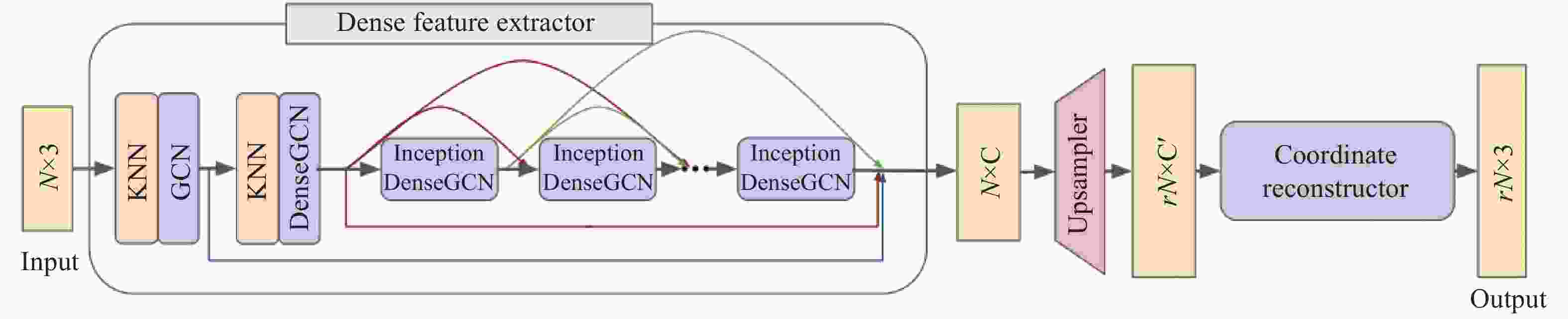
-
摘要: 随着机器视觉技术的发展,如何准确、高效地对真实世界进行精确记录与建模已成为热点问题。由于硬件条件的限制,通常采集到的点云数据分辨率较低,无法满足实际应用需求,因此有必要对点云数据超分辨率技术进行研究。本文介绍三维点云数据超分辨率技术的意义、进展及评价方法,并对经典超分辨率算法和基于机器学习的超分辨率算法分别进行梳理,总结了目前方法的特点,指出了目前点云数据超分辨率技术中存在的主要问题及面临的挑战,最后展望了点云数据超分辨率技术的发展方向。Abstract: With the development of the computer vision technology, research on recording and modeling the real world accurately and efficiently has become a key issue. Due to the limitation of hardware, the resolution of a point cloud is usually low, which cannot meet the applications. Therefore, it is necessary to study the super-resolution technology of point clouds. In this paper, we sort out the significance, progress, and evaluation methods of 3D point cloud super-resolution technology, introduce the classical super-resolution algorithm and the super-resolution algorithm based on machine learning, summarize the characteristics of the current methods, and point out the main problems and challenges in current point cloud data super-resolution technology. Finally, the future direction in point cloud super-resolution technology is proposed.
-
Key words:
- point cloud /
- point cloud up-sampling /
- super-resolution /
- machine learning
-
表 1 均方误差比较
Table 1. RMSE comparison
局部/全局 数据集与倍数 Art Moebius Books 4× 8× 4× 8× 4× 8× 基于局部信息 边缘特征引导的JBUF[26] 1.08 1.93 − − − − 基于局部信息 改进的双边滤波器[27] 1.93 2.45 1.63 2.06 1.47 1.81 基于局部信息 具有噪声感知的双边滤波[28] 2.90 4.75 1.55 2.28 1.36 1.94 基于局部信息 基于引导图像的滤波器[29] 2.40 3.32 2.03 2.60 1.82 2.31 基于全局优化 二阶TGV[30] 1.29 2.06 0.90 1.38 0.75 1.16 基于全局优化 二阶TGV+边缘指示函数[31] 1.21 1.93 0.81 1.32 0.65 1.07 基于全局优化 MRF[33] 2.24 3.85 2.29 3.09 2.08 2.85 基于全局优化 改进的MRF[34] 1.00 1.50 − − − − 基于全局优化 改进的MRF[35] 1.82 2.78 1.49 2.13 1.43 1.98 -
[1] 李松泰. 三维金宝搏188软件怎么用 扫描仪点云数据的应用研究[J]. 地矿测绘,2020,3(2):141-142.LI S T. Application of point cloud in 3D laser scanner[J]. Geological and Mineral Surveying and Mapping, 2020, 3(2): 141-142. (in Chinese) [2] 杜瑞建, 葛宝臻, 陈雷. 多视高分辨率纹理图像与双目三维点云的映射方法[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(5):1055-1064. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0034DU R J, GE B ZH, CHEN L. Texture mapping of multi-view high-resolution images and binocular 3D point clouds[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(5): 1055-1064. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0034 [3] 杜钦生, 李丹丹, 陈浩, 等. 结构光3D点云的PIN针针尖提取[J]. 液晶与显示,2021,36(9):1331-1340. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0321DU Q SH, LI D D, CHEN H, et al. PIN tip extraction from 3D point cloud of structured light[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2021, 36(9): 1331-1340. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0321 [4] 吴坤帅, 魏仲慧, 何昕, 等. 基于笔划三维深度特征的签名识别[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(10):1013-1020. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193410.1013WU K SH, WEI ZH H, HE X, et al. Signatures recognition based on strokes 3D depth feature[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(10): 1013-1020. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193410.1013 [5] 谭红春, 耿英保, 杜炜. 一种高效的人脸三维点云超分辨率融合方法[J]. 光学技术,2016,42(6):501-505.TAN H CH, GENG Y B, DU W. An efficient method of face super-resolution fusion using 3D cloud points[J]. Optical Technique, 2016, 42(6): 501-505. (in Chinese) [6] 张银, 任国全, 程子阳, 等. 三维金宝搏188软件怎么用 雷达在无人车环境感知中的应用研究[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与光电子学进展,2019,56(13):130001.ZHANG Y, REN G Q, CHENG Z Y, et al. Application research of there-dimensional LiDAR in unmanned vehicle environment perception[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(13): 130001. (in Chinese) [7] 王世峰, 戴祥, 徐宁, 等. 无人驾驶汽车环境感知技术综述[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版),2017,40(1):1-6.WANG SH F, DAI X, XU N, et al. Overview on environment perception technology for unmanned ground vehicle[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition) , 2017, 40(1): 1-6. (in Chinese) [8] 杨必胜, 梁福逊, 黄荣刚. 三维金宝搏188软件怎么用 扫描点云数据处理研究进展、挑战与趋势[J]. 测绘学报,2017,46(10):1509-1516. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170351YANG B SH, LIANG F X, HUANG R G. Progress, challenges and perspectives of 3D LiDAR point cloud processing[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1509-1516. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170351 [9] 张绍阳, 侯旭阳, 崔华, 等. 利用金宝搏188软件怎么用 散斑获取深度图[J]. 中国光学,2016,9(6):633-641.ZHANG SH Y, HOU X Y, CUI H, et al. Depth image acquisition using laser speckle[J]. Chinese Optics, 2016, 9(6): 633-641. (in Chinese) [10] 卜禹铭, 杜小平, 曾朝阳, 等. 无扫描金宝搏188软件怎么用 三维成像雷达研究进展及趋势分析[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(5):711-727. doi: 10.3788/co.20181105.0711BU Y M, DU X P, ZENG ZH Y, et al. Research progress and trend analysis of non-scanning laser 3D imaging radar[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(5): 711-727. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20181105.0711 [11] 苏东, 张艳, 曲承志, 等. 基于彩色图像轮廓的深度图像修复方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2021,36(3):456-464. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0222SU D, ZHANG Y, QU CH ZH, et al. Depth image restoration method based on color image contour[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2021, 36(3): 456-464. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0222 [12] FOIX S, ALENYA G, TORRAS C. Lock-in Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras: a survey[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2011, 11(9): 1917-1926. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2010.2101060 [13] SCHUON S, THEOBALT C, DAVIS J, et al. . High-quality scanning using time-of-flight depth superresolution[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, IEEE, 2008: 1-7. [14] BALURE C S, KINI M R. Depth image super-resolution: a review and wavelet perspective[C]. Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision and Image Processing, Springer, 2017: 543-555. [15] 肖宿, 韩国强, 沃焱. 数字图像超分辨率重建技术综述[J]. 计算机科学,2009,36(12):8-13,54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2009.12.003XIAO S, HAN G Q, WO Y. Survey of digital image super resolution reconstruction technology[J]. Computer Science, 2009, 36(12): 8-13,54. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2009.12.003 [16] HARRIS J L. Diffraction and resolving power[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1964, 54(7): 931-936. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.54.000931 [17] GOODMAN J W. Introduction to Fourier Optics[M]. San Francisco: McGraw-Hill, 1968. [18] 谢海平, 谢凯利, 杨海涛. 图像超分辨率方法研究进展[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2020,56(19):34-41.XIE H P, XIE K L, YANG H T. Research progress of image super-resolution methods[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2020, 56(19): 34-41. (in Chinese) [19] VAN OUWERKERK J D. Image super-resolution survey[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2006, 24(10): 1039-1052. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2006.02.026 [20] 王浩, 张叶, 沈宏海, 等. 图像增强算法综述[J]. 中国光学,2017,10(4):438-448. doi: 10.3788/co.20171004.0438WANG H, ZHANG Y, SHEN H H, et al. Review of image enhancement algorithms[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(4): 438-448. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20171004.0438 [21] STARK H, OSKOUI P. High-resolution image recovery from image-plane arrays, using convex projections[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1989, 6(11): 1715-1726. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.6.001715 [22] GEVREKCI M, PAKIN K. Depth map super resolution[C]. Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, IEEE, 2011: 3449-3452. [23] PATTI A J, ALTUNBASAK Y. Artifact reduction for set theoretic super resolution image reconstruction with edge adaptive constraints and higher-order interpolants[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(1): 179-186. doi: 10.1109/83.892456 [24] TOMASI C, MANDUCHI R. Bilateral filtering for gray and color images[C]. Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 1998: 839-846. [25] KOPF J, COHEN M F, LISCHINSKI D, et al. Joint bilateral upsampling[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2007, 26(3): 96-es. doi: 10.1145/1276377.1276497 [26] 涂义福, 张旭东, 张骏, 等. 基于边缘特征引导的深度图像超分率重建[J]. 计算机应用与软件,2017,34(2):220-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2017.02.039TU Y F, ZHANG X D, ZHANG J, et al. Depth map super-resolution reconstruction based on the edge feature-guided[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2017, 34(2): 220-225. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2017.02.039 [27] YANG Q X, YANG R G, DAVIS J, et al.. Spatial-depth super resolution for range images[C]. Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2007: 1-8. [28] CHAN D, BUISMAN H, THEOBALT C, et al.. A Noise-Aware Filter for Real-Time Depth Upsampling[C]. Multi-camera & Multi-modal Sensor Fusion Algorithms and Applications, Marseille, France: M2SFA2, 2008: inria-00326784. [29] HE K M, SUN J, TANG X O. Guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(6): 1397-1409. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.213 [30] FERSTL D, REINBACHER C, RANFTL R, et al. . Image guided depth upsampling using anisotropic total generalized variation[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2013: 993-1000. [31] 邸维巍, 张旭东, 胡良梅, 等. 彩色图约束的二阶广义总变分深度图超分辨率重建[J]. 中国图象图形学报,2014,19(8):1162-1167. doi: 10.11834/jig.20140807DI W W, ZHANG X D, HU L M, et al. Depth image super-resolution based on second-order total generalized variation constrained by color image[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2014, 19(8): 1162-1167. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11834/jig.20140807 [32] 王宇, 朴燕, 孙荣春. 结合同场景彩色图像的深度图超分辨率重建[J]. 光学学报,2017,37(8):0810002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0810002WANG Y, PIAO Y, SUN R CH. Depth image super-resolution construction combined with high-resolution color image of the same scene[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(8): 0810002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0810002 [33] DIEBEL J, THRUN S. An application of markov random fields to range sensing[C]. Proceedings of the 18th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, ACM, 2005: 291-298. [34] 陈金奇, 李榕. 一种基于改进MRF的深度图超分辨率重建[J]. 微处理机,2017,38(4):60-63,71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2279.2017.04.015CHEN J Q, LI R. A depth map super-resolution reconstruction based on improved markov random field[J]. Microprocessors, 2017, 38(4): 60-63,71. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2279.2017.04.015 [35] PARK J, KIM H, TAI Y W, et al.. High quality depth map upsampling for 3D-TOF cameras[C]. 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2011: 1623-1630. [36] SCHARSTEIN D, PAL C. Learning conditional random fields for stereo[C]. 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2007: 1-8. [37] DONG CH, LOY C C, HE K M, et al.. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]. Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2014: 184-199. [38] DONG CH, LOY C C, HE K M, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295-307. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 [39] YU L Q, LI X ZH, FU C W, et al.. PU-Net: point cloud upsampling network[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 2790-2799. [40] CHARLES R Q, SU H, KAICHUN M, et al.. PointNet: deep learning on point Sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2017: 77-85. [41] QI C R, YI L, SU H, et al.. PointNet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, ACM, 2017: 5105-5114. [42] WANG Y F, WU SH H, HUANG H, et al.. Patch-based progressive 3D point set upsampling[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2019: 5951-5960. [43] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139-144. doi: 10.1145/3422622 [44] LI R H, LI X ZH, FU C W, et al.. PU-GAN: a point cloud upsampling adversarial network[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2019: 7202-7211. [45] YANG Y Q, FENG CH, SHEN Y R, et al.. FoldingNet: point cloud auto-encoder via deep grid deformation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 206-215. [46] KIPF T N, WELLING M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[C]. 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, OpenReview. net, 2017. [47] QIAN G CH, ABUALSHOUR A, LI G H, et al.. PU-GCN: point cloud upsampling using graph convolutional networks[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2021: 11678-11687. [48] WU H, ZHANG J, HUANG K. Point Cloud Super Resolution with Adversarial Residual Graph Networks[J]. arXiv preprint, 2019: arXiv: 1908.02111. [49] YANG L B, WANG SH SH, MA S W, et al.. HiFaceGAN: face renovation via collaborative suppression and replenishment[C]. Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, ACM, 2020: 1551-1560. [50] SHAN T X, WANG J K, CHEN F F, et al. Simulation-based lidar super-resolution for ground vehicles[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2020, 134: 103647. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2020.103647 -






 下载:
下载: