Generating method of non-diffracting beam with long-distance propagation and controllable parameters
-
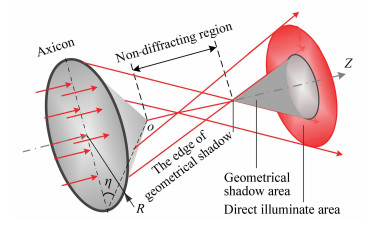
摘要: 为了消除光学器件几何参数对无衍射光束传播特性调整的限制,实现长距空间中无衍射光束传播时特性参数的可控性,首先,通过研究axicon折射阴影区的电场分布特征,发现axicon无衍射区外过临界面后的近轴区域虽处于几何折射阴影近轴区域内,但仍存在光强服从第一类零阶贝赛尔函数分布的球面波;以此为基础,提出了一种不受传播空间距离限制的无衍射光束的生成方式;最后,在近12 m的尺度范围内进行无衍射光传播特性参数测试,发现其实验参数与理论计算值的差值不超过0.1 μm。该无衍射光通过对第一类零阶贝塞尔函数分布的球面衍射光斑准直生成,本质上区别于传统的干涉无衍射光束生成方式,易于生成大尺度空间无衍射光束。该无衍射光生成方式适合用于非能量使用情况下大尺度空间的直线基准、光束空间通讯等领域,具有较大的价值与意义。Abstract: In order to eliminate the restriction of optical device geometrical parameters on the propagation characteristics of non-diffracting beams and to achieve the controllability of the characteristic parameters of non-diffracting beams propagating in long-distance space, the generation method of parameter controlled non-diffracting beam over long distance is studied in this paper. First of all, by studying the electric field distribution of the axicon refraction shadow area, it is found that although the paraxial area beyond the critical surface of the axicon non-diffractive area is in the paraxial area of the geometric refraction shadow, there is still a spherical wave whose intensity follows first kind of zero-order Bessel function distribution. On this basis, a non-diffracting light generation method is proposed which is not limited by the distance of the propagation space. Finally, the parameters of the non-diffracing light propagation characteristics are tested in the range of nearly 12 m, and it is found that the difference between the experimental and theoretical values is less than 0.1 μm. The non-diffracting beam is generated by collimating spherical diffracted light spots of the first kind of zero-order Bessel function distribution, which is essentially different from the traditional method of generating interference and non-diffracting light beams and is easy to generate large-scale space non-diffracting beams. In general, this method is particularly suitable for the use in non-energy conditions, such as large-scale linear reference space, beam space communications, and has enormous engineering application value.
-
图 3 axicon近轴折射阴影区不同横截面处的光强分布。图像传感器(CCD)的曝光时间用ET表示,在近轴区所有图像的大为1.32 mm×1.32 mm:(a)z=1 200 mm<zmax, ET=0.1 ms; (b)z=2 916 mm≈zmax, ET=1 ms; (c)z=4 582 mm, ET=2 ms; (d)z=5 076 mm, ET=3 ms; (e)z=7 285 mm, ET=10 ms; (f)z=11 797 mm, ET=40 ms。图片(c)~(f)是超出最大无衍射距离的Arago-Poisson衍射点
Figure 3. Intensity distributions in paraxial refraction shadow area of axicon at different longitudinal sections. The ET is used to represents corresponding exposure time for image sensor(CCD), and the shot-size of all images is 1.32 mm×1.32 mm in paraxial region:(a)z=1 200 mm < zmax, ET=0.1 ms; (b)z=2 916 mm≈zmax, ET=1ms; (c)z=4 582 mm, ET=2 ms; (d)z=5 076 mm, ET=3 ms; (e)z=7 285 mm, ET=10 ms; (f)z=11 797 mm, ET=40 ms. The figure (c)~(f) are Arago-Poisson diffraction spots, which shoot in out of the region of non-diffracting area
图 4 axicon从无衍射区过渡到几何折射阴影区光强分布随传播距离变化情况。用ET表示CCD的曝光时间,在近轴区所有图像的大为2.89 mm× 2.89 mm:(a)z=2 866<zmax, ET=0.5 ms; (b)z=2 916≈zmax, ET=2 ms; (c)z=3 095>zmax, ET=2 ms; (d)z=3 615>zmax, ET=5 ms; (e)z=3 704>zmax, ET=20 ms; (f)z=4 147>zmax, ET=100 ms; 图(b)~(d)为axicon无衍射临界点处的光强分布
Figure 4. Intensity distribution changes with propagation distance for axicon transition from non-diffraction area to geometrically refracted shadow area. Where the ET is used to represents the exposure time of the CCD, and the shot-size of all images is 2.89 mm×2.89 mm in paraxial region:(a)z=2 866 < zmax, ET=0.5 ms; (b)z=2 916≈zmax, ET=2 ms; (c)z=3 095 > zmax, ET=2 ms; (d)z=3 615 > zmax, ET=5 ms; (e)z=3 704 > zmax, ET=20 ms; (f)z=4 147 > zmax, ET=100 ms; The figure (b)~(d) is the distribution of intensity in paraxial critical point of the axicon′s non-diffracting
图 5 axicon几何折射阴影区测试曲线:(a)对应于图 3(c)光强沿径向的归一化光强分布与第一类理想零阶贝赛尔函数对比曲线;(b)实验测试的axicon衍射斑直径随传播方向距离变化曲线
Figure 5. Experimental curves in geometrical shadow area of the axicon lens. (a)Comparison curves of radial intensity distribution and the first kind ideal zero-order Bessel function for Fig. 3(c); (b)Observed diameters of diffraction spot for axicon lens varies with distance along the z-axis
-
[1] DURNIN J. Exact solutions for nondiffracting beams.Ⅰ.the scalar theory[J]. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 1987, 4(4):651-654. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.4.000651 [2] SERVANDO L A, CESAR R V, BENJAMIN P G, et al.. Quasi-one-dimensional optical lattices for soliton manipulation[J]. Opt. Lett., 2014, 39(22):6545-6548. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.006545 [3] SELCUK A, ARNOLD C L, BERNARD P, et al.. Generation of high quality tunable Bessel beams using a liquid-immersion axicon[J]. Opt. Commun., 2009, 282(16):3206-3209. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2009.05.026 [4] 王硕琛, 梅小华, 吴逢铁, 等.无衍射光束簇[J].华侨大学学报, 2016, 2:149-154. doi: 10.11830/ISSN.1000-5013.2016.02.0149WANG SH C, MEI X H, WU F T, et al.. The bunch of non-diffracing beam[J]. Journal of Huaqiao University, 2016, 2:149-154.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11830/ISSN.1000-5013.2016.02.0149 [5] TURUNEN J, VASARA A, FRIBERG A T. Holographic generation of diffraction-free beams[J]. Appl Opt., 1988, 27:3959-3962. doi: 10.1364/AO.27.003959 [6] 马国鹭, 曾国英, 赵斌.基于无衍射姿态探针和全站仪组合测量空间隐藏坐标[J].光学精密工程, 2015, 23(2):363-370. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/1dc38fed1eb91a37f0115c06.htmlMA G L, ZENG G Y, ZHAO B. Measurement of space coordinates in hidden parts by combining non-diffracting attitude probe and total station[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2015, 23(2):363-370.(in Chinese) https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/1dc38fed1eb91a37f0115c06.html [7] 刘华.利用汉克尔变换设计高斯光束整形衍射元件的应用研究[J].中国光学, 2016, 9(2):277-283. //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract9407.shtmlLIU H. Gaussian beam shaping diffractive optical element designed by Hankel transformation[J]. Chinese Optics., 2016, 9(2):277-283.(in Chinese) //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract9407.shtml [8] 张健, 栗孟娟, 阴刚华, 等.用于太空望远镜的大口径薄膜菲涅尔衍射元件[J].光学精密工程, 2016, 24(6):1289-1296. http://www.eope.net/gxjmgc/CN/abstract/abstract16420.shtmlZHANG J, LI M J, YIN G H, et al.. Large-diameter membrane Fresnel diffraction elements for space telescope[J]. Opt. Precision Eng., 2016, 24(6):1289-1296.(in Chinese) http://www.eope.net/gxjmgc/CN/abstract/abstract16420.shtml [9] 吕强, 李文昊, 巴音贺希格, 等.基于衍射光栅的干涉式精密位移测量系统[J].中国光学, 2017, 10(1):39-50. //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract9490.shtmlLV Q, LI W H, BAYANHESHIG, et al.. Interferometric precision displacement measurement system based on diffraction grating[J]. Chinese Optics., 2017, 10(1):39-50.(in Chinese) //www.illord.com/CN/abstract/abstract9490.shtml [10] GREENGARD A, SCHECHNER Y Y, PIESTUN R, et al.. Depth from diffracted rotation[J]. Opt. Lett., 2006, 31(21):181-183. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7332689_Depth_from_diffracted_rotation [11] 马国鹭, 刘丽贤, 赵斌.基于无衍射光的空间入射角测量及其自动标定[J].仪器仪表学报, 2016, 37(8):1906-1912. https://www.cnki.com.cn/lunwen-1016058201.htmlMA G L, LIU L X, ZHAO B. Measurement and automatic calibration of spatial incident angle based on non-diffracting L beam[J]. Chinese Journal of Science Instrument, 2016, 37(8):1906-1912.(in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/lunwen-1016058201.html [12] DAVIS J A, CARCOLE E, COTTRELL D M, et al.. Intensity and phase measurements of nondiffracting beams generated with a magneto-optic spatial light modulator[J]. Appl. Opt., 1996, 35(4):593-598. doi: 10.1364/AO.35.000593 [13] OZTAS Z, YUCE C. Discrete parametric oscillation and nondiffracting beams in a Glauber-Fock oscillator[J]. Physics Letters A, 2016, 380(40):3307-3311. doi: 10.1016/j.physleta.2016.07.054 [14] ZIOLKOWSKI R W, LEWIS D K, COOK B D, et al.. Evidence of localized wave transmission[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett., 1989, 62(2):147-150. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.62.147 [15] COX A J, DIBBLE D C. Nondiffracting beam from a spatially filtered Fabry-Perot resonator[J]. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 1992, 9(2):282-286. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.9.000282 [16] LÓPEZ-MARISCAL C, GUTIERREZ-VEGA C. The generation of nondiffracting beams using inexpensive computer-generated holograms[J]. J. Phys Am., 2007, 75(1):36-42. doi: 10.1119/1.2359001 [17] DAVIS J A, CARCOLE E, COTTRELL D M. Nondiffracting interference patterns generated with programmable spatial light modulators[J]. Appl. Opt., 1996, 35(4):599-602. doi: 10.1364/AO.35.000599 [18] INDEBETOUW G. Nondiffracting optical fields:some remarks on their analysis and synthesis[J]. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 1989, 6(1):150-152. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.6.000150 [19] JAROSZEWICZ Z, ROM N DOPAZO J F, GOMEZ-REINO C, et al.. Uniformizaion of the axial intensity of diffraction axicons by poly chromatic illumination[J]. Appl. Opt., 1996, 35(7):1025-1031. doi: 10.1364/AO.35.001025 [20] BRZOBOHATY' O, ČIŽMÁR T, ZEMÁNEK P, et al.. High quality quasi-bessel beam generated by round-tip axicon[J]. Opt. Express, 2008, 16(17):12688-12700. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.012688 [21] MA G L, ZENG G Y, ZHAO B, et al.. Arago-Poisson diffraction spot observed in the shadow area of an axicon lens[J]. J. Opt., 2015, 44(4):391-396. doi: 10.1007/s12596-015-0271-8 -






 下载:
下载: