-
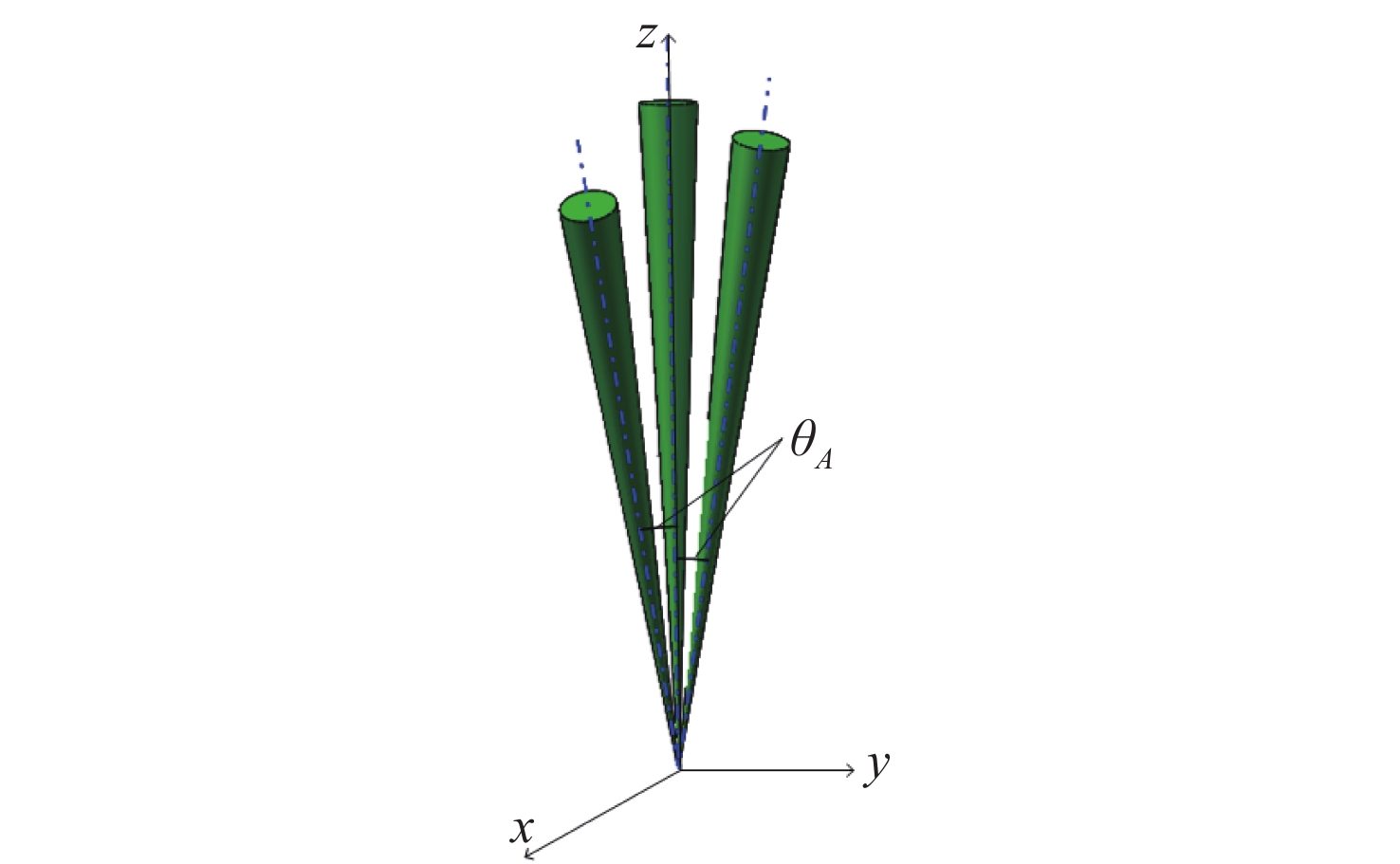
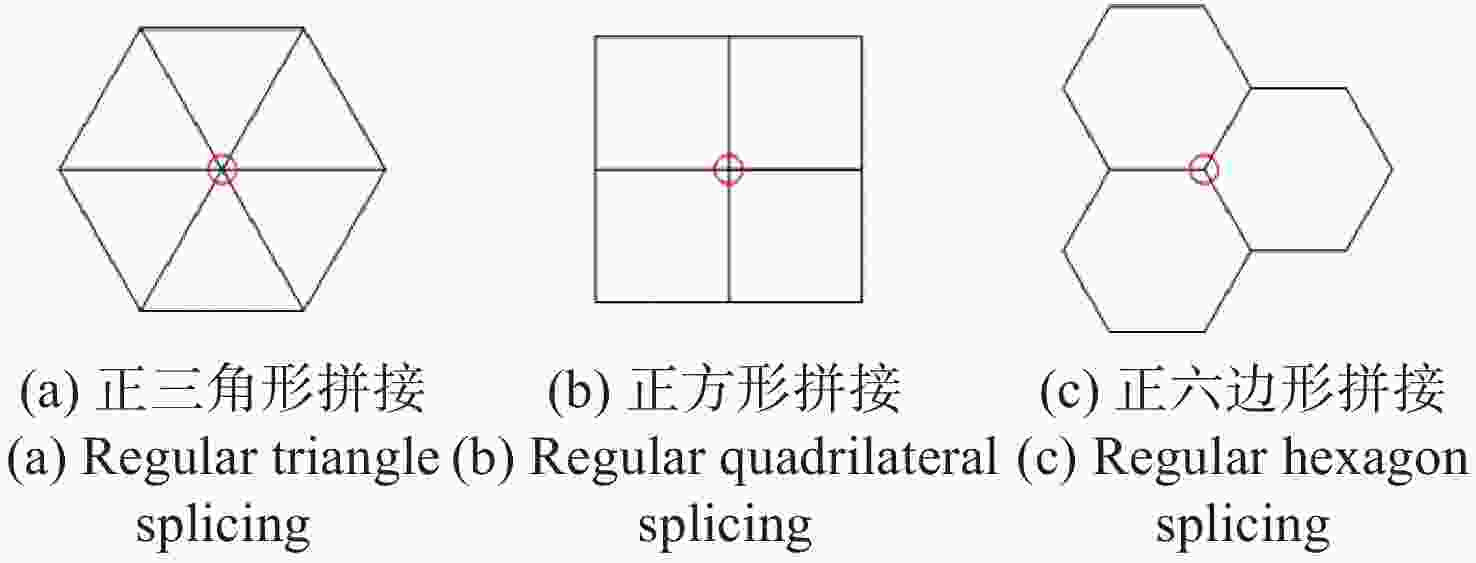
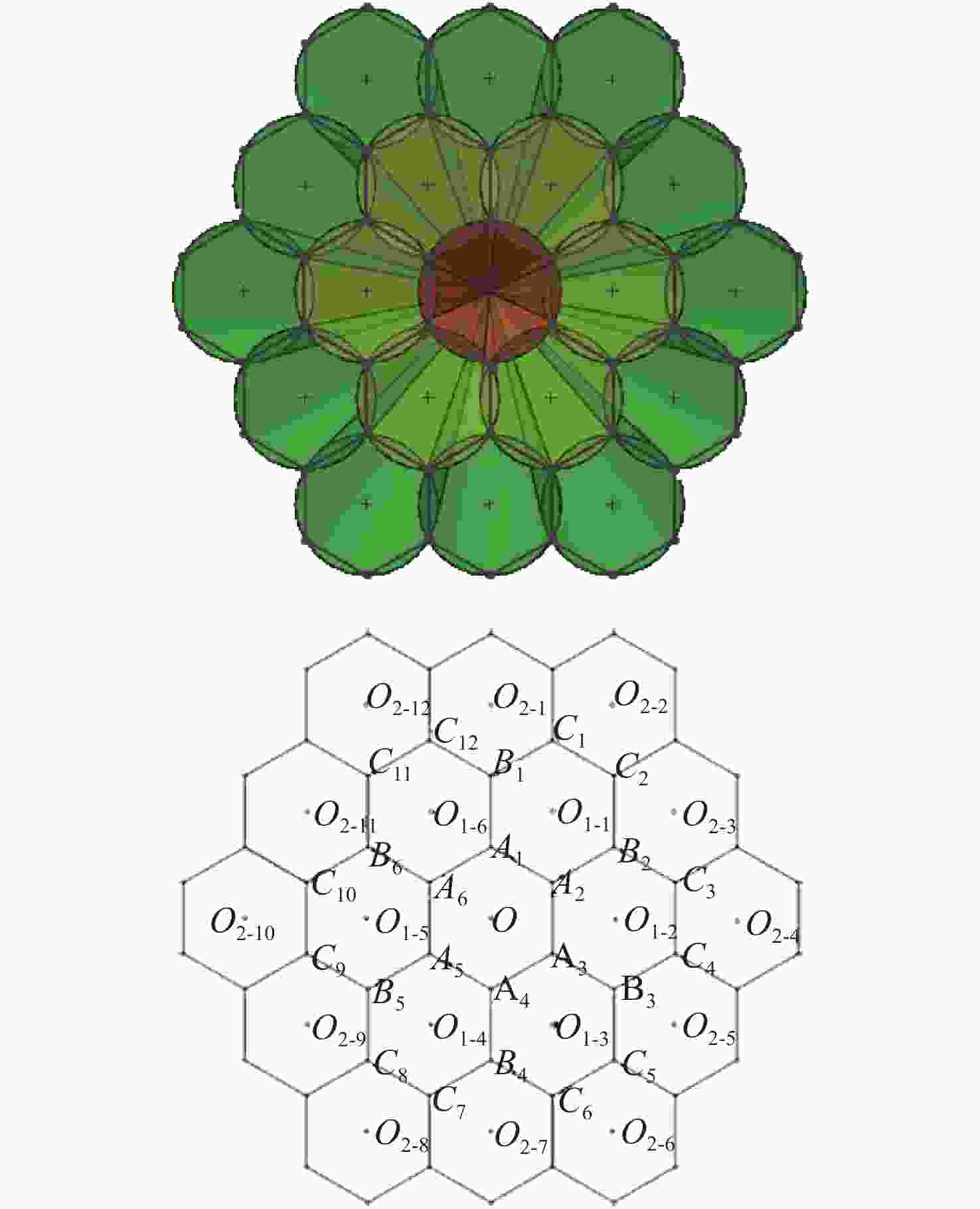
摘要: 大视场星模拟器可以提供更广的星图范围。但是现有星模拟器受显示芯片尺寸的限制,最大视场不超过30°。为了增大星模拟器光学系统视场,本文提出一种将同一规格的星模拟器视场进行拼接从而扩大视场的方法。为了降低成本及系统复杂程度、减少系统整体重量,以最少的拼接数目实现最大的拼接视场,文中针对视场重叠区域进行了详细计算与分析,提出以平面拼接为基础的形式简化拼接模型,得到正三角形、正四边形、正六边形3种典型的拼接方式,并推导了3种拼接方式下视场利用率的计算方法。提出了单一视场坐标计算方法,据此确定每个视场的中心位置,得到准确拼接数目。对比结果显示,正六边形拼接方式具有视场利用率更高、拼接数目更少的突出优势,为大视场星模拟器设计提供依据。Abstract: The large field-of-view (FOV) star simulator provides wider star maps but the existing star simulator is limited by the size of the display chip, and the maximum FOV is not more than 30°. In order to increase the FOV of the star simulator, a splicing method is proposed. In order to reduce the cost, the overall weight and complexity of the system, and to achieve the largest splice FOV with the least amount of splicing, we carry out detailed calculation and analysis of the overlapping area of the field of view and propose a simplified splicing model based on plane splicing. Three typical splicing methods are produced including a regular triangle, a regular quadrilateral and a regular hexagon, and the calculation of the FOV utilization is deduced. This paper also provides a coordinate calculation method, determining the center position of each FOV and obtaining an accurate number of the stitching. The final comparison result shows that the regular hexagon splicing method has the outstanding advantages of a higher utilization of the FOV and fewer splicing numbers, which provides a basis for the design of a large FOV star simulator.
-
Key words:
- field of view splicing /
- star simulator /
- large field of view /
- splicing model
-
表 1 正三角形拼接方式的圈数与个数关系
Table 1. Relationship between the number of circles and the number of regular triangle splicing method
圈数$C$ 1 2 3 4 5 6 每圈个数${a_{3C}}$ 15 33 51 69 87 105 表 2 正四边形拼接方式的圈数与个数关系
Table 2. Relationship between the number of circles and the number of square splicing method
圈数$C$ 1 2 3 4 5 6 每圈个数${a_{4C}}$ 8 16 24 32 40 48 表 3 正六边形拼接方式的圈数与个数关系
Table 3. Relationship between the number of circles and the number of regular hexagon splicing method
圈数$C$ 1 2 3 4 5 6 每圈个数${a_{6C}}$ 6 12 18 24 30 36 表 4 3种方式的视场利用率对比
Table 4. Comparison of FOV utilization of three methods
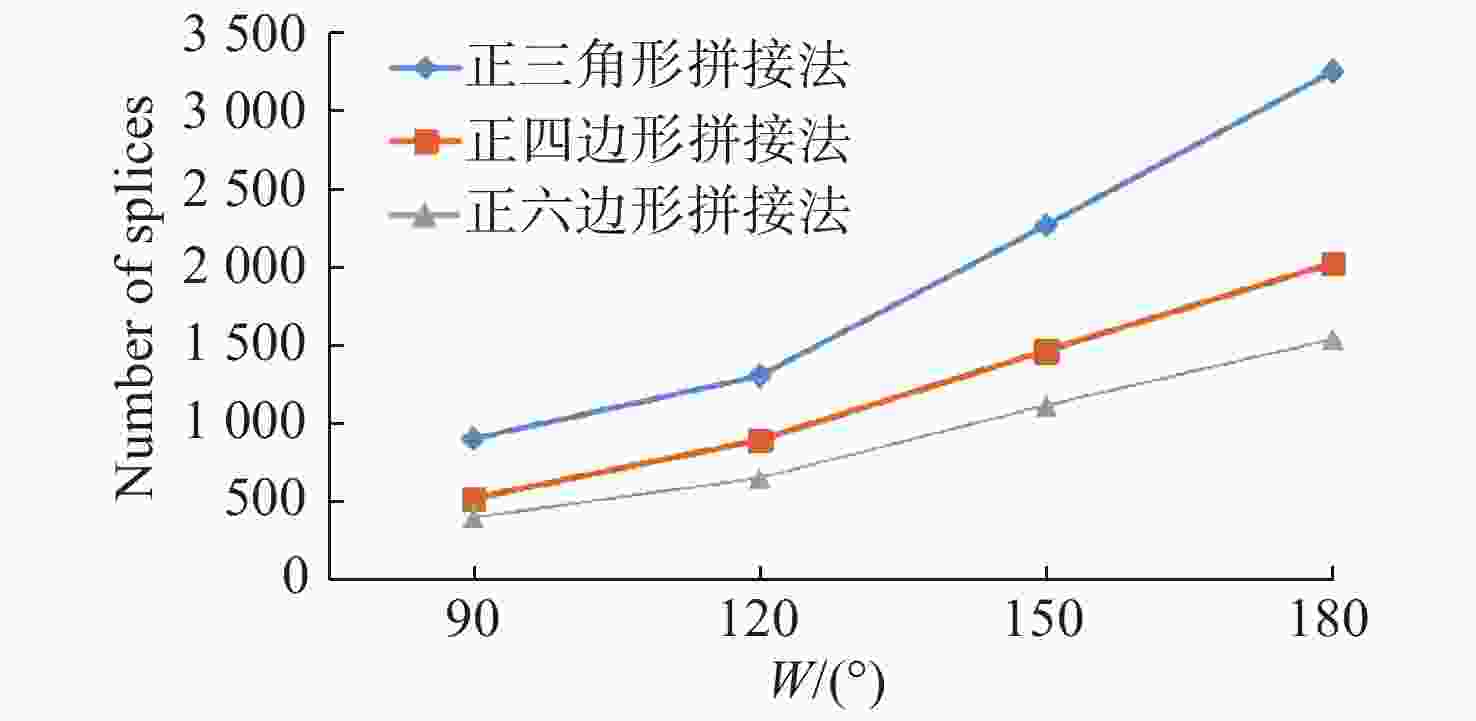
拼接方式 n $\eta $ 正三角形 3 63.1% 正四边形 4 73.4% 正六边形 6 86.2% 表 5 3种方式的拼接数目对比
Table 5. Comparison of the number of splices for three methods
拼接方式 拼接角度 90° 120° 150° 180° 正三角形 921 1321 2277 3255 正四边形 542 914 1481 2037 正六边形 421 673 1134 1554 -
[1] 许洪刚, 韩冰, 李曼丽, 等. 高精度大视场多星模拟器设计与验证[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1343-1351. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0024XU H G, HAN B, LI M L, et al. Design and verification of high-precision multi-star simulator with a wide field of view[J]. Chinese Optics, , 2020, 13(6): 1343-1351. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0024 [2] 陈娜, 王凌云, 李光茜, 等. 静态星模拟器准直光学系统设计[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,42(5):23-26.CHEN N, WANG L Y, LI G X, et al. Design of collimating optical system for static star simulator[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition) , 2019, 42(5): 23-26. (in Chinese) [3] 郭敬明, 魏仲慧, 何昕, 等. CCD星图模拟器的设计及验证[J]. 中国光学与应用光学,2010,3(5):486-493.GUO J M, WEI ZH H, HE X, et al. Design of CCD star map simulator and its validation[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics and Applied Optics, 2010, 3(5): 486-493. (in Chinese) [4] 梁斌, 朱海龙, 张涛, 等. 星敏感器技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 中国光学,2016,9(1):16-29. doi: 10.3788/co.20160901.0016LIANG B, ZHU H L, ZHANG T, et al. Research status and development tendency of star tracker technique[J]. Chinese Optics, 2016, 9(1): 16-29. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20160901.0016 [5] 李曼丽, 韩冰, 刘航, 等. 大视场多星模拟器标定技术研究[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,43(3):17-22.LI M L, HAN B, LIU H, et al. Study on calibration technology of large field of view multi-star simulator[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition) , 2020, 43(3): 17-22. (in Chinese) [6] 李成浩, 何煦, 姬琪, 等. 高时空分辨率动态星模拟器设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(3):515-525. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202803.0515LI CH H, HE X, JI Q, et al. Design of high spatiotemporal resolution dynamic star simulator[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(3): 515-525. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202803.0515 [7] 孟遥, 张国玉, 孙高飞, 等. 基于硅基液晶拼接的高对比度动态星模拟器光学系统[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(3):511-520. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162403.0511MENG Y, ZHANG G Y, SUN G F, et al. Optical system of high contrast dynamic star simulator based on LCOS splicing technology[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(3): 511-520. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162403.0511 [8] 陈启梦, 张国玉, 孙向阳, 等. 高精度LCOS动态星模拟器的光学系统设计[J]. 中国金宝搏188软件怎么用 ,2014,41(7):0716003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0716003CHEN Q M, ZHANG G Y, SUN X Y, et al. Optical system design of LCOS-based and high precision dynamic star simulator[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(7): 0716003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0716003 [9] 刘欢. 大视场单星模拟器关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2018.LIU H. Key technology of single star simulator of large-field-view[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2018. (in Chinese). [10] 代雨, 程欣, 张文明, 等. 基于DMD的大视场长出瞳距星模拟器光学系统设计[J]. 应用光学,2020,41(5):891-897. doi: 10.5768/JAO202041.0501003DAI Y, CHEN X, ZHANG W M, et al. Design of optical system based on DMD for simulator with large field of view and long exit pupil distance[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2020, 41(5): 891-897. (in Chinese) doi: 10.5768/JAO202041.0501003 [11] 代雨. 大视场高动态星模拟器光学系统的设计与研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院光电技术研究所), 2020.DAI Y. Design and research of optical system for large field of view dynamic star simulator[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Science (Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2020. (in Chinese). [12] 史立芳, 曹阿秀, 刘艳, 等. 大视场人工复眼结构设计方法与实验[J]. 光电工程,2013,40(7):27-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2013.07.005SHI L F, CAO A X, LIU Y, et al. Design and experiments of artificial compound eye with large view field[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2013, 40(7): 27-33. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2013.07.005 [13] 史立芳. 大视场人工复眼成像结构研究与实验[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2014.SHI L F. Research and experiment on artificial compound eye imaging system with large field of view[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2014. (in Chinese). [14] CLARE B W, KEPERT D L. The closest packing of equal circles on a sphere[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A. Mathematical,Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1986, 405(1829): 329-344. -






 下载:
下载: