Carbon dioxide detection technology based on the laser occultation absorption spectrum
-
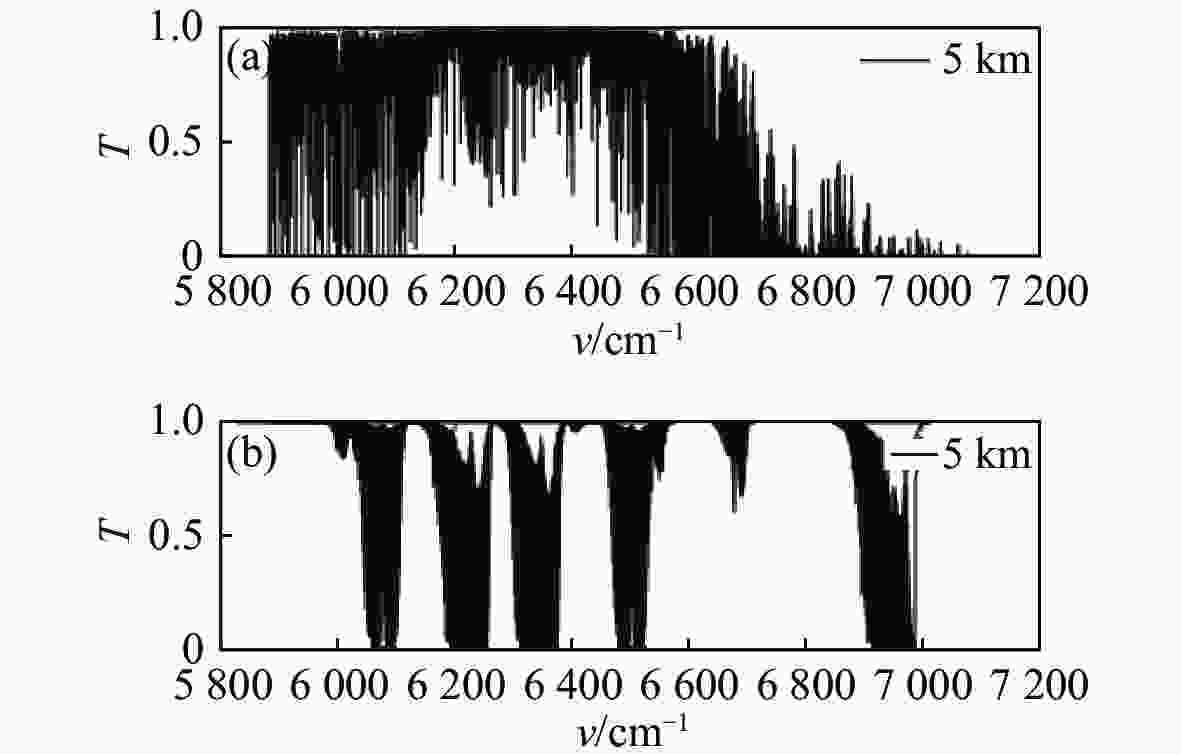
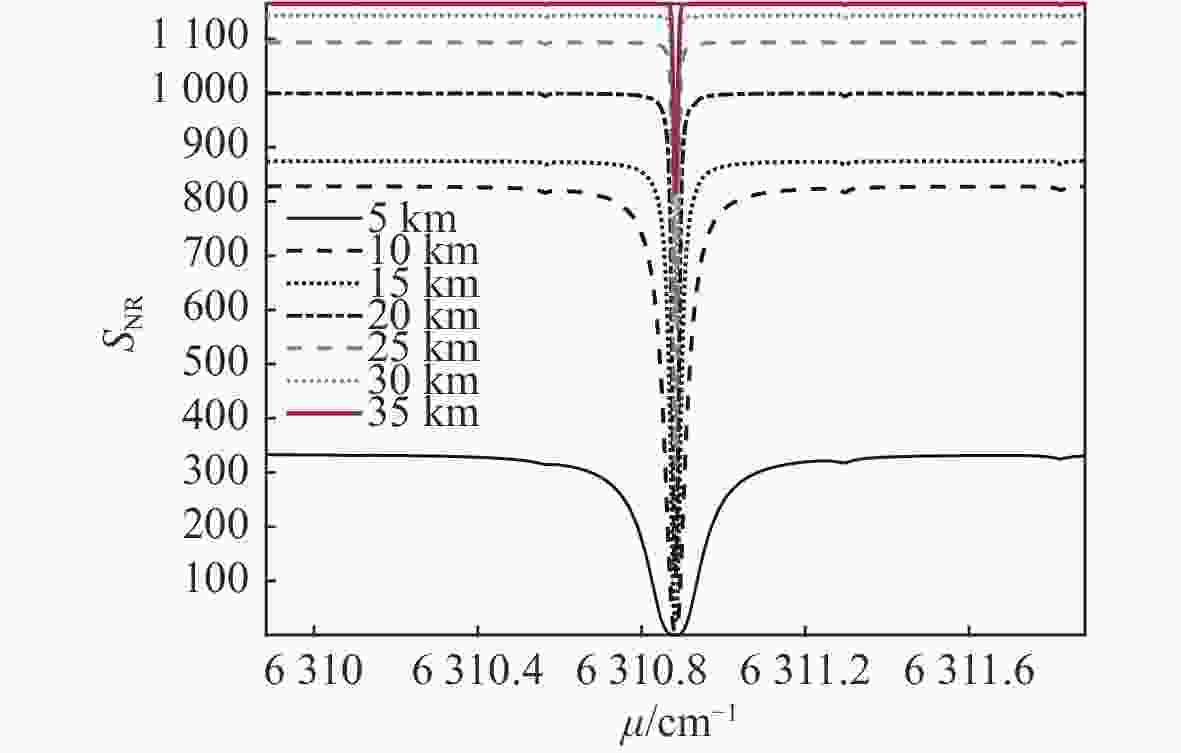
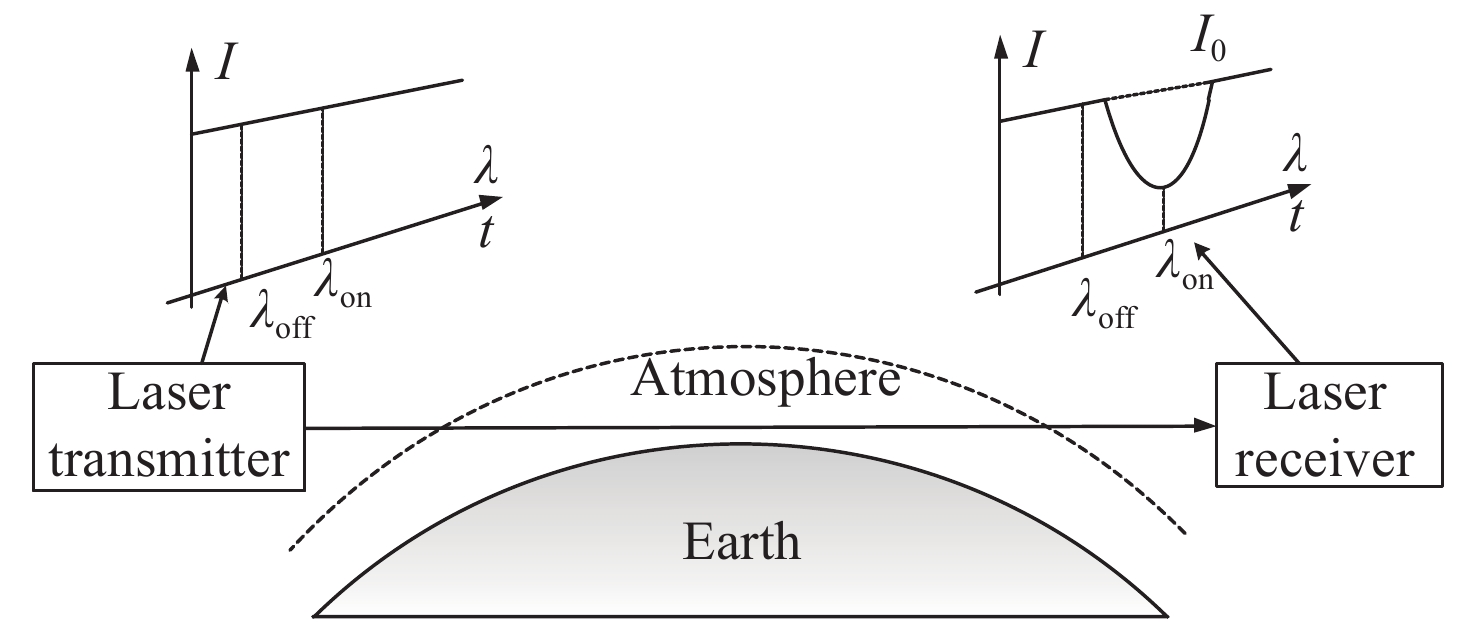
摘要: 本文分析了固定波长金宝搏188软件怎么用 掩星差分吸收技术的优点和不足,介绍了可调谐金宝搏188软件怎么用 直接吸收光谱技术测量原理。分析了最优波长透过率与信噪比的关系以及测量误差与背景光干扰的关系。根据高灵敏度探测器的工作波长范围,选择了6310.915 cm−1、6310.893 cm−1、6310.890 cm−1、6310.8834 cm−1作为吸收的工作波长,同时选择6310.15 cm−1作为参考波长,并对各波长的探测能力进行了仿真分析。通过仿真结果可知,在1 km垂直分辨率下,在5~35 km内CO2浓度探测误差优于0.9%,7~42 km范围内的探测误差优于0.4%。该技术降低了系统成本和复杂度,有利于星载产品的设计和实现。
-
关键词:
- 金宝搏188软件怎么用 掩星 /
- 二氧化碳 /
- 直接吸收光谱
Abstract: The advantages and disadvantages of fixed-wavelength laser occultation differential absorption technology are analyzed, and the measurement principle of tunable laser direct absorption spectroscopy technology is introduced. The relationship between optimal wavelength transmittance and signal-to-noise ratio and the relationship between measurement error and background light interference are analyzed. According to the working wavelength range of the high-sensitivity detector, 6310.915 cm−1, 6310.893 cm−1, 6310.890 cm−1 and 6310.8834 cm−1 are selected as the absorption working wavelengths, and 6310.15 cm−1 is selected as the reference wavelength, and the detection ability of each wavelength is simulated and analyzed. Simulation results show that the detection error of a CO2 concentration is better than 0.9% in the range of 5~35 km and better than 0.4% in the range of 7~42 km with a vertical resolution of 1 km. This technology reduces the cost and complexity of the system, and is beneficial to the design and implementation of space-borne products.-
Key words:
- laser occultation /
- carbon dioxide /
- direct absorption spectrum
-
表 1 系统仿真参数
Table 1. System simulation parameters
System parameter Value Unit Orbit altitude of laser transmitter 500 km Orbit altitude of laser receiver 600 km repetition rate 40 Hz Laser power 1 W Laser wavenumber 6309.8834~6311.8834 cm−1 Absorption wavenumber 6310.915@5~10 km, 6310.893@11~18 km,
6310.890@19~26 km, 6310.8834 @27~39 kmcm−1 Reference wavenumber 6310.15 cm−1 Laser line width 10 MHz Laser beam divergence 0.3 mrad Telescope diameter 0.3 m System optical efficiency 0.5 1 Detector responsivity (InGaAs-APD,
C30662, 1584.6 nm)10.3 A/W Nominal gain 10 1 Noise factor 5.5 1 Dark current 45 nA Spectral noise current 0.7 pA/rt (Hz) Bandwidth 3000 Hz -
[1] IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014. [2] 熊伟. 高分五号卫星大气主要温室气体监测仪优化设计及数据分析[J]. 上海航天,2019,36(S2):167-172.XIONG W. Optimum design and data analysis of greenhouse gases monitoring instrument on GF-5satellite[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2019, 36(S2): 167-172. (in Chinese) [3] FRANKENBERG C, POLLOCK R, LEE R A M, et al. The Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO-2): spectrometer performance evaluation using pre-launch direct sun measurements[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2015, 8(1): 301-313. doi: 10.5194/amt-8-301-2015 [4] 谢杨易, 刘继桥, 姜佳欣, 等. 使CO2浓度测量误差减小的星载金宝搏188软件怎么用 雷达波长优化[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2014,43(1):88-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.01.015XIE Y Y, LIU J Q, JIANG J X, et al. Wavelengths optimization to decrease error for a space-borne lidar measuring CO2 concentration[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(1): 88-93. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.01.015 [5] 宗雪梅. 大气红外辐射超高光谱探测仪临边探测—污染气体的反演精度和光谱通道评估[J]. 环境科学学报,2020,40(4):1410-1421.ZONG X M. Inversion accuracy and spectral channel evaluation of atmospheric polluted gases of atmospheric infrared radiation ultra-high detector under limb sounding[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(4): 1410-1421. (in Chinese) [6] 王雅鹏, 李小英, 陈良富, 等. 红外临边探测发展现状[J]. 遥感学报,2016,20(4):513-527.WANG Y P, LI X Y, CHEN L F, et al. Overview of infrared limb sounding[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 20(4): 513-527. (in Chinese) [7] KIRCHENGAST G. ACCURATE-Climate benchmark profiling of greenhouse gases and thermo-dynamic variables and wind from space, ESA Earth Explorer Opportunity Mission EE8 Proposal, Scientific Report 36-2010[R]. Graz, Austria: Wegener Center Verlag, 2010. [8] 李文冬, 刘继桥, 朱亚丹, 等. LEO-LEO红外金宝搏188软件怎么用 掩星CO2浓度测量技术研究[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2019,46(8):0810001. doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0810001LI W D, LIU J Q, ZHU Y D, et al. LEO-LEO infrared laser occultation technique to measure atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2019, 46(8): 0810001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0810001 [9] MOTTINI S, LOESCHER A, AGUIRRE M. A new approach to climatology from space: laser occultation[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 10565: 1056565. [10] 苏俊宏, 尚小燕, 弥谦. 光电技术基础[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2011.SU J H, SHANG X Y, MI Q. Fundamentals of Photoelectric Technology[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2011. (in Chinese) [11] 王玉诏, 陶宇亮, 杨超, 等. 一种基于可调谐金宝搏188软件怎么用 的掩星大气密度廓线测量系统及方法: 中国, 201911032531.8[P]. 2019-10-28.WANG Y ZH, TAO Y L, YANG CH, et al.. Occultation atmospheric density profile measurement system and method based on tunable laser: CN, 201911032531.8[P]. 2019-10-28. (in Chinese) [12] C30659 Series-900/1060/1550/1550E[R]. Excelitas Technologies, 2012. [13] WERLE P. Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy: recent findings and novel approaches[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 1996, 37(l): 59-66. [14] 屈东胜, 洪延姬, 王广宇, 等. 基于波长调制光谱的多参数测量方法研究[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2016,35(4):470-476. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2016.04.015QU D SH, HONG Y J, WANG G Y, et al. Measurement of multi-parameters of gas based on the wavelength modulation spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2016, 35(4): 470-476. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2016.04.015 [15] 王玉诏. 基于matlab的金宝搏188软件怎么用 掩星大气探测仿真系统[C]. 第三十一届全国空间探测学术研讨会. 银川: 中国空间科学学会, 2018: 47-55.WANG Y ZH. Laser occultation detection simulation system based on matlab[C]. The 31th National Conference on Space Exploration. Yinchuan: Chinese Society of Space Research, 2018. (in Chinese) [16] 饶瑞中. 现代大气光学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.RAO R ZH. Modern Atmospheric Optics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: