3D small-field surface imaging based on microscopic fringe projection profilometry:a review
-
摘要: 智能制造不断向着精密化、微型化、集成化的方向发展,具有代表性的集成电路技术及其衍生出的MEMS等微型传感器技术等得以迅猛发展,快速精确地获取微型器件表面信息并进行缺陷检测对于集成电路和MEMS等产业发展具有重要意义。基于结构光的条纹投影技术具有非接触、高精度、高效率、全场测量等优点,在精密测量中发挥着重要的作用。近年来,显微条纹投影测量系统,包括其光学系统结构,系统标定,相位获取以及三维重建方法等各个方面取得了重大发展。本文回顾了显微条纹投影三维测量系统的结构原理,分析了不同于传统投射模型的小视场系统标定问题,介绍了显微投影系统结构发展过程,同时对由系统结构以及金属测量时造成的反光问题进行了分析,在此基础上,对显微条纹投影三维测量系统的发展前景进行了展望。Abstract: Intelligent manufacturing has become more precise, miniaturized and integrated. Representative integrated circuit technology and its derived miniature sensors such as Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) have become widely used. Therefore, it is important for intelligent manufacturing development to accurately obtain the surface morphology information of micro-devices and implement rapid detection of device surface defects. Fringe Projection Profilometry (FPP) based on structural light projection has the advantages of being non-contact, highly precise, highly efficient and having full-field measurement, which plays an important role in the field of precision measurement. Microscopic Fringe Projection Profilometry (MFPP) has been developed rapidly during recent decades. In recent years, MFPP has made great progress in many aspects, including its optical system structures, corresponding system calibration methods, phase extraction algorithms, and 3D coordinate reconstruction methods. In this paper, the structure and principle of a three-dimensional measurement system of microscopic fringe projection are reviewed, and the calibration problem of a small field-of-view system that is different from the traditional projection model is analyzed. After that, the development and improvement process of the micro-projection system structure is introduced, and the reflection in the measurment caused by the system structure and metal material is analyzed. On this basis, the prospects of the development of microscopic fringe projection of 3D measurement system are discussed.
-
表 1 基于体视显微镜的MFPP系统的比较
Table 1. Comparison of MFPP systems based on off-the-shelf microscopes
文章 投影技术 系统复杂度 测量视场大小 Leonhardt等[7] Ronchi光栅 高 0.10 mm×0.10 mm~
2.50 mm×2.50 mmProll等[9] LCD芯片 高 1.40 mm×1.00 mm~
16.5 mm×12.0 mmZhang等[12] DMD芯片 高 1.20 mm×0.90 mm~
7.60 mm×5.70 mmProll等[9] LCOS芯片 高 0.83 mm×0.62 mm~
21.2 mm×15.7 mmChen等[30] DLP投影仪 中 未给出 Li等[31] LCOS投影仪 中 3.0 mm×3.0 mm(变倍可调) 肖[28] LightCrafter 中 20.0 mm×15.0 mm(变倍可调) Jeught等[29] LightCrafter 低 10.7 mm×8.0 mm(变倍可调) Hu等[26] LightCrafter 低 8.0 mm×6.0 mm(变倍可调) 表 2 基于LWD镜头的MFPP系统对比
Table 2. Comparison of MFPP systems based on an LWD lens
文章 投影技术 长工作距离镜头类型 测量视场大小 Quan等[8] LCD投影 针孔+针孔镜头 1.2 mm×1.5 mm Quan等[38] 精细的正弦光栅 针孔+针孔镜头 0.1 mm×0.1 mm Wang等[39] LCD投影 针孔+针孔镜头 768 pixel×576 pixel Yin等[34] DLP投影 针孔+针孔镜头 5.0 mm×4.0 mm Li等[20] LightCrafter 针孔+远心镜头 10.0 mm×8.0 mm Li等[32] DLP投影仪 远心+远心镜头 30.0 mm×20.0 mm Liu等[21] LCD投影仪 远心+远心镜头 34.6 mm×29.0 mm Peng等[33] DMD芯片 远心+远心镜头 1280 pixel×
1024 pixelWang等[35] DMD芯片 远心+4个远心镜头 1280 pixel×
1024 pixelHu等[36] LightCrafter 远心+2个远心镜头 10.0 mm×7.0 mm 表 3 两类MFPP系统对比
Table 3. Comparison of the two kinds of method for MFPP
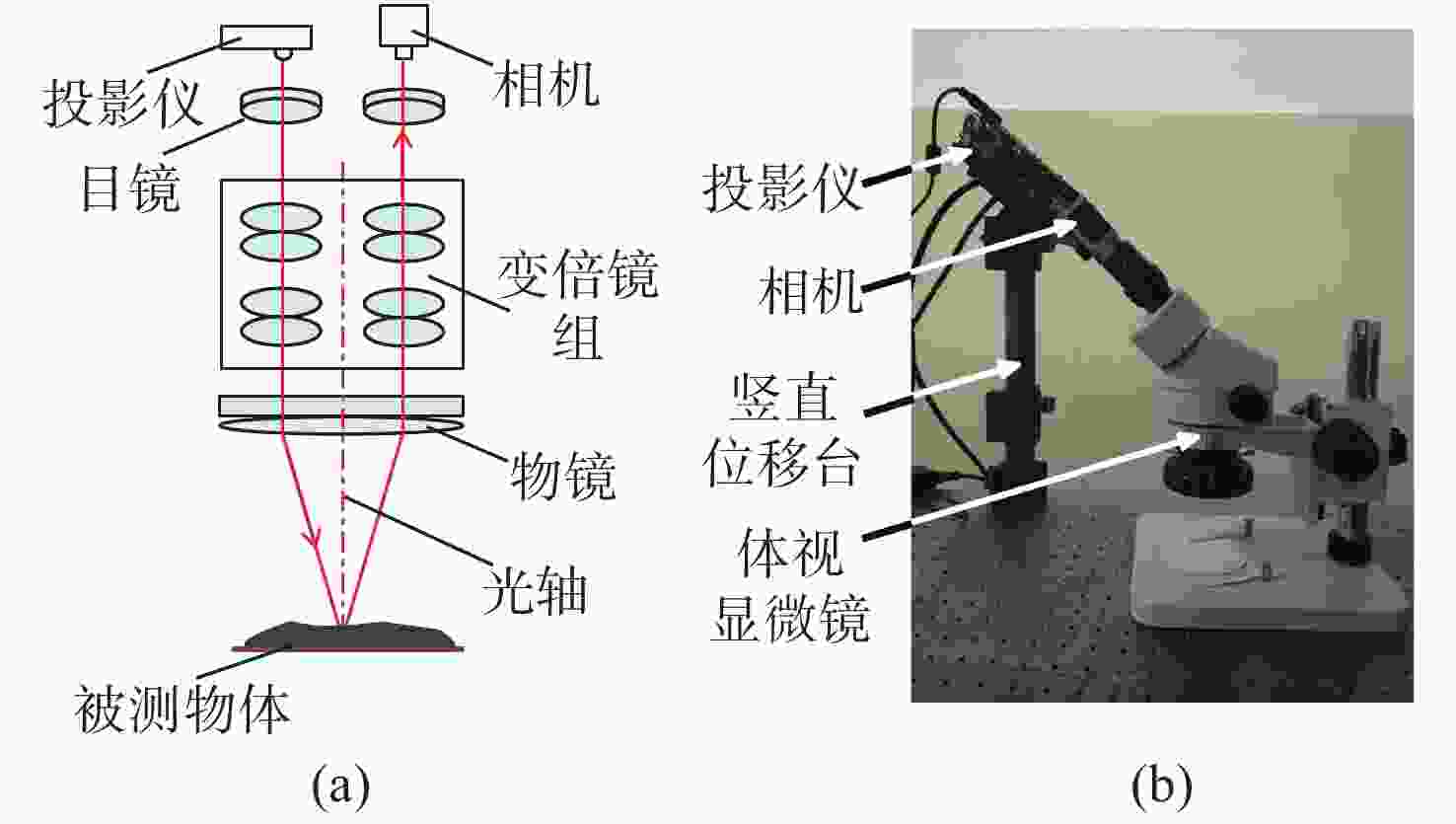
基于立体显微镜的MFPP 基于LWD透镜的MFPP 优点 灵活调整放大率
良好的景深
仅单相机系统
条纹对比度高良好的景深
标定结构简单
结构紧凑缺点 系统体积大
构造复杂
标定费时放大倍数固定
公共视野受限适用领域 需要快速调整
视场的被测物表面形貌复杂,小空间
物体测量表 4 HDR 技术中各类方法的优缺点对比
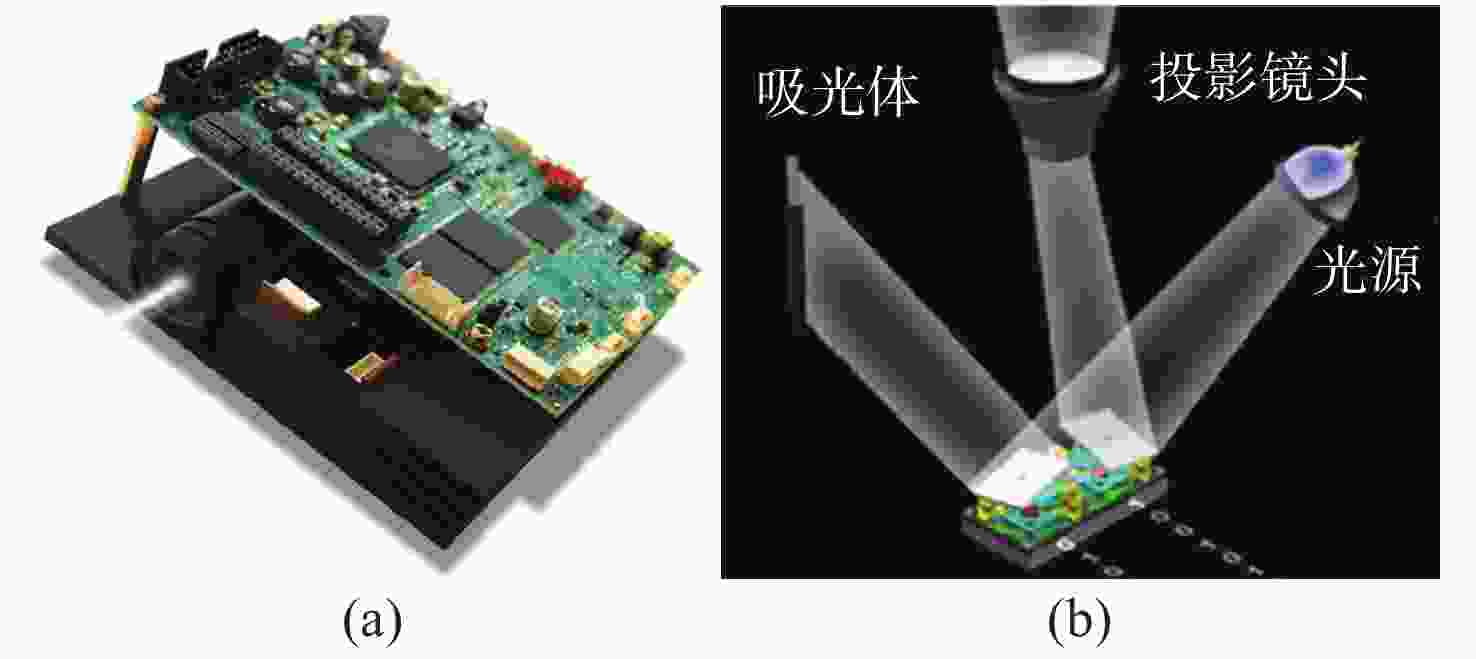
Table 4. Comparison of typical methods in HDR technology
文章 实现方法 优点 缺点 适用范围 Zhang等[47] 相机多重曝光法 测量精度和信噪比较高,不需要搭建额外的硬件系统 大范围反射率变化表面需采集大量的条纹图像,测量效率降低,未知场景有一定的盲目性 复杂纹理表面;多颜色的表面;反射率变化不大表面;静态物体 Chen等[48] 调整投影图案强度法 高信噪比,不受环境
约束对未知的场景有一定的盲目性,测量效率低,不能自动预测参数 复杂纹理表面;多颜色的表面;反射率变化不大表面;静态物体 Feng等[54] 偏振滤光片法 测量精度高 信噪比低,空间分辨率降低,硬件系统相对复杂 镜面物体测量;快速动态测量 Benveniste R等[56] 颜色不变量法 无需前期参数设置 容易受到表面颜色和复杂纹理的影响,精度低 快速动态测量 Meng等[58] 光度立体技术 测量精度高 系统结构的限制,单次测量的表面范围很小 小范围物体测量;静态物体 -
[1] WANG J H, YANG Y X, SHAO M W, et al. Three-dimensional measurement for rigid moving objects based on multi-fringe projection[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2020, 12(4): 6802114. [2] XIA P, WANG Q H, RI SH E. Random phase-shifting digital holography based on a self-calibrated system[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(14): 19988-19996. doi: 10.1364/OE.395819 [3] 屈铭, 郑俊杰, 李敏, 等. 基于扫描白光干涉法的LCOS芯片像素级相位分析[J]. 光子学报,2019,48(9):0911004. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194809.0911004QU M, ZHENG J J, LI M, et al. Pixel-level observation of phase profile in liquid crystal on silicon device by white light scanning interferometry[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2019, 48(9): 0911004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194809.0911004 [4] MURAKAMI H, KATSUKI A, SAJIMA T, et al. Investigation of factors affecting sensitivity enhancement of an optical fiber probe for microstructure measurement using oblique incident light[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(9): 3191. doi: 10.3390/app10093191 [5] 李成辉, 田云飞, 闫曙光. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 扫描共聚焦显微成像技术与应用[J]. 实验科学与技术,2020,18(4):33-38. doi: 10.12179/1672-4550.20190257LI CH H, TIAN Y F, YAN SH G. Laser scanning confocal microscopy and its application[J]. Experiment Science and Technology, 2020, 18(4): 33-38. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12179/1672-4550.20190257 [6] HU Y, CHEN Q, FENG SH J, et al. Microscopic fringe projection profilometry: a review[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 135: 106192. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106192 [7] LEONHARDT K, DROSTE U, TIZIANI H J. Microshape and rough-surface analysis by fringe projection[J]. Applied Optics, 1994, 33(31): 7477-7488. doi: 10.1364/AO.33.007477 [8] QUAN C, HE X Y, WANG C F, et al. Shape measurement of small objects using LCD fringe projection with phase shifting[J]. Optics Communications, 2001, 189(1-3): 21-29. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(01)01038-0 [9] PROLL K P, NIVET J M, KÖRNER K, et al. Microscopic three-dimensional topometry with ferroelectric liquid-crystal-on-silicon displays[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(10): 1773-1778. doi: 10.1364/AO.42.001773 [10] NOTNI G, RIEHEMANN S, KUEHMSTEDT P, et al. OLED microdisplays: a new key element for fringe projection setups[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5532: 170-177. doi: 10.1117/12.560433 [11] ZHANG SH F, LI B, REN F J, et al. High-precision measurement of binocular telecentric vision system with novel calibration and matching methods[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 54682-54692. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2913181 [12] ZHANG CH P, HUANG P S, CHIANG F P. Microscopic phase-shifting profilometry based on digital micromirror device technology[J]. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(28): 5896-5904. doi: 10.1364/AO.41.005896 [13] LIU Y H, ZHANG Q C, ZHANG H H, et al. Improve temporal Fourier transform profilometry for complex dynamic three-dimensional shape measurement[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(7): 1808. doi: 10.3390/s20071808 [14] ZHANG H H, ZHANG Q C, LI Y, et al. High speed 3D shape measurement with temporal Fourier transform profilometry[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(19): 4123. doi: 10.3390/app9194123 [15] 史耀群, 邓林嘉, 王朝旭, 等. 一种基于结构光条纹投影的微小物体测量系统[J]. 应用光学,2019,40(6):1120-1125. doi: 10.5768/JAO201940.0603007SHI Y Q, DENG L J, WANG ZH X, et al. Micro-objects measurement system based on structured light fringe projection[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2019, 40(6): 1120-1125. (in Chinese) doi: 10.5768/JAO201940.0603007 [16] ZHONG M, CUI J, HYUN J S, et al. Uniaxial three-dimensional phase-shifting profilometry using a dual-telecentric structured light system in micro-scale devices[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2020, 31(8): 085003. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab63b2 [17] 殷永凯, 张宗华, 刘晓利, 等. 条纹投影轮廓术系统模型与标定综述[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2020,49(3):0303008. doi: 10.3788/IRLA202049.0303008YIN Y K, ZHANG Z H, LIU X L, et al. Review of the system model and calibration for fringe projection profilometry[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(3): 0303008. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA202049.0303008 [18] ZHANG ZH Y. A flexible new technique for camera calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(11): 1330-1334. doi: 10.1109/34.888718 [19] LI B W, KARPINSKY N, ZHANG S. Novel calibration method for structured-light system with an out-of-focus projector[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(16): 3415-3426. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.003415 [20] LI B W, ZHANG S. Flexible calibration method for microscopic structured light system using telecentric lens[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(20): 25795-25803. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.025795 [21] LIU H B, LIN H J, YAO L SH. Calibration method for projector-camera-based telecentric fringe projection profilometry system[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(25): 31492-31508. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.031492 [22] 安东, 陈李, 丁一飞, 等. 光栅投影相位法系统模型及标定方法[J]. 中国光学,2015,8(2):248-254. doi: 10.3788/co.20150802.0248AN D, CHEN L, DING Y F, et al. Optical system model and calibration of grating projection phase method[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(2): 248-254. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20150802.0248 [23] 丁一飞, 王永红, 胡悦, 等. 样本块匹配光栅投影阶梯标定方法[J]. 中国测试,2016,42(8):7-12. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2016.08.002DING Y F, WANG Y H, HU Y, et al. Step calibration method of grating projection based on exemplar matching[J]. China Measurement &Test, 2016, 42(8): 7-12. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2016.08.002 [24] LU P, SUN CH K, LIU B, et al. Accurate and robust calibration method based on pattern geometric constraints for fringe projection profilometry[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(4): 784-794. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.000784 [25] CHEN Z, LIAO H Y, ZHANG X M. Telecentric stereo micro-vision system: calibration method and experiments[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2014, 57: 82-92. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2014.01.021 [26] HU Y, CHEN Q, LI H Y, et al. Absolute three-dimensional micro surface profile measurement based on a Greenough-type stereomicroscope[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2017, 28(4): 045004. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/aa5a2d [27] Overview: DLP products[EB/OL]. [2020-10-18]. http://www.ti.com/dlp-chip/overview.html. [28] 肖萍萍. 基于光栅投射的小尺寸物体三维形状测量系统研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019.XIAO P P. Research on 3D shape measurement system of small scale object based on grating projection[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese). [29] VAN DER JEUGHT S, SOONS J A M, DIRCKX J J J. Real-time microscopic phase-shifting profilometry[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(15): 4953-4959. [30] CHEN L C, LIAO CH CH, LAI M J. Full-field micro surface profilometry using digital fringe projection with spatial encoding principle[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2005, 13: 147-150. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/13/1/034 [31] LI A M, PENG X, YIN Y K, et al. Fringe projection based quantitative 3D microscopy[J]. Optik, 2013, 124(21): 5052-5056. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.03.070 [32] LI D, LIU CH Y, TIAN J D. Telecentric 3D profilometry based on phase-shifting fringe projection[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(26): 31826-31835. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.031826 [33] PENG J ZH, WANG M, DENG N N, et al. Distortion correction for microscopic fringe projection system with Scheimpflug telecentric lens[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(34): 10055-10062. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.010055 [34] YIN Y K, WANG M, GAO B Z, et al. Fringe projection 3D microscopy with the general imaging model[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(5): 6846-6857. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.006846 [35] WANG M, YIN Y K, DENG D N, et al. Improved performance of multi-view fringe projection 3D microscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(16): 19408-19421. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.019408 [36] HU Y, CHEN Q, FENG SH J, et al. A new microscopic telecentric stereo vision system-calibration, rectification, and three-dimensional reconstruction[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2019, 113: 14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2018.09.011 [37] HU Y, LIANG Y CH, TAO T Y, et al. Dynamic 3D measurement of thermal deformation based on geometric-constrained stereo-matching with a stereo microscopic system[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2019, 30(12): 125007. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab35a1 [38] QUAN C, TAY C J, HE X Y, et al. Microscopic surface contouring by fringe projection method[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2002, 34(7): 547-552. [39] WANG W H, WONG Y S, HONG G S. 3D measurement of crater wear by phase shifting method[J]. Wear, 2006, 261(2): 164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2005.09.036 [40] 张莲涛, 卢荣胜, 程子怡. 基于相移偏折法的高反射表面面形测量技术[J]. 光子学报,2020,49(1):0112002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204901.0112002ZHANG L T, LU R SH, CHENG Z Y. Measurement technique of high-reflected surface based on phase measuring deflectometry[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2020, 49(1): 0112002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204901.0112002 [41] LIU X H, ZHANG Z H, GAO N, et al. 3D shape measurement of diffused/specular surface by combining fringe projection and direct phase measuring deflectometry[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(19): 27561-27574. doi: 10.1364/OE.402432 [42] 陶迁, 周志峰, 吴明晖, 等. 基于相位测量偏折术的反射表面缺陷检测[J]. 液晶与显示,2020,35(12):1315-1322. doi: 10.37188/YJYXS20203512.1315TAO Q, ZHOU ZH F, WU M H, et al. Detection of reflective surface defects based on phase measuring deflectometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2020, 35(12): 1315-1322. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/YJYXS20203512.1315 [43] 王月敏, 张宗华, 高楠. 基于全场条纹反射的镜面物体三维面形测量综述[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(5):1014-1027. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182605.1014WANG Y M, ZHANG Z H, GAO N. Review on three-dimensional surface measurements of specular objects based on full-field fringe reflection[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(5): 1014-1027. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182605.1014 [44] ZHANG L, CHEN Q, ZUO CH, et al. High-speed high dynamic range 3D shape measurement based on deep learning[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 134: 106245. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106245 [45] JIANG H ZH, ZHAO H J, LI X D. High dynamic range fringe acquisition: a novel 3-D scanning technique for high-reflective surfaces[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2012, 50(10): 1484-1493. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2011.11.021 [46] RAO L, DA F P. High dynamic range 3D shape determination based on automatic exposure selection[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2018, 50: 217-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2017.12.003 [47] ZHANG S. Rapid and automatic optimal exposure control for digital fringe projection technique[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 128: 106029. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106029 [48] CHEN CH, GAO N, WANG X J, et al. Adaptive projection intensity adjustment for avoiding saturation in three-dimensional shape measurement[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 410: 694-702. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.11.009 [49] WANG J H, YANG Y X. High-speed three-dimensional measurement technique for object surface with a large range of reflectivity variations[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(30): 9172-9182. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.009172 [50] SONG ZH, JIANG H L, LIN H B, et al. A high dynamic range structured light means for the 3D measurement of specular surface[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2017, 95: 8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2017.03.008 [51] LIU Y ZH, FU Y J, CAI X Q, et al. A novel high dynamic range 3D measurement method based on adaptive fringe projection technique[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 128: 106004. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106004 [52] 万钇良, 王建立, 张楠. 一种基于相位相关与子图像的偏振图像配准方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(5):530-536. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193405.0530WAN Y L, WANG J L, ZHANG N. Polarized image registration method based on phase correlation and sub-graph[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(5): 530-536. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193405.0530 [53] RIVIERE J, RESHETOUSKI I, FILIPI L, et al. Polarization imaging reflectometry in the wild[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(6): 206. [54] FENG SH J, ZHANG Y ZH, CHEN Q, et al. General solution for high dynamic range three-dimensional shape measurement using the fringe projection technique[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2014, 59: 56-71. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2014.03.003 [55] BENVENISTE R, ÜNSALAN C. Binary and ternary coded structured light 3D scanner for shiny objects[M]//GELENBE E, LENT R, SAKELLARI G, et al. . Computer and Information Sciences. Dordrecht: Springer, 2011: 241-244. [56] BENVENISTE R, ÜNSALAN C. A color invariant for line stripe-based range scanners[J]. The Computer Journal, 2011, 54(5): 738-753. doi: 10.1093/comjnl/bxq014 [57] BENVENISTE R, ÜNSALAN C. Nary coded structured light-based range scanners using color invariants[J]. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2014, 9(2): 359-377. doi: 10.1007/s11554-011-0235-4 [58] MENG L F, LU L Y, BEDARD N, et al. . Single-shot specular surface reconstruction with gonio-plenoptic imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2015. [59] ZHANG L, CHEN Q, ZUO CH, et al. High dynamic range and real-time 3D measurement based on a multi-view system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11427: 1142715. [60] HU Y, CHEN Q, LIANG Y CH, et al. Microscopic 3D measurement of shiny surfaces based on a multi-frequency phase-shifting scheme[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2019, 122: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.05.019 -





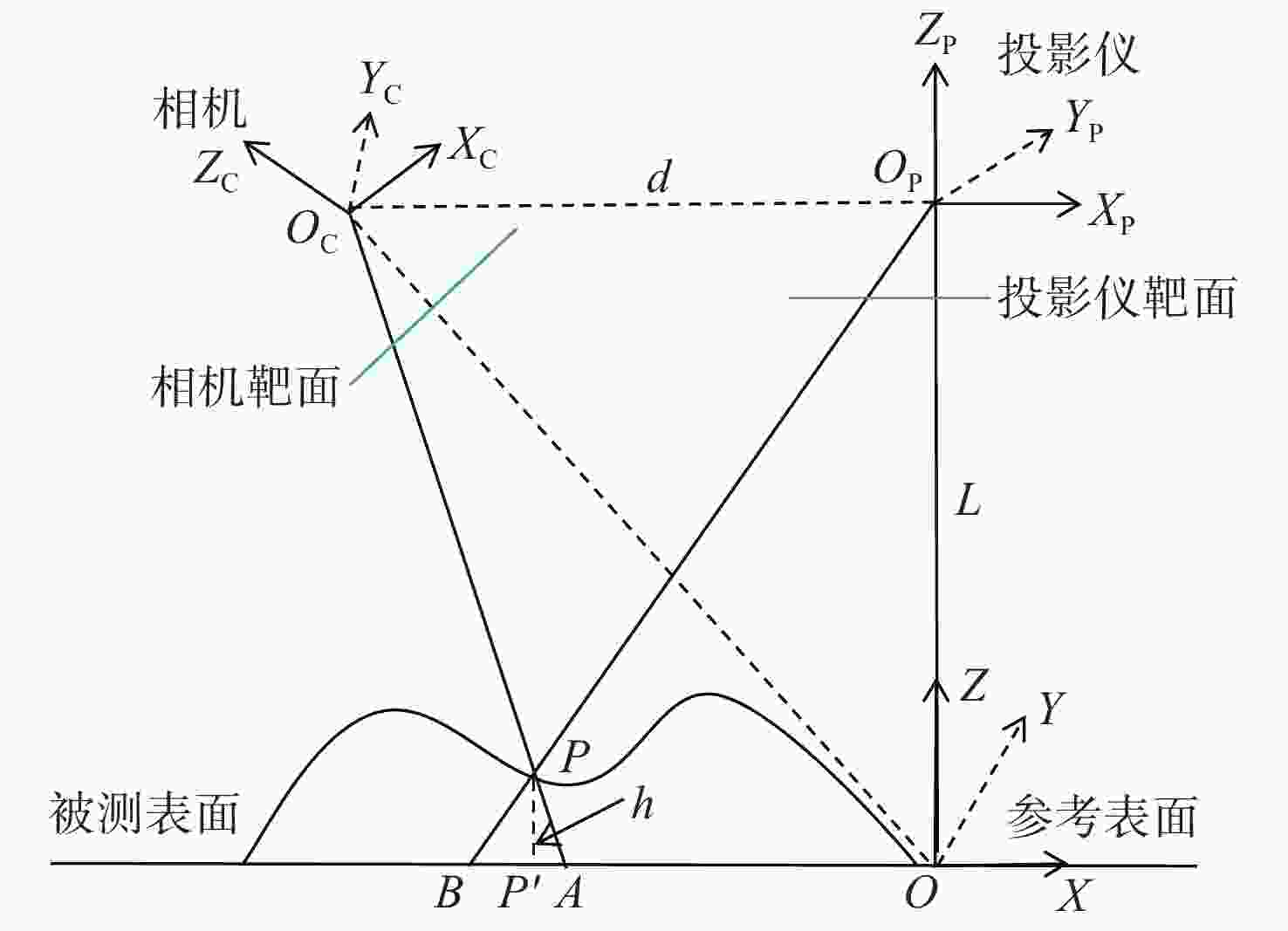
 下载:
下载: