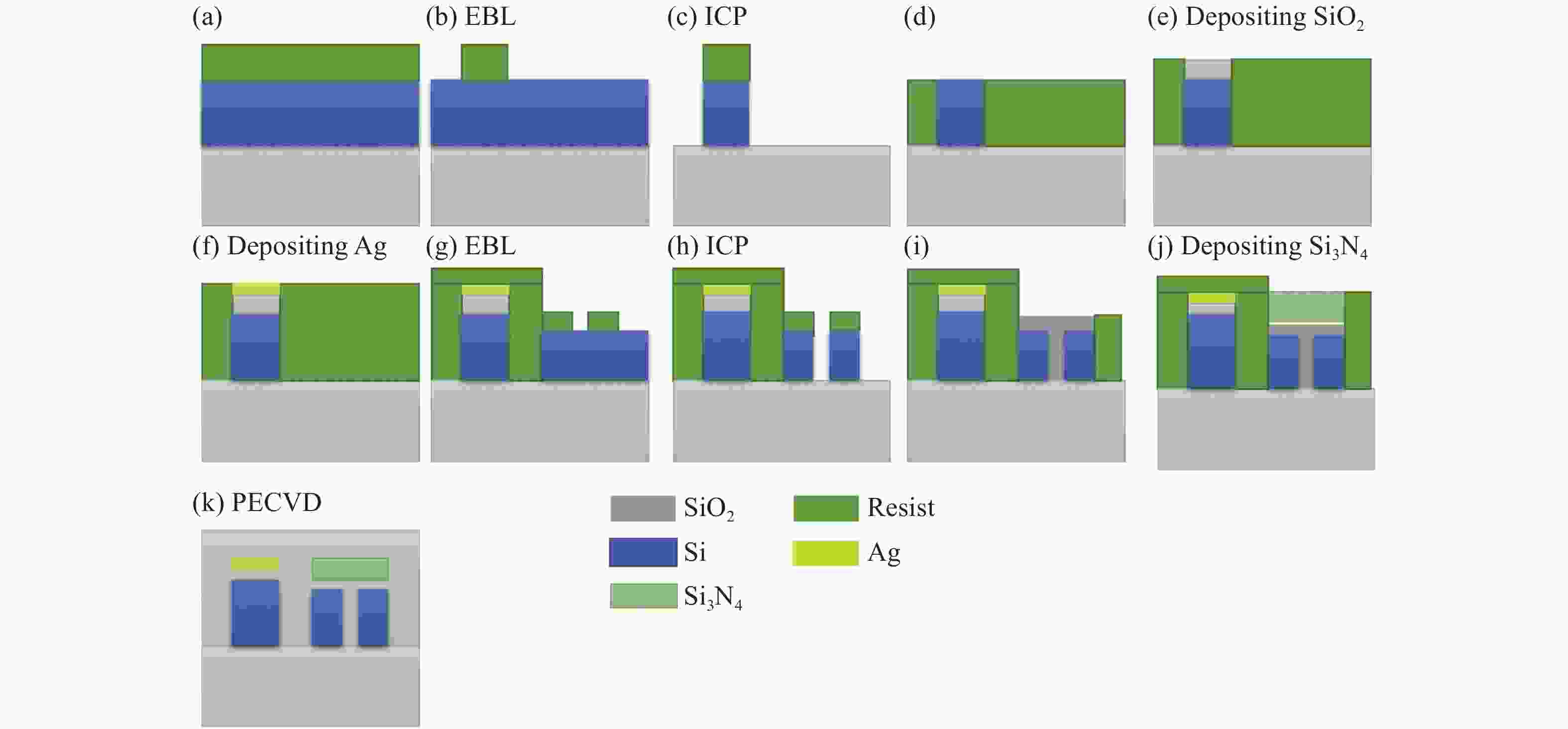
Double-slot ultra-compact polarization beam splitter based on asymmetric hybrid plasmonic structure
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN.2022-0028
-
摘要:
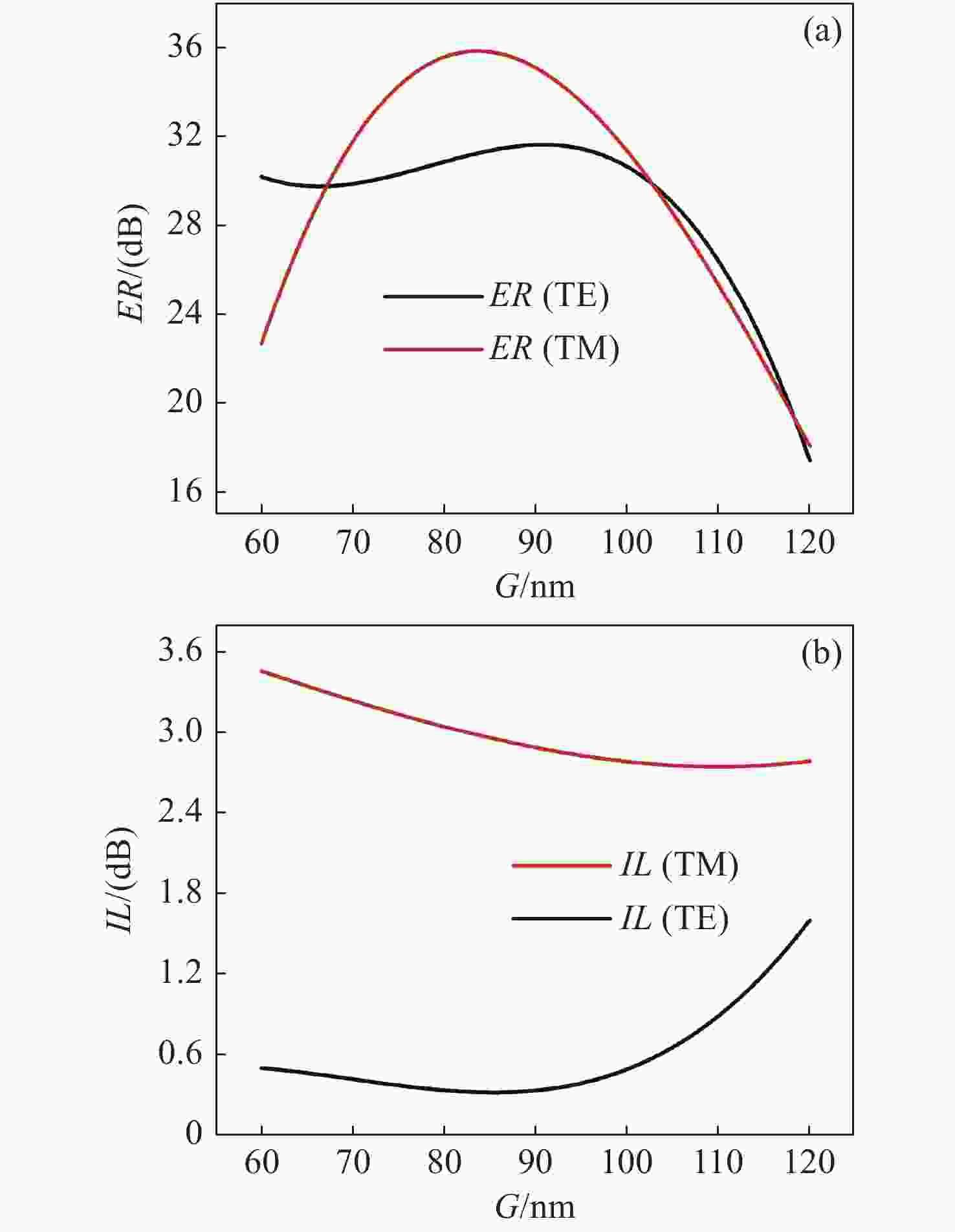
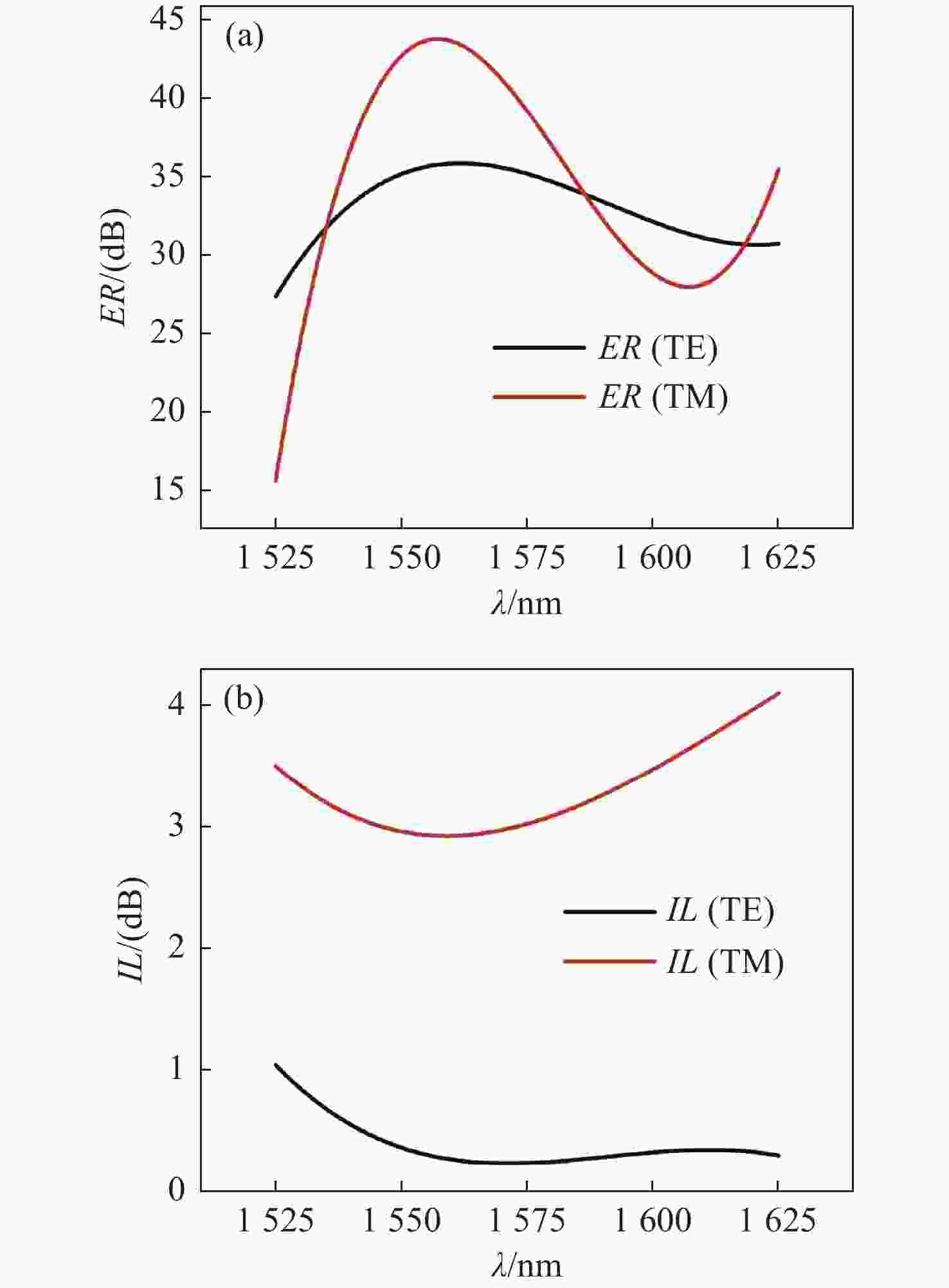
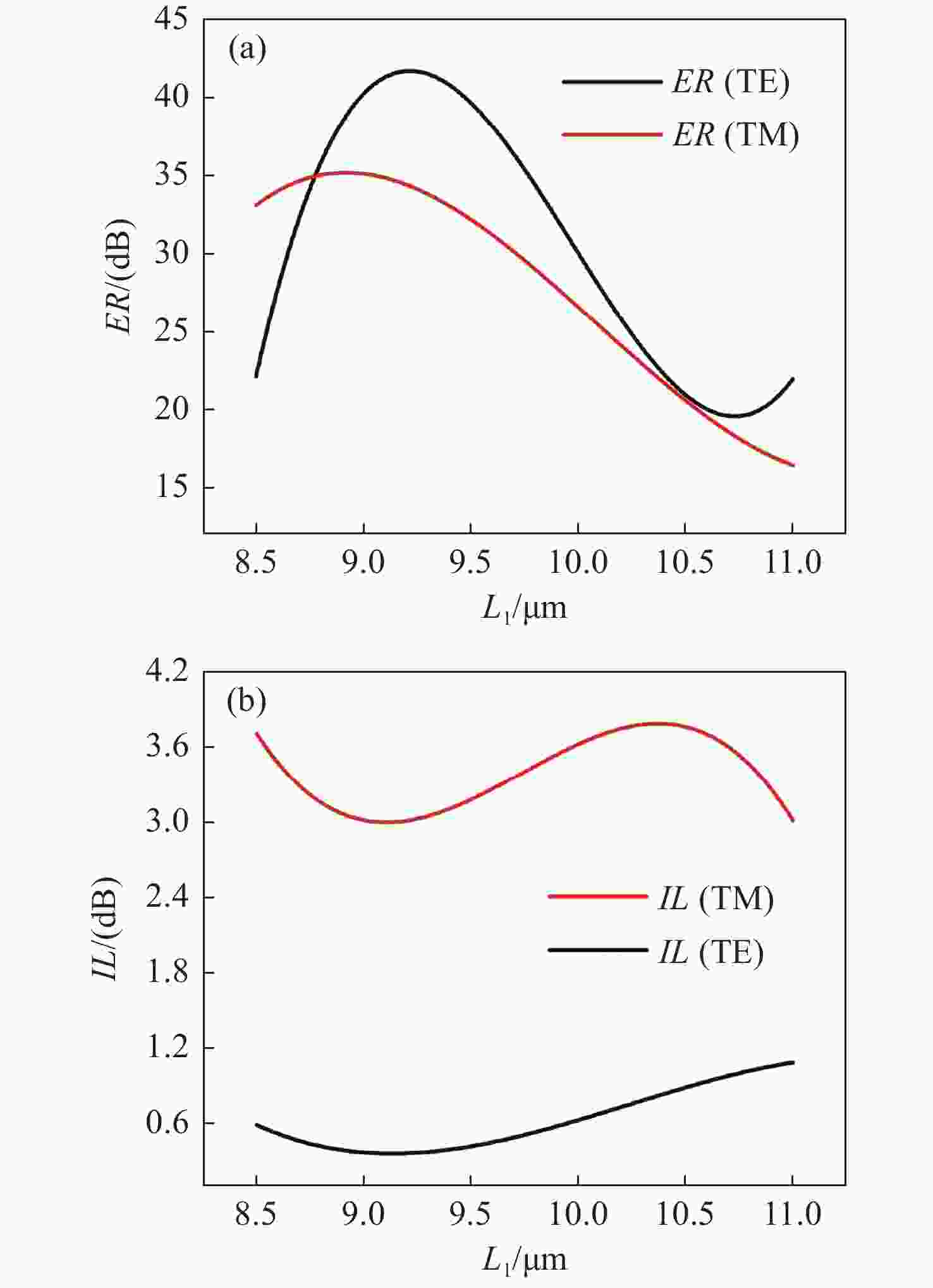
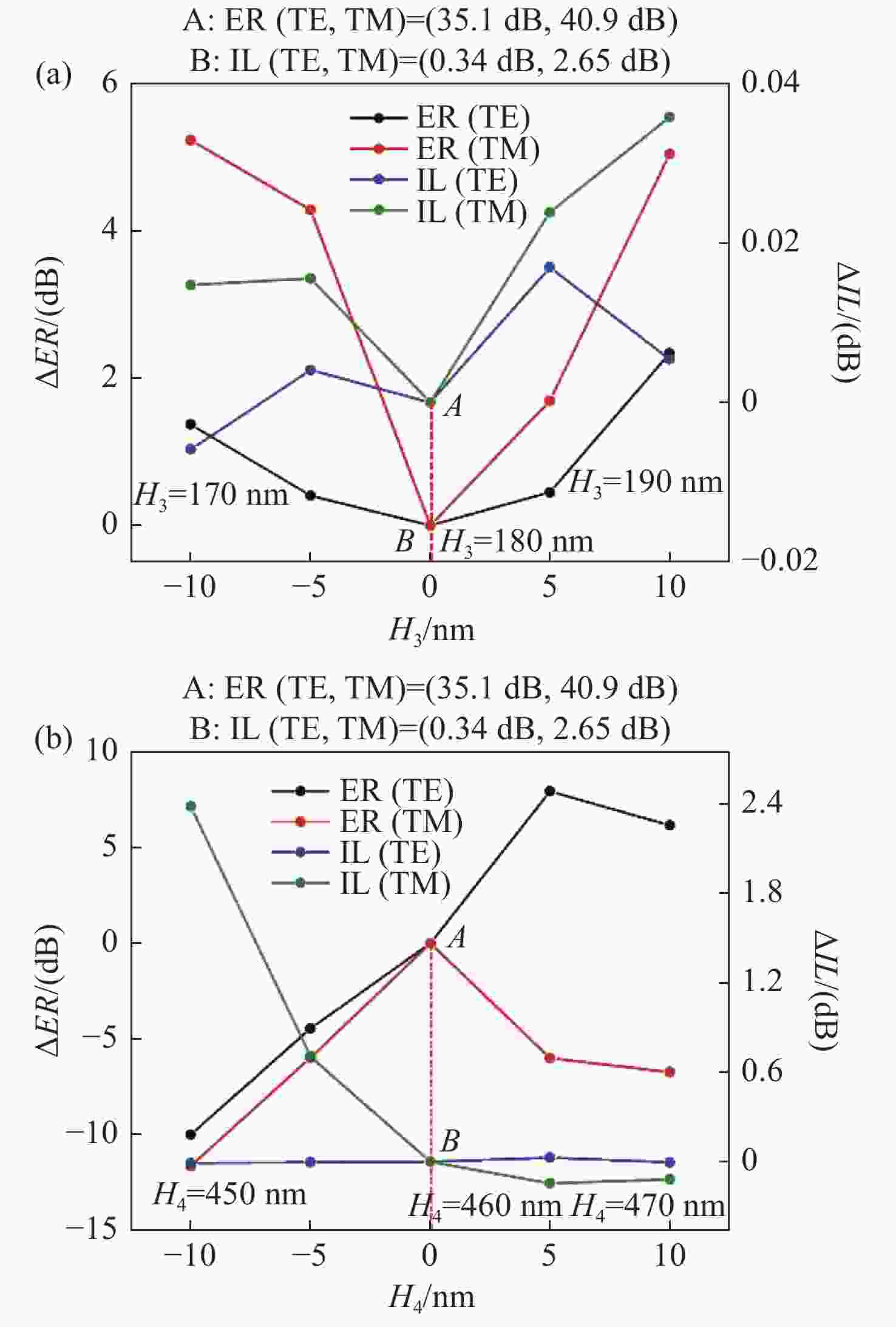
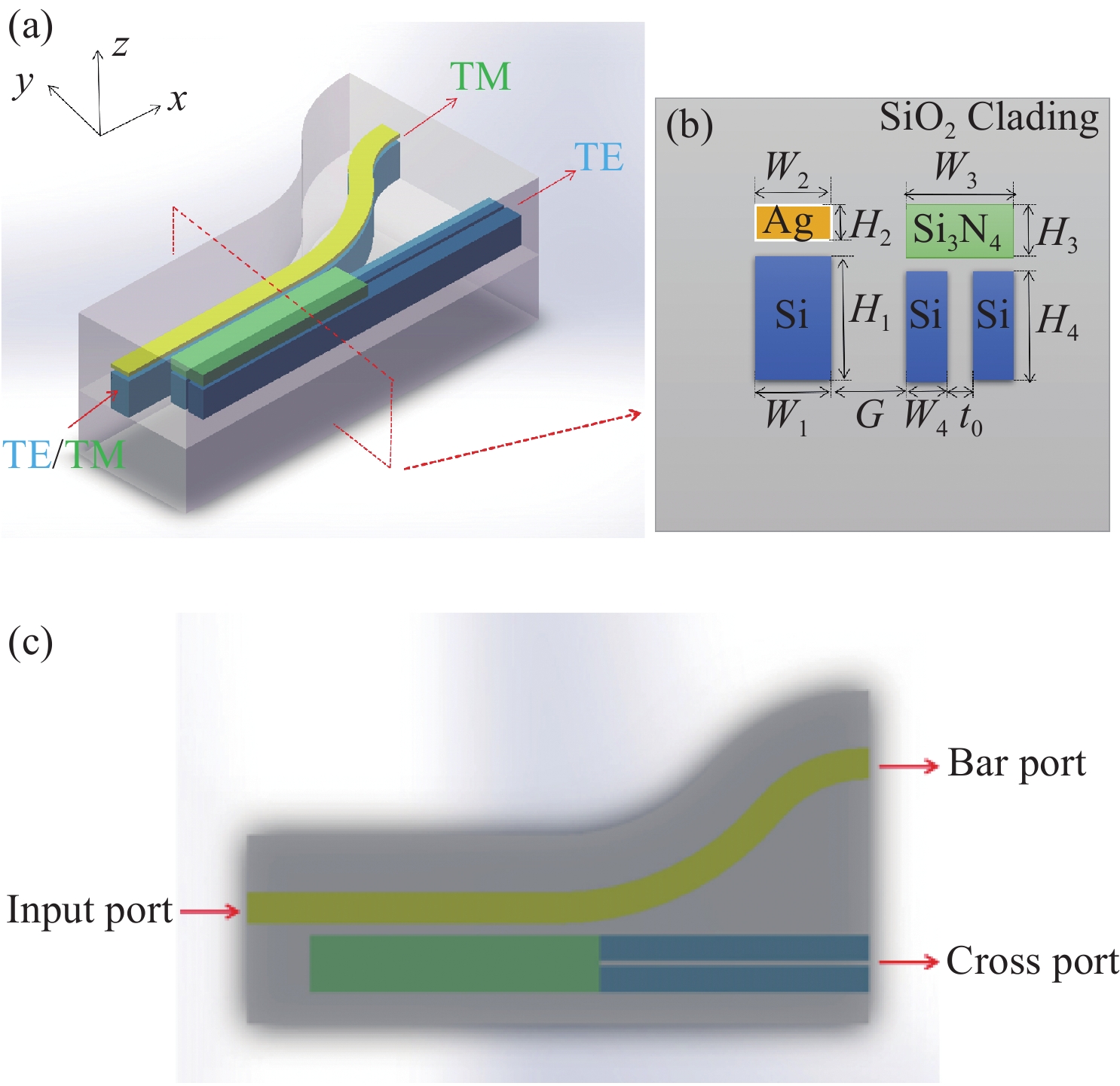
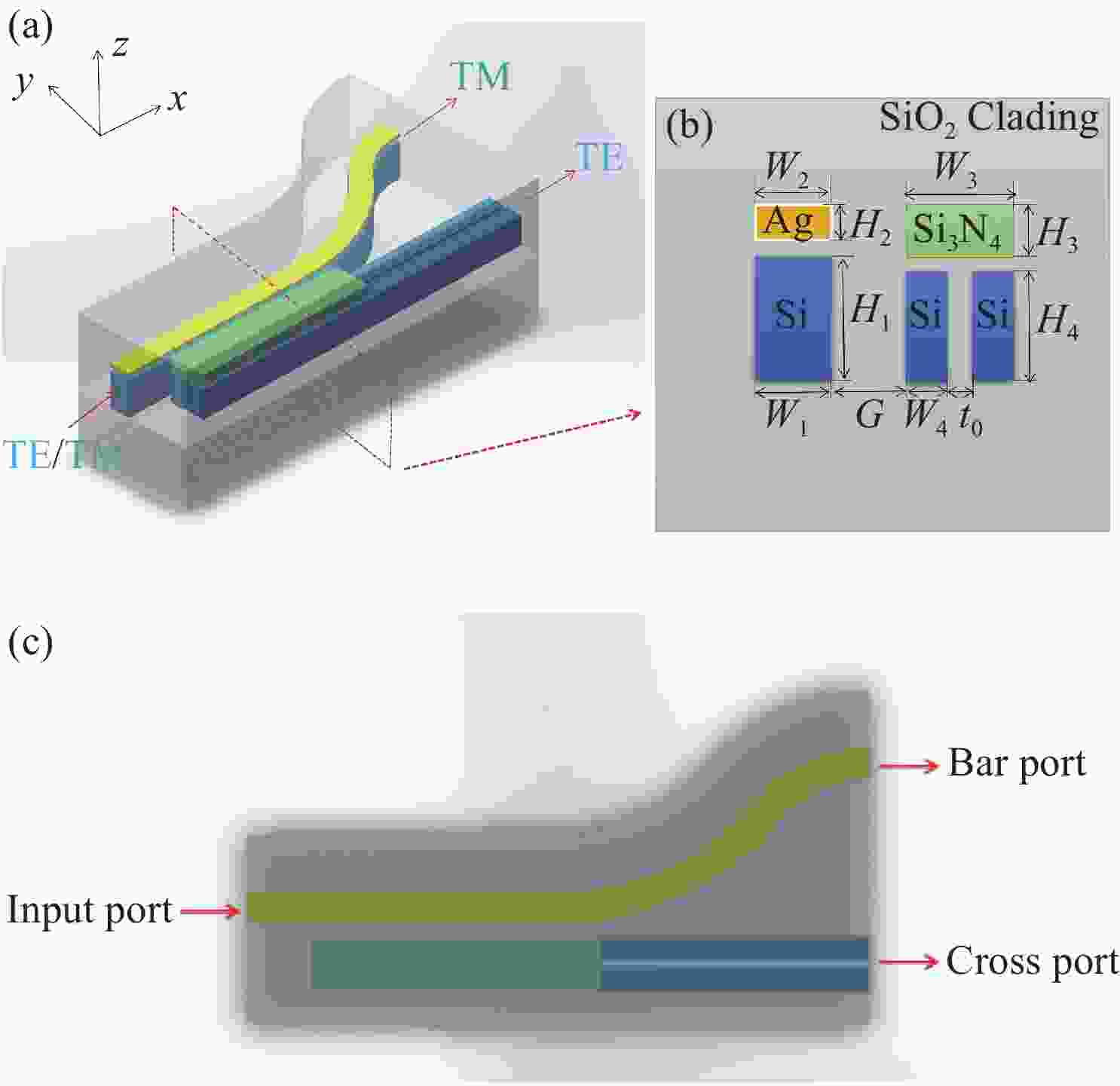
为了提高偏振分束器的消光比,提出了一种由混合等离子体水平狭缝波导(HSW)和氮化硅混合垂直狭缝波导(VSW)组成的双槽超紧凑偏振分束器(PBS)。同时,包层材料为二氧化硅,既能防止混合等离子体氧化,又便于与其他器件集成。采用有限元方法仿真HSW和VSW的模态特性。HSW和VSW波导在特定的宽度下TE偏振模式是满足相位匹配的,而TM偏振模式相位不匹配。因此,HSW波导中的TE模式与VSW波导发生强耦合,而TM模式直接通过HSW波导。结果表明:在1.55 μm的TE模式下,PBS的消光比(ER)为35.1 dB,插入损耗(IL)为0.34 dB,在TM模式下,PBS的ER和IL分别为40.9 dB和2.65 dB。所设计的PBS有100 nm的工作带宽,具有高ER,低IL的特点,适用于光子集成电路(PICs)。
Abstract:To improve the extinction ratio of a polarization beam splitter, we propose a dual-slot ultra-compact polarization splitter (PBS) consisting of a hybrid plasma Horizontal Slot Waveguide (HSW) and a silicon nitride hybrid Vertical Slot Waveguide (VSW). The coating material is silicon dioxide, which can prevent the oxidation of the mixed plasma and also facilitate integration with other devices. The mode characteristics of the HSW and VSW are simulated by using the Finite Element Method (FEM). At suitable HSW and VSW widths, the TE polarization modes in HSW and VSW are phase-matched, while the TM polarization modes are phase mismatched. Therefore, the TE mode in an HSW waveguide is strongly coupled with a VSW waveguide by adopting a dual-slot, while the TM mode directly passes through the HSW waveguide. The results show that PBS achieves an Extinction Ratio (ER) of 35.1 dB and an Insertion Loss (IL) of 0.34 dB for the TE mode at 1.55 μm. For the TM mode, PBS reached 40.9 dB for ER and 2.65 dB for IL. The proposed PBS is designed with 100 nm bandwidth, high ER, and low IL, which can be suitable for photonic integrated circuits (PICs).
-
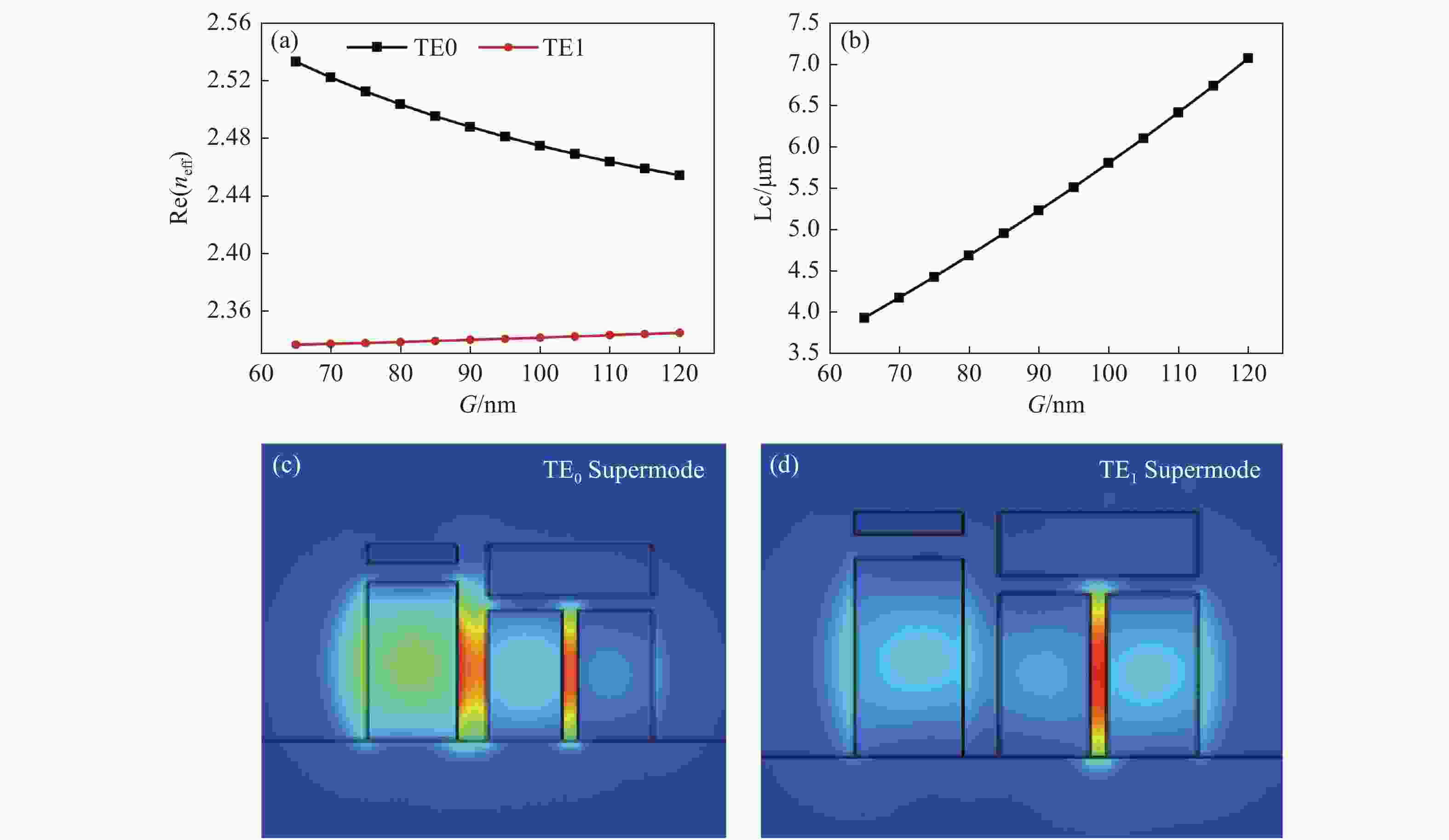
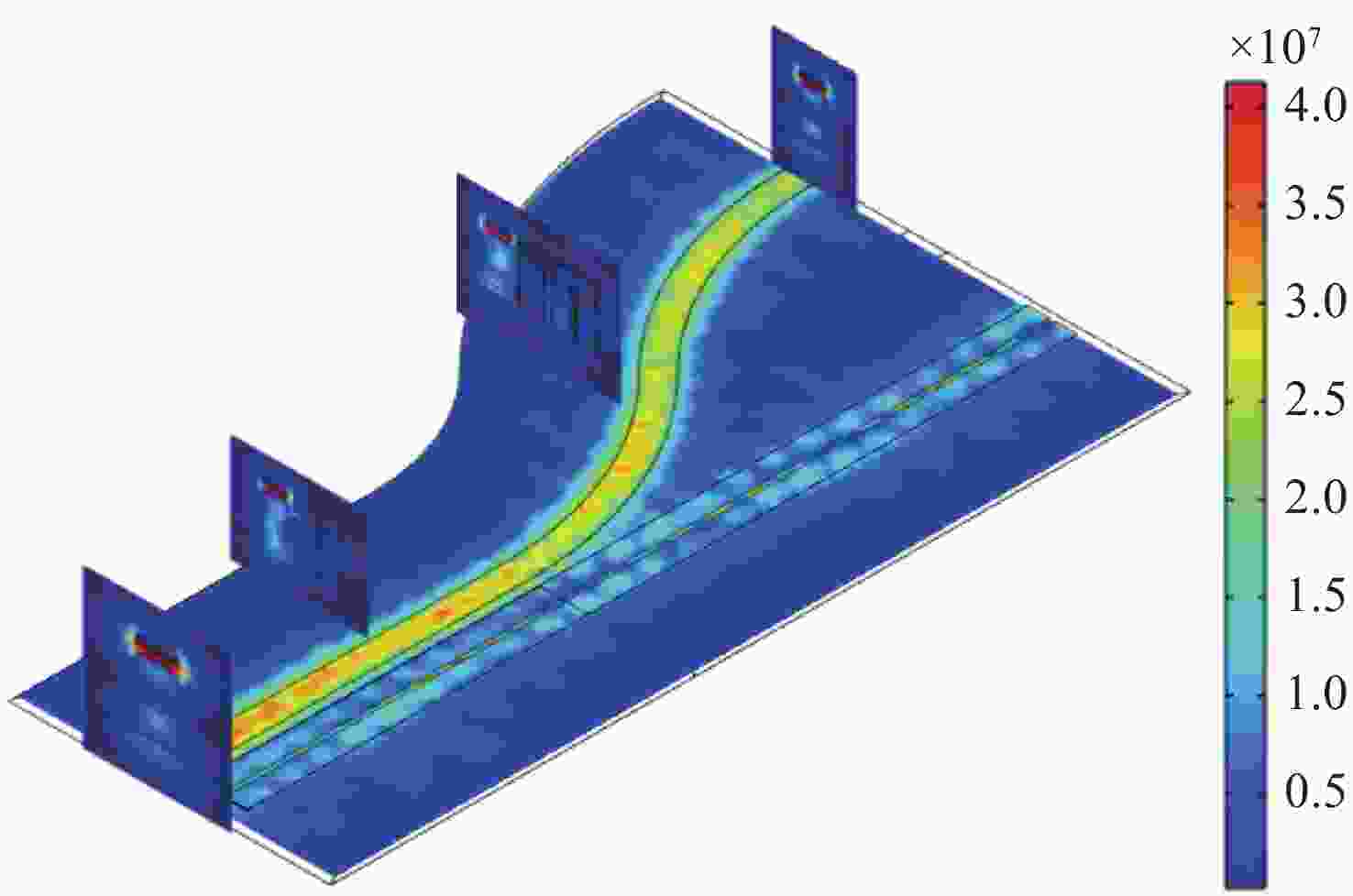
Figure 2. Influence of waveguide width on the effective refractive index. (a) The real part of the refractive index of TE mode and TM mode varying with width in the HSW and VSW; the field distribution of the TE mode in the (b) HSW and (c) VSW, and the field distribution of the TM mode in the (d) HSW and (e) VSW
Table 1. Performance comparison of the polarization
Reference
paperλ
(μm)Length
(μm)ER
(dB)IL
(dB)Input
modeBandwidth
(nm)[29] 1.55 26.27 17 <1 TM 100 27 TM [30] 1.55 11 27.1 0.41 TE 170 [31] 1.55 4 30 1 TE 100 27 0.18 TM [32] 1.55 14 38.4 3.26 TE 100 20.9 0.14 TM [33] 1.55 16 26.7 0.05 TE 140 21.3 TM [34] 1.55 9.9 45.6 <0.3 TE 100 8.3 20 <0.1 TM [35] 3.5 25 19.78 1.64 TE 400 7.78 2.64 TM This work 1.55 5.2 40.9 2.65 TM 100 35.1 0.34 TE -
[1] GAO L F, HU F F, WANG X J, et al. Ultracompact and silicon-on-insulator-compatible polarization splitter based on asymmetric plasmonic–dielectric coupling[J]. Applied Physics B, 2013, 113(2): 199-203. doi: 10.1007/s00340-013-5457-7 [2] ZOU J, XIA X, CHEN G T, et al. Birefringence compensated silicon nanowire arrayed waveguide grating for CWDM optical interconnects[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(7): 1834-1837. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.001834 [3] HOSSEINI A, RAHIMI S, XU X, et al. Ultracompact and fabrication-tolerant integrated polarization splitter[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(20): 4047-4049. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.004047 [4] HUANG Y W, TU ZH, YI H X, et al. High extinction ratio polarization beam splitter with multimode interference coupler on SOI[J]. Optics Communications, 2013, 307: 46-49. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2013.05.055 [5] LIANG T K, TSANG H K. Integrated polarization beam splitter in high index contrast silicon-on-insulator waveguides[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2005, 17(2): 393-395. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2004.839462 [6] DAI D X, WANG ZH, BOWERS J E. Ultrashort broadband polarization beam splitter based on an asymmetrical directional coupler[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(13): 2590-2592. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.002590 [7] FENG J J, AKIMOTO R, ZENG H P. Asymmetric silicon slot-waveguide-assisted polarizing beam splitter[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2016, 28(12): 1294-1297. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2016.2541672 [8] HSU C W, CHANG T K, CHEN J Y, et al. 8.13 μm in length and CMOS compatible polarization beam splitter based on an asymmetrical directional coupler[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(12): 3313-3318. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.003313 [9] KIM D W, LEE M H, KIM Y, et al. Planar-type polarization beam splitter based on a bridged silicon waveguide coupler[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(2): 998-1004. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.000998 [10] KIM S, QI M H. Copper nanorod array assisted silicon waveguide polarization beam splitter[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(8): 9508-9516. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.009508 [11] LIN SH Y, HU J J, CROZIER K B. Ultracompact, broadband slot waveguide polarization splitter[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(15): 151101. doi: 10.1063/1.3579243 [12] NI B, XIAO J B. Ultracompact and broadband silicon-based polarization beam splitter using an asymmetrical directional coupler[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2017, 53(4): 1-8. [13] WU H, TAN Y, DAI D X. Ultra-broadband high-performance polarizing beam splitter on silicon[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(6): 6069-6075. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.006069 [14] XU H N, SHI Y CH. On-chip silicon TE-pass polarizer based on asymmetrical directional couplers[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(11): 861-864. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2693223 [15] XU Y, XIAO J B. Compact and high extinction ratio polarization beam splitter using subwavelength grating couplers[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(4): 773-776. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.000773 [16] KIM D W, LEE M H, KIM Y, et al. Ultra-compact transverse magnetic mode-pass filter based on one-dimensional photonic crystals with subwavelength structures[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(19): 21560-21565. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.021560 [17] ZHANG Y, HE Y, WU J Y, et al. High-extinction-ratio silicon polarization beam splitter with tolerance to waveguide width and coupling length variations[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(6): 6586-6593. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.006586 [18] GALAN J V, SANCHIS P, GARCIA J, et al. Study of asymmetric silicon cross-slot waveguides for polarization diversity schemes[J]. Applied Optics, 2009, 48(14): 2693-2696. doi: 10.1364/AO.48.002693 [19] KOMATSU M A, SAITOH K, KOSHIBA M. Design of highly-nonlinear horizontal slot waveguide with low and flat dispersion[J]. Optics Communications, 2013, 298-299: 180-184. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2013.01.047 [20] SANCHIS P, BLASCO J, MARTINEZ A, et al. Design of silicon-based slot waveguide configurations for optimum nonlinear performance[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2007, 25(5): 1298-1305. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2007.893909 [21] SUN CH W, RONG K X, GAN F Y, et al. An on-chip polarization splitter based on the radiation loss in the bending hybrid plasmonic waveguide structure[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(10): 101105. doi: 10.1063/1.4997234 [22] WANG J, LIANG D, TANG Y B, et al. Realization of an ultra-short silicon polarization beam splitter with an asymmetrical bent directional coupler[J]. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(1): 4-6. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.000004 [23] AO X Y, LIU L, WOSINSKI L, et al. Polarization beam splitter based on a two-dimensional photonic crystal of pillar type[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89(17): 171115. doi: 10.1063/1.2360201 [24] DAI D X, BOWERS J E. Novel ultra-short and ultra-broadband polarization beam splitter based on a bent directional coupler[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(19): 18614-18620. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.018614 [25] HEAVENS O S. Handbook of optical constants of solids II[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2011, 39(1): 189. [26] CHEE J, ZHU SH Y, LO G Q. CMOS compatible polarization splitter using hybrid plasmonic waveguide[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(23): 25345-25355. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.025345 [27] AHMED R, RIFAT A A, SABOURI A, et al. Multimode waveguide based directional coupler[J]. Optics Communications, 2016, 370: 183-191. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.03.015 [28] MA Y Q, FARRELL G, SEMENOVA Y, et al. Low loss, high extinction ration and ultra-compact plasmonic polarization beam splitter[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2014, 26(7): 660-663. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2014.2302354 [29] NIKUFARD M, KHOMAMI A R. Hybrid plasmonic polarization splitter using three-waveguide directional coupler in InGaAsP/InP[J]. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 2016, 48(5): 296. doi: 10.1007/s11082-016-0576-0 [30] NI B, XIAO J B. Plasmonic-assisted TE-pass polarizer for silicon-based slot waveguides[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2018, 30(5): 463-466. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2018.2798709 [31] XIE Y, CHEN ZH X, YAN J, et al. Combination of surface plasmon polaritons and subwavelength grating for polarization beam splitting[J]. Plasmonics, 2020, 15(1): 235-241. doi: 10.1007/s11468-019-01032-6 [32] XU ZH Y, LYU T, SUN X H. Compact silicon-based TM-pass/TE-divide polarization beam splitter using contra-directional grating couplers assisted by horizontal slot waveguide[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 451: 17-22. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.05.054 [33] ZHANG L, ZHANG L, FU X, et al. Compact, broadband and low-loss polarization beam splitter on lithium-niobate-on-insulator using a silicon nanowire assisted waveguide[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2020, 12(5): 6601906. [34] NIU CH Q, LIU ZH, LI X L, et al. High extinction ratio polarization beam splitter realized by separately coupling[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2020, 32(18): 1183-1186. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2020.3016028 [35] WANG F, CHEN Y K, LI CH Q, et al. Ultracompact and broadband mid-infrared polarization beam splitter based on an asymmetric directional coupler consisting of GaAs–CaF2 hybrid plasmonic waveguide and GaAs nanowire[J]. Optics Communications, 2022, 502: 127418. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2021.127418 [36] FILIMONOVA N I, ILYUSHIN V A, VELICHKO A A. Molecular beam epitaxy of BaF2/CaF2 buffer layers on the Si(100) substrate for monolithic photoreceivers[J]. Optoelectronics,Instrumentation and Data Processing, 2017, 53(3): 303-308. doi: 10.3103/S8756699017030153 [37] BARKAI M, LEREAH Y, GRÜNBAUM E, et al. Epitaxial growth of silicon and germanium films on CaF2/Si[J]. Thin Solid Films, 1986, 139(3): 287-297. doi: 10.1016/0040-6090(86)90058-1 [38] CHENG ZH, WANG J, HUANG Y Q, et al. Realization of a compact broadband polarization beam splitter using the three-waveguide coupler[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2019, 31(22): 1807-1810. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2019.2948076 -





 下载:
下载: