-
摘要: 太赫兹频率的相干声子在纳米尺度器件的探测和操控领域具有重要的应用价值。半导体超晶格声子 器是实现太赫兹频率相干声子源稳定输出的重要途径。本文首先回顾了GHz到THz频率范围声学放大的多种方法,然后详细阐述了超晶格声子放大、超晶格声学布拉格镜的工作原理与设计方法以及声子 器的阈值条件,同时总结了电抽运和光抽运结构器件的研究现状,最后简要讨论了亚太赫兹声子 器在声-电子领域的应用。分析表明,这种能够产生强相干太赫兹声子的半导体超晶格声子 器在纳米尺度器件的探测与成像等方面具有广阔的发展前景。Abstract: The coherent phonons at terahertz frequency have important applications in the field of detection and control of nanometer scale devices. Semiconductor superlattice phonon laser is an important way to realize the stable source of terahertz coherent phonon. Firstly, some methods about acoustic amplification in GHz-THz frequency range are reviewed. Next, the phonon amplification in superlattices, the working principles and design methods of superlattice acoustic Bragg reflectors and threshold of phonon laser are all elaborated. Then the research status on electrically pumped and optically pumped phonon lasers are summarized. Lastly, the applications for sub-terahertz phonon laser in the acoustic-electrons field are briefly discussed. The semiconductor superlattice phonon laser producing strong coherent phonons at terahertz frequency will have a much broader development prospect in multiple aspects, such as the detection and imaging of nanoscale devices.
-
Key words:
- phonon laser /
- phononic crystal /
- semiconductor superlattic /
- laser ultrasonic
-
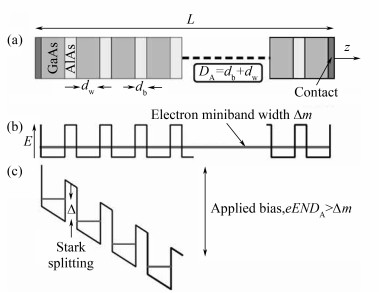
图 1 GaAs/AlAs超晶格示意图; (b)零偏压下的电学能带结构示意图; (c)施加电场E后的能带结构示意图[33]
Figure 1. (a) Schematic diagram of GaAs/AlAs superlattice; (b) Schematic diagram of electronic band structure with zero applied bias; (c) Schematic diagram of band structure under applied bias electric field E
图 2 具有N个周期的周期性超晶格示意图[37]
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of periodic superlattice with N cycles
图 3 50周期GaAs/AlAs超晶格中折叠的声子色散[39]
Figure 3. Folded phonon dispersion for a 50-cycle GaAs/AlAs superlattice
图 4 (a)抽运-探测实验设置及(b)光抽运声子 器样品的电结构示意图[53]
Figure 4. (a) Experiment arrangement for pump-probe measurement and (b) schematic diagram of optical pumped phonon laser sample
图 5 抽运-探测实验信号(插图中展示了440 GHz的声子振荡和傅里叶谱[53])
Figure 5. Signal of pump-probe measurement (440 GHz phonon oscillations and Fourier spectrum are shown in the insets)
图 6 在零偏压时(虚线)和有偏压诱导时(实线)的傅里叶谱[53]
Figure 6. Fourier spectrum at zero bias (dashed line) and bias-induced signal (solid line)
图 7 电抽运声子 器的结构[39]
Figure 7. Structure diagram of an electrical pumped phonon laser
图 8 (a) θ=0°时测辐射热计的声子信号; (b)声子 器的微分电导与斯塔克位移间的关系[39]
Figure 8. (a) Phonon signal of bolometers at θ=0°; (b) Differential conductance of phonon laser as a function of Stark shift
图 9 垂直腔面发射声子 器的示意图[33]
Figure 9. Schematic diagram of vertical cavity surface-emitting phonon laser
图 10 2个测辐射热计上信号与抽运电压间的关系[33]
Figure 10. Time-integrated signal as a function of electrical pump voltage for two bolometers
-
[1] 程旭. 激发声波技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013.CHENG X. Research on laser-generated sonic wave[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2013. (in Chinese) [2] 刘涛, 王江安, 宗思光, 等.水下目标的 声探测技术[J].舰船科学技术, 2012(6):70-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCKX201206019.htmLIU T, WANG J A, ZONG S G, et al.. The detection of the laser induced sound[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2012(6):70-73. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCKX201206019.htm [3] 刘丹. 超声激励与检测技术研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2015.LIU D. Research of the laser ultrasonic excitation and detection technology[D]. Taiyuan:North University of China, 2015. (in Chinese) [4] 刘洋, 项占琴, 唐志峰. 超声技术在钢轨探伤中的应用研究[J].机械设计与制造, 2009(10):60-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2009.10.024LIU Y, XIANG ZH Q, TANG ZH F. Application of laser-induced ultrasound on rail flaw inspection[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2009(10):60-61. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2009.10.024 [5] ARMSTRONG M R, REED E J, KIM K Y, et al.. Observation of terahertz radiation coherently generated by acoustic waves[J]. Nature Physics, 2009, 5(4):285-288. doi: 10.1038/nphys1219 [6] MOSS D M, AKIMOV A V, CAMPION R P, et al.. Ultrafast strain-induced electronic transport in a GaAs pn junction diode[J]. Chinese Journal of Physics, 2011, 49(1):499-505. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/243439722_Ultrafast_acoustical_gating_of_the_photocurrent_in_a_p-i-n_tunneling_diode_incorporating_a_quantum_well [7] MOSS D M, AKIMOV A V, GLAVIN B A, et al.. Ultrafast strain-induced current in a GaAs Schottky diode[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 106(6):066602. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.066602 [8] TUCKER E B. Amplification of 9.3-kMc/sec ultrasonic pulses by maser action in ruby[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1961, 6(10):547. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.6.547 [9] TUCKER E B. Attenuation of longitudinal ultrasonic vibrations by spin-phonon coupling in ruby[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1961, 6(4):183. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.6.183 [10] BRON W E, GRILL W. Stimulated phonon emission[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1978, 40(22):1459. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.40.1459 [11] HU P. Stimulated emission of 29 cm-1 phonons in ruby[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1980, 44(6):417. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.44.417 [12] OVERWIJK M H F, DIJKHUIS J I, de WIJN H W. Superfluorescence and amplified spontaneous emission of 29 cm-1 phonons in ruby[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1990, 65(16):2015. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.65.2015 [13] PRIEUR J Y, DEVAUD M, JOFFRIN J, et al.. Sound amplification by stimulated emission of phonons using two-level systems in glasses[J]. Physica B:Condensed Matter, 1996, 219:235-238. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229247797_Sound_amplification_by_stimulated_emission_of_phonons_using_two-level_systems_in_glasses [14] PHILLIPS W A. Two-level states in glasses[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 1987, 50(12):1657. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/50/12/003 [15] 汪丽杰, 佟存柱, 曾玉刚, 等.高亮度布拉格反射波导 器[J].发光学报, 2013(6):787-791. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FGXB201306022.htmWANG L J, TONG C ZH, ZENG Y G, et al.. High brightness Bragg reflection waveguide laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2013(6):787-791. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FGXB201306022.htm [16] 戎佳敏, 邢恩博, 赵帅, 等. 2 μm GaSb基低垂直发散角布拉格反射波导 器优化设计[J].发光学报, 2015(12):1434-1439.RONG J M, XING E B, ZHAO S H, et al.. Modeling of 2 μm GaSb based Bragg reflection waveguide lasers with ultra-low vertical divergence[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2015(12):1434-1439. (in Chinese) [17] SRIVASTAVA G P. The physics of phonons[M]. Bristol:Adam Hilger, 1990. [18] TRIGO M, BRUCHHAUSEN A, FAINSTEIN A, et al.. Confinement of acoustical vibrations in a semiconductor planar phonon cavity[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 89(22):227402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.227402 [19] HUYNH A, LANZILLOTTI-KIMURA N D, JUSSERAND B, et al.. Subterahertz phonon dynamics in acoustic nanocavities[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 97(11):115502. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.115502 [20] 刘军. 高Q声子晶体声波传感机理及实验研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2013.LIU J. The theoretical and experimental investigation of phononic crystals for high Q acoustic sensing[D]. Changchun:Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013. (in Chinese) [21] KOMIRENKO S M, KIM K W, DEMIDENKO A A, et al.. Generation and amplification of sub-THz coherent acoustic phonons under the drift of two-dimensional electrons[J]. Physical Review B, 2000, 62(11):7459. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.62.7459 [22] MAKLER S S, VASILEVSKIY M I, ANDA E V, et al.. A source of terahertz coherent phonons[J]. Journal of Physics:Condensed Matter, 1998, 10(26):5905. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/10/26/017 [23] NARAYANAMURTI V, STÖRMER H L, CHIN M A, et al.. Selective transmission of high-frequency phonons by a superlattice:the "dielectric" phonon filter[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1979, 43(27):2012. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.43.2012 [24] GLAVIN B A, KOCHELAP V A, LINNIK T L, et al.. Generation of high-frequency coherent acoustic phonons in superlattices under hopping transport-I:linear theory of phonon instability[J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 65(8):085303. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.65.085303 [25] GLAVIN B A, KOCHELAP V A, LINNIK T L, et al.. Generation of high-frequency coherent acoustic phonons in superlattices under hopping transport-Ⅱ:steady-state phonon population and electric current in generation regime[J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 65(8):085304. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.65.085304 [26] GLAVIN B A, KOCHELAP V A, LINNIK T L. Generation of high-frequency coherent acoustic phonons in a weakly coupled superlattice[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1999, 74(23):3525-3527. doi: 10.1063/1.124149 [27] STANTON N M, KINI R N, KENT A J, et al.. Terahertz phonon optics in GaAs/AlAs superlattice structures[J]. Physical Review B, 2003, 68(11):113302. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.68.113302 [28] LANZILLOTTI-KIMURA N D, PERRIN B, FAINSTEIN A, et al.. Nanophononic thin-film filters and mirrors studied by picosecond ultrasonics[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 96(5):053101. doi: 10.1063/1.3295701 [29] ROZAS G, WINTER M F P, JUSSERAND B, et al.. Lifetime of THz acoustic nanocavity modes[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102(1):015502. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.015502 [30] LANZILLOTTI-KIMURA N D, FAINSTEIN A, LEMAÎTRE A, et al.. Nanowave devices for terahertz acoustic phonons[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(8):083113. doi: 10.1063/1.2178415 [31] 吕苏娜. 应用声子晶体滤波器改善声子 器线宽的研究[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2014.LÜ S N. The study on the improvement of linewidth of phonon laser with phonon crystal filter[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 2014. (in Chinese) [32] 徐丹峰. 基于声子光栅调制的声子 器性能分析[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2014.XU D F. Performance analysis on phonon lasers ofphononic grating modulation[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 2014. (in Chinese) [33] MARYAM W, AKIMOV A V, CAMPION R P, et al.. Dynamics of a vertical cavity quantum cascade phonon laser structure[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4(4):2184. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/20023850.pdf [34] KINI R N, KENT A J, STANTON N M, et al.. Angle dependence of acoustic phonon-assisted tunneling in a weakly coupled superlattice:evidence for terahertz phonon amplification[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 98(3):033514-033514. doi: 10.1063/1.1989435 [35] CAVILL S A, CHALLIS L J, KENT A J, et al.. Acoustic phonon-assisted tunneling in GaAs/AlAs superlattices[J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 66(23):235320. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.66.235320 [36] BEARDSLEY R P, CAMPION R P, GLAVIN B A, et al.. A GaAs/AlAs superlattice as an electrically pumped THz acoustic phonon amplifier[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2011, 13(7):073007. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/13/7/073007 [37] MIZUNO S, TAMURA S. Theory of acoustic-phonon transmission in finite-size superlattice systems[J]. Physical Review B, 1992, 45(2):734. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.45.734 [38] KENT A J, BEARDSLEY R. Semiconductor superlattice sasers at terahertz frequencies:design, fabrication and measurement[M]//Length-Scale Dependent Phonon Interactions. New York:Springer, 2014:227-257. [39] KENT A J, KINI R N, STANTON N M, et al.. Acoustic phonon emission from a weakly coupled superlattice under vertical electron transport:observation of phonon resonance[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 96(21):215504. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.215504 [40] RYTOV S M. Acoustical properties of a thinly laminated medium[J]. Soviet Physics Acoustics, 1956, 2:68-80. [41] KENT A J, STANTON N M, CHALLIS L J, et al.. Generation and propagation of monochromatic acoustic phonons in gallium arsenide[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 81(18):3497-3499. doi: 10.1063/1.1515118 [42] VVEDENSKY D. Epitaxial growth of semiconductors[M]//BARNHAM K, VVEDENSKY D. Low-Dimensional Semiconductor Structures:Fundamentals and Device Applications. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2001:1-55. [43] YAMAMOTO A, MISHINA T, MASUMOTO Y, et al.. Coherent oscillation of zone-folded phonon modes in GaAs-AlAs superlattices[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1994, 73(5):740-743. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.73.740 [44] BARTELS A, DEKORSY T, KURZ H, et al.. Coherent zone-folded longitudinal acoustic phonons in semiconductor superlattices:excitation and detection[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1999, 82(5):1044-1047. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.82.1044 [45] SUN C K, LIANG J C, YU X Y. Coherent acoustic phonon oscillations in semiconductor multiple quantum wells with piezoelectric fields[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 84(1):179-182. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.179 [46] MATSUDA O, WRIGHT O B, HURLEY D H, et al.. Coherent shear phonon generation and detection with ultrashort optical pulses[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93(9):095501. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.095501 [47] TRIGO M, ECKHAUSE T A, REASON M, et al.. Observation of surface-avoiding waves:a new class of extended states in periodic media[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 97(12):124301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.124301 [48] DEVOS A, POINSOTTE F, GROENEN J, et al.. Strong generation of coherent acoustic phonons in semiconductor quantum dots[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 98(20):207402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.207402 [49] MOSS D M, AKIMOV A V, KENT A J, et al.. Coherent terahertz acoustic vibrations in polar and semipolar gallium nitride-based superlattices[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(1):011909. doi: 10.1063/1.3056653 [50] LANZILLOTTI-KIMURA N D, FAINSTEIN A, PERRIN B, et al.. Bloch oscillations of THz acoustic phonons in coupled nanocavity structures[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104(19):197402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.197402 [51] BRUCHHAUSEN A, GEBS R, HUDERT F, et al.. Subharmonic resonant optical excitation of confined acoustic modes in a free-standing semiconductor membrane at GHz frequencies with a high-repetition-rate femtosecond laser[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 106(7):077401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.077401 [52] WALKER P M, KENT A J, HENINI M, et al.. Terahertz acoustic oscillations by stimulated phonon emission in an optically pumped superlattice[J]. Physical Review B, 2009, 79(24):245313. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.79.245313 [53] BEARDSLEY R P, AKIMOV A V, HENINI M, et al.. Coherent terahertz sound amplification and spectral line narrowing in a stark ladder superlattice[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104(8):085501. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.085501 [54] WILSON T, KASPER E, OEHME M, et al.. Evidence of longitudinal acoustic phonon generation in Si doping superlattices by Ge prism-coupled THz laser radiation[J]. IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering, 2014, 68:012008. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/68/1/012008 [55] HUYNH A, PERRIN B, LEMAîTRE A. Semiconductor superlattices:a tool for terahertz acoustics[J]. Ultrasonics, 2015, 56:66-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2014.07.009 [56] SHINOKITA K, REIMANN K, WOERNER M, et al.. Strong amplification of coherent acoustic phonons by intraminiband currents in a semiconductor superlattice[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016, 116(7):075504. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.075504 [57] 王立军, 宁永强, 秦莉, 等.大功率半导体 器研究进展[J].发光学报, 2015(1):1-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FGXB201501002.htmWANG L J, NING Y Q, Qin L, et al.. Development of high power diode laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2015, 01:1-19. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FGXB201501002.htm [58] 佟存柱, 汪丽杰, 田思聪, 等.布拉格反射波导半导体 器的研究[J].中国光学, 2015(3):480-498. //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract9311.shtmlTONG C Z, WANG L J, TIAN S C, et al.. Study on Bragg reflection waveguide diode laser[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015(3):480-498. (in Chinese) //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract9311.shtml -






 下载:
下载: