Design and research of fully automatic push-broom hyperspectral microscopic imaging system
-
摘要: 为了将光谱成像技术更方便地引入显微成像领域,本文将高光谱成像技术与显微成像技术相结合,搭建出一套全自动推扫式高光谱显微成像系统。系统以倒置显微镜为主体进行设计,采用棱镜-光栅元件进行光谱分光,利用高精度二维电动运动平台进行推扫,同时结合电动对焦组件完成对焦,最后成像在高灵敏sCMOS科学相机上。根据大多数生物样本光谱检测需求,系统的光谱范围选择420~800 nm。经光谱定标和空间分辨率测试,确定系统的光谱采样率为2.06 nm,光谱分辨率均值优于3.5 nm,空间分辨率优于0.87 μm。系统引入金宝搏188软件怎么用 自动对焦系统作为主动对焦模块,以HE染色的乳腺癌病理切片为研究对象,实验分别采用被动对焦和主动对焦方式进行推扫成像,并比较分析两种方式的优劣,认为两者均可以满足大视场成像需求,但主动对焦成像更快速、更清晰,更加适合推扫式高光谱显微成像系统。通过对全自动推扫式高光谱显微成像系统的设计与研究,解决了高光谱显微成像中无法实时对焦的难题,实现了40倍显微物镜下3.25 mm×3.25 mm范围内全自动成像,有利于促进光谱技术在生物医学等领域中的应用。Abstract: To apply hyperspectral technology to the field of microscopic imaging more conveniently, we designed and built a fully automatic push-broom hyperspectral microscopic imaging system. In this system, an inverted microscope was designed as the main body, a prism-grating component was used for spectrum splitting, a high precision two-dimensional motorized stage was applied for a push-broom. A motor focus module was used to control the focus, and a hyperspectral microscopic image was collected through a highly sensitive sCMOS scientific camera. The system has the advantages of low cost, easy installation and adjustment, real-time focusing and large-field-of-view imaging. The spectral range of the system is from 420 nm to 800 nm to meet the spectrum detection requirements of most biological samples. The spectral resolution was better than 3.5 nm, and the spatial resolution was better than 0.87 μm through the monochromatic collimated light scanning calibration method. Then, the HE-stained breast cancer pathological slices was as the research object. The samples were investigated and compared using passive and active focusing for push-broom imaging. The advantages and disadvantages of the two focusing methods were analyzed and summarized. The results showed that both methods can meet the needs of large-field-of-view imaging, but active focus imaging is faster and clearer, and is more suitable for push-broom hyperspectral microscopy imaging systems. Through the design and research of a fully automatic push-broom hyperspectral microscopy imaging system, real-time focusing in hyperspectral microscopic imaging was realized and 3.25 mm×3.25 mm field of view imaging of biological samples with a 40X objective lens was achieved. This system could be beneficial for promoting the application of hyperspectral technology in the biomedical field.
-
Key words:
- microscopic imaging /
- hyperspectral imaging /
- autofocus
-
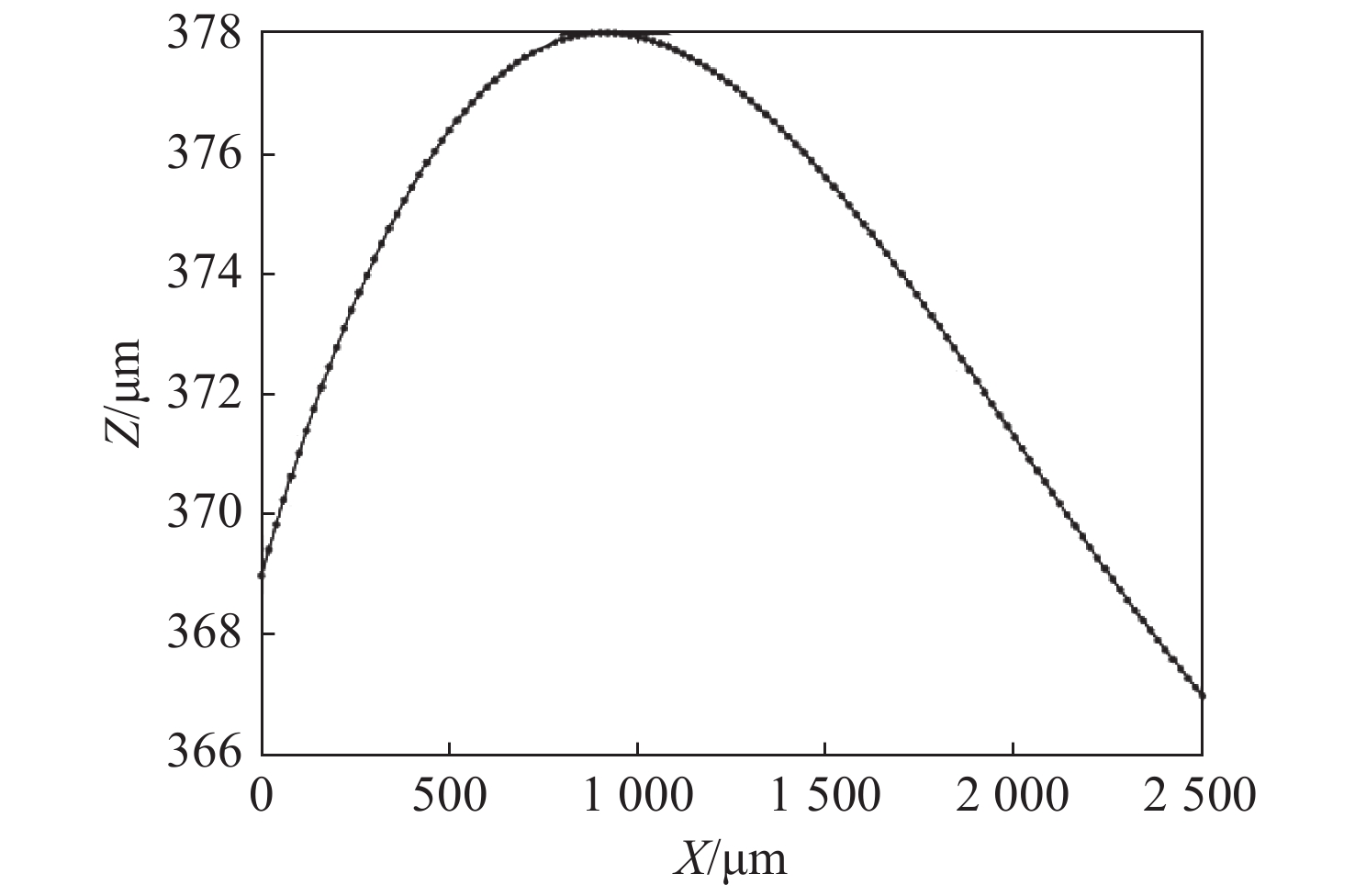
表 1 单帧图像和推扫图像清晰度评价的对焦位置
Table 1. Focus positions for clarity evaluation based on the single-frame image and the push-broom image
Position/μm Single frame image/μm Push scan image/μm 0 357 369 912 376 378 1700 376 374 2500 371 367 表 2 Z值数据
Table 2. Z value data
Z/μm Y/μm X/μm 0 912 1700 2500 0 369 378 374 371 912 378 385 380 376 1700 385 388 385 382 2500 367 376 375 373 表 3 主动对焦推扫图像的对焦位置
Table 3. Focus position based on active focus push-broom image
Position /μm Active focus position/μm Push scan image/μm 0 369 369 500 376 376.2 1000 378 377.9 1500 375 375.7 2000 371 371.1 2500 367 367 -
[1] SORG B S, MOELLER B J, DONOVAN O, et al. Hyperspectral imaging of hemoglobin saturation in tumor microvasculature and tumor hypoxia development[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2005, 10(4): 44004. doi: 10.1117/1.2003369 [2] LIU K X, LIN S F, ZHU S Q, et al. Hyperspectral microscopy combined with DAPI staining for the identification of hepatic carcinoma cells[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2021, 12(1): 173-180. doi: 10.1364/BOE.412158 [3] EADY M, PARK B. An unsupervised prediction model for salmonella detection with hyperspectral microscopy: a multi-year validation[J]. Applied Sciences, , 2021, 11(3): 895. doi: 10.3390/app11030895 [4] WANG J SH, LI Q L. Quantitative analysis of liver tumors at different stages using microscopic hyperspectral imaging technology[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, , 2018, 23(10): 106002. [5] 肖功海, 舒嵘, 薛永祺. 显微高光谱成像系统的设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2004,12(4):367-372.XIAO G H, SHU R, XUE Y Q. Design of microscopic hyperspectral imaging system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2004, 12(4): 367-372. (in Chinese) [6] 李庆利, 薛永祺, 肖功海, 等. 显微高光谱成像的生物组织定量检测机理及方法研究[J]. 科学通报,2008,53(4):493-496. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.04.018LI Q L, XUE Y Q, XIAO G H, et al. Research on the mechanism and method of biological tissue quantitative detection based on micro-hyperspectral imaging[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(4): 493-496. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.04.018 [7] ORTEGA S, GUERRA R, DÍAZ M, et al. Hyperspectral push-broom microscope development and characterization[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 122473-122491. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2937729 [8] ORTEGA S, FABELO H, CAMACHO R, et al. Detecting brain tumor in pathological slides using hyperspectral imaging[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2018, 9(2): 818-831. doi: 10.1364/BOE.9.000818 [9] PU H B, LIN L, SUN D W. Principles of hyperspectral microscope imaging techniques and their applications in food quality and safety detection: a review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2019, 18(4): 853-866. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12432 [10] SELJEBOTN S T. Continuous autofocus for line scanning hyperspectral camera[D]. Trondheim: Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2012. [11] 张佳伦, 郑玉权, 蔺超, 等. 消像散的自由曲面棱镜光谱仪光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(4):842-851. doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0049ZHANG J L, ZHENG Y Q, LIN C, et al. Design of a freeform curved prism imaging spectrometer based on an anastigmatism[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(4): 842-851. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0049 [12] 张天一, 朱永田, 侯永辉, 等. LAMOST高分辨率光谱仪研制[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(1):148-155. doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0148ZHANG T Y, ZHU Y T, HOU Y H, et al. Construction of a LAMOST high resolution spectrograph[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(1): 148-155. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0148 [13] 魏巍, 崔继承, 唐玉国, 等. 医用显微成像光谱仪的光谱定标技术[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(5):1015-1020. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162405.1015WEI W, CUI J CH, TANG Y G, et al. Spectral calibration of medical microscopic imaging spectrometer[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(5): 1015-1020. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162405.1015 [14] 迟明波, 韩欣欣, 徐阳, 等. 宽谱段高分辨扫描光谱定标技术[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(2):249-257. doi: 10.3788/co.20201302.0249CHI M B, HAN X X, XU Y, et al. Broad band and high resolution scanning spectrum calibration technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(2): 249-257. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20201302.0249 -






 下载:
下载: