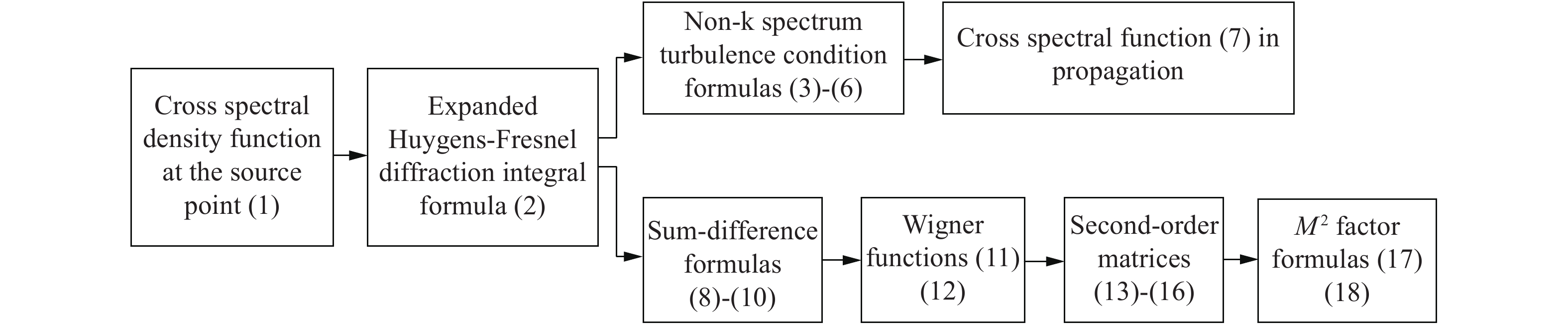
Suppression of the influence of atmospheric turbulence during the propagation of a twisted Laguerre-Gaussian correlated beam
doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0138
-
摘要: 金宝搏188软件怎么用 光束在大气湍流传输过程中会受到环境的影响并导致其光学特性发生变化,而部分相干光相对于传统的完全相干光而言,能够减小大气湍流所带来的负面影响。本文选择携带扭曲相位的拉盖尔—高斯关联光束,并基于拓展的惠更斯—菲涅尔衍射积分理论、Wigner函数分布、扭曲相位的基本性质以及非柯尔莫哥洛夫湍流的功率谱模型,导出了该光束在大气湍流环境中传输的交叉谱密度函数和光束质量因子。本文使用构建的数学模型,数值模拟了在不同扭曲因子、横截面相干度和光束阶数的条件下大气湍流对光束的影响。理论结果表明,携带高扭曲因子、低截面向相干性的高阶拉盖尔—高斯关联光束能够有效抑制大气湍流的影响。
-
关键词:
- 大气湍流 /
- 扭曲相位 /
- 部分相干 /
- 拓展的惠更斯—菲涅尔原理
Abstract: During its propagation in atmospheric turbulence, the optical properties of a laser beam will be changed by the surrounding environment. Compared with a completely coherent laser, a partially coherent laser can more strongly resist the influence of atmospheric turbulence. In this paper, a twisted Laguerre-Gaussian correlated beam was employed to deduce a cross-spectral density function for propagation in atmospheric turbulence. The cross-spectral density and M2 factor were also constructed by using the extended Huygens-Fresnel diffraction integral principle, Wigner distribution function, basic properties of the twisted phase, and power spectrum model of non-Kolmogorov turbulence. Then, the influence of atmospheric turbulence on the beam was numerically simulated, and the results were compared with those for different twist factors, transverse coherence parameters and mode orders. It has been demonstrated that a beam with a high twist factor, low transverse parameter, and high mode order can be used to effectively suppress the influence of atmospheric turbulence. -
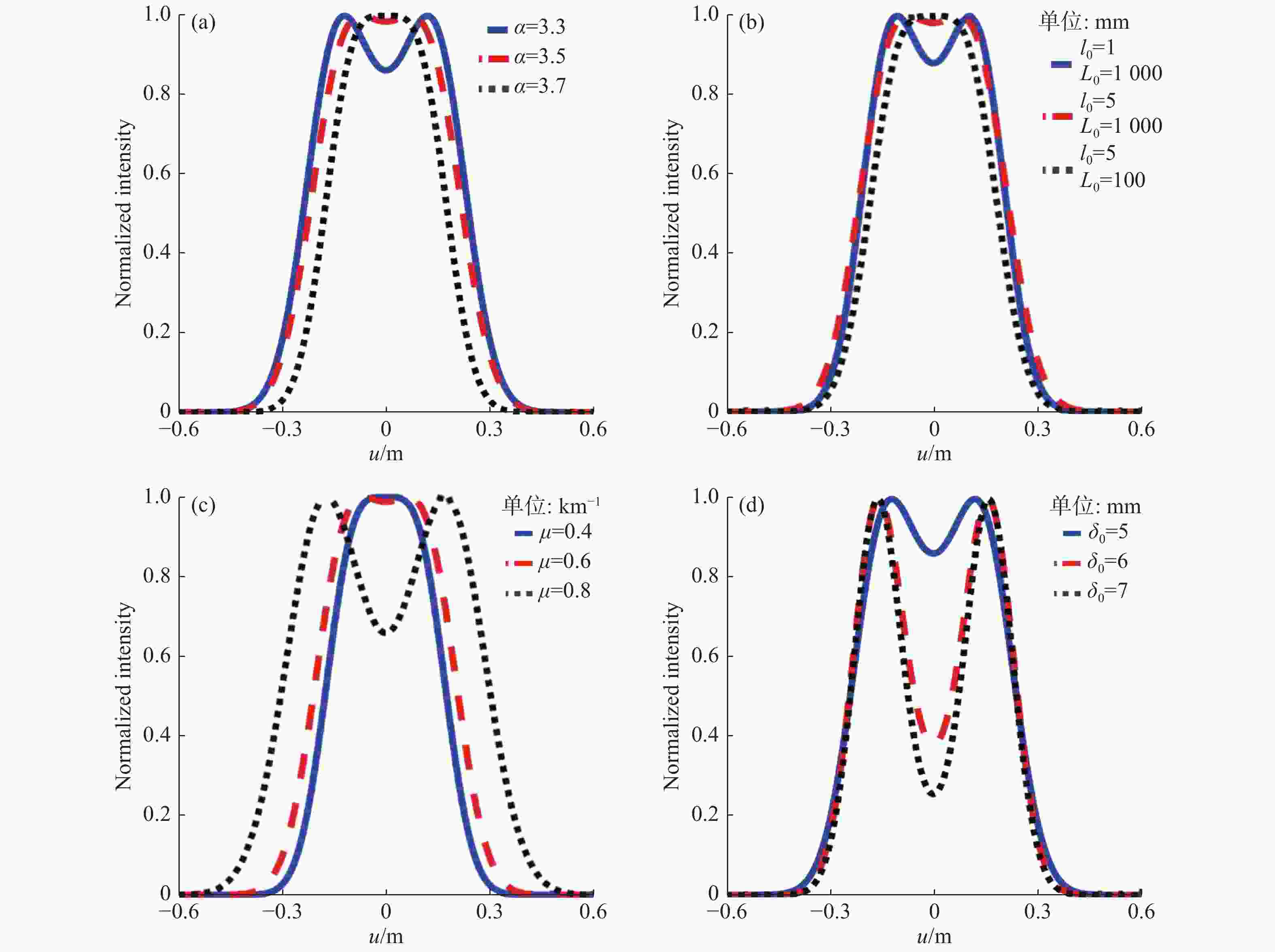
图 3 扭曲拉盖尔—高斯光束在
${\textit{z}} = 5 \;{\rm{km}}$ 处不同参数影响下的平均光强分布。(a)不同功率指数$\alpha $ ;(b)湍流外尺度${L_0}$ 和湍流内尺度${l_0}$ ;(c)扭曲因子$\mu $ ;(d)横截面相干度${\delta _0}$ Figure 3. Average light intensity distribution of a TLGC beam in atmospheric turbulence at
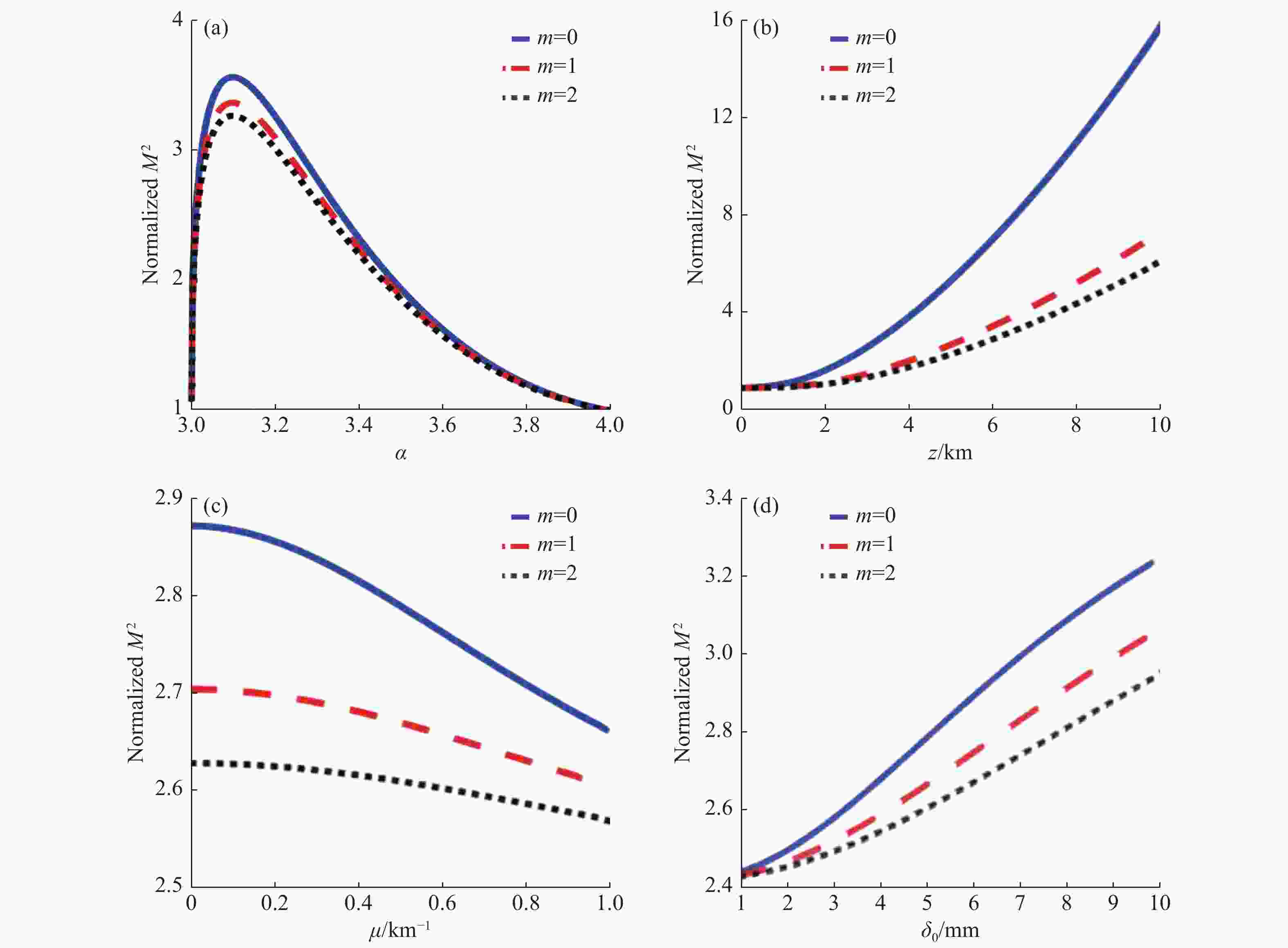
${\textit{z}} = 5 \;{\rm{km}}$ changing with different parameters: (a) power index$\alpha $ ; (b) turbulent outer scale${L_0}$ and turbulent inner scale${l_0}$ ; (c) distortion factor$\mu $ and (d) cross-section coherence${\delta _0}$ 图 4 扭曲拉盖尔—高斯关联光束在大气湍流传输中的归一化M2因子随不同参数的变化情况。(a)功率指数
$\alpha $ ;(b)传输距离${\textit{z}}$ ;(c)扭曲因子$\mu $ ;(d)横截面相干度${\delta _0}$ Figure 4. Normalized M2-factor of a TLGC beam in atmospheric turbulence changing with different parameters: (a) power index
$\alpha $ ; (b) transmission distance${\textit{z}}$ ; (c) distortion factor$\mu $ ; and (d) cross-section coherence${\delta _0}$ -
[1] RICKLIN J C, DAVIDSON F M. Atmospheric optical communication with a Gaussian Schell beam[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2003, 20(5): 856-866. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.20.000856 [2] WANG S C, LI X P. Wavefront manipulation of tightly focused cylindrical vector beams and its applications[J]. Chinese Optics, 2016, 9(2): 185-202. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20160902.0185 [3] LOU Y, CHEN CH Y, ZHAO Y W, et al. Characteristics of Gaussian vortex beam in atmospheric turbulence transmission[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(6): 768-776. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20171006.0768 [4] WANG J, HUANG H K, CHEN Y K, et al. Twisted partially coherent array sources and their transmission in anisotropic turbulence[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(20): 25974-25988. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.025974 [5] CAO M H, WU X, YANG SH X, et al. BER performance of Faster-than-Nyquist communications under Log-normal turbulence channel[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(2): 465-473. (in Chinese) [6] SIMON R, MUKUNDA N. Twisted gaussian schell-model beams[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1993, 10(1): 95-109. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.10.000095 [7] FRIBERG A T, TERVONEN E, TURUNEN J. Interpretation and experimental demonstration of twisted Gaussian Schell-model beams[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1994, 11(6): 1818-1826. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.11.001818 [8] GORI F, SANTARSIERO M. Devising genuine spatial correlation functions[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(24): 3531-3533. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.003531 [9] BORGHI R, GORI F, GUATTARI G, et al. Twisted Schell-model beams with axial symmetry[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(19): 4504-4507. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.004504 [10] BORGHI R. Twisting partially coherent light[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(8): 1627-1630. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.001627 [11] GORI F, SANTARSIERO M. Devising genuine twisted cross-spectral densities[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(3): 595-598. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.000595 [12] CAI Y J, ZHU SH J. Orbital angular moment of a partially coherent beam propagating through an astigmatic ABCD optical system with loss or gain[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(7): 1968-1971. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.001968 [13] LIU M W, LI Y CH. Propagation of OFDM-OAM optical signal in atmospheric turbulence[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(7): 0706002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0706002 [14] WANG H Q, SONG L H, CAO M H, et al. Compressed sensing detection of optical spatial modulation signal in turbulent channel[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(11): 2669-2674. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182611.2669 [15] REN J Y, SUN H Y, ZHAO Y ZH, et al. Light intensity and spatial coherence characteristics of laser coherent detection in a turbulent atmosphere[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(4): 728-736. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0194 [16] ZHUANG Z B, CHEN X, TAI H D, et al. Turbulence alerting algorithm based on singular value decomposition of Lidar[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(3): 671-679. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192703.0671 [17] LUTOMIRSKI R F, YURA H T. Propagation of a finite optical beam in an inhomogeneous medium[J]. Applied Optics, 1971, 10(7): 1652-1658. doi: 10.1364/AO.10.001652 [18] FEIZULIN Z I, KRAVTSOV Y A. Broadening of a laser beam in a turbulent medium[J]. Radiophysics and Quantum Electronics, 1967, 10(1): 33-35. doi: 10.1007/BF01038157 [19] TOSELLI I, ANDREWS L C, PHILLIPS R L, et al. Free-space optical system performance for laser beam propagation through non-Kolmogorov turbulence[J]. Optical Engineering, 2008, 47(2): 026003. doi: 10.1117/1.2870113 [20] JI X L, CHEN X W, LÜ B D. Spreading and directionality of partially coherent Hermite-Gaussian beams propagating through atmospheric turbulence[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2008, 25(1): 21-28. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.25.000021 [21] SHIRAI T, DOGARIU A, WOLF E. Directionality of Gaussian Schell-model beams propagating in atmospheric turbulence[J]. Optics Letters, 2003, 28(8): 610-612. doi: 10.1364/OL.28.000610 [22] SHIRAI T, DOGARIU A, WOLF E. Mode analysis of spreading of partially coherent beams propagating through atmospheric turbulence[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2003, 20(6): 1094-1102. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.20.001094 [23] ZHU SH J, CAI Y J, KOROTKOVA O. Propagation factor of a stochastic electromagnetic Gaussian Schell-model beam[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(12): 12587-12598. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.012587 [24] SANTARSIERO M, GORI F, BORGHI R, et al. Spreading properties of beams radiated by partially coherent Schell-model sources[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1999, 16(1): 106-112. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.16.000106 [25] WANG F, YU J Y, LIU X L, et al. Research progress of partially coherent beams propagation in turbulent atmosphere[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(18): 184203. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20180877 -






 下载:
下载: