Optimization design method for counter-rotating prisms atmospheric dispersion corrector
-
摘要:
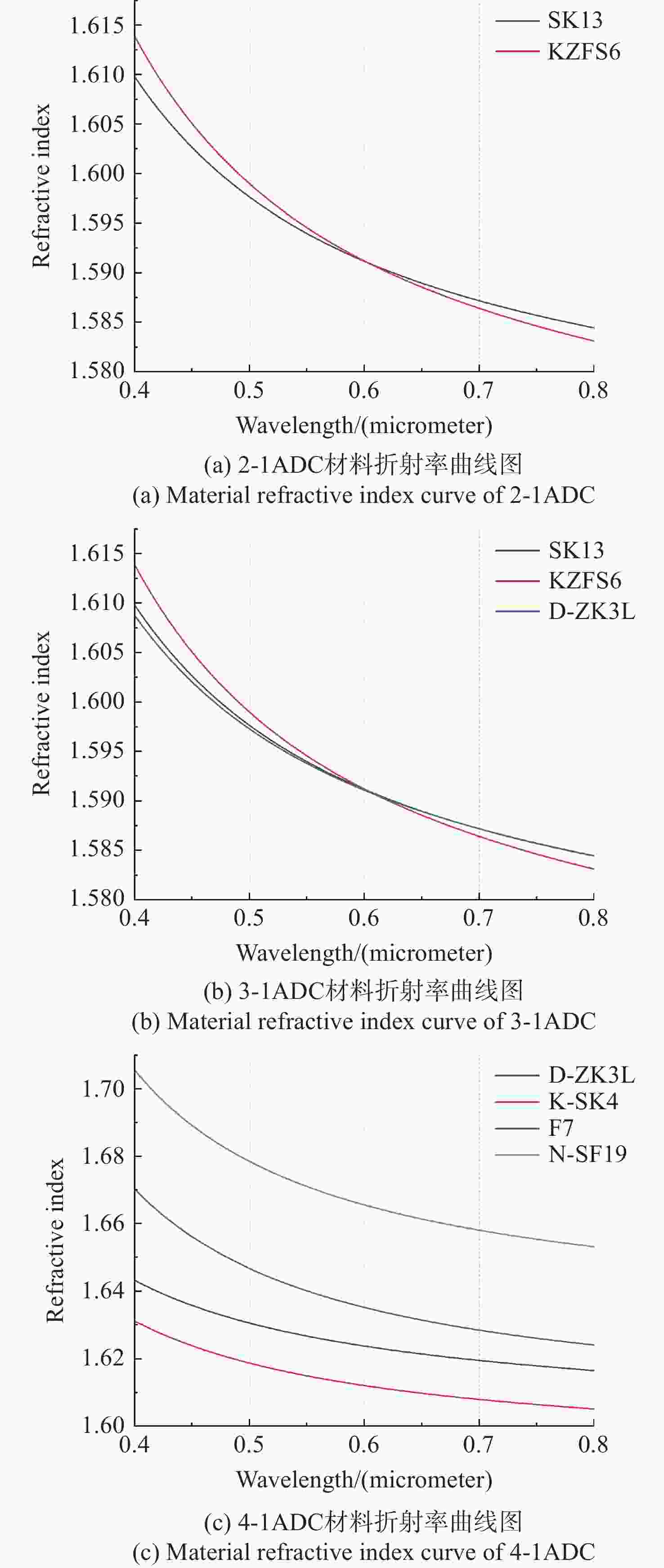
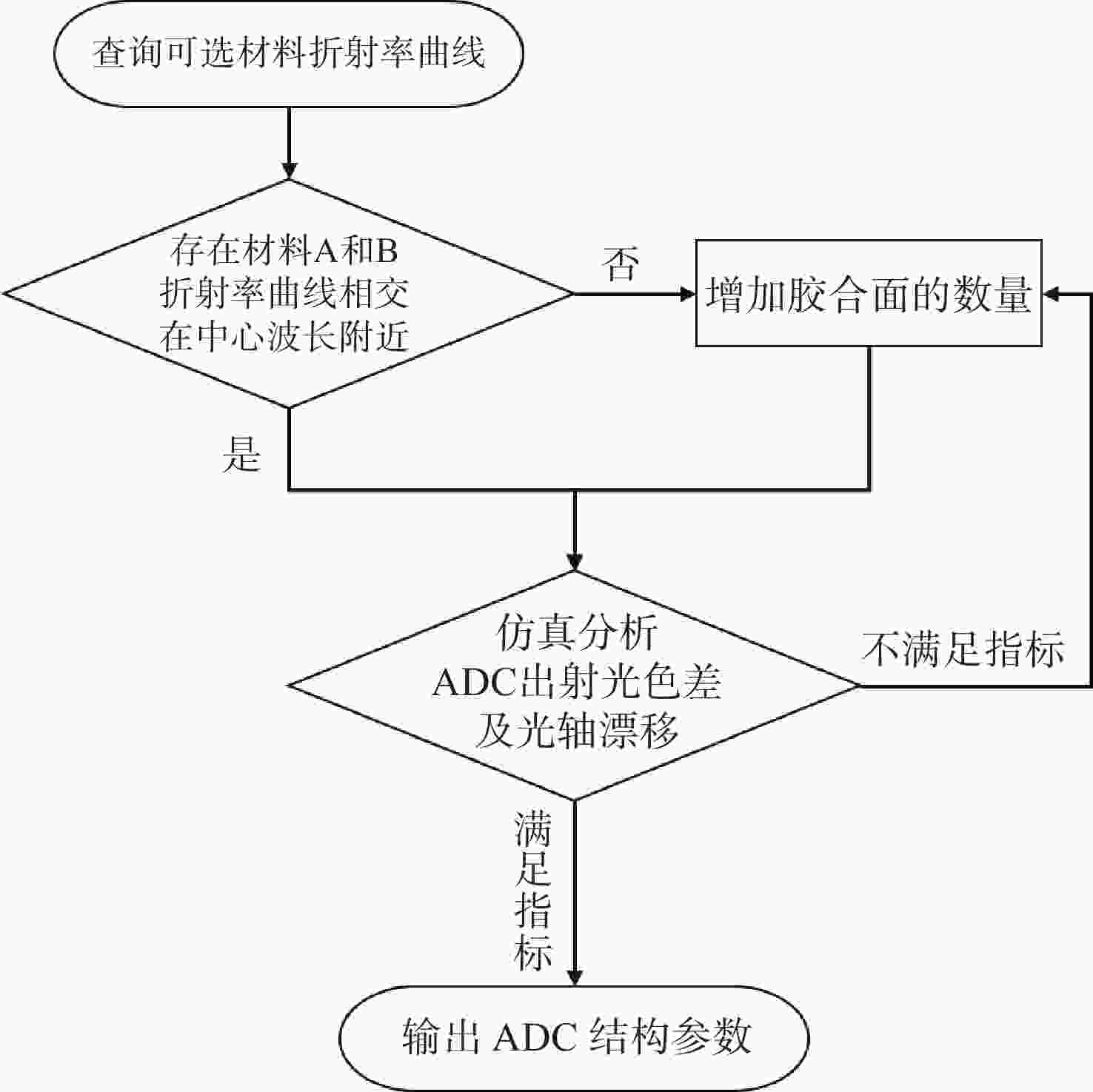
旋转式大气色散校正器(Atmospheric Dispersion Corrector,ADC)在大口径天文望远镜的大气色散校正中得到了广泛应用。为得到旋转式ADC最佳优化设计方法、有效补偿色散并抑制由ADC引入的光轴偏移,本文基于传统的旋转式ADC大气色散补偿理论,建立了旋转式ADC光线路径的矢量模型,进而推导了色散补偿及光轴偏移矢量模型。基于该数学模型仿真分析了ADC不同参数对色散补偿效果、棱镜旋转角度及光轴偏移的影响。仿真结果表明:不同材料组合和不同胶合型式的旋转式ADC,在补偿相同的大气色散时,棱镜组对旋角度相差不大,其差值随天顶角的增加而增加;选择折射率在中心波长附近位置相同的材料,可以降低ADC出射光色散残差,提高色散补偿效果。ADC旋转补偿不同天顶角的大气色散时,系统光轴偏移角度随胶合面数量的增加而减小;每增加一个胶合面数量,光轴偏移角度可下降一个数量级。实际应用设计ADC时,可通过控制胶合数量及材料选取的方法有效补偿色散并抑制光轴偏移。
Abstract:The counter-rotating prisms Atmospheric Dispersion Corrector (ADC) has been widely used for the calibration of large-aperture astronomical telescopes. To achieve an optimal design method for the counter-rotating prism ADC, effectively compensate for dispersion, and suppress optical axis drift introduced by the ADC, this study establishes a vector model for ray tracing of the counter-rotating prism ADC based on traditional atmospheric dispersion compensation theory. The vector models of dispersion compensation and optical axis drift are then derived. Using this mathematical model, the impacts of ADCs with different parameters on the dispersion compensation, prism rotation angle, and optical axis drift are simulated and analyzed. The simulation results show that when compensating for the same atmospheric dispersion with different material combinations and bonding types, the rotation angle of the prism group remains relatively consistent, with differences increasing as the zenith angle increases. Choosing materials with similar refractive indices near the central wavelength reduces chromatic aberration in the ADC output light and improves dispersion compensation. When compensating for large dispersions at different zenith angles, the optical axis offset angle of the system decreases as the number of bonded surfaces increases. Specifically, each additional bonded surface can reduce the optical axis drift angle by one order of magnitude. In practical ADC design, dispersion can be effectively compensated, and optical axis drift can be suppressed by controlling the number of bonded surfaces and material selection.
-
表 1 仿真参数表
Table 1. Simulation parameter table
仿真参数 大气压强 约 78640 Pa气温 约20 °C 工作波长 0.4 μm~0.8 μm 天顶角 0°~70° 表 2 ADC结构仿真数据表
Table 2. Structure simulation data of ADC
ADC型式 材料组成 胶合面倾角仿真结果/° 双胶合 2-1 SK13、KZFS6 39.154 2-2 P-SK100、KZFS6 34.64 2-3 D-ZK3L、KZFS6 34.313 三胶合 3-1 SK13、KZFS6、D-ZK3L 38.810、0.534 3-2 SK8、KZFS1、SK9 13.160、-20.212 四胶合 4-1 D-ZK21、K-SK4、
F7、N-SF19−35.605、20.515、−29.321 4-2 K-LAFK65(M)、SF9、
SK13、KZFS60.149、0.143、38.366 表 3 不同型式的旋转式ADC对旋角度随天顶角变化仿真结果表(单位:°)
Table 3. Simulation results of different types of ADC with varying rotation angles with respect to the zenith angle (Unit: °)
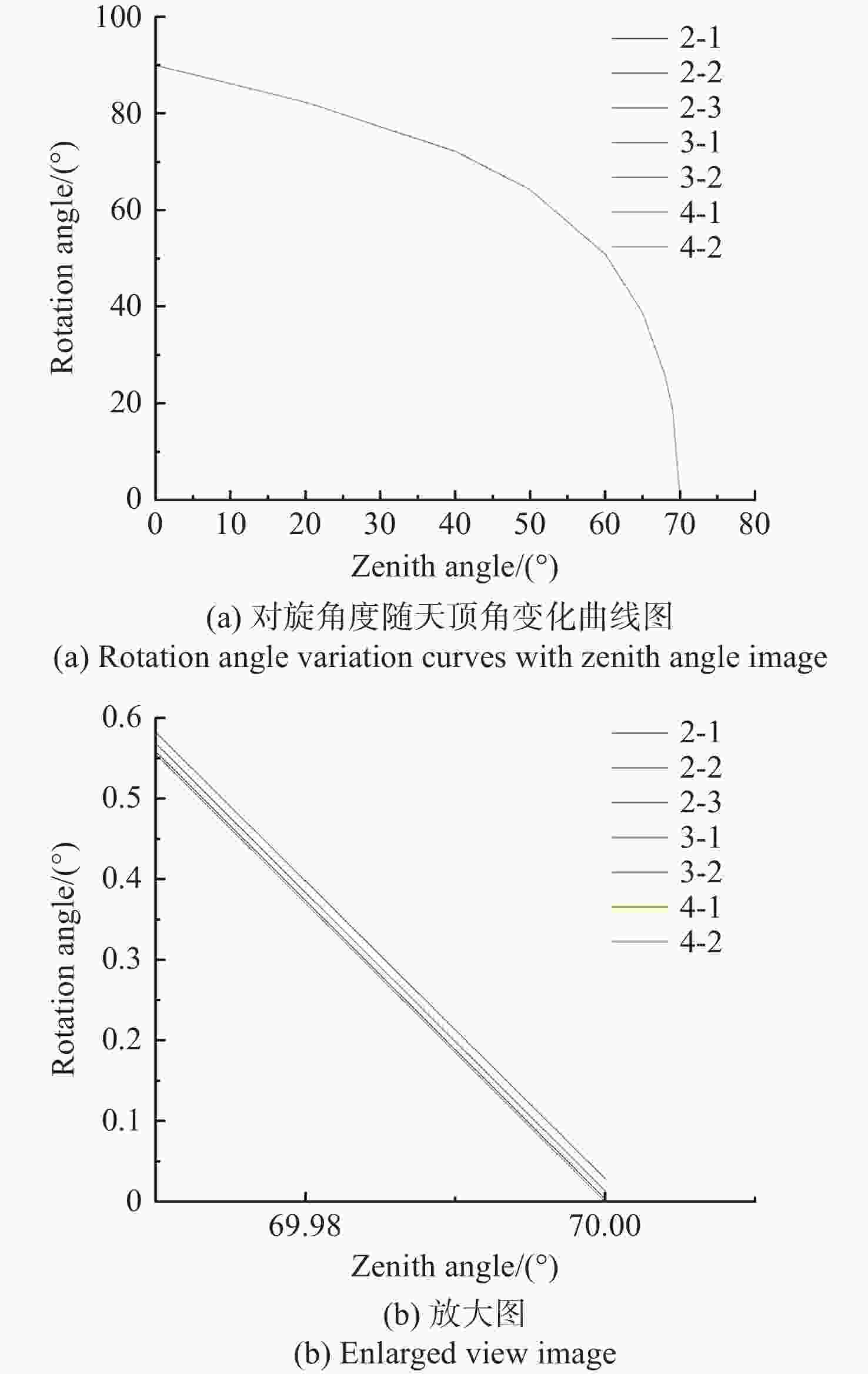
天顶角 棱镜组旋转角 2-1 2-2 2-3 3-1 3-2 4-1 4-2 70 0.004 0.029 0.014 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 69 18.502 18.485 18.510 18.501 18.500 18.500 18.497 68 25.697 25.688 25.707 25.703 25.701 25.695 25.691 65 38.651 38.649 38.663 38.657 38.651 38.647 38.643 60 50.887 50.881 50.892 50.884 50.878 50.883 50.874 50 64.269 64.269 64.272 64.269 64.258 64.266 64.261 40 72.200 72.201 72.201 72.198 72.194 72.198 72.195 20 82.380 82.381 82.380 82.380 82.376 82.379 82.379 0 90.000 90.000 90.000 89.994 90.000 90.000 90.000 表 4 所有胶合类型的ADC旋转角度差值统计结果表
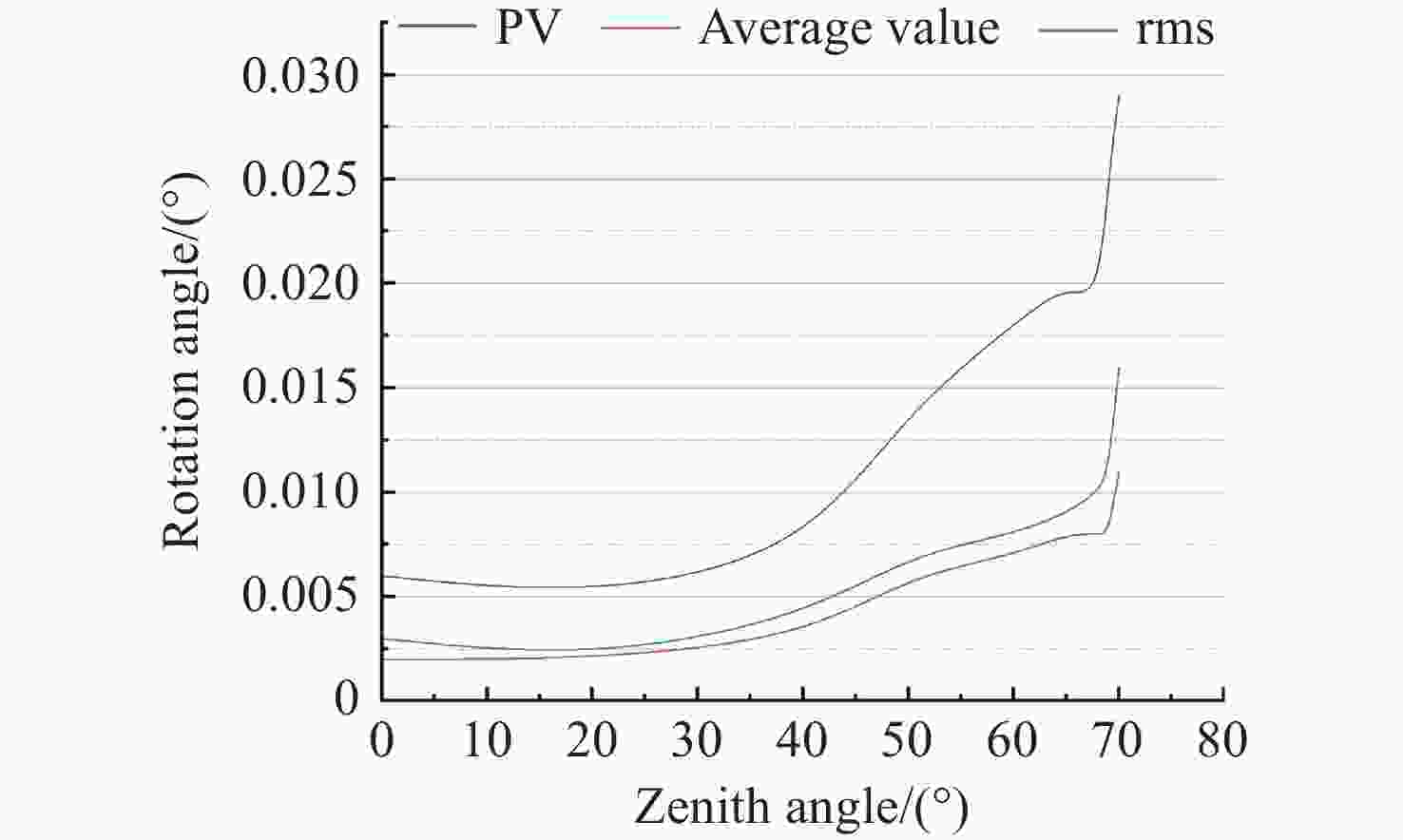
Table 4. Statistical results of rotation angle differences for all types of ADCs
天顶角(°) 所有胶合类型ADC旋转角度差值(°) PV 平均值 rms 70 0.029 0.011 0.016 69 0.025 0.008 0.011 68 0.019 0.008 0.010 65 0.02 0.008 0.009 60 0.018 0.007 0.008 50 0.014 0.006 0.007 40 0.007 0.003 0.004 20 0.005 0.002 0.002 0 0.006 0.002 0.003 表 5 不同型式的ADC出射光色差统计数据表(单位:″)
Table 5. Different Types of ADC Output Color Deviation Statistical Data Table (Unit:″)
ADC结构型式 出射光色差 最大值 平均值 双胶合 2-1 0.0015 0.0008 2-2 0.0048 0.0025 2-3 0.1038 0.0591 三胶合 3-1 0.0015 0.0008 3-2 0.0021 0.0013 四胶合 4-1 0.0004 0.0002 4-2 0.0016 0.0008 表 6 不同型式ADC光轴偏移角度统计表(单位:″)
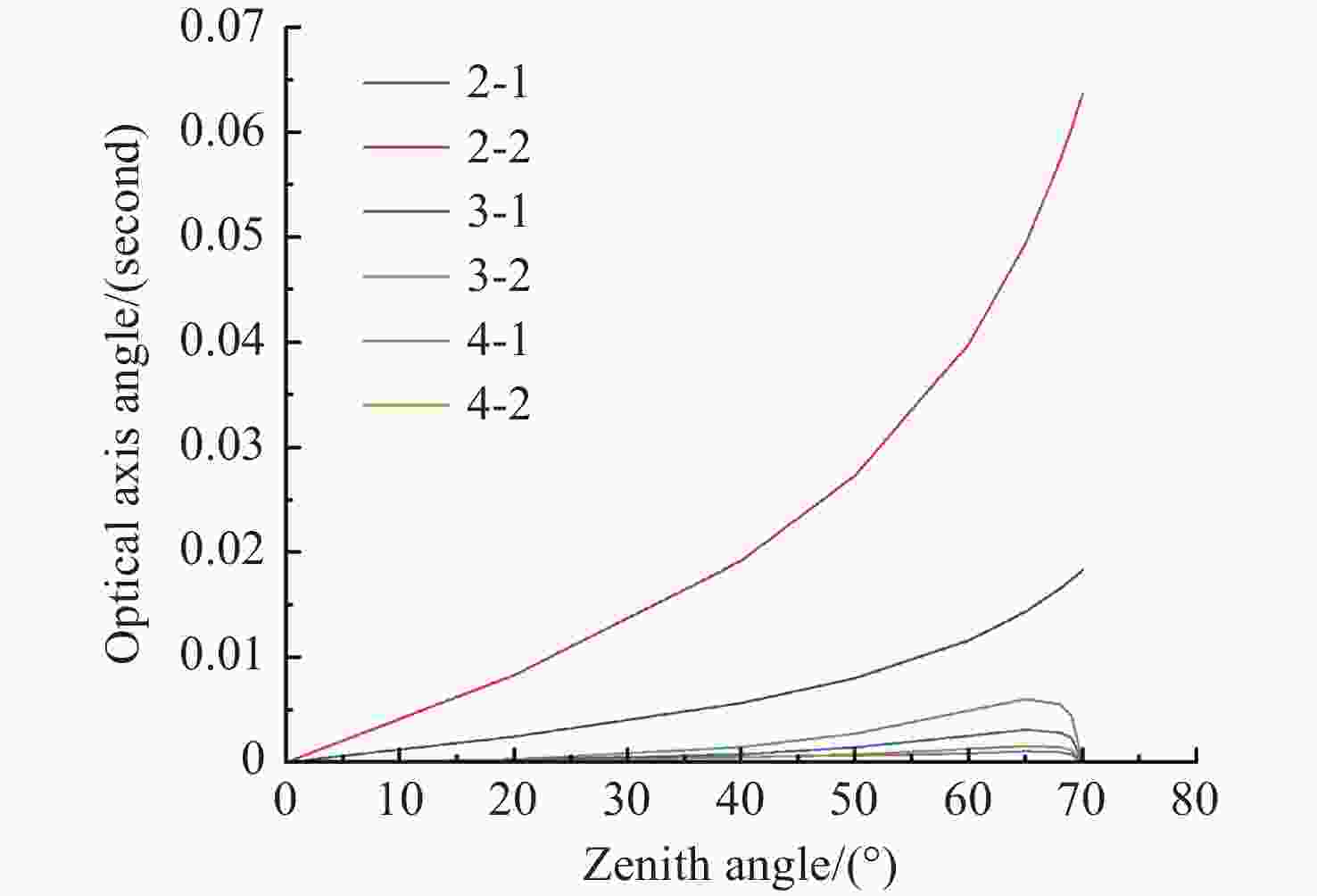
Table 6. Statistical Table of Optical Axis Offset Angle for Different Types of ADCs (Unit: ″)
结构形式 材料组成 光轴偏移角度最大值 光轴偏移角度平均值 平均光轴偏移角度 双胶合 2-1 SK13、KZFS6 1.83E-02 1.05E-02 2.34E-02 2-2 P-SK100、KZFS6 6.37E-02 3.62E-02 三胶合 3-1 SK2、KZFS1、P-SK57Q1 3.01E-03 1.64E-03 2.39E-03 3-2 N-ZK7、KZFS6、SK1 6.08E-03 3.15E-03 四胶合 4-1 SSK1、D-ZK21-25、KZFS4、LAK21 1.04E-03 6.05E-04 7.26E-04 4-2 K-LAFK65(M)、SF9、SK13、KZFS6 1.58E-03 8.47E-04 -
[1] 谈昊. “南天光谱巡天望远镜”望远镜本体光学方案设计及性能分析[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2021: 25-27.TAN H. Design and analyze of the telescope of Southern Spectroscopic Survey Telescope project[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2021: 25-27. (in Chinese). [2] 孔思捷, 周进, 尧联群, 等. 基于多次收敛分割反卷积算法的大气色散补偿方法[J]. 半导体光电,2019,40(6):862-868.KONG S J, ZHOU J, YAO L Q, et al. Atmospheric dispersion compensation based on multiple convergence deconvolution algorithm[J]. Semiconductor Optoelectronics, 2019, 40(6): 862-868. (in Chinese). [3] 明名, 吕天宇, 吴小霞, 等. 大气色散对4m望远镜成像分辨力的影响与校正[J]. 中国光学,2015,8(5):814-822. doi: 10.3788/co.20150805.0814MING M, LÜ T Y, WU X X, et al. Influence of atmospheric dispersion on image resolution of 4 m telescope and correction method[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(5): 814-822. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20150805.0814 [4] PHILLIPS A C, MILLER J, COWLEY D, et al. The Keck-I Cassegrain ADC[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7014: 701453. doi: 10.1117/12.789930 [5] RAKICH A. A new type of atmospheric dispersion corrector suitable for wide-field high-resolution imaging and spectroscopy on large telescopes[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(14): 6261. doi: 10.3390/app11146261 [6] SPANÒ P. A super-corrected atmospheric dispersion corrector[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7018: 70181G. doi: 10.1117/12.789161 [7] EGNER S, IKEDA Y, WATANABE M, et al. Atmospheric dispersion correction for the Subaru AO system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7736: 77364V. doi: 10.1117/12.856579 [8] WEHBE B, CABRAL A, ÁVILA G. The development of an optical design tool for atmospheric dispersion correction[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11207: 112070P. [9] TAN H, MA D L. Recommended optical system design for the SSST[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(11): 3508-3517. doi: 10.1364/AO.387948 [10] 周健文, 姚纳, 赵汗青, 等. 大气湍流下超振荡望远成像的理论研究[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 技术,2023,47(1):115-120. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2023.01.018 [11] ZHOU J W, YAO N, ZHAO H Q, et al. Theoretical study of super-oscillation telescope imaging with atmospheric turbulence[J]. Laser Technology, 2023, 47(1): 115-120. (in Chinese) (查阅网上资料, 本条文献为第10条文献的英文翻译, 请确认) . [12] 温婉莎. 宽视场光学成像光谱仪大气色散校正器光机结构与集成技术研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2023: 2-8.WEN W SH. Research on optical and mechanical structure and integration technology of atmospheric dispersion corrector for wide-field optical spectrometer[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023: 2-8. (in Chinese). [13] 吴之旭, 陈超, 姜鹏, 等. 南极大视场望远镜光学系统研究进展[J]. 极地研究,2024,36(1):84-98.WU ZH X, CHEN CH, JIANG P, et al. Progress of the Antarctic large field of view telescope[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2024, 36(1): 84-98. (in Chinese). [14] 毛红敏, 丁致雅, 杨燕燕, 等. 大气湍流对高分辨率遥感卫星的成像影响研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(1):167-177. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0083MAO H M, DING ZH Y, YANG Y Y, et al. Effect of atmospheric turbulence on imaging quality of high-resolution remote sensing satellites[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(1): 167-177. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0083 [15] SHIKHOVTSEV A Y. Reference optical turbulence characteristics at the Large Solar Vacuum Telescope site[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan, 2024, 76(3): 538-549. doi: 10.1093/pasj/psae031 [16] 安其昌, 吴小霞, 李洪文, 等. 基于曲率传感的主焦巡天望远镜集成检测方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(3):535-541. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0010AN Q CH, WU X X, LI H W, et al. Assembling and test method for main focus survey telescope based on curvature sensing[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(3): 535-541. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0010 [17] 谢云辉. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 打孔光楔扫描光学系统的设计与研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2011: 28-30.XIE Y H. Design and research of optical wedge scanning system for laser drilling[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2011: 28-30. (in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: