Multi-scale singular value decomposition polarization image fusion defogging algorithm and experiment
-
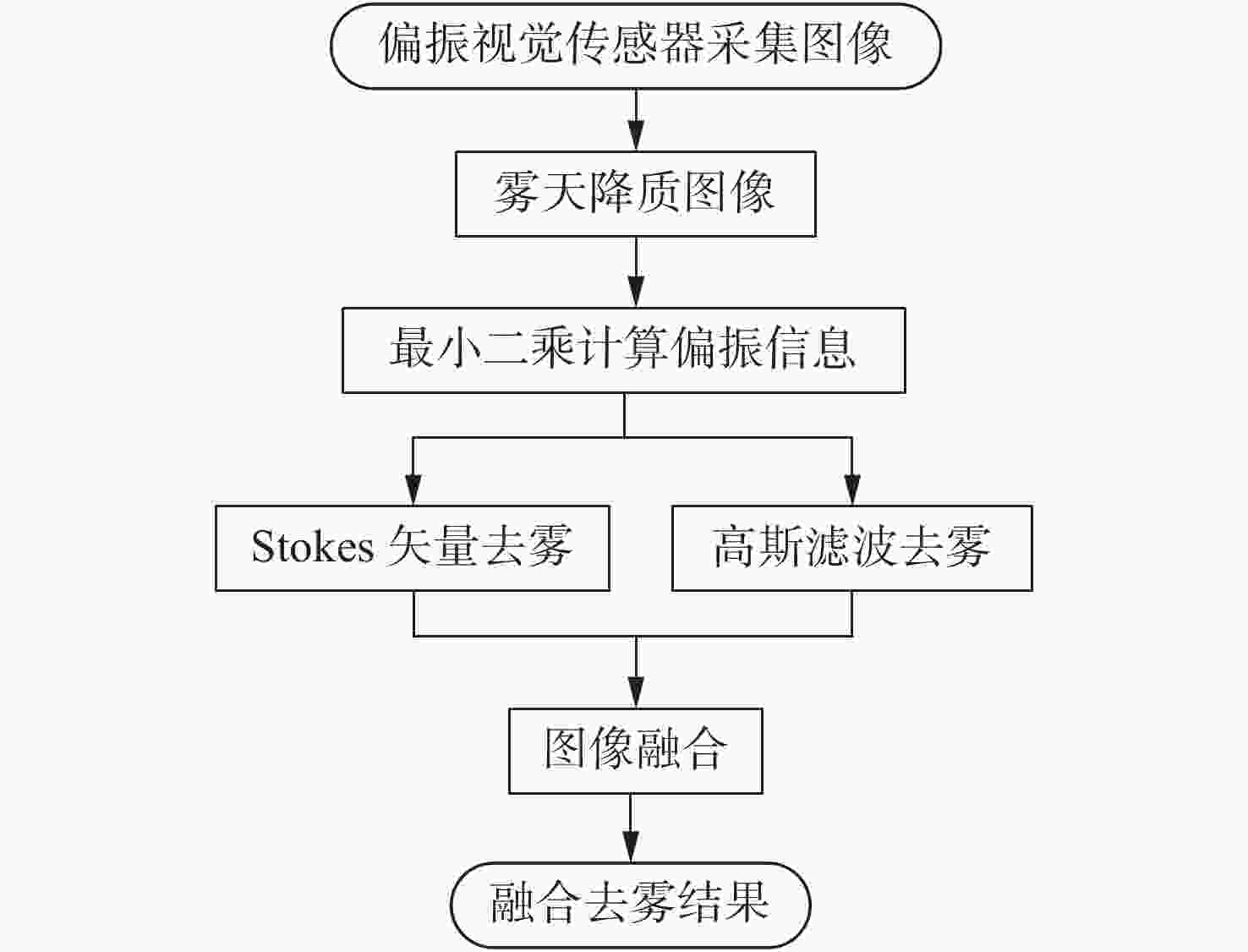
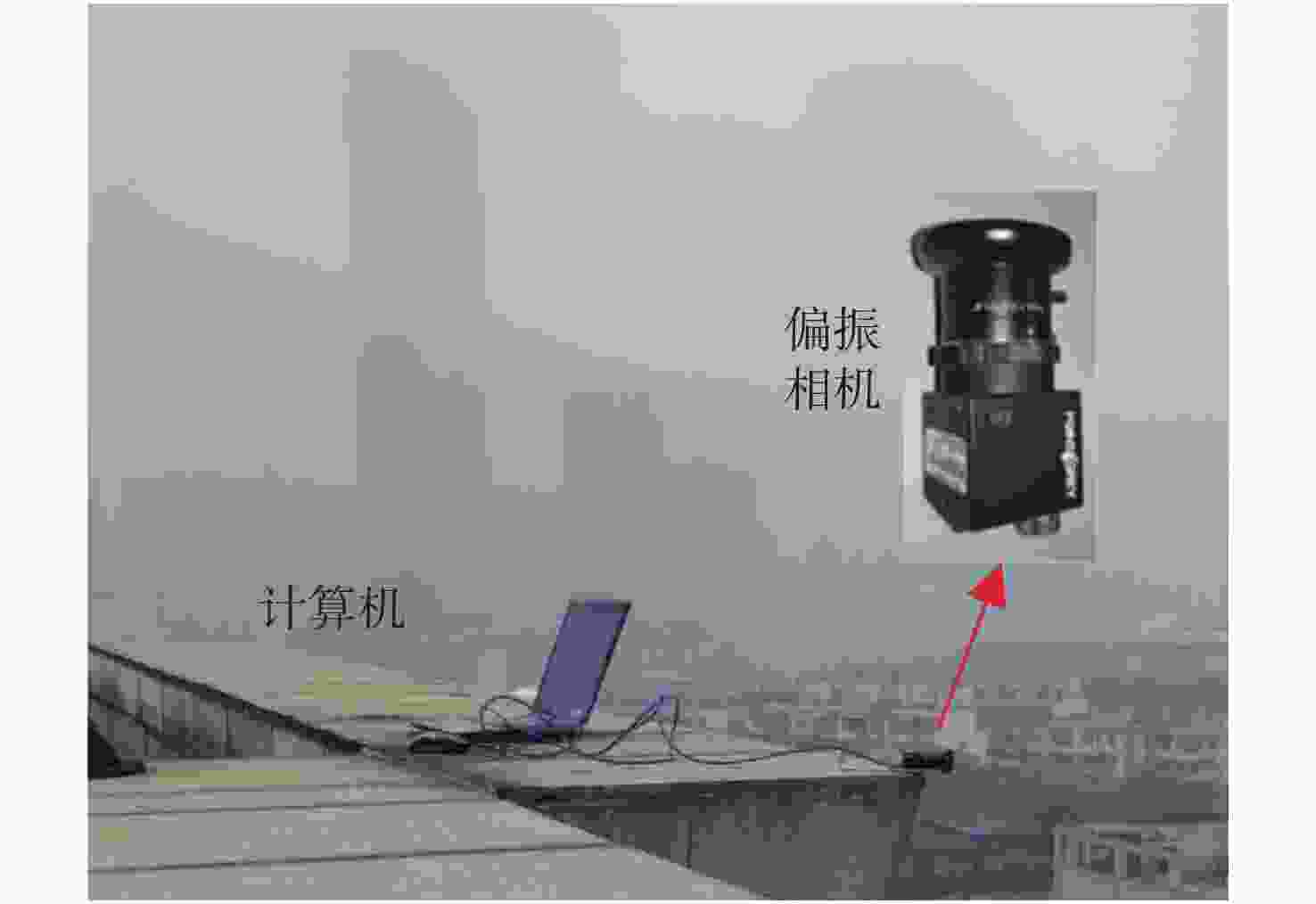
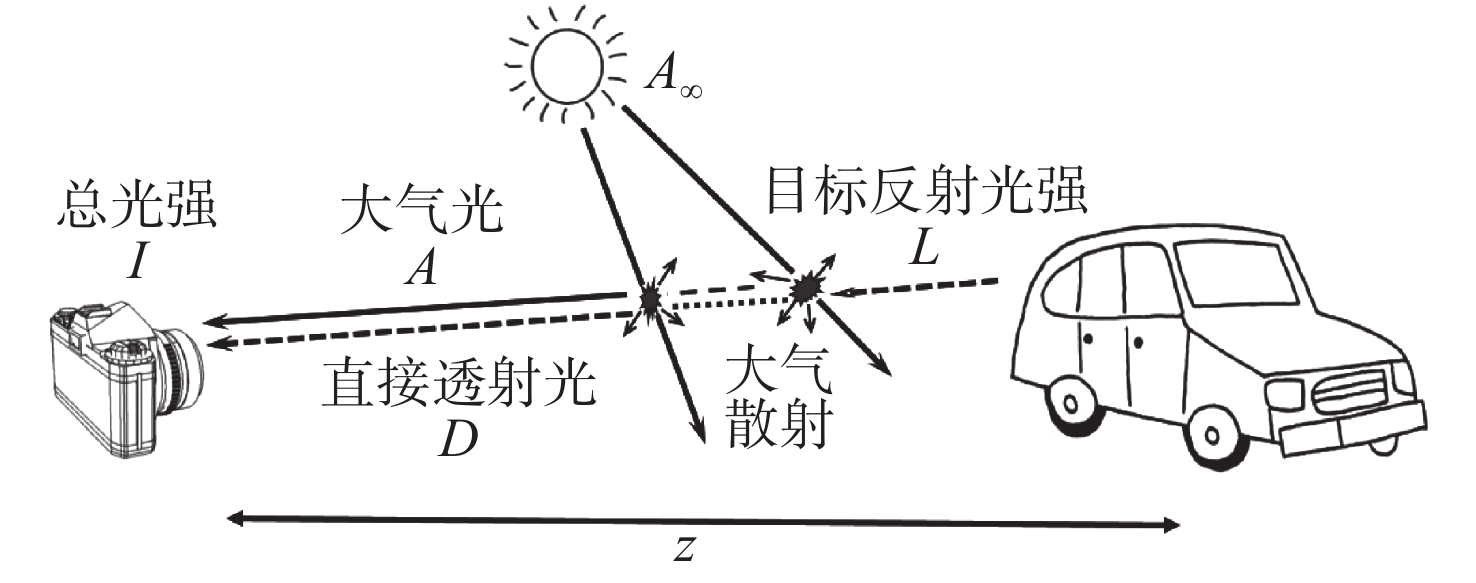
摘要: 针对现有偏振去雾算法鲁棒性不强和图像增强效果有限的问题,提出一种基于多尺度奇异值分解的图像融合去雾算法。首先,利用偏振测量信息的冗余特性,采用最小二乘法,提高了传统偏振图像去雾算法中偏振信息的准确度;然后,从传统偏振图像去雾算法的局限性出发,定性分析了偏振图像融合去雾的可行性,并提出了一种基于多尺度奇异值分解的偏振图像融合去雾算法;最后,设计了不同能见度条件下的验证实验并进行了量化评价。结果表明,与经典偏振图像去雾算法相比,该算法不需要进行人工参数调节,具有较强的自适应性和鲁棒性,能够有效改善传统算法中出现的光晕以及天空区域过曝的问题,图像信息熵与平均梯度最大可分别提高18.9%和38.4%,有效地增强了复杂光照条件下的视觉成像质量,具有较广泛的应用前景。Abstract: Aiming at the problems that the robust of existing polarization defogging algorithms is poor and image enhancement abilities are limited, an image fusion defogging algorithm based on Multi-scale Singular Value Decomposition (MSVD) is proposed. Firstly, considering the redundancy in polarization measurement information, the least square method is used to improve the accuracy of the polarization information in the traditional defogging algorithm for polarized images; then, with respect to the limitations of that algorithm, a qualitative analysis of the feasibility of image fusion defogging is implemented, and a polarized image fusion defogging algorithm based on multi-scale singular value decomposition is proposed. Finally, a verification experiment under different visibility conditions is designed and quantified. The results show that compared with the classic polarized image defogging algorithm, this algorithm does not require manual parameter adjustment, it has strong adaptability and robustness, and can effectively improve the halos and overexposure of sky areas that occur in the traditional algorithm. The image information entropy and the average gradient can be increased by 18.9% and 38.4% respectively, which effectively improves the quality of visual imaging under complex lighting conditions. The proposed algorithm has great application prospects.
-
Key words:
- polarized vision /
- image defogging and enhancement /
- gaussian filtering /
- Stokes vector
-
表 1 晴天计算结果
Table 1. Calculation results in sunny conditions
平均梯度 信息熵 SSIM 传统方法 12.8627 2.3589 0.9886 最小二乘方法 14.6039 2.7229 0.9896 表 2 雾天计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results in foggy conditions
平均梯度 信息熵 SSIM 传统方法 45.6613 2.5432 0.9709 最小二乘方法 59.3331 2.9357 0.9177 表 3 去雾效果定量比较
Table 3. Quantitative comparison of different defogging algorithms
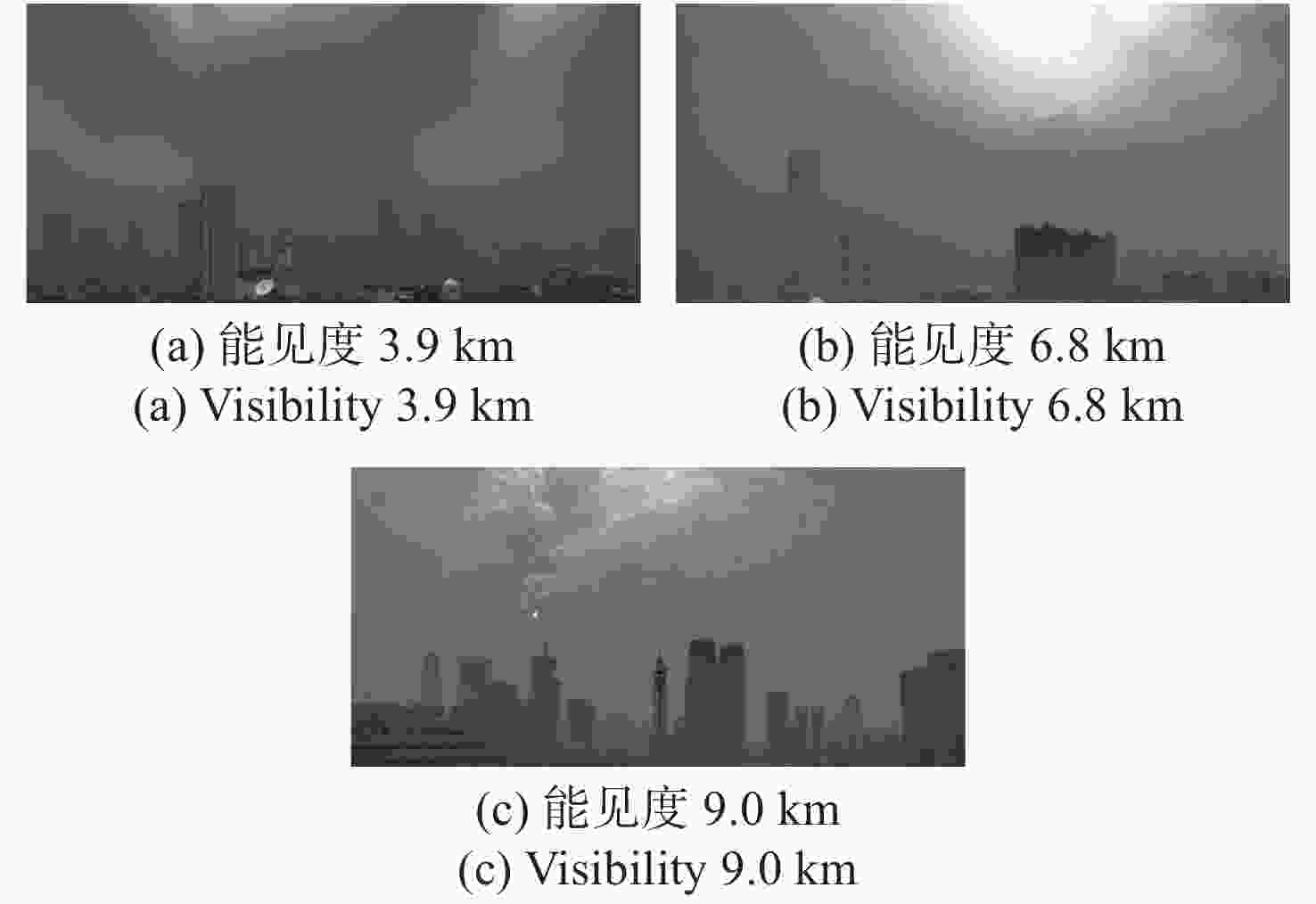
能见度/m 信息熵 平均梯度 原图 高斯滤波算法 Stokes矢量算法 MSCNN 图像融合算法 原图 高斯滤波算法 Stokes矢量算法 MSCNN 图像融合算法 3900 7.16 6.73 7.42 7.19 7.26 1.53 4.85 6.14 5.13 6.18 6800 6.56 5.50 7.18 7.11 6.55 1.22 5.79 4.01 5.18 5.55 9000 7.15 5.46 7.09 7.16 6.28 1.43 4.94 4.05 5.16 5.11 表 4 去雾时间成本定量比较
Table 4. Time-cost comparison of different defogging algorithms
能见度/m 去雾时间/s 高斯滤波算法 Stokes矢量算法 MSCNN 图像融合用时 3900 3.25 30.90 37.15 7.25 6800 4.13 31.01 34.36 7.71 9000 3.26 30.14 34.33 6.57 -
[1] PATEL S P, NAKRANI M. A review on methods of image dehazing[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2016, 133(12): 44-49. doi: 10.5120/ijca2016908076 [2] FATTAL R. Single image dehazing[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2008, 27(3): 547-555. [3] HE K M, SUN J, TANG X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341-2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [4] 邓莉. 针对明亮区域的自适应全局暗原色先验去雾[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(4):892-901. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162404.0892DENG L. Adaptive image dehazing for bright areas based on global dark channel prior[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(4): 892-901. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162404.0892 [5] 杨燕, 刘珑珑, 张得欣, 等. 结合自适应雾气估计的快速单幅图像去雾[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(10):2263-2271. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192710.2263YANG Y, LIU L L, ZHANG D X, et al. Fast single image dehazing combined with adaptive haze estimation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(10): 2263-2271. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192710.2263 [6] 杨燕, 张国强, 姜沛沛. 结合景深估计的高斯衰减与自适应补偿去雾[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(11):2439-2449. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192711.2439YANG Y, ZHANG G Q, JIANG P P. Gaussian decay and adaptive compensation dehazing algorithm combined with scene depth estimation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(11): 2439-2449. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192711.2439 [7] CAI B L, XU X M, JIA K, et al. DehazeNet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5187-5198. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2598681 [8] SCHECHNER Y Y, NARASIMHAN S G, NAYAR S K. Polarization-based vision through haze[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(3): 511-525. doi: 10.1364/AO.42.000511 [9] MUDGE J, VIRGEN M. Real time polarimetric dehazing[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(9): 1932-1938. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.001932 [10] NAMER E, SHWARTZ S, SCHECHNER Y Y. Skyless polarimetric calibration and visibility enhancement[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(2): 472-493. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.000472 [11] SCHECHNER Y Y, NARASIMHAN S G, NAYAR S K. Instant dehazing of images using polarization[C]. Proceedings of 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2003. [12] LIANG J, REN L Y, QU E SH, et al. Method for enhancing visibility of hazy images based on polarimetric imaging[J]. Photonics Research, 2014, 2(1): 38-44. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.2.000038 [13] 曾佳. 基于大气散射模型的雾天图像复原方法研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2015.ZENG J. Research of fog-degraded image restoration method based on the atmospheric scattering model[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese). [14] FAN CH, HU X P, LIAN J X, et al. Design and calibration of a novel camera-based bio-inspired polarization navigation sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(10): 3640-3648. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2533628 [15] FANG S, XIA X S, HUO X, et al. Image dehazing using polarization effects of objects and airlight[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(16): 19523-19537. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.019523 [16] 高隽, 毕冉, 赵录建. 利用偏振信息的雾天图像全局最优重构[J]. 光学 精密工程,2017,25(8):2212-2220. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172508.2212GAO J, BI R, ZHAO L J. Global optimized hazed image reconstruction based on polarization information[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(8): 2212-2220. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172508.2212 [17] 汪晓波, 刘斌. 基于多分辨奇异值分解的多聚焦图像融合[J]. 量子电子学报,2014,31(3):257-263.WANG X B, LIU B. Multi-focus image fusion based on multi-resolution singular value decomposition[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2014, 31(3): 257-263. (in Chinese) [18] BURT P J, ADELSON E H. The Laplacian pyramid as a Compact image code[J]. Reading in Computer Vision, 1987, 31(4): 671-679. -






 下载:
下载: