Study of bonding layer for integrated structure of space gravitational wave detector telescope
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2024-0025
-
Abstract:
To detect gravitational waves in space, the telescope and optical platform require high stability and reliability. However, the cantilevered design presents challenges, especially in the glass-metal hetero-bonding process. This study focuses on the analysis and experimental research of the bonding layer in the integrated structure. By optimizing the structural configuration and selecting suitable bonding processes, the reliability of the telescope system is enhanced. The research indicates that the use of J-133 adhesive achieves the best performance, with a bonding layer thickness of 0.30 mm and a metal substrate surface roughness of Ra 0.8. These findings significantly enhance the reliability of the optical system while minimizing potential risks.
-
Figure 3. Stress cloud map of bonding layer in random vibration analysis. (a) Flexures bonded on with epoxy. (b) Maximum normal stress cloud map when excitations are applied in the x-direction. (c) Maximum normal stress cloud map when excitations are applied in the y-direction. (d) Random vibration inputs. (e) Maximum normal stress cloud map when excitations are applied in the z-direction. (f) Maximum shear stress cloud map of the bonding layer.
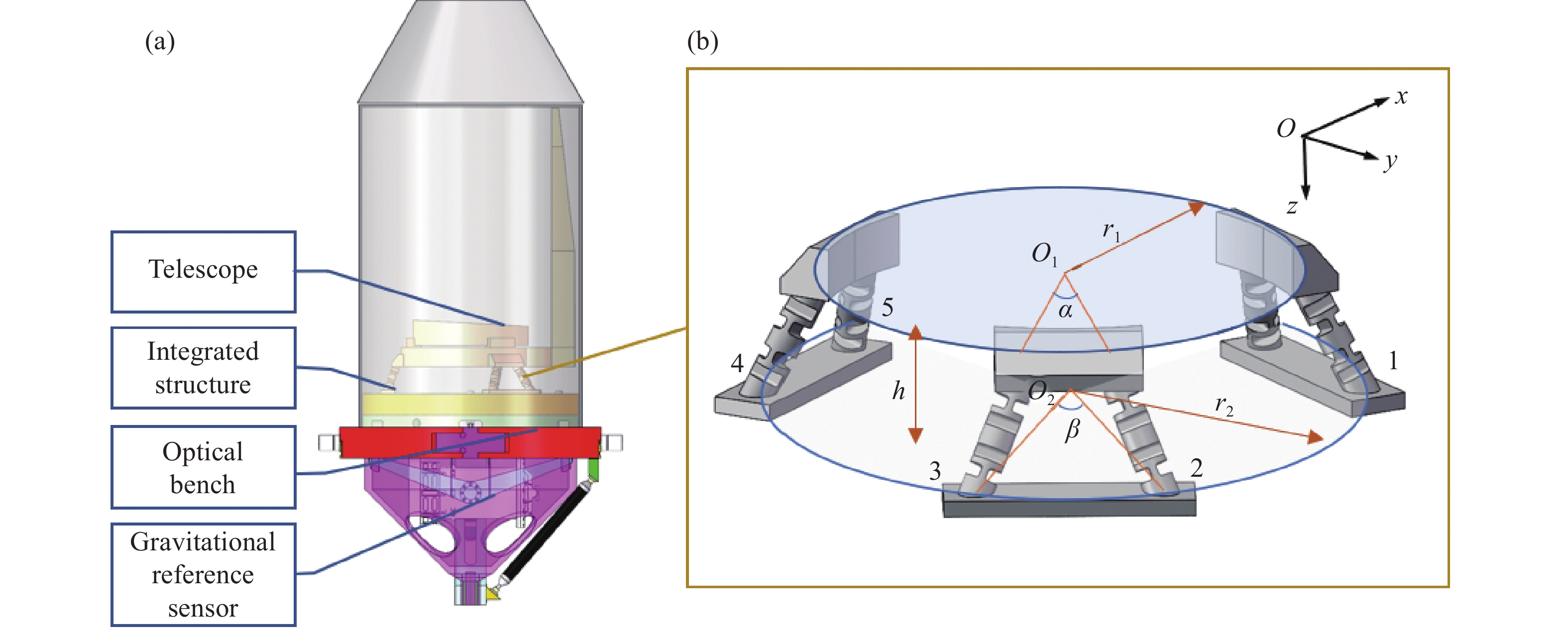
Table 1. Optimal solution of integrated structural parameters.
Variables Range of
valuesOptimization
resultsThe upper ring support radii r1/mm 150–180 180.0 The lower ring support radii r2/mm 180–240 206.5 The angle between the upper
support points α/°5–20 15.7 The angle between the lower
support points β/°15–40 35.0 Table 2. Alternative epoxy adhesive and experimental design.
Variables Epoxy adhesive J-133 GHJ-01(Z) 3M-DP2216 Bonding-layer thickness /mm 0.15 0.3 0.5 Surface roughness /μm Ra0.8 Ra1.6 Ra3.2 Ra6.3 Single group specimens 36 Total specimens 108 -
[1] KAWAMURA S, NAKAMURA T, ANDO M, et al. Space gravitational-wave antennas DECIGO and B-DECIGO[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics D, 2019, 28(12): 1845001. doi: 10.1142/S0218271818450013 [2] TORRES-ORJUELA A, HUANG SH J, LIANG ZH CH, et al. Detection of astrophysical gravitational wave sources by TianQin and LISA[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2024, 67(5): 259511. [3] WANG H T, JIANG ZH, SESANA A, et al. Science with the TianQin observatory: preliminary results on massive black hole binaries[J]. Physical Review D, 2019, 100(4): 043003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.100.043003 [4] FAN Z C, ZHAO L J, CAO SH Y, et al. High performance telescope system design for the TianQin project[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2022, 39(19): 195017. doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ac8b57 [5] LIVAS J C, SANKAR S R. Optical telescope system-level design considerations for a space-based gravitational wave mission[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9904: 99041K. [6] YU M, LI J C, LIN H G, et al. Optical system design of large-aperture space gravitational wave telescope[J]. Optical Engineering, 2023, 62(6): 065107. [7] ZHANG S, ZHAO D L. Aerospace Materials Handbook[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2012: 781. [8] SANJUÁN J, PRESTON A, KORYTOV D, et al. Carbon fiber reinforced polymer dimensional stability investigations for use on the laser interferometer space antenna mission telescope[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2011, 82: 124501. doi: 10.1063/1.3662470 [9] CHWALLA M, DANZMANN K, ÁLVAREZ M D, et al. Optical suppression of tilt-to-length coupling in the LISA long-arm interferometer[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2020, 14(1): 014030. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.14.014030 [10] LIGHTSEY P A, ATKINSON C, CLAMPIN M, et al. James Webb Space Telescope: large deployable cryogenic telescope in space[J]. Optical Engineering, 2012, 51(1): 011003. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.51.1.011003 [11] HU H F, ZHOU D, ZHAO CH CH, et al. Hetero-bonding strength investigation into opto-mechanical interface[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2024, 11: 1406090. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2024.1406090 [12] ELLIFFE E J, BOGENSTAHL J, DESHPANDE A, et al. Hydroxide-catalysis bonding for stable optical systems for space[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2005, 22(10): S257-S267. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/22/10/018 [13] MASSO REID M, HAUGHIAN K, CUMMING A V, et al. Temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity of hydroxide catalysis bonds between silicon substrates[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2023, 40(24): 245006. doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/ad0923 [14] FAULKS H, GEHBAUER K, BISI M. LISA final technical report[C]. Proceedings of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, 2000. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认) . [15] AGARWAL P, KUMAR M, CHOUDHARY M, et al. Experimental and numerical analysis of mechanical, thermal and thermomechanical properties of hybrid glass/metal fiber reinforced epoxy composites[J]. Fibers and Polymers, 2022, 23(5): 1342-1365. doi: 10.1007/s12221-022-4760-5 [16] LI SH H, HU K J, HUI W CH, et al. Shear strength and interfacial characterization of borosilicate glass-to-metal seals[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 827: 154275. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154275 [17] WANG H R. Research on a bimorph piezoelectric deformable mirror for adaptive optics in optical telescope[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(7): 8115-8122. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.008115 [18] LI SH H, CAI Y Y, ZHU Q Y, et al. Interface degradation of glass-to-metal seals during thermo-oxidative aging[J]. Corrosion Science, 2022, 199: 110189. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2022.110189 [19] LANCKER B V, CORTE W D, BELIS J. Investigation of the structural performance of continuous adhesive glass-metal connections using structural silicone and hybrid polymer adhesives[J]. Engineering Structures, 2024, 304: 117612. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2024.117612 [20] WANG W, XIAO Y Y, WU X Y, et al. Optimization of laser-assisted glass frit bonding process by response surface methodology[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2016, 77: 111-115. [21] RICHET P. Encyclopedia of Glass Science, Technology, History, and Culture[M]. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley: American Ceramic Society, 2021: 629-638. -







 下载:
下载: