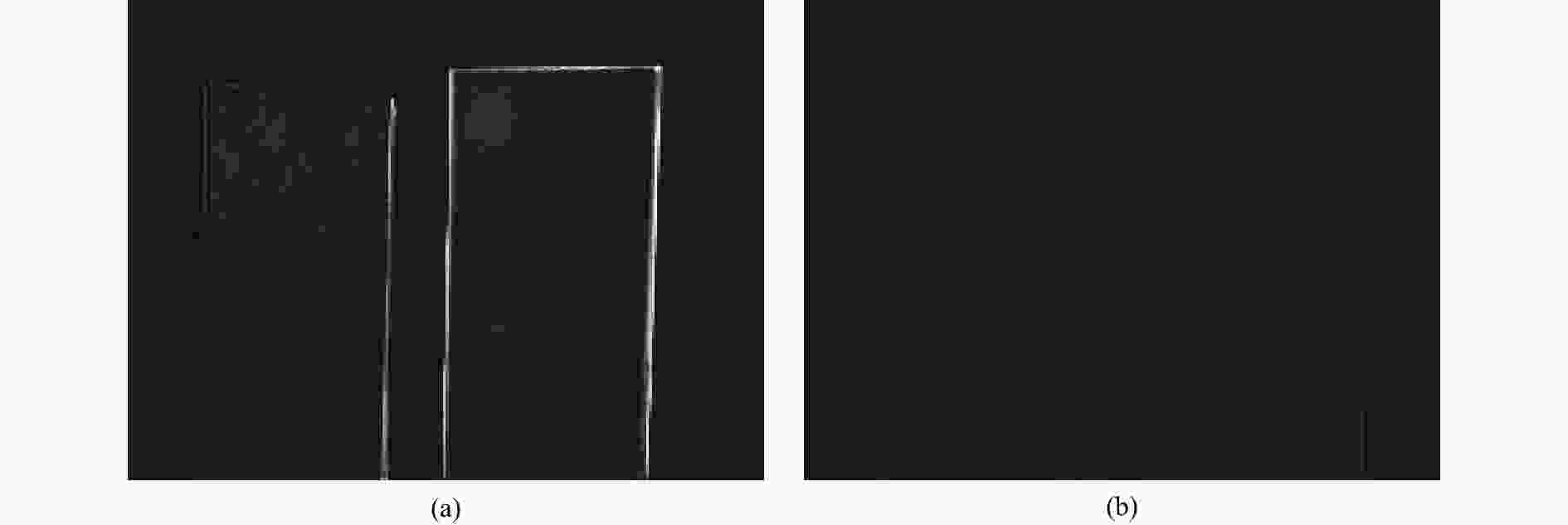-
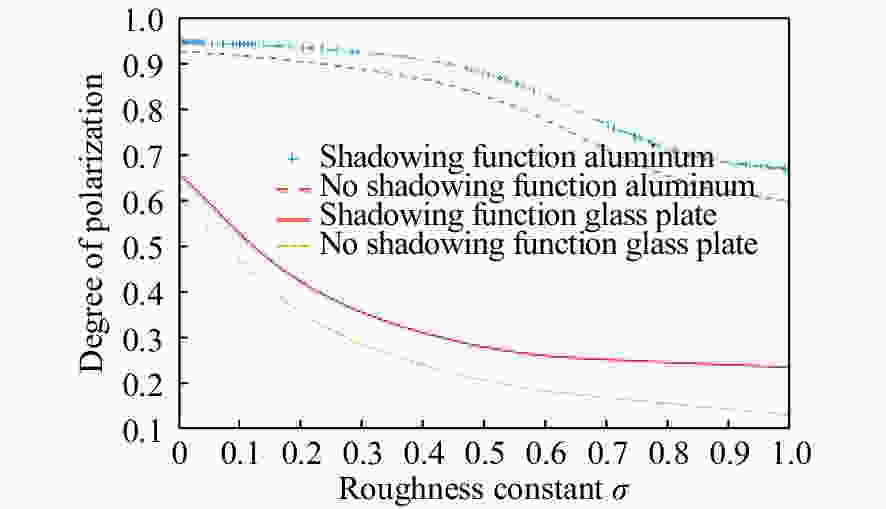
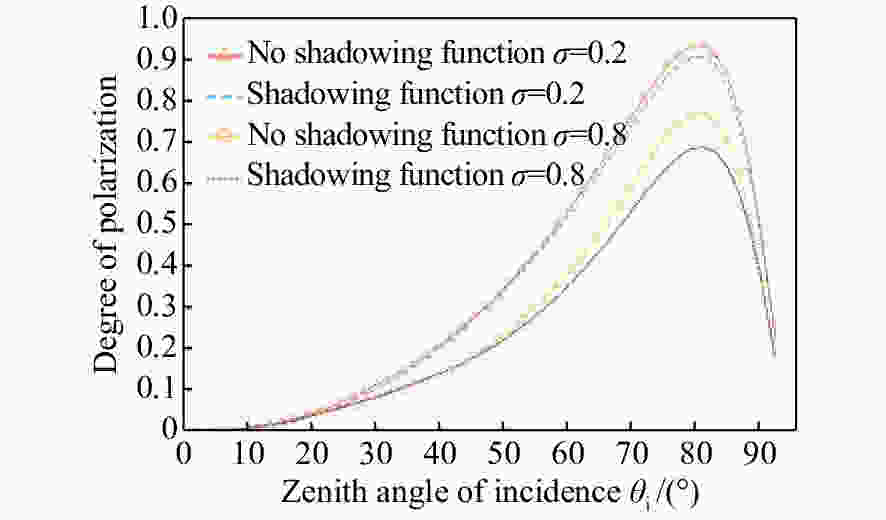
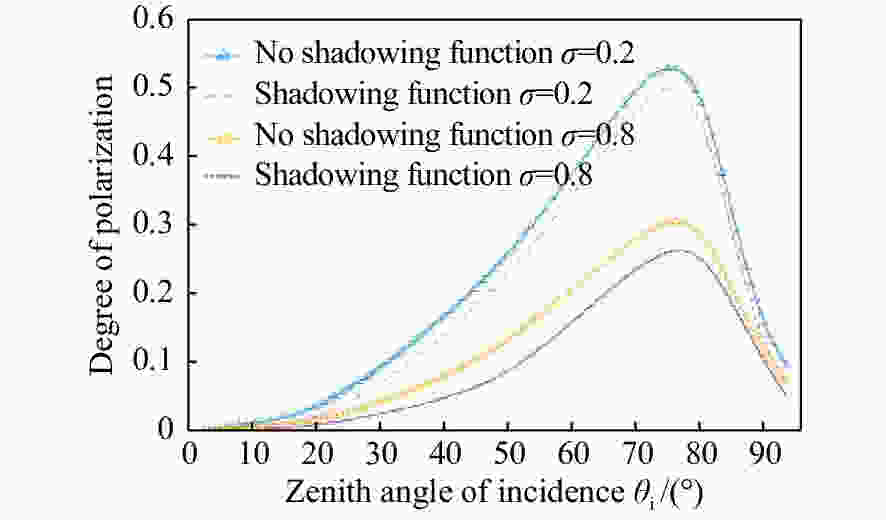
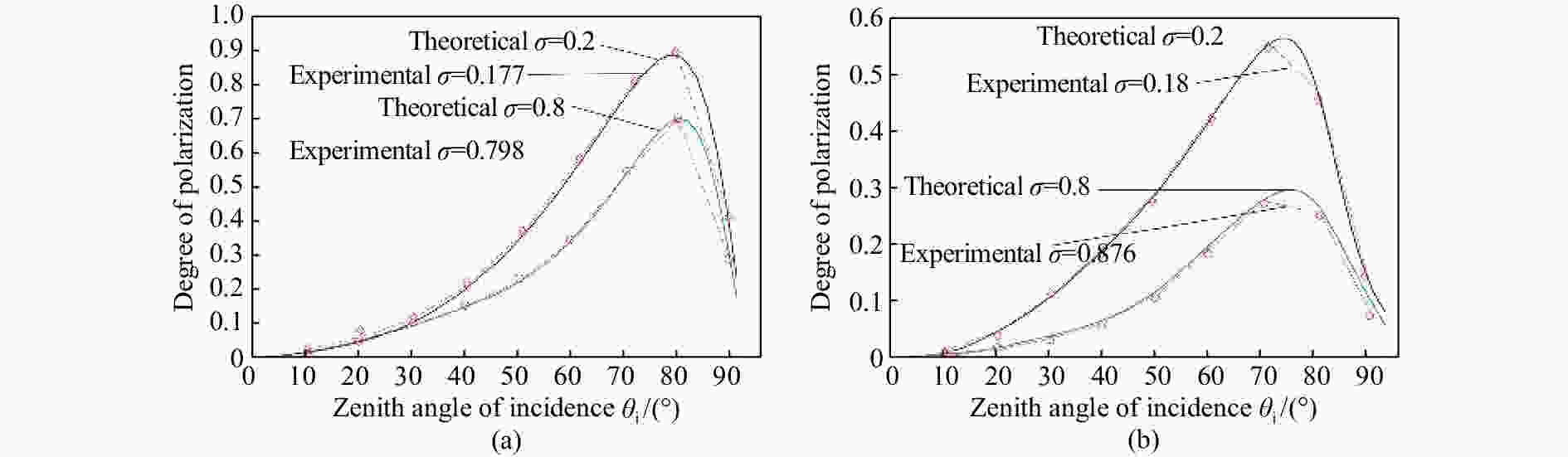
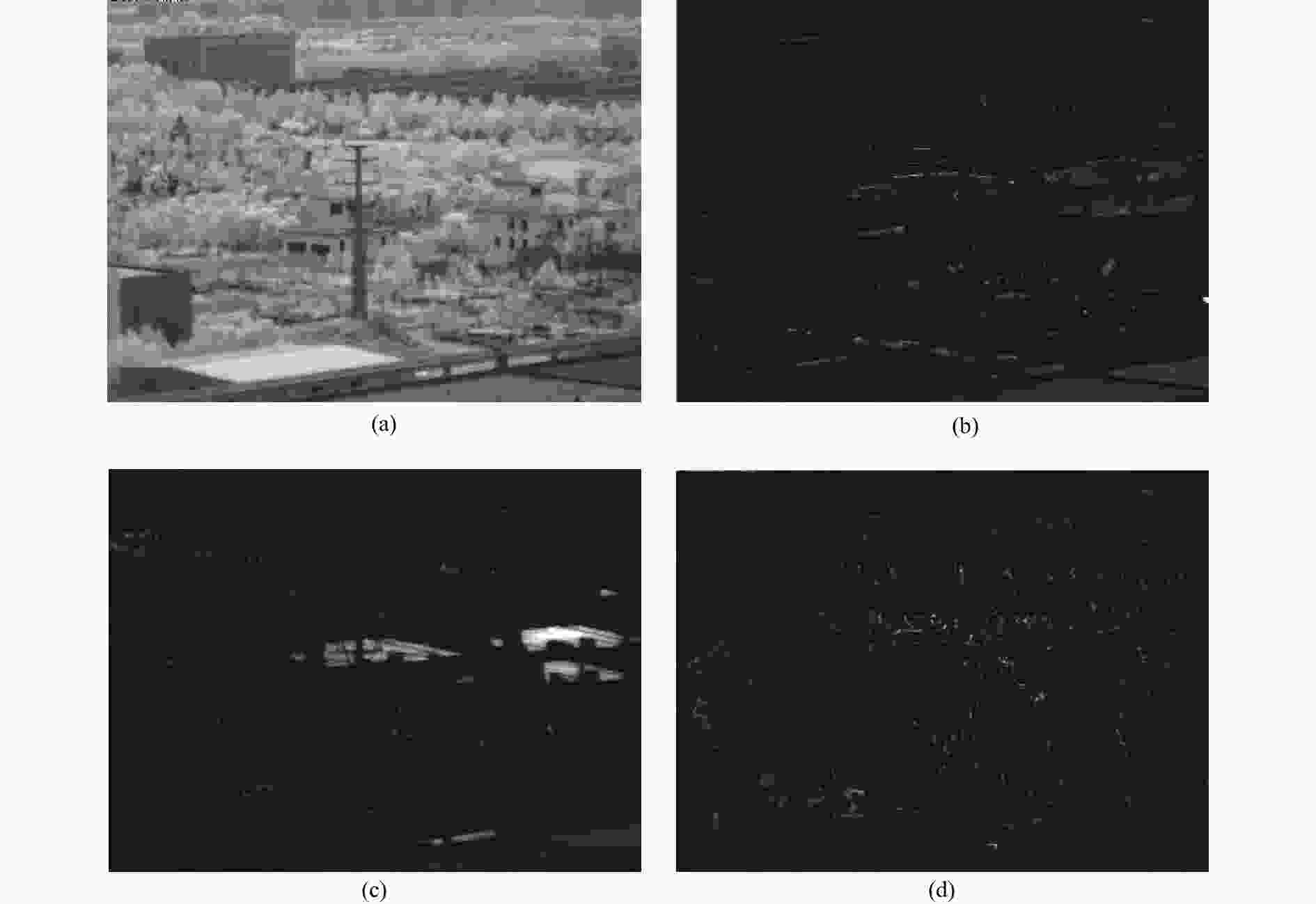
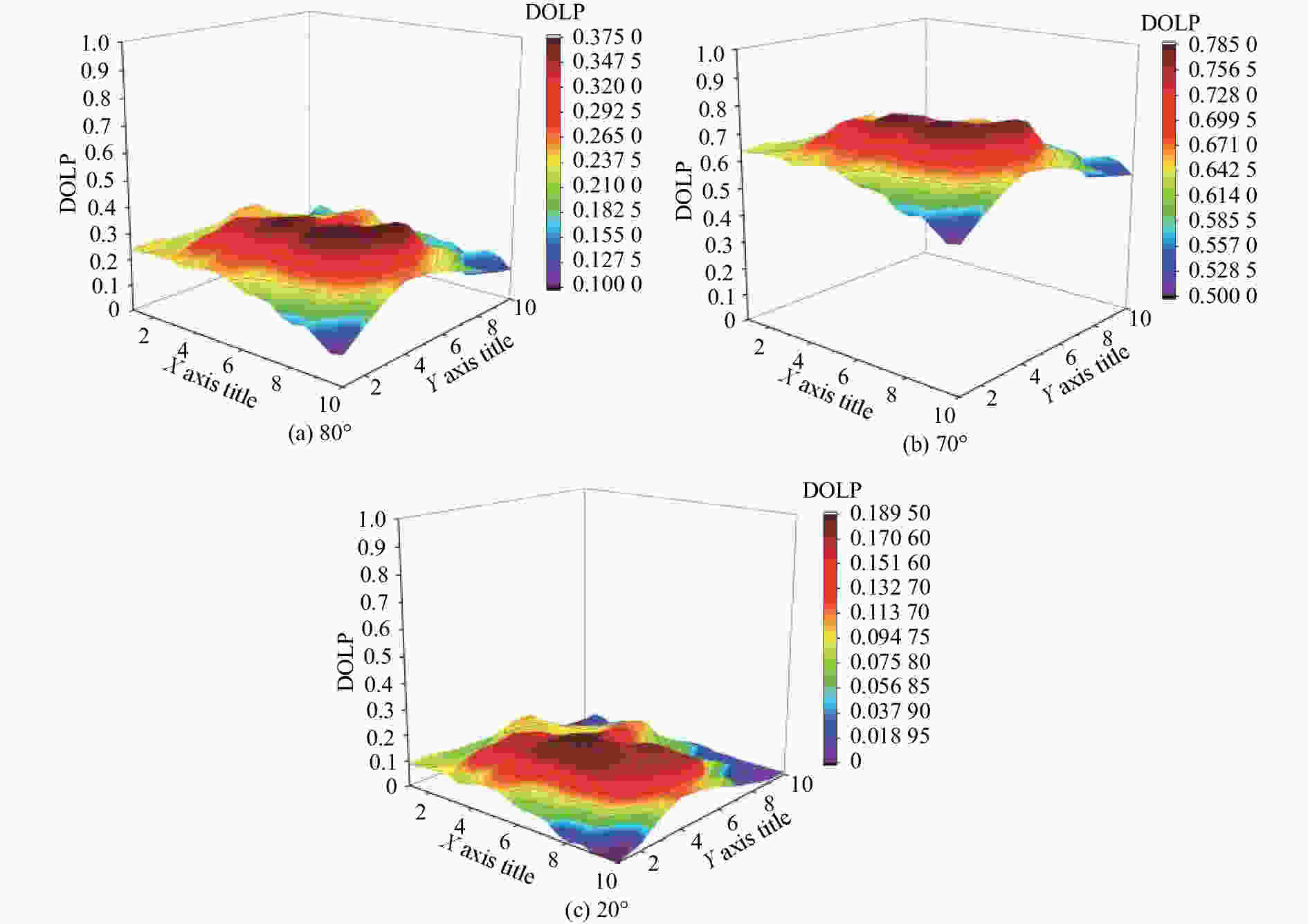
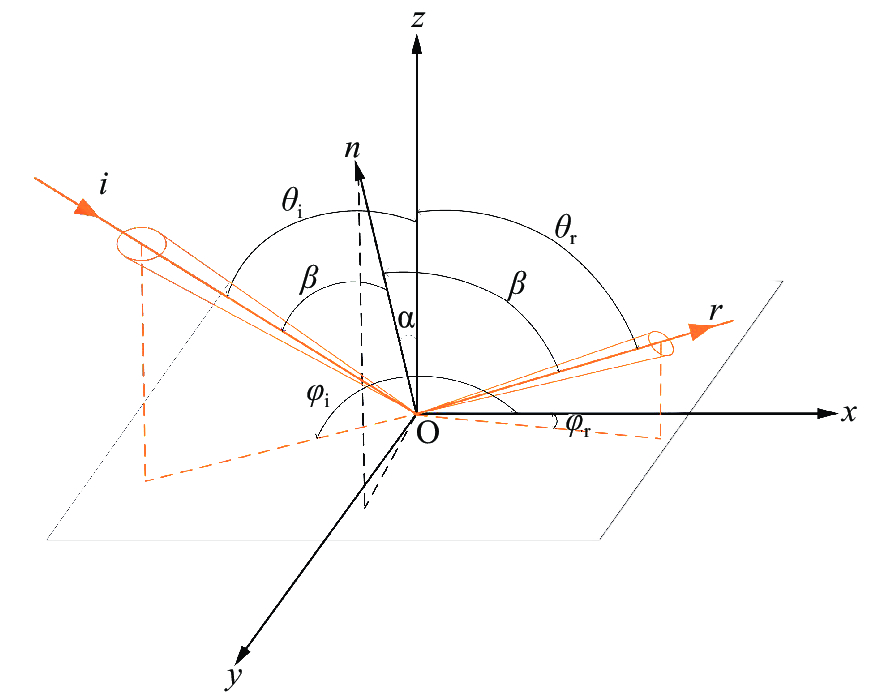
摘要: 红外偏振成像可突显目标、识别真伪,准确掌握目标红外辐射偏振特性可有效提高目标的探测识别概率。针对现有目标红外辐射偏振特性模型未考虑粗糙表面导致的遮蔽效应的问题,本文基于微面元双向反射分布函数模型,利用穆勒矩阵构建出含有遮蔽函数的粗糙表面红外辐射偏振度的斯托克斯解析模型。针对光线表面粗糙度和入射角对金属和非金属目标红外辐射偏振度的影响进行定量分析。分析结果表明:无论是金属还是非金属,其红外自发辐射偏振度都随粗糙度的增大而减小,非金属自发辐射偏振度下降的幅度大于金属偏振度;当粗糙度及温度相同时,金属的红外辐射偏振度始终大于非金属;红外辐射偏振度先随入射角的增加而增加,而后在特定入射角下达到峰值,超过一定入射角后,偏振度大幅下降,金属和非金属的红外辐射偏振度间的差异在一定入射角度范围内将达到最大,这有助于区分金属与非金属。最后,利用长波红外微偏振成像系统和近红外偏振成像系统进行不同场景目标的图像采集,获取目标的红外辐射偏振特性,实验结果与理论分析结果基本吻合。本文对研究目标偏振特性、优化设计红外偏振系统以及后续偏振图像处理均具有重要意义。Abstract: Infrared polarization imaging is advantageous for its ability to enhance image contrast and identify true-false targets. In order to improve detection and identification probability, it is necessary to accurately obtain the infrared radiation polarization properties of the targets. However, the traditional analytical model of infrared radiation polarization ignores the shadowing effect caused by rough surfaces. Based on the surface microelement bidirectional reflectance distribution function and by using a Muller matrix, the stocks analytical model of the infrared radiation polarization degree of the rough surface is constructed with a shadowing function. The effects of the incident angle and the surface roughness on the polarization of the metallic and nonmetallic targets are analyzed quantitatively. The analysis results show that the polarization degree of infrared spontaneous radiation decreases with an increase in the roughness of both the metal and the nonmetal, and the decrease of polarization degree of nonmetallic is greater than that of metal. Under the same roughness and temperature, the degree of polarization of the infrared radiation of the metal is always greater than that of the nonmetal. The polarization degree of infrared radiation firstly increases with the incident angle, and reaches a peak value within a specific range of incident angle, and then decreases dramatically. The difference in the degree of polarization between the metallic and nonmetallic infrared radiation reaches a maximum within a certain range of incident angle. This property is useful for distinguishing the metal and nonmetal. Finally, a long-wave infrared micro-polarization imaging system and near-infrared polarization imaging system are used to collect different images. The infrared radiation polarization properties of the targets are reasonably consistent with the results of the theoretical analysis. This research is of great significance for analyzing the polarization properties of real targets, designing infrared polarization systems and processing polarization images.
-
Key words:
- infrared polarization /
- rough surface /
- shadowing function /
- polarization degree /
- radiation
-
表 1 成像系统主要技术参数
Table 1. Main technical parameters of the imaging system
Long-wave infrared
micro-polarization cameraNear infrared detector Wavelength/μm 8~12 0.9~1.7 Focal length/mm 60 50 F 1 1.4 Pixel number 640×512 640×512 Pixel size/μm 17 15 -
[1] DUAN J, FU Q, MO CH H, et al. Review of polarization imaging for international military application[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8908: 890813. doi: 10.1117/12.2033042 [2] 汪震, 洪津, 叶松, 等. 金属表面粗糙度对热红外偏振特性影响研究[J]. 光子学报,2007,36(8):1500-1503.WANG ZH, HONG J, YE S, et al. Study on effect of metal surface roughness on polarized thermal emission[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2007, 36(8): 1500-1503. (in Chinese) [3] 徐文斌, 陈伟力, 李军伟, 等. 采用长波红外高光谱偏振技术的目标探测实验[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2017,46(5):0504005. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0504005XU W B, CHEN W L, LI J W, et al. Experiment of target detection based on long-wave infrared hyperspectral polarization technology[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(5): 0504005. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0504005 [4] JORDAN D L, LEWIS G. Measurements of the effect of surface roughness on the polarization state of thermally emitted radiation[J]. Optics Letters, 1994, 19(10): 692-694. doi: 10.1364/OL.19.000692 [5] WOLFF L B, LUNDBERG A, TANG R. Image understanding from thermal emission polarization[C]. Proceedings of 1998 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 1998: 625-631. [6] GURTON K P, DAHMANI R, VIDEEN G. Measured degree of infrared polarization for a variety of thermal emitting surfaces[R]. Adelphi: Army Research Laborary, 2004: 1-19. [7] GURTON K P, DAHMANI R. Effect of surface roughness and complex indices of refraction on polarized thermal emission[J]. Applied Optics, 2005, 44(26): 5361-5367. doi: 10.1364/AO.44.005361 [8] 汤倩. 红外辐射偏振建模与仿真研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2015: 1-62.TANG Q. Research on modeling and simulation of infrared radiation polarization[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2015: 1-62. (in Chinese) [9] 陈伟力, 李军伟, 孙仲秋, 等. 典型卫星表面材料可见光偏振特性分析[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(10):1026001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.1026001CHEN W L, LI J W, SUN ZH Q, et al. Analysis of visible polarization characteristics of typical satellite surface materials[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(10): 1026001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.1026001 [10] NICODEMUS F E, RICHMOND J C, HSIA J J, et al.. Geometrical Considerations and Nomenclature for Reflectance[M]. Washington: National Bureau of Standards, 1977: 629. [11] TORRANCE K E, SPARROW E M. Theory for off-specular reflection from roughened surfaces[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1967, 57(9): 1105-1114. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.57.001105 [12] 汪杰君, 王鹏, 王方原, 等. 材料表面偏振双向反射分布函数模型修正[J]. 光子学报,2019,48(1):0126001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194801.0126001WANG J J, WANG P, WANG F Y, et al. Modified model of polarized bidirectional reflectance distribution function on material surface[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2019, 48(1): 0126001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194801.0126001 [13] 王安祥, 吴振森. 光散射模型中遮蔽函数的参数反演[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2014,43(1):332-337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.01.059WANG A X, WU ZH S. Parameter inversion of shadowing function in light scattering model[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(1): 332-337. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.01.059 [14] PRIEST R G, GERMER T A. Polarimetric BRDF in the microfacet model: theory and measurements[C]. Proceedings of the 2000 Meeting of the Military Sensing Symposia Specialty Group on Passive Sensors, Infrared Information Analysis Center, 2000: 169-181. [15] GARTLEY M G, BROWN S D, GOODENOUGH A D, et al. Polarimetric scene modeling in the thermal infrared[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6682: 66820C. doi: 10.1117/12.740528 [16] 马帅, 白廷柱, 曹峰梅, 等. 基于双向反射分布函数模型的红外偏振仿真[J]. 光学学报,2009,29(12):3357-3361. doi: 10.3788/AOS20092912.3357MA SH, BAI T ZH, CAO F M, et al. Infrared polarimetric scene simulation based on bidirectional reflectance distribution function model[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2009, 29(12): 3357-3361. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS20092912.3357 [17] 张景华, 张焱, 石志广. 基于长波红外的海面场景偏振特性分析与建模[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2018,37(5):586-594. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2018.05.011ZHANG J H, ZHANG Y, SHI ZH G. Study and modeling of infrared polarization characteristics based on sea scene in long wave band[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2018, 37(5): 586-594. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2018.05.011 [18] RESNICK A, PERSONS C, LINDQUIST G. Polarized emissivity and Kirchhoff’s law[J]. Applied Optics, 1999, 38(8): 1384-1387. doi: 10.1364/AO.38.001384 [19] 张海越. 基于穆勒矩阵的目标光学反射特性研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2017: 1-61.ZHANG H Y. Study on optical reflection characteristics of target based on Muller matrix[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2017: 1-61. (in Chinese) [20] 李刚. 空间目标天基红外探测光学系统研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所, 2013: 1-63.LI G. Research about space-based IR-optical system for space object detection[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechnics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013: 1-63. (in Chinese) [21] 王晓娟. 基于长波的红外偏振成像技术研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2016: 1-56.WANG X J. Research on infrared polarization image technology based on long wave infrared[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2016: 1-56. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: