-
摘要: 超快 技术是目前 乃至物理学和信息科学领域最活跃的研究前沿之一,在工业加工、生物医学和 雷达等领域具有广泛应用。二维材料具有独特的物理结构及优异的光电特性,作为可饱和吸收体应用于超快 器时,具备工作波段宽、调制深度可控和恢复时间快等优势。其中,过渡金属硫化物因具有带隙连续可调等特点,已成为二维材料研究领域的重点。本文从过渡金属硫化物的特性出发,介绍了可饱和吸收器件的制作方法,综述了基于新型过渡金属硫化物的超快 器的研究进展,并对其发展趋势进行了展望。Abstract: Ultrafast laser technology is one of the most active research frontiers in lasers, physics and information science. It is widely applied in industrial processing, biomedicine, lidar and other fields. Because of their unique physical structure and excellent photoelectric properties, two-dimensional materials have a wide operating band, controllable modulation depth and short recovery time when they are employed as saturable absorbers in ultrafast lasers. Among them, transition metal dichalcogenides have become a focus of research because their band-gap is continuously adjustable. In this paper, we introduce the characteristics of transition metal dichalcogenides and the fabrication methods of saturable absorber devices. The research progress of ultrafast lasers based on emerging transition metal dichalcogenides is reviewed, and the development trend is highlighted.
-
图 1 典型TMD图像。(a)光学图像;(b)扫描电镜图像;(c)原子力显微镜图像;(d、e)低倍、高倍透射电镜图像[40]
Figure 1. Typical images of TMD. (a) Optical image. (b) SEM image. (c) AFM image. (d, e) Low- and high-magnification TEM images
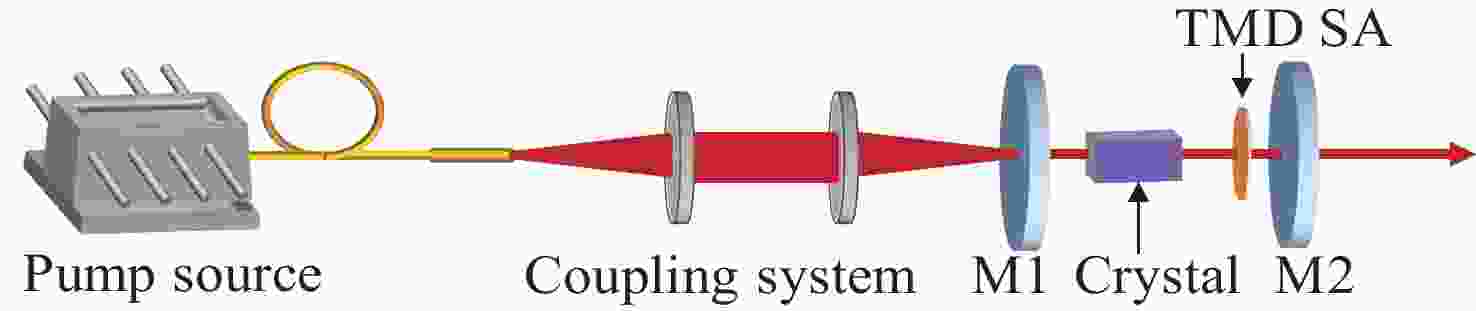
表 1 基于新型TMD可饱和吸收体的超快固体 器
Table 1. Ultrafast solid-state lasers with emerging TMD saturable absorbers
TMD 饱和能量 调制深度 调制方式 增益介质 中心波长 重复频率 脉冲宽度 单脉冲能量/平均功率 参考
文献ReS2 22.6 μJ/cm2 9.7% 调Q Er:YSGG 2.8 μm 126 kHz 324 ns 104 mW [69] 58.2 μJ/cm2 21.5 μJ/cm2 2.7 μJ/cm2 3%
5.2%
2.9%调Q/锁模 Pr:YLF、
Nd:YAG、
Tm:YAP调Q:0.64 μm、1.064 μm、1.991 μm,锁模:
1.06 μm调Q:520 kHz、644 kHz、67.7 kHz,锁模:
50.7 MHz调Q:160 ns、139 ns、415 ns,锁模:323 fs 调Q:0.625 W、1.34 W、8.72 W,锁模:350 mW 11.89 GW/cm2 48% 调Q Nd:YAG 0.95 μm/
1.06 μm165 kHz 834 ns 81 mW [70] 23.5 μJ/cm2 10.2% 调Q Ho,Pr:LiLuF4 2.95 μm 91.5 kHz 676 ns 1.13 μJ [44] 15.6 μJ/cm2 15% 调Q Nd:YAG 1.3 μm 214 kHz 403 ns 0.42 μJ [71] PtSe2 17.1 μJ/cm2 12.6% 锁模 Nd:LuVO4 1066 nm 61.3 MHz 15.8 ps 180 mW [72] 3.2 μJ/cm2 6.6% 调Q Tm:YAP 1 987 nm 58 kHz 244 ns 24.3 μJ [73] 0.47 GW/cm2 1.9% 调Q锁模 Nd:YAG 1064 nm 8.8 GHz 27 ps 127 mW [74] ReSe2 — — 调Q Tm:YLF/Tm:Y2O3 1 900 nm/
2050 nm54 kHz/
106 kHz527.9 ns/
727 ns862 mW/
1.04 W[75] 12.8 GW/cm2 2.9% 调Q Nd:Y3Al5O12 1.06 μm 274 MHz 1.08 μs 2.5 μJ [76] 14.5 μJ/cm2 7.5% 调Q Er:YAP 2.73 μm/
2.8 μm244.6 kHz 202.8 ns 526 mW [77] 12.8 GW/cm2 2.9% 锁模 固体波导 1064 nm 6.5 GHz 29 ps 250 mW [78] 6.37 MW/cm2 1.89% 调Q Nd:YVO4 1064.4 nm 84.16 kHz 682 ns 125 mW [79] 4.3 μJ/cm2 7.3% 调Q Tm:YAP 2 μm 89.4 kHz 925.8 ns 17.6 μJ [46] MoTe2 0.14 mJ/cm2 22% 调Q Ho,Pr:LiLuF4 2.95 μm 76.46 kHz 670 ns 0.95 μJ [80] 1.71 MW/cm2 — 调Q Yb:LaCa4O(BO3)3 1.03~1.04 μm 357 kHz 103 ns 6.6 μJ [81] 18 MW/cm2 4% 调Q Tm:CaYAlO4 1 929 nm 70.9 kHz 0.69 μs 10.58 μJ [82] 6.87 mJ/cm2 1.3% 调Q Er:YAG 1645 nm 41.59 kHz 1.048 μs 27.4 μJ [83] 2.26 μJ/cm2 6.0% 调Q Tm:YAP 2 μm 144 kHz 380 ns 8.4 μJ [84] 1.71 MW/cm2 0.9% 调Q Yb:YCOB 1.03 μm 704 kHz 52 ns 2.25 μJ [85] 1.71 MW/cm2 0.9% 调Q Yb:KLu(WO4)2 1030.6 nm 2.18 MHz 36 ns 1.3 μJ [86] WTe2 5.1 μJ/cm2 7.2% 调Q Tm:YAP 1 938 nm 78 kHz 368 ns 4.8 μJ [87] 1.97 mJ/cm2 20.9% 调Q Ho,Pr:LiLuF4 2 954.7 nm 92 kHz 366 ns 1.4 μJ [88] TiS2 3.37 mJ/cm2 8% 调Q Er:YAG 1645 nm 38 kHz 1.2 μs 37.4 μJ [89] 表 2 基于新型TMD可饱和吸收体的超快光纤 器
Table 2. Ultrafast fiber lasers with emerging TMD saturable absorbers
TMD 饱和能量 调制深度 调制方式 光纤掺杂 中心波长 重复频率 脉冲宽度 单脉冲能量/平均功率 参考
文献ReS2 27 μJ/cm2 1% 锁模 Er 1564 nm 3.43 MHz 1.25 ps — [91] 74 MW /cm2 0.12% 调Q/锁模 Er 1558.6 nm 12.6~19 kHz/
5.48 MHz23~5.49 μs/1.6 ps 22~62.8 μJ [92] — — 锁模 Er 1.5 μm 1.896 MHz — 12 mW [93] 8.4 MW/cm2 44% 调Q Yb 1047 nm 134 kHz 1.56 μs 13.02 nJ [94] 27.5 μJ/cm2 6.9% 锁模 Er 1573.6 nm/
1591.1 nm/
1592.6 nm13.39 MHz — — [95] PtSe2 0.346 GW/cm2 26% 锁模 Yb 1064.47 nm 4.08 MHz 470 ps 2.31 nJ [96] 9.48 MW/cm2 6.9% 锁模 Er 1550 nm 8.24 MHz 861 fs 78.52 nJ [45] 0.34~1.23 GW/cm2 1.11%~4.9% 调Q/锁模 Er 1560 nm 锁模:23.3 MHz 锁模:1.02 ps 调Q:143.2 nJ
锁模:0.53 nJ[97] ReSe2 — — 调Q Yb 1.06 μm 17.89~39.86 kHz 2.27 μs 30.4 nJ [98] — 3.9% 锁模 Er 1560 nm 14.97 MHz 862 fs 0.5 mW [99] — 7% 调Q Er 1566 nm 16.64 kHz 4.98 μs 36 nJ [100] MoTe2 3.46 MW/cm2 48.85% 锁模 Er 1559 nm 1.8 MHz 2.46 ps 0.11 mW [101] 0.969 MW/cm2 26.97% 锁模 Er 1561 nm 96.323 MHz 111.9 fs 23.4 mW [102] 26.45 MW/cm2 17.47% 调Q Er 1559 nm 148~228 kHz 677 ns 109 nJ [103] 8.3 MW /cm2 5.7% 锁模 Tm 1 930 nm 14.353 MHz 952 fs 2.56 nJ [47] 9.6 MW/cm2@
1.5 μm、12.3 MW/cm2@2 μm25.5%@1.5 μm、22.1%@
2 μm锁模 Er/Tm 1.5 μm/2 μm 25.601 MHz/
15.37 MHz229 fs/1.3 ps 2.14 nJ/13.8 nJ [104] WTe2 7.6 MW/cm2 31% 锁模 Tm 1915.5 nm 18.72 MHz 1.25 ps 39.9 mW [48] — 2.18% 调Q Yb 1044 nm 19~79 kHz 1 μs 28.3 nJ [105] 0.515 MW/cm2 31.06% 调Q Er 1531 nm 144.7~240 kHz 583 ns 58.625 nJ [106] TiS2 — 8.3% 锁模/调Q Er 1563.3 nm/
1560.2 nm22.7 MHz/
33.387 kHz1.25 ps/4.01 μs 25.3 pJ/9.5 nJ [107] 772.2 GW /cm2 — 锁模 Er 1550 nm 5.7 MHz 618 fs 0.28~1.2 mW [49] -
[1] SIBBETT W, LAGATSKY A A, BROWN C T A. The development and application of femtosecond laser systems[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(7): 6989-7001. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.006989 [2] YE J. Absolute measurement of a long, arbitrary distance to less than an optical fringe[J]. Optics Letters, 2004, 29(10): 1153-1155. doi: 10.1364/OL.29.001153 [3] 岱钦, 毛有明, 吴凯旋, 等. 脉冲 测距中高速精密时间间隔测量研究[J]. 液晶与显示,2015,30(1):83-88. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153001.0083DAI Q, MAO Y M, WU K X, et al. High speed and high precision time-interval measurement system in pulsed laser ranging[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2015, 30(1): 83-88. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153001.0083 [4] 高慧, 赵佳宇, 刘伟伟. 超快 成丝现象的多丝控制[J]. 光学 精密工程,2013,21(3):698-607.GAO H, ZHAO J Y, LIU W W. Control of multiple filamentation induced by ultrafast laser pulse[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2013, 21(3): 698-607. (in Chinese) [5] TRÄGER F. Handbook of Lasers and Optics[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Springer, 2012. [6] 姜可, 谢冀江, 杨贵龙, 等. GaSe晶体的双光子吸收对太赫兹输出的影响[J]. 发光学报,2015,36(3):361-365. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20153603.0361JIANG K, XIE J J, YANG G L, et al. Two-photon absorption attenuated THz generation in GaSe[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2015, 36(3): 361-365. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20153603.0361 [7] TANTER M, TOUBOUL D, GENNISSON J L, et al. High-resolution quantitative imaging of cornea elasticity using supersonic shear imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2009, 28(12): 1881-1893. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2021471 [8] CHOU S Y, KEIMEL C, GU J. Ultrafast and direct imprint of nanostructures in silicon[J]. Nature, 2002, 417(6891): 835-837. doi: 10.1038/nature00792 [9] KELLER U. Recent developments in compact ultrafast lasers[J]. Nature, 2003, 424(6950): 831-838. doi: 10.1038/nature01938 [10] 李景照, 陈振强, 朱思祁. 基于Yb: YAG/Cr4+: YAG/YAG键合晶体的被动调Q 器[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(1):55-61. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182601.0055LI J ZH, CHEN ZH Q, ZHU S Q. Passively Q-switched laser with a Yb: YAG/Cr4+: YAG/YAG composite crystal[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(1): 55-61. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182601.0055 [11] 程秀凤, 陈丽娟, 韩树娟, 等. LD端面泵浦Nd: LiGd(MoO4)2晶体的主动调Q脉冲 特性[J]. 光学 精密工程,2013,21(4):836-840.CHENG X F, CHEN L J, HAN SH J, et al. Actively Q-switched pulse laser from LD end-pumped Nd: LiGd(MoO4)2 crystals[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2013, 21(4): 836-840. (in Chinese) [12] 王加贤, 庄鑫巍. 基于半导体可饱和吸收镜实现闪光灯抽运Nd: YAG 器的被动调Q与锁模[J]. 光学 精密工程,2006,14(4):584-588.WANG J X, ZHUANG X W. Passive Q-switching and mode-locking in a flashlamp-pumped Nd: YAG laser with semiconductor saturable absorption mirror[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2006, 14(4): 584-588. (in Chinese) [13] 余锦, 刘伟仁. 1.0 μm掺钕介质全固化调Q脉冲 技术[J]. 光学 精密工程,2000,8(2):297-302.YU J, LIU W R. All-solid-state Q-switched lasers with Nd3+-doped crystals oscillating at 1.0 μm[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2000, 8(2): 297-302. (in Chinese) [14] 王蓟, 王国政, 刘洋, 等. 全光纤声光调Q铒镱共掺双包层光纤 器[J]. 发光学报,2008,29(6):1018-1022.WANG J, WANG G ZH, LIU Y, et al. All-fiber acousto-optic Q-switched Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped double-cladding fiber lasers[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2008, 29(6): 1018-1022. (in Chinese) [15] 王国立, 郭亨群, 苏培林, 等. nc-Si/SiNx超晶格薄膜实现Nd: YAG 器调Q和锁模[J]. 发光学报,2008,29(5):905-909.WANG G L, GUO H Q, SU P L, et al. Passive Q-switching and mode locking of pulsed Nd: YAG laser with nc-Si/SiNx multilayer[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2008, 29(5): 905-909. (in Chinese) [16] 张伶莉, 孙秀冬, 刘永军, 等. 具有外部谐振腔的胆甾相液晶 器的研究[J]. 液晶与显示,2013,28(5):679-682. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20132805.0679ZHANG L L, SUN X D, LIU Y J, et al. Cholesteric liquid crystals laser with external cavity[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2013, 28(5): 679-682. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20132805.0679 [17] 苏晶, 刘玉荣, 莫昌文, 等. ZnO基薄膜晶体管有源层制备技术的研究进展[J]. 液晶与显示,2013,28(3):315-322. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20132803.0315SU J, LIU Y R, MO CH W, et al. Research development on preparation technologies of active layer preparation of ZnO-based thin film[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2013, 28(3): 315-322. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20132803.0315 [18] ZIRNGIBL M, STULZ L W, STONE J, et al. 1.2 ps pulses from passively mode-locked laser diode pumped Er-doped fibre ring laser[J]. Electronics Letters, 1991, 27(19): 1734-1735. doi: 10.1049/el:19911079 [19] WEI CH, SHI H X, LUO H Y, et al. 34 nm-wavelength-tunable picosecond Ho3+/Pr3+-codoped ZBLAN fiber laser[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(16): 19170-19178. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.019170 [20] TANG P H, QIN ZH P, LIU J, et al. Watt-level passively mode-locked Er3+-doped ZBLAN fiber laser at 2.8 μm[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(21): 4855-4858. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.004855 [21] NOVOSELOV K S, JIANG D, SCHEDIN F, et al. Two-dimensional atomic crystals[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(30): 10451-10453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502848102 [22] WANG Q H, KALANTAR-ZADEH K, KIS A, et al. Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2012, 7(11): 699-712. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.193 [23] CHEN Y, JIANG G B, CHEN SH Q, et al. Mechanically exfoliated black phosphorus as a new saturable absorber for both Q-switching and mode-locking laser operation[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(10): 12823-12833. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.012823 [24] JIANG X T, LIU SH X, LIANG W Y, et al. Broadband nonlinear photonics in few-layer MXene Ti3C2Tx(T = F, O, or OH)[J]. Laser &Photonics Review, 2018, 12(2): 1700229. [25] WANG SH X, YU H H, ZHANG H J, et al. Broadband few-layer MoS2 saturable absorbers[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(21): 3538-3544. doi: 10.1002/adma.201306322 [26] WANG M X, ZHANG F, WANG ZH P, et al. Passively Q-switched Nd3+ solid-state lasers with antimonene as saturable absorber[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(4): 4085-4095. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.004085 [27] GUO J, HUANG D ZH, ZHANG Y, et al.. 2D GeP as a novel broadband nonlinear optical material for ultrafast photonics[J]. Laser &Photonics Reviews, 2019, 13: 1900123. [28] MOHANRAJ J, VELMURUGAN V, SIVABALAN S. Transition metal dichalcogenides based saturable absorbers for pulsed laser technology[J]. Optical Materials, 2016, 60: 601-617. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2016.09.007 [29] TIU Z C, OOI S I, GUO J, et al. Review: application of transition metal dichalcogenide in pulsed fiber laser system[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(8): 082004. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab2257 [30] LI H, LU G, WANG Y L, et al. Mechanical exfoliation and characterization of single- and few-layer nanosheets of WSe2, TaS2, and TaSe2[J]. Small, 2013, 9(11): 1974-1981. doi: 10.1002/smll.201202919 [31] COLEMAN J N, LOTYA M, O’NEILL A, et al. Two-dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials[J]. Science, 2011, 331(6017): 568-571. doi: 10.1126/science.1194975 [32] MAK K F, HE K L, SHAN J, et al. Control of valley polarization in monolayer MoS2 by optical helicity[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2012, 7(8): 494-498. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.96 [33] BERTOLAZZI S, BRIVIO J, KIS A. Stretching and breaking of ultrathin MoS2[J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(12): 9703-9709. doi: 10.1021/nn203879f [34] LEE Y H, ZHANG X Q, ZHANG W J, et al. Synthesis of large-area MoS2 atomic layers with chemical vapor deposition[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(17): 2320-2325. doi: 10.1002/adma.201104798 [35] NAJMAEI S, LIU ZH, ZHOU W, et al. Vapour phase growth and grain boundary structure of molybdenum disulphide atomic layers[J]. Nature Materials, 2013, 12(8): 754-759. doi: 10.1038/nmat3673 [36] REN L, QI X, LIU Y D, et al. Large-scale production of ultrathin topological insulator bismuth telluride nanosheets by a hydrothermal intercalation and exfoliation route[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(11): 4921-4926. doi: 10.1039/c2jm15973b [37] PRADO G, FOURNÈS L, DELMAS C. On the LixNi0.70Fe0.15Co0.15O2 system: an X-ray diffraction and mössbauer study[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2001, 159(1): 103-112. doi: 10.1006/jssc.2001.9137 [38] RAMAKRISHNA MATTE H S S, GOMATHI A, et al. MoS2 and WS2 analogues of graphene[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(24): 4059-4062. doi: 10.1002/anie.201000009 [39] FOMINSKI V Y, NEVOLIN V N, ROMANOV R I, et al. Ion-assisted deposition of MoSx films from laser-generated plume under pulsed electric field[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(2): 1449-1457. doi: 10.1063/1.1330558 [40] CONG CH X, SHANG J ZH, WU X, et al. Synthesis and optical properties of large-area single-crystalline 2D semiconductor WS2 monolayer from chemical vapor deposition[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2014, 2(2): 131-136. doi: 10.1002/adom.201300428 [41] REICHARDT S, WIRTZ L. Raman Spectroscopy of Graphene[M]. BINDER R. Optical Properties of Graphene. Singapore: World Scientific, 2017. [42] DRESSELHAUS M S, JORIO A, SAITO R. Characterizing graphene, graphite, and carbon nanotubes by raman spectroscopy[J]. Annual Review of Condensed Matter Physics, 2010, 1: 89-108. doi: 10.1146/annurev-conmatphys-070909-103919 [43] DRESSELHAUS M S, JORIO A, HOFMAN M, et al. Perspectives on carbon nanotubes and graphene raman spectroscopy[J]. Nano Letters, 2010, 10(3): 751-758. doi: 10.1021/nl904286r [44] ZUO CH H, CAO Y P, YANG Q, et al. Passively Q-switched 295-μm bulk laser based on rhenium disulfide as saturable absorber[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2019, 31(3): 206-209. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2018.2886784 [45] HUANG B, DU L, YI Q, et al. Bulk-structured PtSe2 for femtosecond fiber laser mode-locking[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(3): 2604-2611. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.002604 [46] YAO Y P, LI X W, SONG R G, et al. The energy band structure analysis and 2 μm Q-switched laser application of layered rhenium diselenide[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(25): 14417-14421. doi: 10.1039/C9RA02311A [47] WANG J T, CHEN H, JIANG Z K, et al. Mode-locked thulium-doped fiber laser with chemical vapor deposited molybdenum ditelluride[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(9): 1998-2001. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.001998 [48] WANG J T, JIANG Z K, CHEN H, et al. Magnetron-sputtering deposited WTe2 for an ultrafast thulium-doped fiber laser[J]. Optics Letters, 2017, 42(23): 5010-5013. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.005010 [49] TIAN X L, WEI R F, LIU M, et al. Ultrafast saturable absorption in TiS2 induced by non-equilibrium electrons and the generation of a femtosecond mode-locked laser[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(20): 9608-9615. doi: 10.1039/C8NR01573B [50] WU K, CHEN B H, ZHANG X Y, et al. High-performance mode-locked and Q-switched fiber lasers based on novel 2D materials of topological insulators, transition metal dichalcogenides and black phosphorus: review and perspective (invited)[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 406: 214-229. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.02.024 [51] TIAN Z, WU K, KONG L CH, et al. Mode-locked thulium fiber laser with MoS2[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2015, 12(6): 065104. doi: 10.1088/1612-2011/12/6/065104 [52] WEI CH, LUO H Y, ZHANG H, et al. Passively Q-switched mid-infrared fluoride fiber laser around 3 μm using a tungsten disulfide (WS2) saturable absorber[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2016, 13(10): 105108. doi: 10.1088/1612-2011/13/10/105108 [53] HOU J, ZHAO G, WU Y ZH, et al. Femtosecond solid-state laser based on tungsten disulfide saturable absorber[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(21): 27292-27298. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.027292 [54] CHEN B H, ZHANG X Y, WU K, et al. Q-switched fiber laser based on transition metal dichalcogenides MoS2, MoSe2, WS2, and WSe2[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(20): 26723-26737. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.026723 [55] WU K, ZHANG X Y, WANG J, et al. WS2 as a saturable absorber for ultrafast photonic applications of mode-locked and Q-switched lasers[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(9): 11453-11461. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.011453 [56] WU K, ZHANG X Y, WANG J, et al. 463-MHz fundamental mode-locked fiber laser based on few-layer MoS2 saturable absorber[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(7): 1374-1377. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.001374 [57] WANG Q K, CHEN Y, MIAO L L, et al. Wide spectral and wavelength-tunable dissipative soliton fiber laser with topological insulator nano-sheets self-assembly films sandwiched by PMMA polymer[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(6): 7681-7693. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.007681 [58] XING CH Y, XIE ZH J, LIANG ZH M, et al. 2D nonlayered selenium nanosheets: facile synthesis, photoluminescence, and ultrafast photonics[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2017, 5(24): 1700884. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700884 [59] YAN P G, LIN R Y, CHEN H, et al. Topological insulator solution filled in photonic crystal fiber for passive mode-locked fiber laser[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2015, 27(3): 264-267. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2014.2361915 [60] YAN P G, LIU A J, CHEN Y SH, et al. Passively mode-locked fiber laser by a cell-type WS2 nanosheets saturable absorber[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 12587. doi: 10.1038/srep12587 [61] WANG K P, WANG J, FAN J T, et al. Ultrafast saturable absorption of two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheets[J]. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(10): 9260-9267. doi: 10.1021/nn403886t [62] XU B, CHENG Y J, WANG Y, et al. Passively Q-switched Nd: YAlO3 nanosecond laser using MoS2 as saturable absorber[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(23): 28934-28940. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.028934 [63] TONGAY S, SAHIN H, KO C, et al. Monolayer behaviour in bulk ReS2 due to electronic and vibrational decoupling[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 3252. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4252 [64] CHHOWALLA M, SHIN H S, EDA G, et al. The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2013, 5(4): 263-275. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1589 [65] XU M SH, LIANG T, SHI M M, et al. Graphene-like two-dimensional materials[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(5): 3766-3798. doi: 10.1021/cr300263a [66] LIU E F, FU Y J, WANG Y J, et al. Integrated digital inverters based on two-dimensional anisotropic ReS2 field-effect transistors[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 6991. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7991 [67] TIAN H, CHIN M L, NAJMAEI S, et al. Optoelectronic devices based on two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides[J]. Nano Research, 2016, 9(6): 1543-1560. doi: 10.1007/s12274-016-1034-9 [68] ZHANG E Z, JIN Y B, YUAN X, et al. ReS2-based field-effect transistors and photodetectors[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(26): 4076-4082. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201500969 [69] SU X C, ZHANG B T, WANG Y R, et al. Broadband rhenium disulfide optical modulator for solid-state lasers[J]. Photonics Research, 2018, 6(6): 498-505. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.6.000498 [70] HAN SH, ZHOU SH SH, LIU X L, et al. Rhenium disulfide-based passively Q-switched dual-wavelength laser at 0.95 μm and 1.06 μm in Nd: YAG[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2018, 15(8): 085804. doi: 10.1088/1612-202X/aac983 [71] LIN M X, PENG Q Q, HOU W, et al. 1.3 μm Q-switched solid-state laser based on few-layer ReS2 saturable absorber[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2019, 109: 90-93. [72] TAO L L, HUANG X W, HE J SH, et al. Vertically standing PtSe2 film: a saturable absorber for a passively mode-locked Nd: LuVO4 laser[J]. Photonics Research, 2018, 6(7): 750-755. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.6.000750 [73] YAN B ZH, ZHANG B T, NIE H K, et al. Bilayer platinum diselenide saturable absorber for 2.0 μm passively Q-switched bulk lasers[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(24): 31657-31663. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.031657 [74] LI Z Q, LI R, PANG CH, et al. 8.8 GHz Q-switched mode-locked waveguide lasers modulated by PtSe2 saturable absorber[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(6): 8727-8737. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.008727 [75] WANG SH Q, HUANG H T, LIU X, et al. Rhenium diselenide as the broadband saturable absorber for the nanosecond passively Q-switched thulium solid-state lasers[J]. Optical Materials, 2019, 88: 630-634. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2018.12.042 [76] XUE Y CH, LI L, ZHANG B, et al. ReSe2 passively Q-switched Nd: Y3Al5 O12 laser with near repetition rate limit of microsecond pulse output[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 455: 165-170. [77] YAO Y P, CUI N, WANG Q G, et al. Highly efficient continuous-wave and ReSe2 Q-switched ~3 μm dual-wavelength Er: YAP crystal lasers[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(11): 2839-2842. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.002839 [78] LI Z Q, DONG N N, ZHANG Y X, et al. Invited Article: mode-locked waveguide lasers modulated by rhenium diselenide as a new saturable absorber[J]. APL Photonics, 2018, 3(8): 080802. doi: 10.1063/1.5032243 [79] LI CH, LENG Y X, HUO J J. Diode-pumped solid-state Q-switched laser with rhenium diselenide as saturable absorber[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(10): 1753. doi: 10.3390/app8101753 [80] YAN ZH Y, LI T, ZHAO SH ZH, et al. MoTe2 saturable absorber for passively Q-switched Ho, Pr: LiLuF4 laser at ~3 μm[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2018, 100: 261-264. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.10.012 [81] LI Y H, XU Y F, XU G Y, et al. Performance of an Yb: LaCa4O(BO3)3 crystal laser at 1.03~1.04 μm passively Q-switched with 2D MoTe2 saturable absorber[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2019, 99: 167-171. [82] ZHANG Y ZH, WANG J W, GUAN X F, et al. MoTe2-based broadband wavelength tunable eye-safe pulsed laser source at 1.9 μm[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2018, 30(21): 1890-1893. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2018.2871467 [83] LIANG Y Y, ZHAO J, QIAO W CH, et al. Passively Q-switched Er: YAG laser at 1645 nm utilizing a multilayer molybdenum ditelluride (MoTe2) saturable absorber[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2018, 15(9): 095801. doi: 10.1088/1612-202X/aacfae [84] YAN B ZH, ZHANG B T, NIE H K, et al. High-power passively Q-switched 2.0 μm all-solid-state laser based on a MoTe2 saturable absorber[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(14): 18505-18512. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.018505 [85] MA Y J, TIAN K, DOU X D, et al. Passive Q-switching induced by few-layer MoTe2 in an Yb: YCOB microchip laser[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(19): 25147-25155. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.025147 [86] TIAN K, LI Y H, YANG J N, et al. Passively Q-switched Yb: KLu(WO4)2 laser with 2D MoTe2 acting as saturable absorber[J]. Applied Physics B, 2019, 125(2): 24. doi: 10.1007/s00340-019-7135-x [87] CHEN L J, LI X, ZHANG H K, et al. Passively Q-switched 1.989 μm all-solid-state laser based on a WTe2 saturable absorber[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(35): 10239-10242. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.010239 [88] YAN ZH Y, LI T, ZHAO J, et al. Tungsten ditelluride for a nanosecond Ho, Pr: LiLuF4 laser at 2.95 μm[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2018, 15(4): 045801. doi: 10.1088/1612-202X/aaa94b [89] LI G Q, WU CH, YAN ZH Y, et al. TiS2 as a novel saturable absorber for a 1645 nm passively Q-switched laser[J]. Laser Physics, 2019, 29(5): 055801. doi: 10.1088/1555-6611/ab0d13 [90] WOODWARD R I, KELLEHER E J R, HOWE R C T, et al. Tunable Q-switched fiber laser based on saturable edge-state absorption in few-layer Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2)[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(25): 31113-31122. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.031113 [91] CUI Y D, LU F F, LIU X M. Nonlinear saturable and polarization-induced absorption of rhenium disulfide[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 40080. doi: 10.1038/srep40080 [92] MAO D, CUI X Q, GAN X T, et al. Passively Q-switched and mode-locked fiber laser based on an ReS2 saturable absorber[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2018, 24(3): 1100406. [93] LU F F. Passively harmonic mode-locked fiber laser based on ReS2 saturable absorber[J]. Modern Physics Letters B, 2017, 31(18): 1750206. doi: 10.1142/S0217984917502062 [94] ZHAO R W, LI G R, ZHANG B T, et al. Multi-wavelength bright-dark pulse pair fiber laser based on rhenium disulfide[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(5): 5819-5826. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.005819 [95] LU B L, WEN Z R, HUANG K X, et al. Passively Q-switched Yb3+-doped fiber laser with ReS2 Saturable absorber[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2019, 25(4): 1600104. [96] YUAN J, MU H R, LI L, et al. Few-layer platinum diselenide as a new saturable absorber for ultrafast fiber lasers[J]. ACS Applied Materials &Interfaces, 2018, 10(25): 21534-21540. [97] ZHANG K, FENG M, REN Y Y, et al. Q-switched and mode-locked Er-doped fiber laser using PtSe2 as a saturable absorber[J]. Photonics Research, 2018, 6(9): 893-899. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.6.000893 [98] LI Y H, LOU Y J, HE J S, et al. Q-switched ytterbium fiber laser based on rhenium diselenide as a saturable absorber[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2019, 52(46): 465101. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ab3883 [99] LEE J, LEE K, KWON S, et al. Investigation of nonlinear optical properties of rhenium diselenide and its application as a femtosecond mode-locker[J]. Photonics Research, 2019, 7(9): 984-993. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.7.000984 [100] DU L, JIANG G B, MIAO L L, et al. Few-layer rhenium diselenide: an ambient-stable nonlinear optical modulator[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2018, 8(4): 926-935. doi: 10.1364/OME.8.000926 [101] WANG G M. Wavelength-switchable passively mode-locked fiber laser with mechanically exfoliated molybdenum ditelluride on side-polished fiber[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2017, 96: 307-312. [102] LIU M L, LIU W J, WEI ZH Y. MoTe2 saturable absorber with high modulation depth for erbium-doped fiber laser[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2019, 37(13): 3100-3105. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2019.2910892 [103] LIU M L, LIU W J, YAN P G, et al. High-power MoTe2-based passively Q-switched erbium-doped fiber laser[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16(2): 020007. doi: 10.3788/COL201816.020007 [104] WANG J T, JIANG Z K, CHEN H, et al. High energy soliton pulse generation by a magnetron -sputtering- deposition -grown MoTe2 saturable absorber[J]. Photonics Research, 2018, 6(6): 535-541. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.6.000535 [105] KO S, LEE J, LEE J H. Passively Q-switched ytterbium-doped fiber laser using the evanescent field interaction with bulk-like WTe2 particles[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16(2): 020017. doi: 10.3788/COL201816.020017 [106] LIU M L, OUYANG Y Y, HOU H R, et al. Q-switched fiber laser operating at 1.5 μm based on WTe2[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2019, 17(2): 020006. doi: 10.3788/COL201917.020006 [107] ZHU X, CHEN S, ZHANG M, et al. TiS2-based saturable absorber for ultrafast fiber lasers[J]. Photonics Research, 2018, 6(10): C44-C48. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.6.000C44 -






 下载:
下载: