SSFM-global-error-local-energy method for improving computational efficiency of passively mode-locked fiber laser
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN.2022-0016
-
摘要:
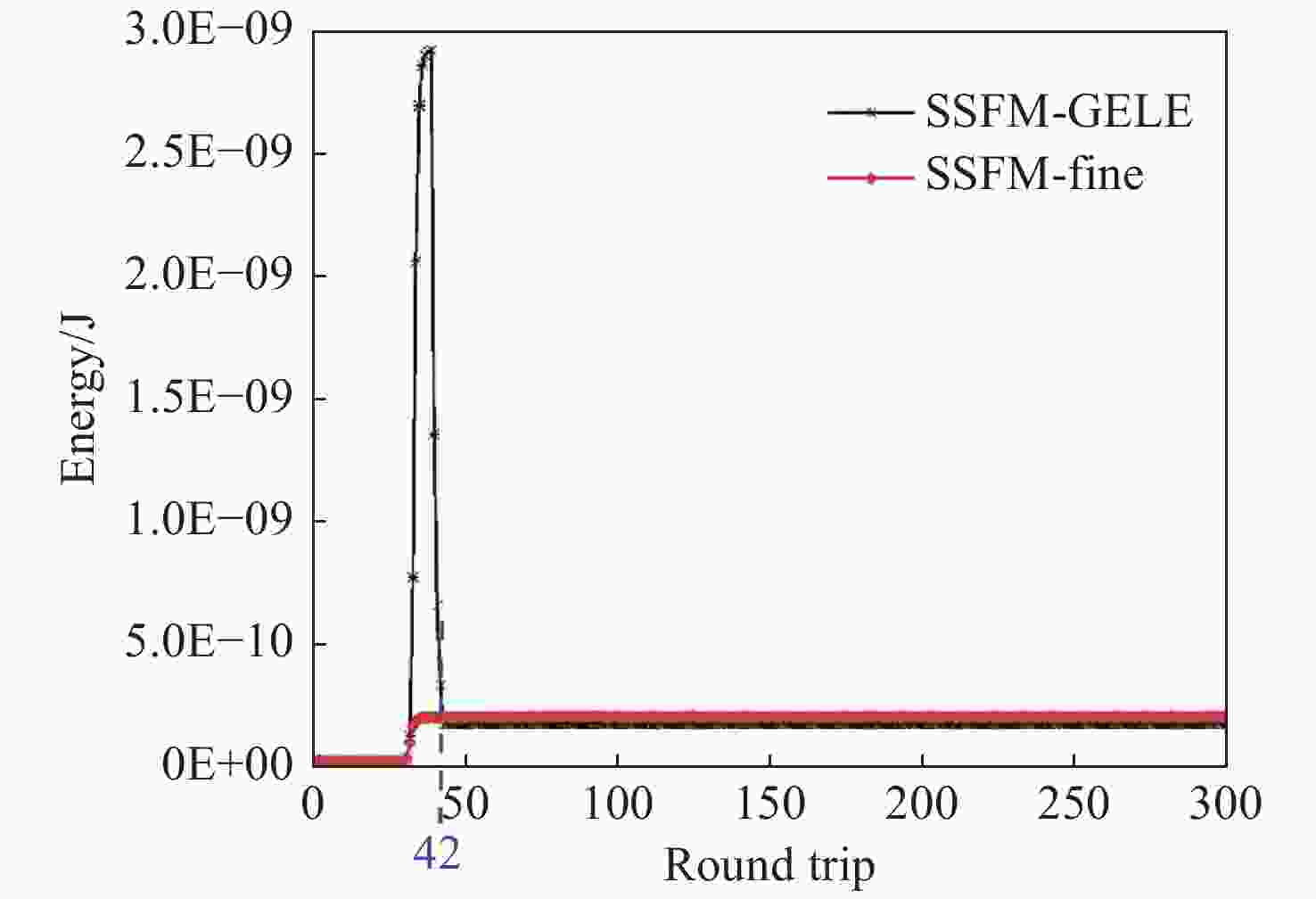
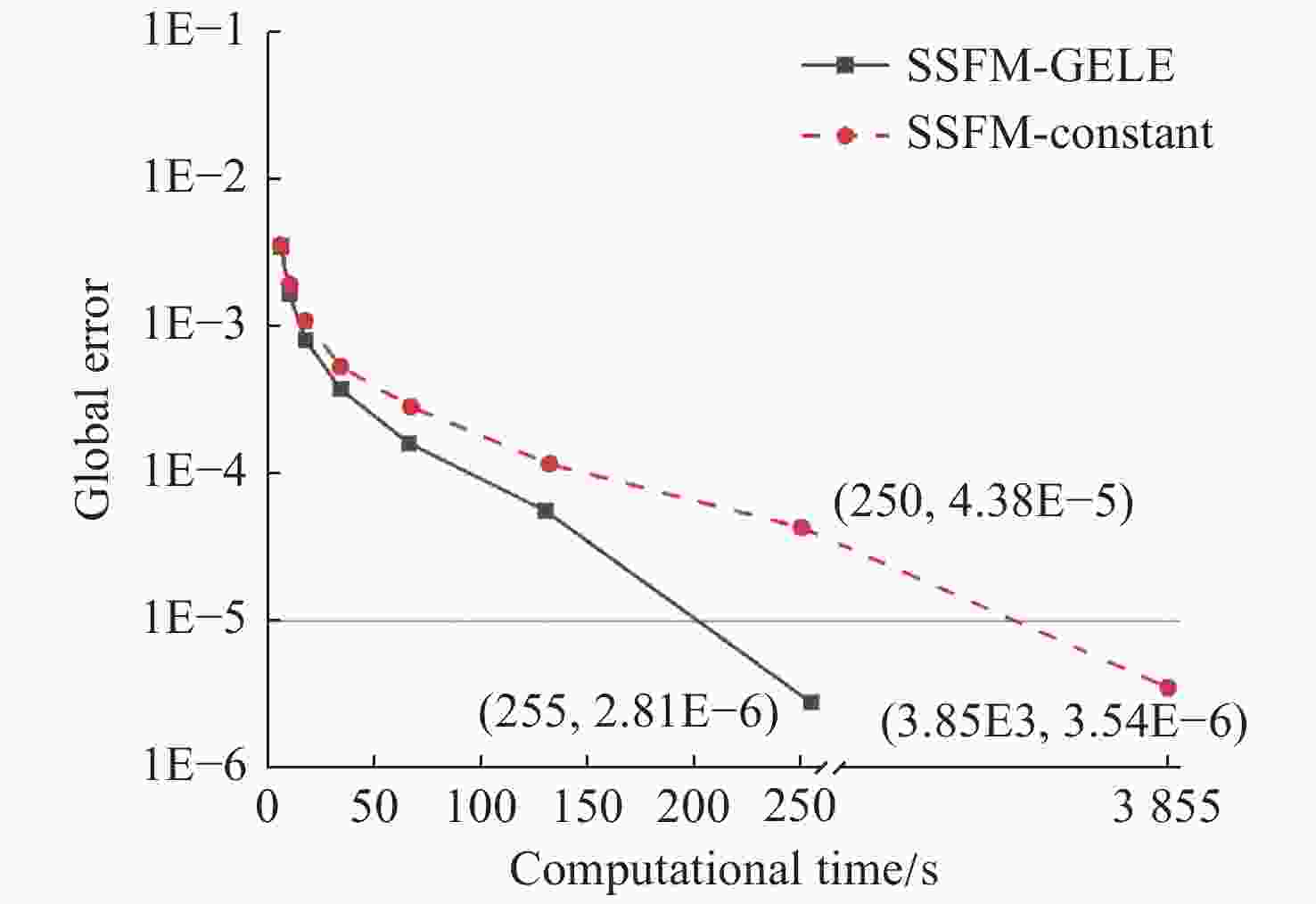
本文提出了一种提高被动锁模光纤金宝搏188软件怎么用 器计算效率的方法,该方法由对称分步傅立叶方法(SSFM)和全局误差局部能量(GELE)方法组成。该方法可将与全局误差相关的局部能量增量限制在一定范围内来控制步长。该方法具有自动步长调整机制。达到同程度的计算精度,本文方法的计算时间为255 s,而小的恒定步长SSFM方法需要3855 s。这表明本文方法可以将计算效率提高10余倍。本文方法还可以通过RK4IP、Adams、预测-校正等高阶算法进行扩展,以提高精度。
-
关键词:
- 锁模光纤金宝搏188软件怎么用 器 /
- 耗散孤子 /
- 分步傅里叶法 /
- 自适应方法
Abstract:We propose a method for improving the computational efficiency of passively mode-locked fiber laser, which is composed by Symmetric Split-step Fourier Method (SSFM) and the Global-Error-Local-Energy (GELE) method for solving propagating equations. Our proposed method relies on the limitation of local energy increment related with global error within a certain value to control the selection of step size. This method has advantage of an automatic step adjustment mechanism. To achieve the same order of computation accuracy, the computational time of our method is 255 s, while SSFM with small constant step size method needs to calculate 3855 s. The computational time of our proposed method is one or two orders of magnitude less than that of the SSFM, which indicates our method can enhance the computational efficiency by a factor up to 10. It could be expanded with high-order algorithms, such as the fourth-order Runge-Kutta in the interaction picture (RK4IP), Adams, predictor–corrector, etc. for improving the accuracy.
-
-
[1] ZHAO T X, LIU G X, DAI L L, et al. Narrow bandwidth spatiotemporal mode-locked Yb-doped fiber laser[J]. Optics Letters, 2022, 47(15): 3848-3851. doi: 10.1364/OL.465533 [2] ZHAO Z H, JIN L, SET S Y, et al. Broadband similariton generation in a mode-locked Yb-doped fiber laser[J]. Optics Letters, 2022, 47(9): 2238-2241. doi: 10.1364/OL.456808 [3] AGRAWAL G P. Nonlinear Fiber Optics[M]. 6th ed. San Diego: Academic Press, 2019. [4] LIMA I T, DEMENEZES T D S, GRIGORYAN V S, et al. Nonlinear compensation in optical communications systems with normal dispersion fibers using the nonlinear Fourier transform[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2017, 35(23): 5056-5068. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2017.2766622 [5] DEITERDING R, GLOWINSKI R, OLIVER H, et al. A reliable split-step fourier method for the propagation equation of ultra-fast pulses in single-mode optical fibers[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2013, 31(12): 2008-2017. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2013.2262654 [6] SAFAEI A, BOLORIZADEH M A. Solving nonlinear Schrödinger equation by a new and fast method[J]. Physica Scripta, 2021, 96(12): 125238. doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/ac2efe [7] COOLEY J W, TUKEY J W. An algorithm for the machine calculation of complex fourier series[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1965, 19(90): 297-301. doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-1965-0178586-1 [8] CRISTIANI I, TEDIOSI R, TARTARA L, et al. Dispersive wave generation by solitons in microstructured optical fibers[J]. Optics Express, 2004, 12(1): 124-135. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.12.000124 [9] BREHLER M, SCHIRWON M, GÖDDEKE D, et al. A GPU-accelerated fourth-order runge-kutta in the interaction picture method for the simulation of nonlinear signal propagation in multimode fibers[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2017, 35(17): 3622-3628. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2017.2715358 [10] LAUTERIO-CRUZ J P, HERNANDEZ-GARCIA J C, POTTIEZ O, et al. Numerical study of supercontinuum generation using noise-like pulses in standard fibre[J]. Laser Physics, 2018, 28(9): 095106. doi: 10.1088/1555-6611/aacca6 [11] IBARRA-VILLALÓN H E, POTTIEZ O, GÓMEZ-VIEYRA A, et al. Numerical approaches for solving the nonlinear Schrödinger equation in the nonlinear fiber optics formalism[J]. Journal of Optics, 2020, 22(4): 043501. [12] IBARRA-VILLALON H E, POTTIEZ O, GÓMEZ-VIEYRA A, et al. Embedded split-step methods optimized with a step size control for solving the femtosecond pulse propagation problem in the nonlinear fiber optics formalism[J]. Physica Scripta, 2021, 96(7): 075502. doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/abf7fb [13] SINKIN O V, HOLZLÖHNER R, ZWECK J, et al. Optimization of the split-step Fourier method in modeling optical-fiber communications systems[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2003, 21(1): 61-68. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2003.808628 [14] LI SH G, XING G L, ZHOU G Y, et al. Adaptive split-step Fourier method for simulating ultrashort laser pulse propagation in photonic crystal fibres[J]. Chinese Physics, 2006, 15(2): 437-443. doi: 10.1088/1009-1963/15/2/034 [15] HEIDT A M. Efficient adaptive step size method for the simulation of supercontinuum generation in optical fibers[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2009, 27(18): 3984-3991. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2009.2021538 [16] MUSETTI S, SERENA P, BONONI A. On the accuracy of split-step fourier simulations for wideband nonlinear optical communications[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2018, 36(23): 5669-5677. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2018.2877384 [17] HUANG W T, LIU F F, LV X, et al. Dynamics and numerical simulation of optical pulses in the passively mode-locked Er-doped fiber laser[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2022, 114: 106658. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2022.106658 [18] HAN Y, GAO B, LI Y Y, et al. Numerical simulation of two-soliton and three-soliton molecules evolution in passively mode-locked fiber laser[J]. Optik, 2020, 223: 165381. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165381 [19] BÉLANGER P A, GAGNON L, PARÉ C. Solitary pulses in an amplified nonlinear dispersive medium[J]. Optics Letters, 1989, 14(17): 943-45. doi: 10.1364/OL.14.000943 [20] ZHANG X Y, SONG Y R. Mode-locked fiber lasers based on doped fiber arrays[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(14): 2998-3003. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.002998 -





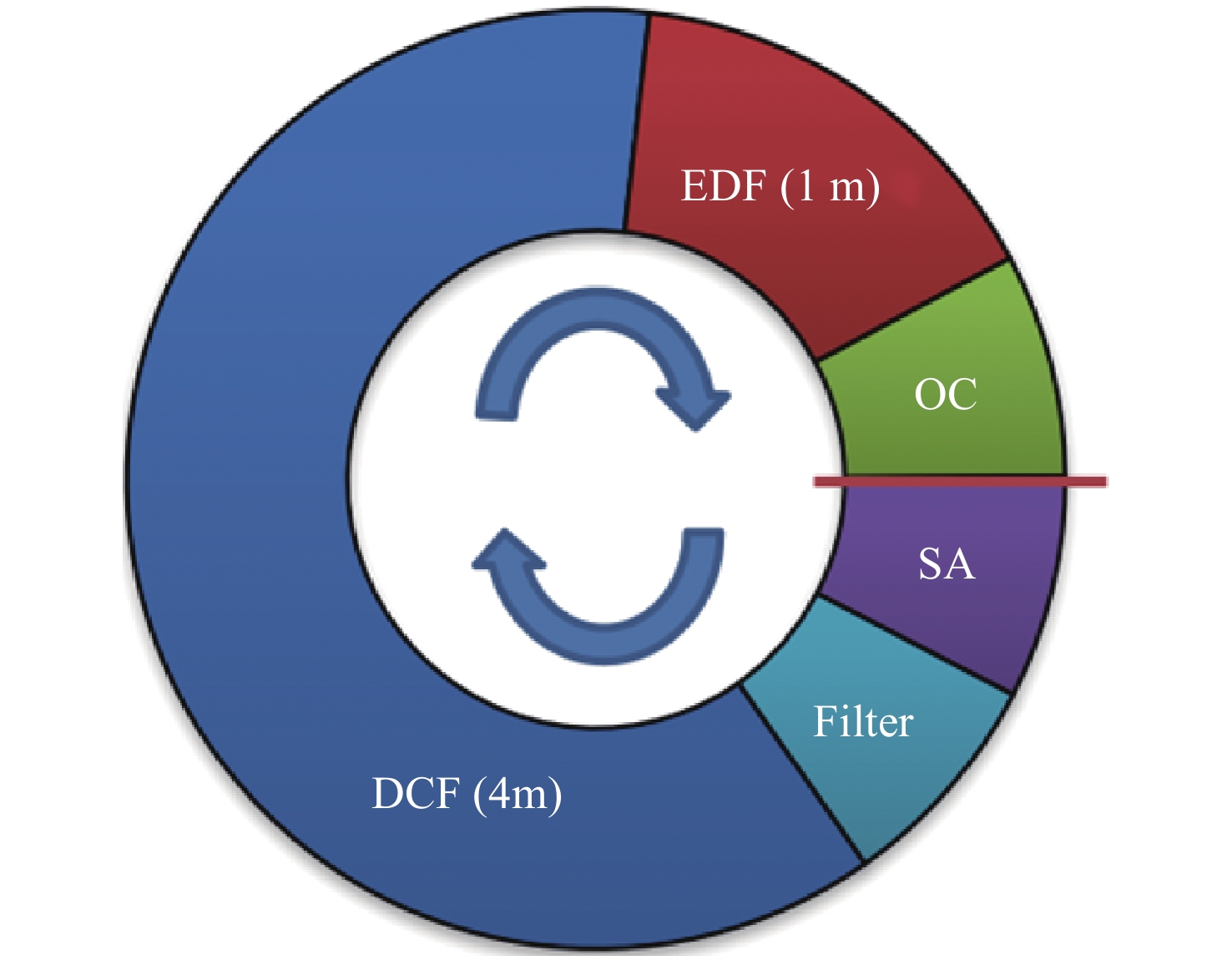
 下载:
下载: