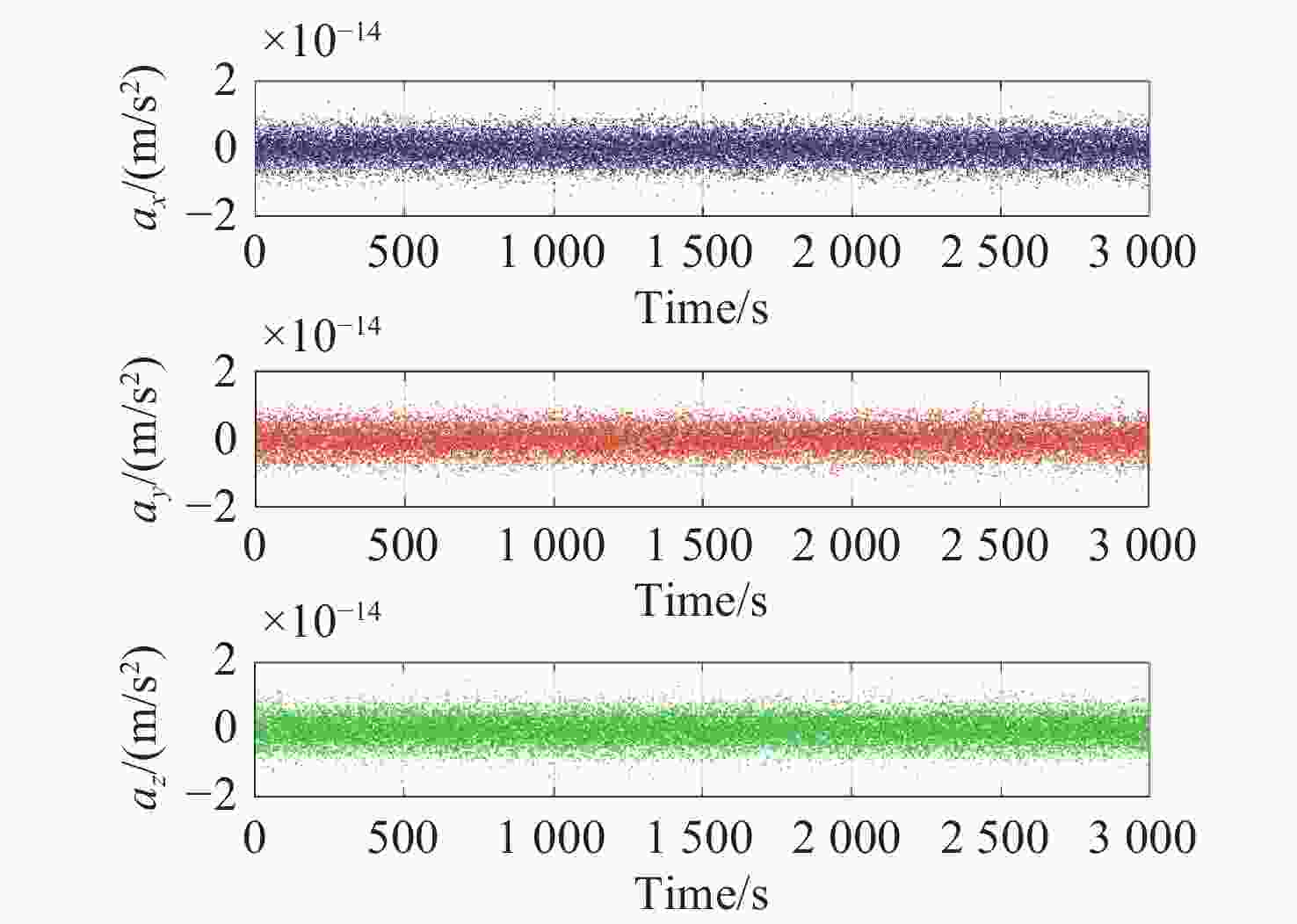
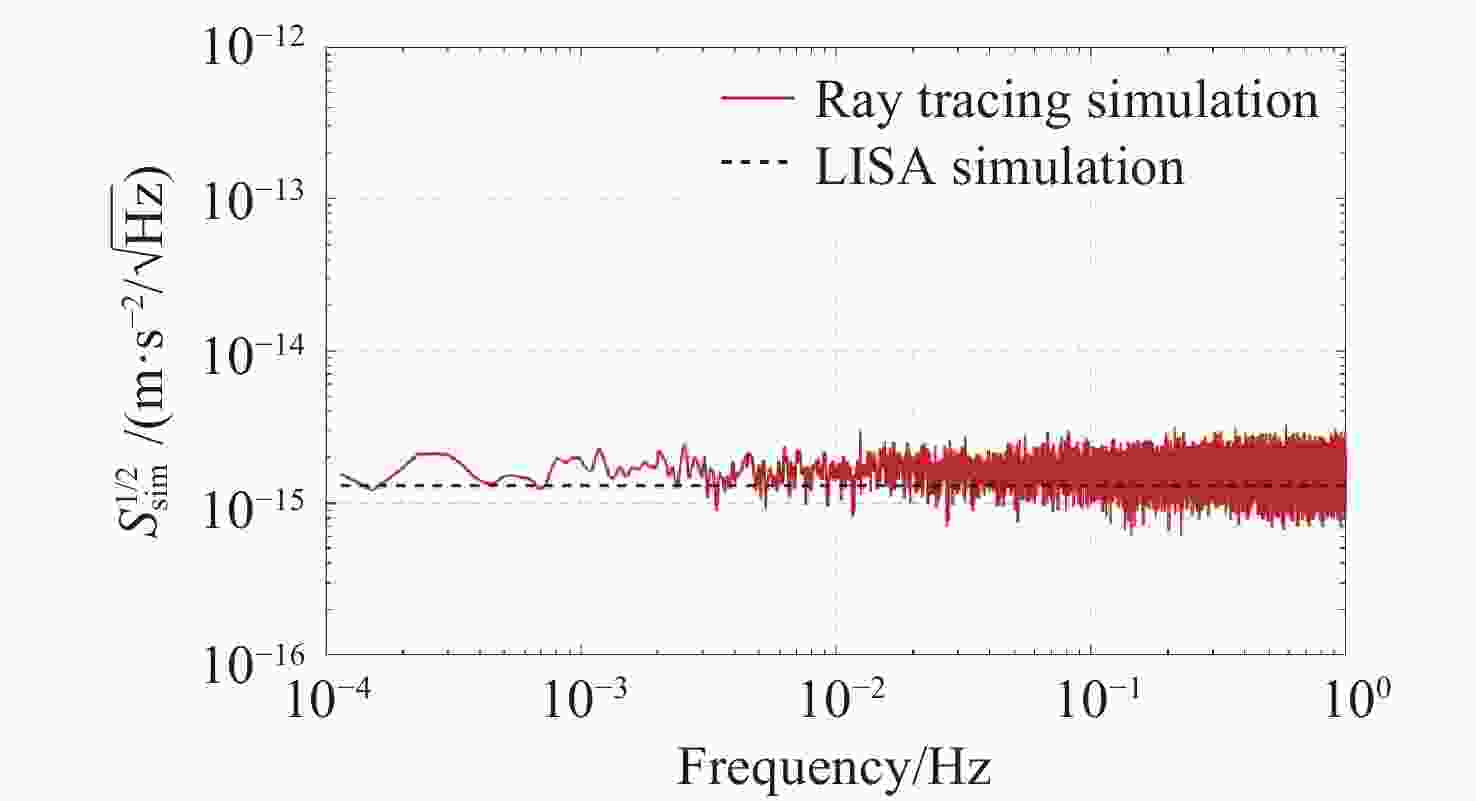
$ {10}^{-15} $ 量级的高精度仿真。温度和压强对残气加速度噪声水平具有显著影响,且电极笼与测试质量的间隙减小将导致惯性传感器残气噪声功率谱增大。Abstract:High-precision inertial sensors have broad application prospects in fields such as aerospace, navigation, and precision measurement. However, the accurate evaluation of noise in these sensors is imperative for optimal performance, with residual gas noise being a significant source of noise in inertial sensors. The current methods for calculating the level of residual gas noise lack numerical simulations based on the actual structure of inertial sensors, which hinders the ability to meet the demands of high-precision noise analysis. This paper proposes a novel residual gas noise simulation method based on ray tracing technology. Firstly, the method simulates the trajectories of residual gas inside the electrode cage of the inertial sensor under orbital conditions using a real inertial sensor model to obtain the statistical characteristics of the residual gas acceleration noise. Secondly, the influence of different pressures and temperatures on the residual gas noise is investigated. Finally, the dependence of the residual gas noise on the gap size of the non-sensitive axis is analyzed. The simulation results demonstrate the efficacy of Ray Tracing technology in simulating and tracking the interaction between the residual gas and the sensitive structures, achieving a high-precision simulation of residual gas acceleration noise at the level of 10−15. Temperature and pressure have been shown to significantly affect the level of residual gas acceleration noise, and reducing the gap between the electrode cage and the test mass will increase the power spectrum of the residual gas noise in the inertial sensor.
-
Key words:
- space-based gravitational wave detection /
- inertial sensor /
- residual noise /
- ray tracing
-
-
[1] AHARONI J. The Special Theory of Relativity[J]. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1959. [2] HOGAN C J. Gravitational wave sources from new physics[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2006, 873(1): 30-40. [3] SCHILLING G. Ripples in Spacetime: Einstein, Gravitational Waves, and the Future of Astronomy[M]. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2017. [4] WU Y L, HU W R, WANG J Y, et al. Review and scientific objectives of spaceborne gravitational wave detection missions[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2023, 43(4): 589-599. doi: 10.11728/cjss2023.04.yg08 [5] WANNER G. Space-based gravitational wave detection and how LISA pathfinder successfully paved the way[J]. Nature Physics, 2019, 15(3): 200-202. doi: 10.1038/s41567-019-0462-3 [6] ARAÚJO H, BOATELLA C, CHMEISSANI M, et al. LISA and LISA PathFinder, the Endeavour to detect low frequency GWs[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2007, 66: 012003. [7] EINSTEIN A, ROSEN N. On gravitational waves[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 1937, 223(1): 43-54. doi: 10.1016/S0016-0032(37)90583-0 [8] WANNER G. Complex optical systems in space: numerical modelling of the heterodyne interferometry of LISA Pathfinder and LISA[D]. Hannover: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität Hannover, 2010. [9] DANZMANN K, PRINCE T A, BINETRUY P, et al. LISA: unveiling a hidden universe[R]. Assessment Study Report ESA/SRE, 2011, 3(2). [10] SALA L. Residual test mass acceleration in LISA Pathfinder: in-depth statistical analysis and physical sources[D]. Trento: University of Trento, 2023. [11] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, AUGER G, et al. Sub-femto-g free fall for space-based gravitational wave observatories: LISA pathfinder results[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016, 116(23): 231101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.231101 [12] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. Beyond the required LISA free-fall performance: new LISA pathfinder results down to 20 μ Hz[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(6): 061101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.061101 [13] ZHANG H Y, XU P, YE Z Q, et al. A systematic approach for inertial sensor calibration of gravity recovery satellites and its application to Taiji-1 mission[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(15): 3817. doi: 10.3390/rs15153817 [14] BADARACCO F, VAN HEIJNINGEN J V, FERREIRA E, et al. A cryogenic and superconducting inertial sensor for the lunar gravitational–wave antenna, the Einstein telescope and selene-physics[C]. The Sixteenth Marcel Grossmann Meeting on Recent Developments in Theoretical and Experimental General Relativity, Astrophysics and Relativistic Field Theories: Proceedings of the MG16 Meeting on General Relativity Online; 5-10 July 2021, World Scientific, 2023: 3245-3253. [15] BERMÚDEZ A, HERVELLA-NIETO L, RODRÍGUEZ R. Finite element computation of the vibrations of a plate-fluid system with interface damping[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2001, 190(24-25): 3021-3038. doi: 10.1016/S0045-7825(00)00380-7 [16] CHRISTIAN R G. The theory of oscillating-vane vacuum gauges[J]. Vacuum, 1966, 16(4): 175-178. doi: 10.1016/0042-207X(66)91162-6 [17] BAO M H, YANG H, YIN H, et al. Energy transfer model for squeeze-film air damping in low vacuum[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2002, 12(3): 341-346. doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/12/3/322 [18] SUIJLEN M A G, KONING J J, VAN GILS M A J, et al. Squeeze film damping in the free molecular flow regime with full thermal accommodation[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2009, 156(1): 171-179. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2009.03.025 [19] DOLESI R, HUELLER M, NICOLODI D, et al. Brownian force noise from molecular collisions and the sensitivity of advanced gravitational wave observatories[J]. Physical Review D, 2011, 84(6): 063007. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.84.063007 [20] ZHAO Y J, LI G L, LIU L, et al. Experimental verification of and physical interpretation for adsorption-dependent squeeze-film damping[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2023, 19(4): 044005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.19.044005 [21] HUELLER M, CAVALLERI A, DOLESI R, et al. Torsion pendulum facility for ground testing of gravitational sensors for LISA[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2002, 19(7): 1757-1765. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/19/7/372 [22] HOLLINGTON D. The charge management system for LISA and LISA Pathfinder[D]. London: Imperial College London, 2011. [23] 同济学应用数学系. 高等数学(下册)[M]. 5版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2002.Tongji University Department of Applied Mathematics. Higher Mathematics (Volume Two)[M]. 5th ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2002. [24] CAVALLERI A, CIANI G, DOLESI R, et al. Increased Brownian force noise from molecular impacts in a constrained volume[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(14): 140601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.140601 -






 下载:
下载: