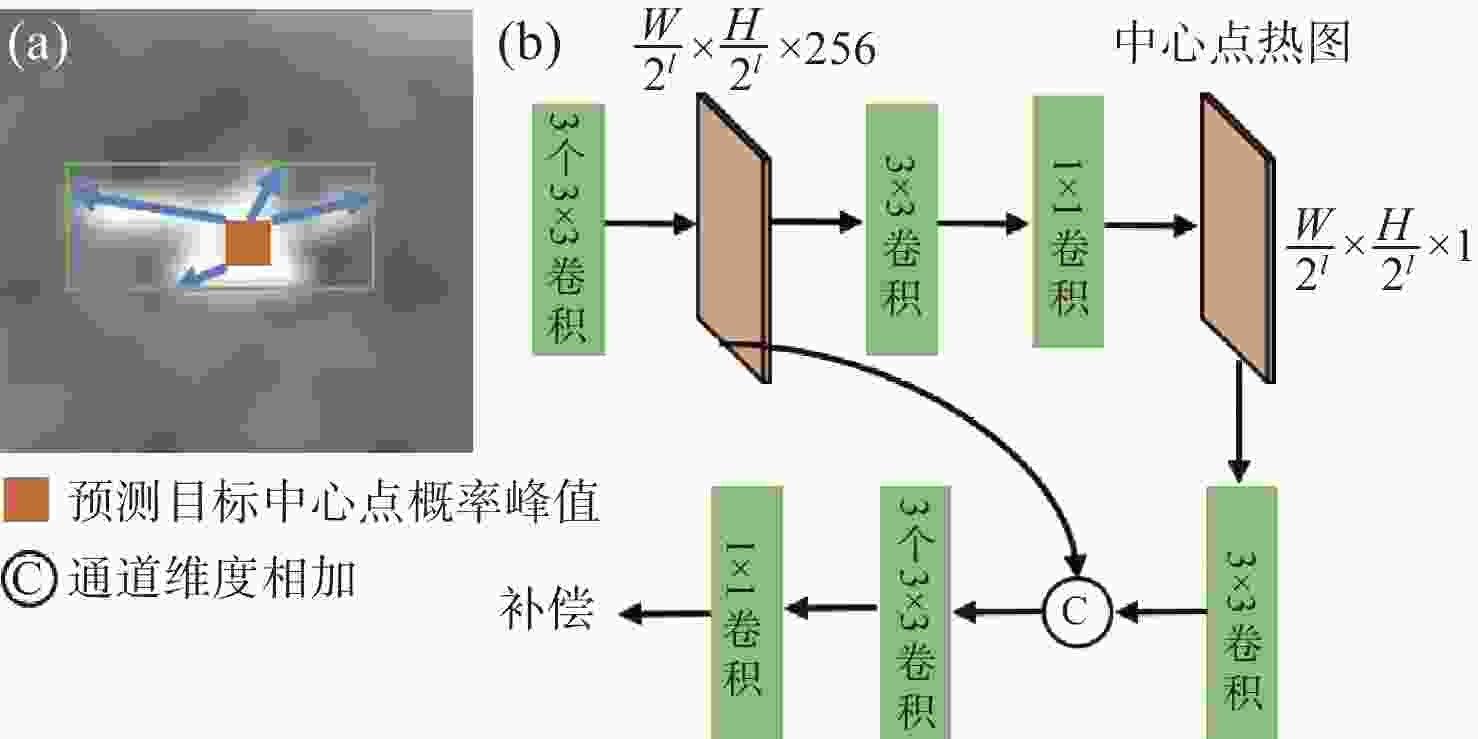
Indistinguishable points attention-aware network for infrared small object detection
-
摘要:
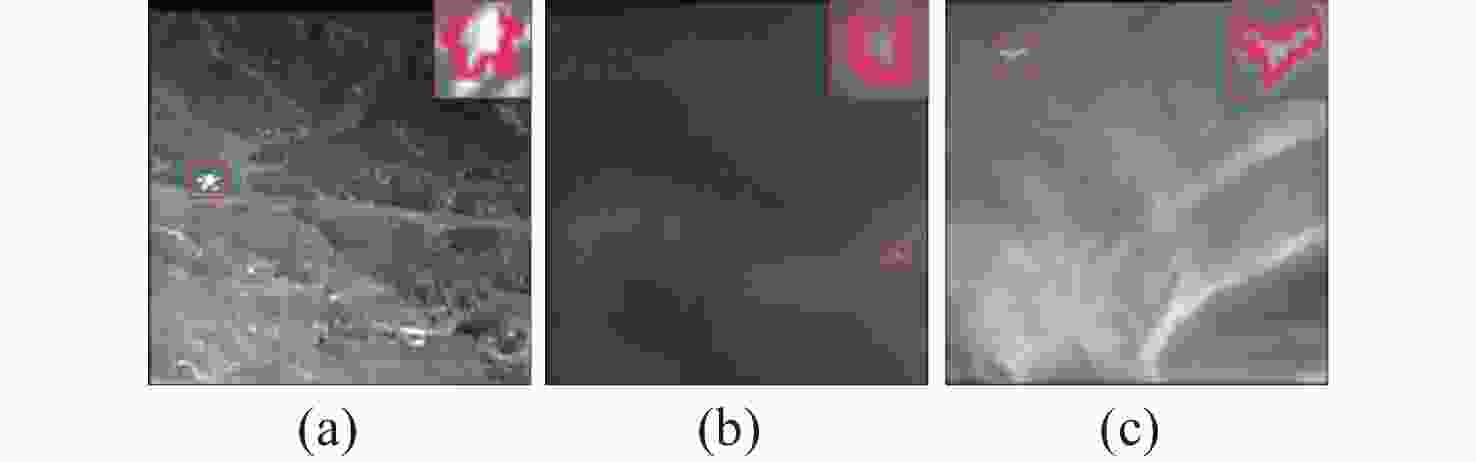
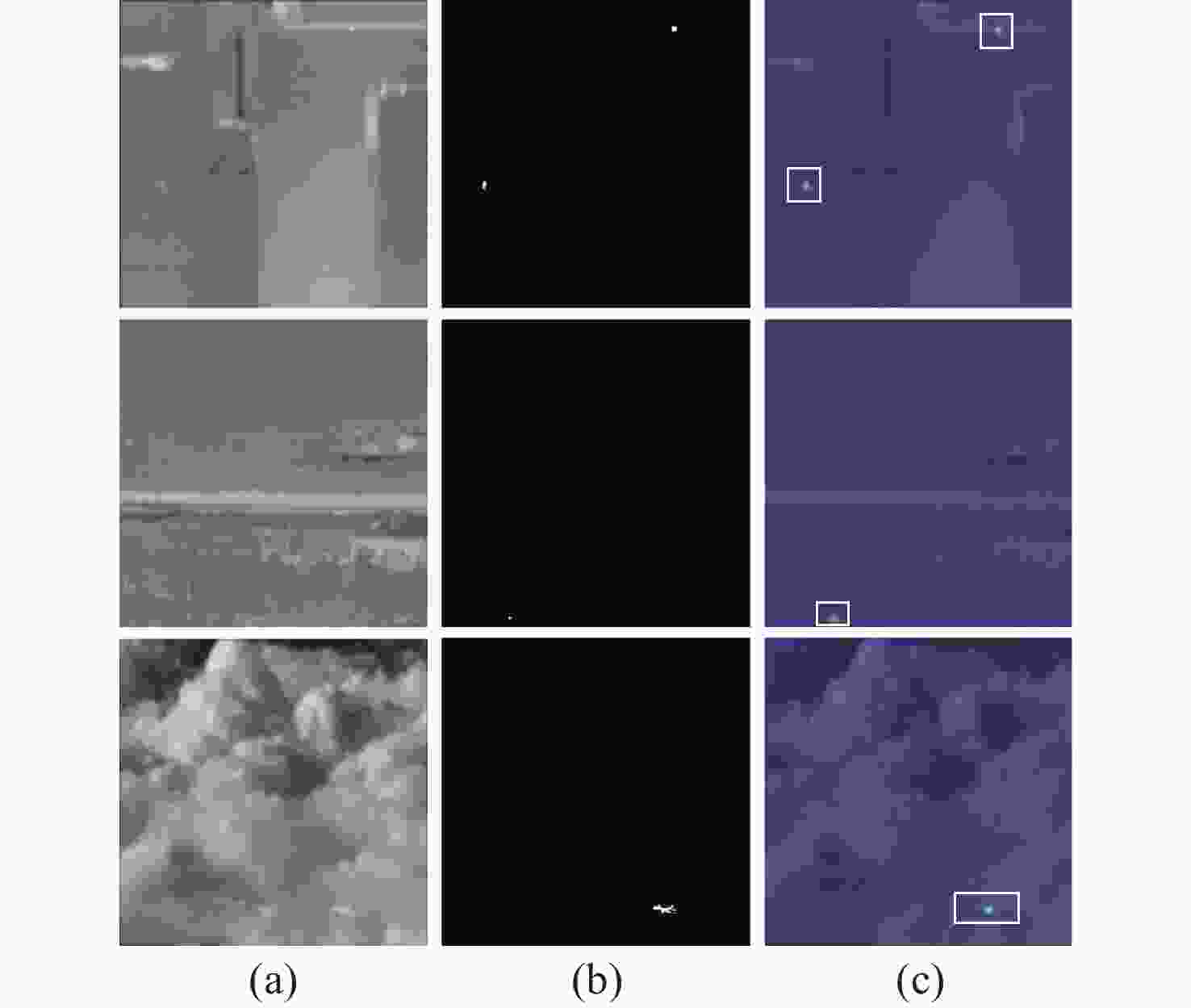
随着飞行器机动性能的提升,多帧红外小目标检测方法不足以满足检测要求。近年来,基于深度学习的单帧红外小目标检测方法取得了巨大成功。然而,红外小目标通常缺少形状特征,而且边界与背景模糊不清,给准确分割带来了一定的挑战。针对上述问题,本文提出难点注意力感知红外小目标检测网络。通过基于点的区域建议模块获取目标潜在区域,同时滤除多余背景。为实现高质量分割、细化掩码边界模块、判断粗掩码中无序、非局部难以分辨点,融合这些难点的多尺度特征,进行逐像素注意力建模。最后,由点检测头对难点注意力感知特征重新预测,生成精细分割掩码。在公开数据集NUDT-SIRST和IRDST上进行测试,平均精度均值mAP达到87.4和63.4,F值达到0.8935和0.7056。本文提出的难点注意力感知红外小目标检测网络可在多检测场景、多目标形态下实现准确分割,抑制误报信息,同时控制计算开销。
Abstract:As aircraft maneuverability increases, multi-frame infrared small target detection methods are becoming insufficient to meet detection requirements. In recent years, significant progress has been achieved in single-frame infrared small-target detection method based on deep learning. However, infrared small targets often lack shape features and have blurred boundaries and backgrounds, obstructing accurate segmentation. According to the problems, an indistinguishable points attention-aware network for infrared small object detection was proposed. First, potential target areas were acquired through a point-based region proposal module while filtering out redundant backgrounds. Then, to achieve high-quality segmentation, the mask boundary refinement module was utilized to identify disordered, non-local indistinguishable points in the coarse mask. Multi-scale features of these difficult points were then fused to perform pixel-wise attention modeling. Finally, A fine segmentation mask was generated through re-predicting the indistinguishable points attention-aware features by point detection head. The mAP of the proposed method reached 87.4 and 63.4 on the publicly available datasets NUDT-SIRST and IRDST, and the F-measure reached 0.8935 and 0.7056, respectively. It can achieve accurate segmentation in multi-detection scenarios and multi-target morphology, suppressing false alarm information while controlling the computational overhead.
-
表 1 传统算法超参数设置
Table 1. Hyperparameter settings of traditional algorithms
传统算法 超参数设置 Top-hat Nhood=ones(5) LEF h=0.2,α=0.5, P=9 AADCDD 内窗口尺寸={3, 5, 7, 9},外窗口尺寸=19 TLLCM 窗口尺寸={3, 5, 7, 9},k=9 表 2 各方法在NUDT-SIRST及IRDST数据集定量结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of quantitative results of different methods on NUDT-SIRST and IRDST datasets
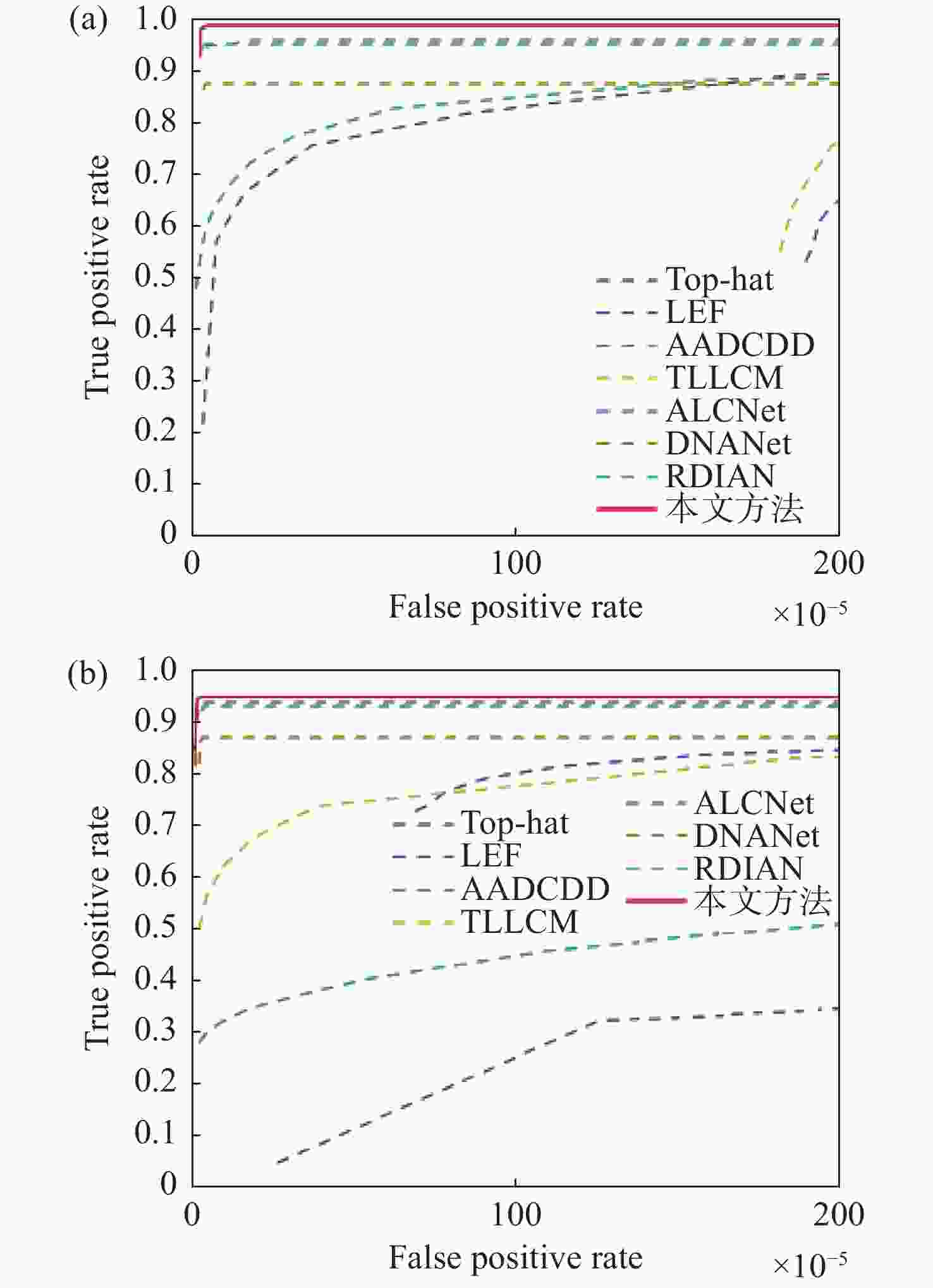
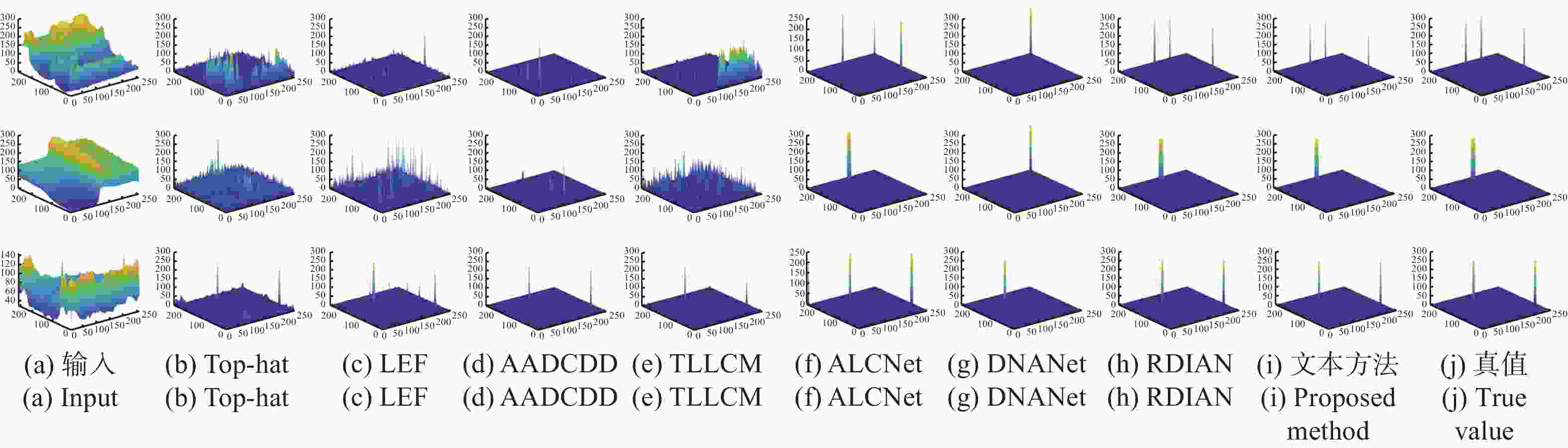
检测算法 NUDT-SIRST IRDST mAP F值(Pre,Rec) mAP F值(Pre,Rec) Top-hat 1.5 0.3599(0.2850,0.4884) 0.7 0.0088(0.0045,0.4107) LEF 6.4 0.1151(0.0748,0.2498) 2.5 0.1219(0.0686,0.5470) AADCDD 1.6 0.1490(0.3838,0.0924) 1.4 0.0705(0.0521,0.1090) TLLCM 16.5 0.0724(0.0479,0.1476) 6.1 0.1881(0.1254,0.3759) ALCNet 69.3 0.7595(0.7035,0.8251) 46.5 0.5929(0.5461,0.6486) DNANet 86.9 0.8645(0.9070,0.8259) 62.1 0.6697(0.712 4,0.6319) RDIAN 82.4 0.890 0(0.899 0,0.881 1) 60.0 0.7102(0.7092,0.7113) 本文方法 87.4 0.8935(0.8923,0.8948) 63.4 0.7056(0.7183,0.6935) 表 3 深度学习方法单张图片平均推理时间
Table 3. Average inference times of a single image for deep learning methods
(s) 检测算法 NUDT-SIRST IRDST ALCNet 0.104 0.166 DNANet 0.089 0.259 RDIAN 0.065 0.114 本文算法 0.099 0.121 表 4 不同区域建议模块对比表
Table 4. Comparison of different region proposal modules
建议数量 基于点的区域建议 RPN mAP F值 mAP F值 1000 87.9 0.8927 86.2 0.8425 256 87.5 0.8962 85.8 0.8412 128 87.4 0.8935 85.2 0.8406 64 86.0 0.8901 84.5 0.8397 表 5 不同选点策略检测结果
Table 5. Detection results of different point selection strategies
选点策略 mAP 均匀选点 86.7 k=1,γ=0.00 86.9 k=3,γ=0.75 87.4 k=10,γ=1.00 85.8 表 6 难点不同特征融合结果
Table 6. Fusion results of different features at indistinguishable points
细粒度特征 粗糙掩码 位置嵌入 mAP √ 85.5 √ √ 85.8 √ √ √ 87.4 表 7 不同细化方案检测结果
Table 7. Results of different refinement strategies
细化方案 mAP CNN(16×16) 85.5 MLP(16×16) 86.2 细化掩码边界模块(S=3) 87.4 细化掩码边界模块(S=6) 87.6 -
[1] 单秋莎, 谢梅林, 刘朝晖, 等. 制冷型长波红外光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(1):72-78. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0116SHAN Q SH, XIE M L, LIU ZH H, et al. Design of cooled long-wavelength infrared imaging optical system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(1): 72-78. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0116 [2] MA T L, YANG ZH, WANG J Q, et al. Infrared small target detection network with generate label and feature mapping[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 6505405. [3] SUN Y, YANG J G, AN W. Infrared dim and small target detection via multiple subspace learning and spatial-temporal patch-tensor model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(5): 3737-3752. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3022069 [4] 赵鹏鹏, 李庶中, 李迅, 等. 融合视觉显著性和局部熵的红外弱小目标检测[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):267-275. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0170ZHAO P P, LI SH ZH, LI X, et al. Infrared dim small target detection based on visual saliency and local entropy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 267-275. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0170 [5] GAO C Q, MENG D Y, YANG Y, et al. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(12): 4996-5009. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2281420 [6] CHEN C L P, LI H, WEI Y T, et al. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 574-581. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242477 [7] XIA CH Q, LI X R, ZHAO L Y, et al. Infrared small target detection based on multiscale local contrast measure using local energy factor[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(1): 157-161. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2914432 [8] HAN J H, MORADI S, FARAMARZI I, et al. A local contrast method for infrared small-target detection utilizing a tri-layer window[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(10): 1822-1826. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2954578 [9] 刘彦磊, 李孟喆, 王宣宣. 轻量型YOLOv5s车载红外图像目标检测[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(5):1045-1055. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0254LIU Y L, LI M ZH, WANG X X. Lightweight YOLOv5s vehicle infrared image target detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 1045-1055. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0254 [10] PANG Y W, WANG T C, ANWER R M, et al. Efficient featurized image pyramid network for single shot detector[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2019: 7328-7336. [11] YANG X, YAN J CH, FENG Z M, et al. R3Det: Refined single-stage detector with feature refinement for rotating object[C]. Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI Press, 2020. [12] LIU Y ZH, CAO S, LASANG P, et al. Modular lightweight network for road object detection using a feature fusion approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(8): 4716-4728. [13] ZHANG SH F, WEN L Y, BIAN X, et al. Single-shot refinement neural network for object detection [C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 4203-4212. [14] YUAN Y, XIONG ZH T, WANG Q. VSSA-NET: Vertical spatial sequence attention network for traffic sign detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(7): 3423-3434. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2896952 [15] PANG Y W, CAO J L, WANG J, et al. JCS-Net: Joint classification and super-resolution network for small-scale pedestrian detection in surveillance images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(12): 3322-3331. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2916592 [16] DAI Y M, WU Y Q, ZHOU F, et al. Attentional local contrast networks for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(11): 9813-9824. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3044958 [17] LI B Y, XIAO CH, WANG L G, et al. Dense nested attention network for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 1745-1758. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3199107 [18] WANG K W, DU SH Y, LIU CH X, et al. Interior attention-aware network for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5002013. [19] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE, 2015: 1440-1448. [20] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An Image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, OpenReview. net, 2021. [21] SUN H, BAI J X, YANG F, et al. Receptive-field and direction induced attention network for infrared dim small target detection with a large-scale dataset IRDST[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 1-13. [22] ZHOU X Y, KARPUR A, LUO L J, et al. StarMap for category-agnostic keypoint and viewpoint estimation[C]. Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2018: 328-345. [23] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE, 2017: 2999-3007. [24] YANG Z, LIU SH H, HU H, et al. RepPoints: Point set representation for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE, 2019: 9656-9665. [25] XU B, WANG N Y, CHEN T Q, et al. Empirical evaluation of rectified activations in convolutional network[Z]. Computerence, 2015. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1505.00853. [26] ZHU X ZH, SU W J, LU L W, et al. Deformable DETR: deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, OpenReview. net, 2020. [27] WU Y, KIRILLOV A, Massa F, et al. Detectron2[CP/OL]. (2019)[2023-8-24]. https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2. [28] TAN M X, PANG R M, LE Q V. EfficientDet: Scalable and efficient object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2020: 10778-10787. [29] YU F, WANG D Q, SHELHAMER E, et al. Deep layer aggregation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 2403-2412. [30] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context[M]. FLEET D, PAJDLA T, SCHIELE B, et al. Computer Vision – ECCV 2014. Cham: Springer, 2014: 740-755. [31] WANG H, ZHOU L P, WANG L. Miss detection vs. false alarm: adversarial learning for small object segmentation in infrared images[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE, 2019: 8508-8517. [32] RIVEST J F, FORTIN R. Detection of dim targets in digital infrared imagery by morphological image processing[J]. Optical Engineering, 1996, 35(7): 1886-1893. doi: 10.1117/1.600620 [33] AGHAZIYARATI S, MORADI S, TALEBI H. Small infrared target detection using absolute average difference weighted by cumulative directional derivatives[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2019, 101: 78-87. [34] HE K M, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE, 2017: 2980-2988. [35] KIRILLOV A, WU Y X, HE K M, et al. PointRend: Image segmentation as rendering[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2020: 9796-9805. -






 下载:
下载: