Research on highly sensitive detection of oxygen concentrations based on tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy
-
摘要:
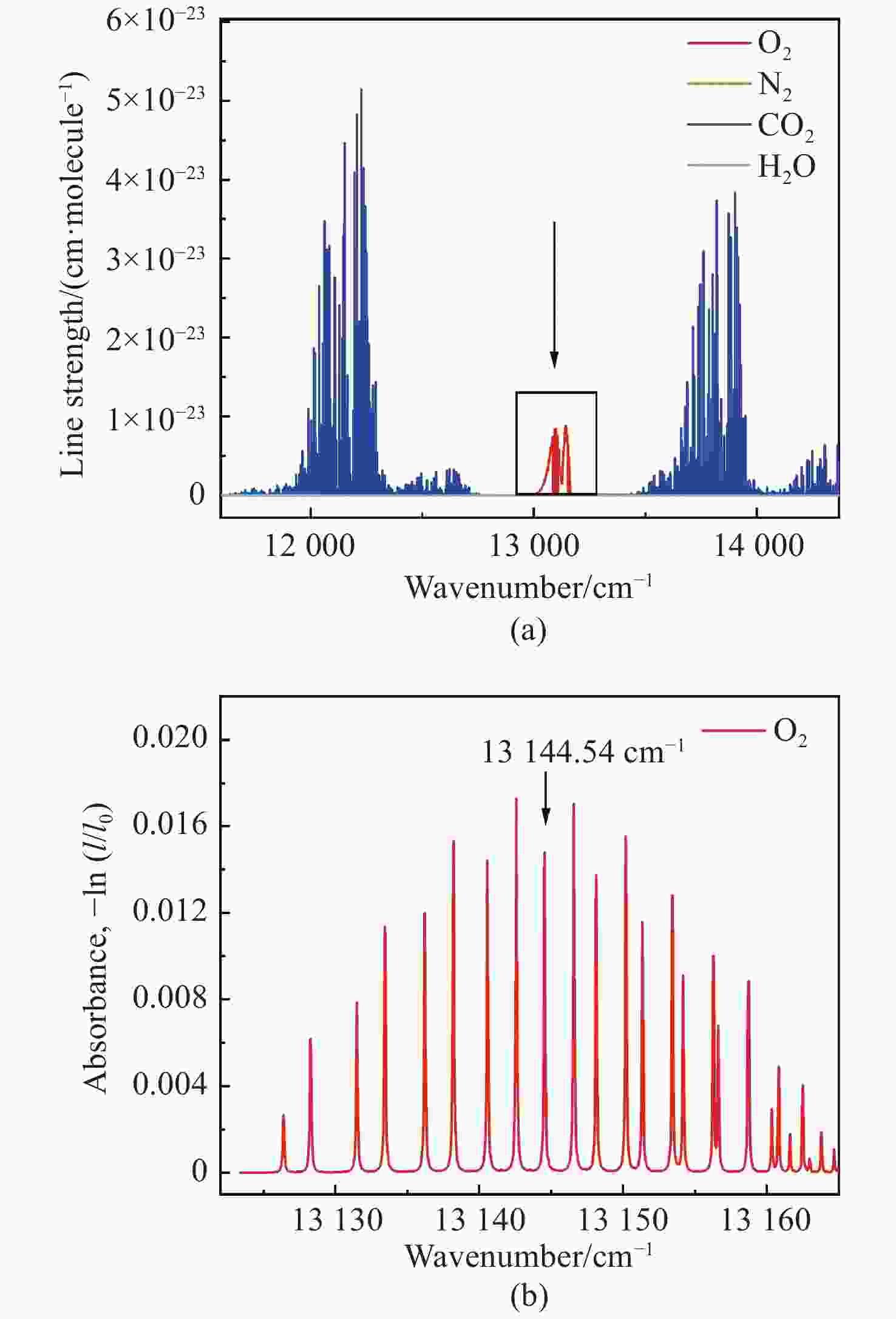
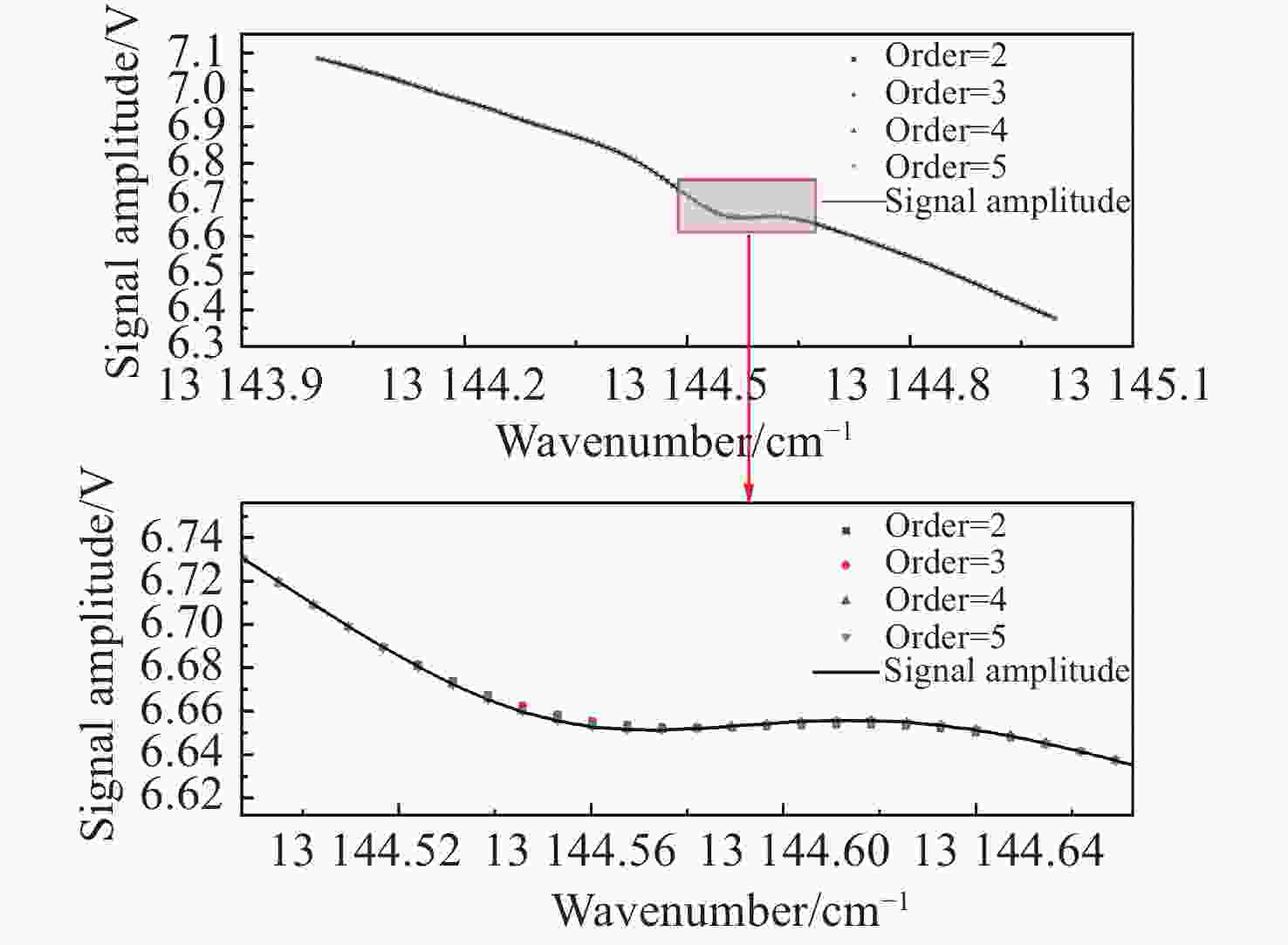
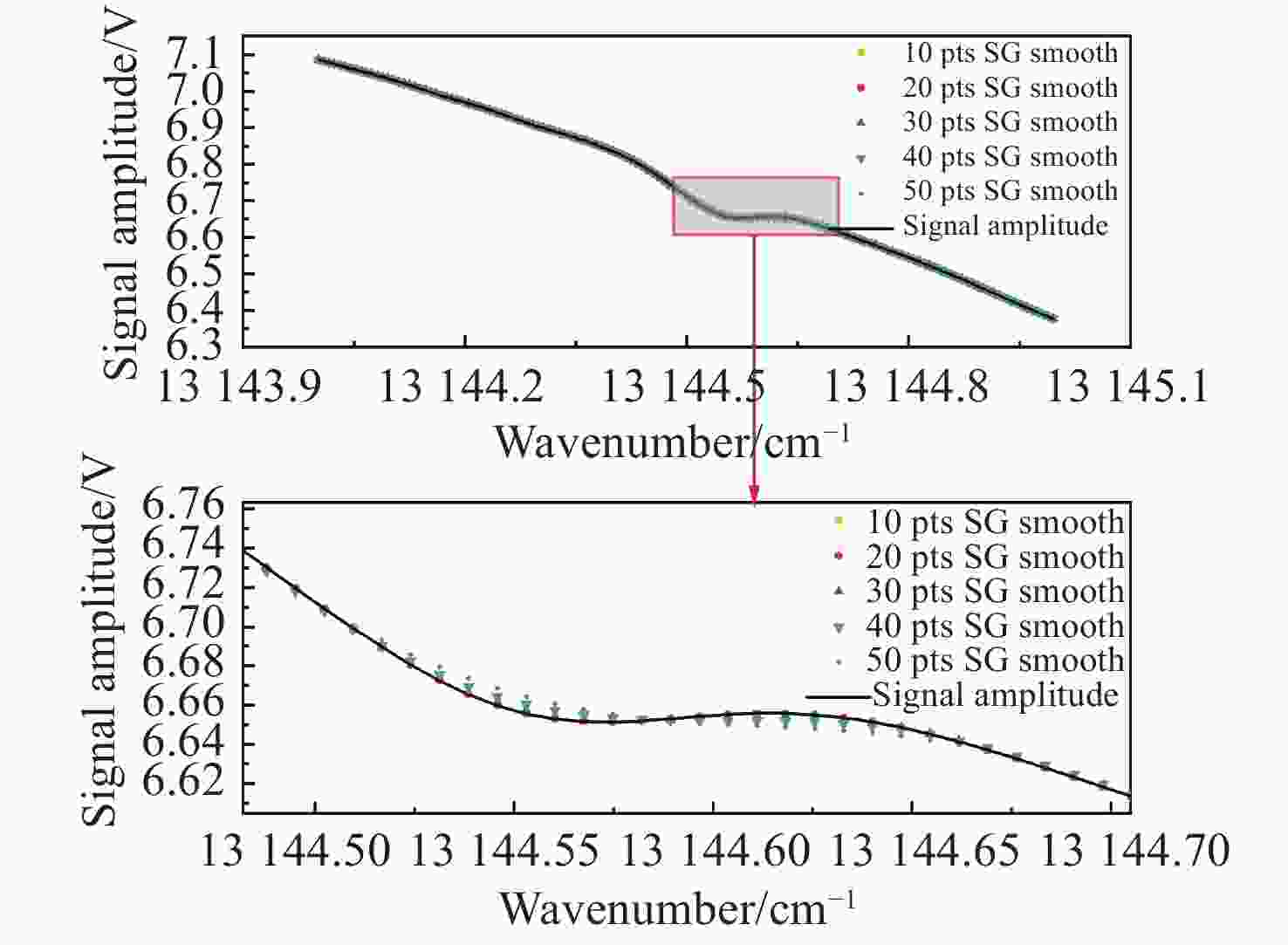
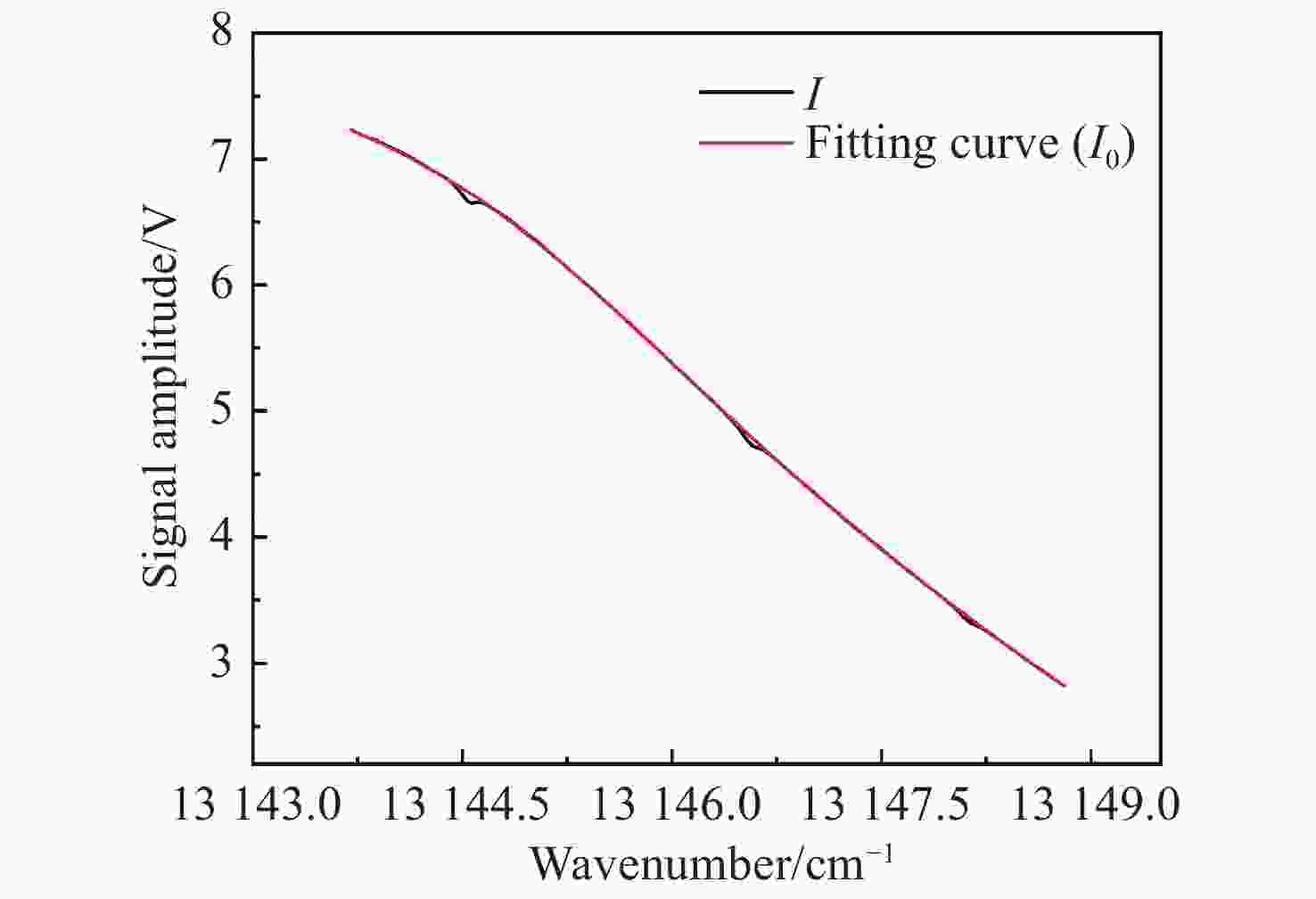
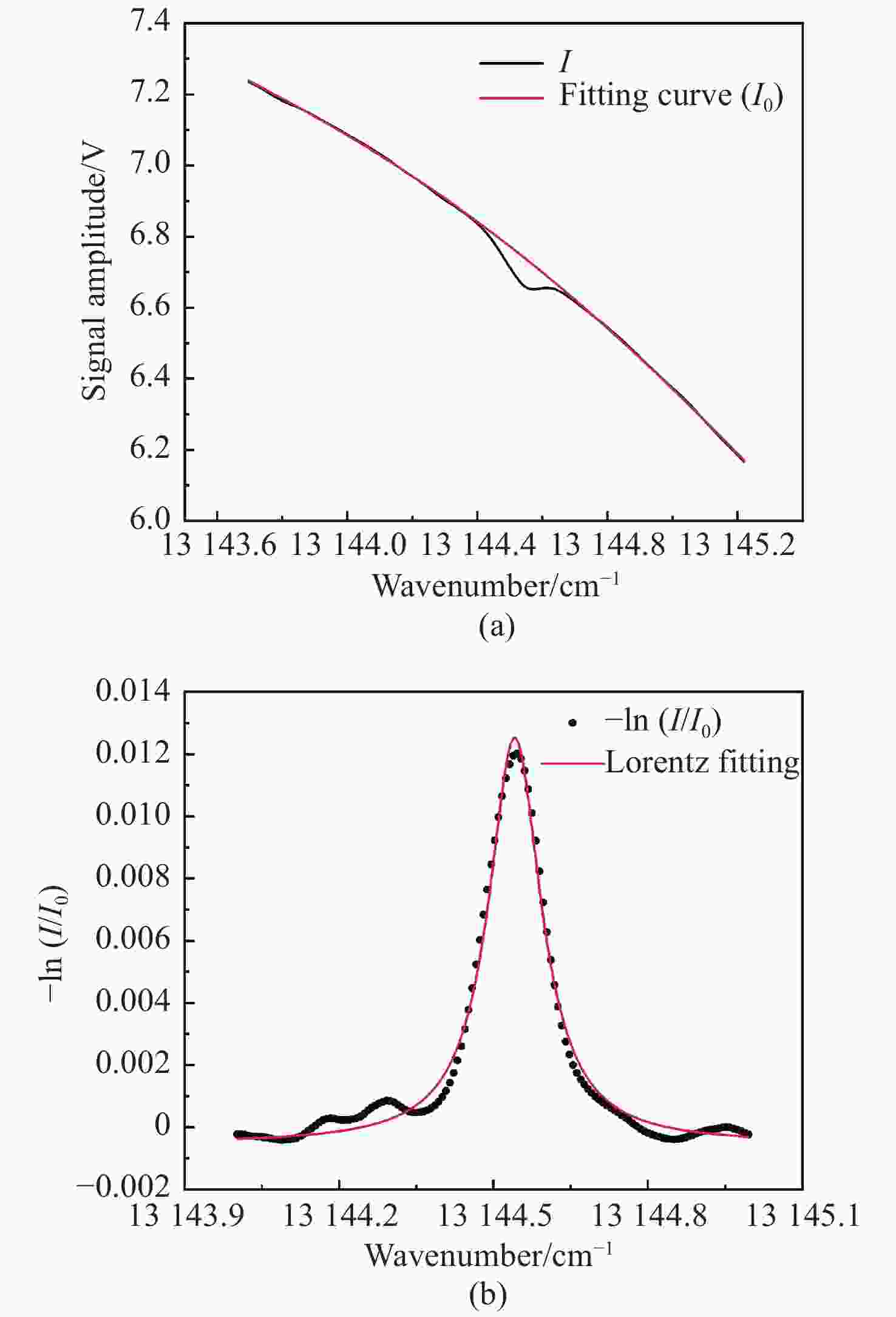
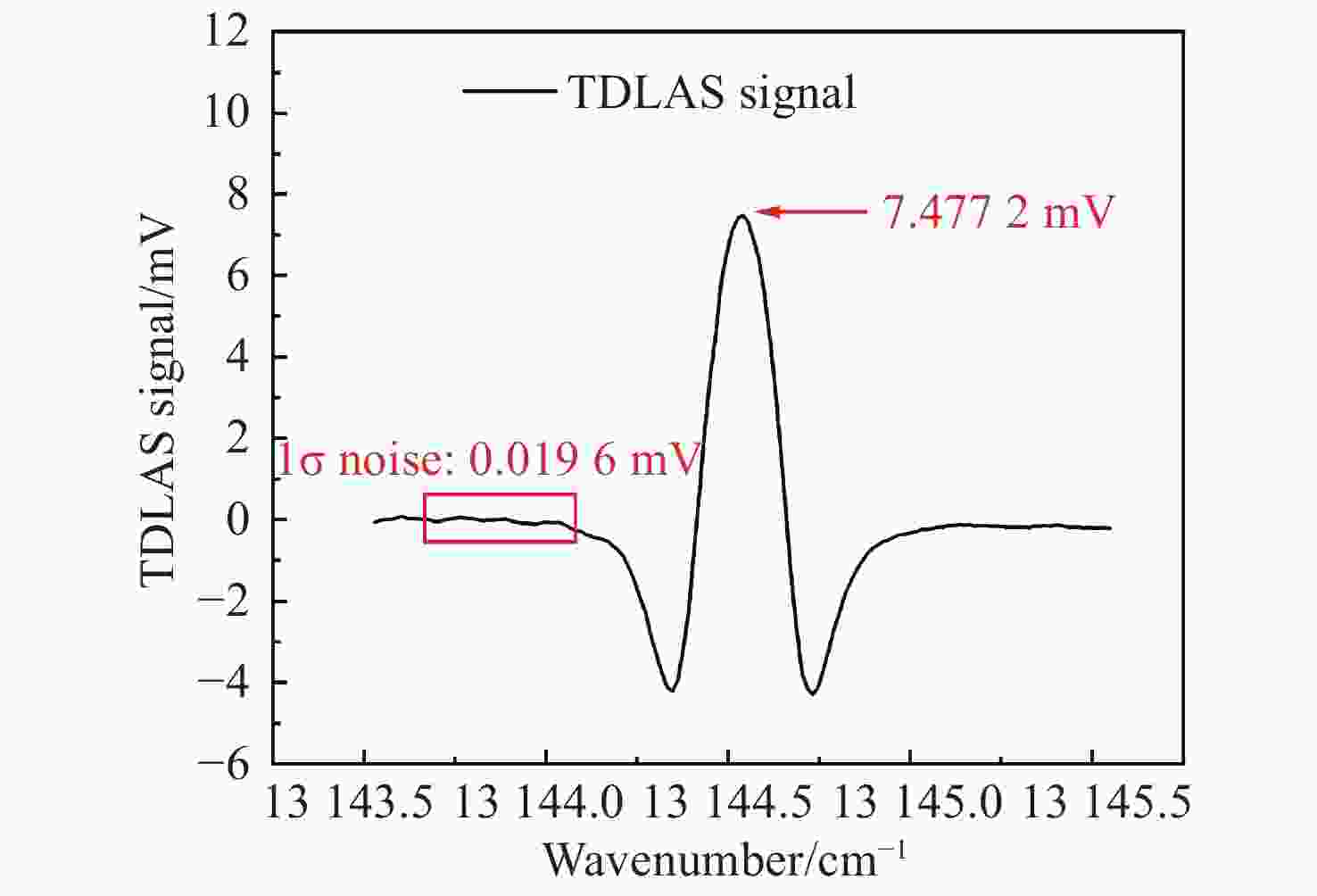
可调谐半导体金宝搏188软件怎么用 吸收光谱(TDLAS)是近年发展起来的一种金宝搏188软件怎么用 光谱气体检测技术,相比于常见的电化学、离子导电陶瓷等技术,其具有选择性强、灵敏度高、响应快、可在线测量、抗背景光谱干扰能力强等优点,适用于复杂环境中气体的长期在线检测。氧气(O2)是人类生存环境中的重要气体,O2浓度的检测在生产生活各个领域应用广泛、意义重大。基于此,本文采用TDLAS技术对空气中的O2进行高灵敏度测量。采用输出波长为760 nm的半导体金宝搏188软件怎么用 器作为光源,直接吸收光谱法获得环境中的氧气浓度为20.56%,最小检测极限为5.53×10−3。在波长调制方法中,优化了金宝搏188软件怎么用 波长调制深度,得到了完整的二次谐波波形,可用于标定氧气浓度。此系统的信噪比为380.74,最小检测极限约为540×10−6。本文的传感系统具有良好的O2检测能力,可广泛用于各个领域中的O2浓度检测。
-
关键词:
- TDLAS /
- 氧气(O2)浓度检测 /
- 直接测量 /
- 波长调制 /
- 半导体金宝搏188软件怎么用 器
Abstract:Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (TDLAS) is a recently developed laser spectral gas detection technology. Compared with common oxygen sensors such as electrochemical devices and ionic conductive ceramics, TDLAS has the advantages of high selectivity and sensitivity, fast response, on-line measurement and strong anti-background spectral interference ability. Oxygen (O2) is an important gas in habitable environments and is greatly significant to industrial production and human life, and the detection of O2 concentration is also widely used in these fields. Based on this, we adopt TDLAS technology to carry out high sensitivity measurements of O2 in air. Using a semiconductor laser with an output wavelength of 760 nm as the light source, the oxygen concentration in the environment is 20.56% by direct absorption spectroscopy, and the minimum detection limit is 5.53×10−3. In the wavelength modulation spectroscopy method, the laser wavelength modulation depth is optimized to obtain a complete second harmonic waveform, which can be used to calibrate the oxygen concentration. The SNR of the system is 380.74, and the minimum detection limit is about 540×10−6. The system realized in this paper has good oxygen detection ability and can be widely used in various fields of oxygen concentration detection.
-
-
[1] 隋丽丽, 黄微微, 王平, 等. 原位生长的α-Fe2O3/ZnO异质纳米棒阵列对乙醇气体的高选择性检测[J]. 应用化学,2021,38(7):857-865.SUI L L, HUANG W W, WANG P, et al. In situ deposited heterogeneous α-Fe2O3/ZnO nanorod arrays for highly selective detection of ethanol[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2021, 38(7): 857-865. (in Chinese) [2] 伞晓广, 巩晓辉, 陆一鸣, 等. NiO-WO3纳米立方块的制备及在甲醛检测中的应用[J]. 应用化学,2020,37(10):1203-1210. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2020.10.200059SAN X G, GONG X H, LU Y M, et al. Synthesis of NiO-WO3 nanocubes and their application in detecting formaldehyde[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2020, 37(10): 1203-1210. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2020.10.200059 [3] 李佳祁, 付大友, 王竹青, 等. 基于气液相化学发光技术的臭氧在线检测方法[J]. 应用化学,2020,37(1):96-102. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2020.01.190136LI J Q, FU D Y, WANG ZH Q, et al. Online ozone detection method based on gas-liquid phase chemiluminescence technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2020, 37(1): 96-102. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2020.01.190136 [4] KOCACHE R. The measurement of oxygen on gas mixtures[J]. Journal of Physics E:Scientific Instruments, 1986, 19(6): 401-410. doi: 10.1088/0022-3735/19/6/001 [5] KOCACHE R M A, SWAN J, HOLMAN D F. A miniature rugged and accurate solid electrolyte oxygen sensor[J]. Journal of Physics E:Scientific Instruments, 1984, 17(6): 477-482. doi: 10.1088/0022-3735/17/6/014 [6] MERILÄINEN P T. Sensors for oxygen analysis: paramagnetic, electrochemical, polarographic, and zirconium oxide technologies[J]. Biomedical Instrumentation &Technology, 1989, 23(6): 462-466. [7] 刘云燕, 潘教青, 程传福, 等. 半导体金宝搏188软件怎么用 器在氧气探测中的应用及关键技术[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与红外,2011,41(5):501-505. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2011.05.004LIU Y Y, PAN J Q, CHENG CH F, et al. Application and key technologies of semiconductor laser in the detection of oxygen[J]. Laser &Infrared, 2011, 41(5): 501-505. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2011.05.004 [8] 谢耀, 华道柱, 齐宇, 等. GFC-IFC技术在多组分微量气体分析中的应用[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(6):1378-1386. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0064XIE Y, HUA D ZH, QI Y, et al. Applications of GFC-IFC in trace multi-component gas analysis[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(6): 1378-1386. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0064 [9] MA Y F, HE Y, TONG Y, et al. Quartz-tuning-fork enhanced photothermal spectroscopy for ultra-high sensitive trace gas detection[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(24): 32103-32110. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.032103 [10] MA Y F, LEWICKI R, RAZEGHI M, et al. QEPAS based ppb-level detection of CO and N2O using a high power CW DFB-QCL[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(1): 1008-1019. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.001008 [11] 张步强, 许振宇, 刘建国, 等. 基于波长调制技术的金宝搏188软件怎么用 器调制特性研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2019,39(9):2702-2707.ZHANG B Q, XU ZH Y, LIU J G, et al. Modulation characteristics of laser based on wavelength modulation technology[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(9): 2702-2707. (in Chinese) [12] 钟笠, 宋迪, 焦月, 等. 具有复杂光谱特征的丙烯气体的TDLAS检测技术研究[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(5):1044-1054. doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0203ZHONG L, SONG D, JIAO Y, et al. TDLAS detection of propylene with complex spectral features[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(5): 1044-1054. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0203 [13] SCHLOSSER H E, WOLFROM J, EBERT V, et al. In situ determination of molecular oxygen concentrations in full-scale fire-suppression tests using tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2001: 353-360. [14] 张春晓. 基于可调谐半导体金宝搏188软件怎么用 吸收光谱技术的O2和CO气体测量[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2010: 86.ZHANG CH X. O2 and CO sensing based on tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2010: 86. (in Chinese) [15] GAO Y W, ZHANG Y J, CHEN D, et al. Real-time O2 measurement in a cement kiln with a TDLAS analyzer[J]. Proceedings of the SPIE, 2016, 10155: 101552R. [16] ZHOU X, YU J, WANG L, et al. Sensitive detection of oxygen using a diffused integrating cavity as a gas absorption cell[J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2017, 241: 1076-1081. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.033 [17] 臧益鹏, 聂伟, 许振宇, 等. 基于可调谐二极管金宝搏188软件怎么用 吸收光谱的痕量水汽测量[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(11):1130004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.1130004ZANG Y P, NIE W, XU ZH Y, et al. Measurement of trace water vapor based on tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(11): 1130004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.1130004 [18] 袁志国, 马修真, 刘晓楠, 等. 利用可调谐金宝搏188软件怎么用 吸收光谱技术的柴油机排放温度测试研究[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(2):281-289. doi: 10.3788/co.20201302.0281YUAN ZH G, MA X ZH, LIU X N, et al. Testing on diesel engine emission temperature using tunable laser absorption spectroscopy technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(2): 281-289. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20201302.0281 [19] 邓瑶, 唐雯, 李峥辉, 等. 基于直接吸收峰峰值标定的气体浓度反演方法研究[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与光电子学进展,2021,58(3):0330002.DENG Y, TANG W, LI ZH H, et al. Gas concentration inversion method based on calibration of direct absorption peak value[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(3): 0330002. (in Chinese) -





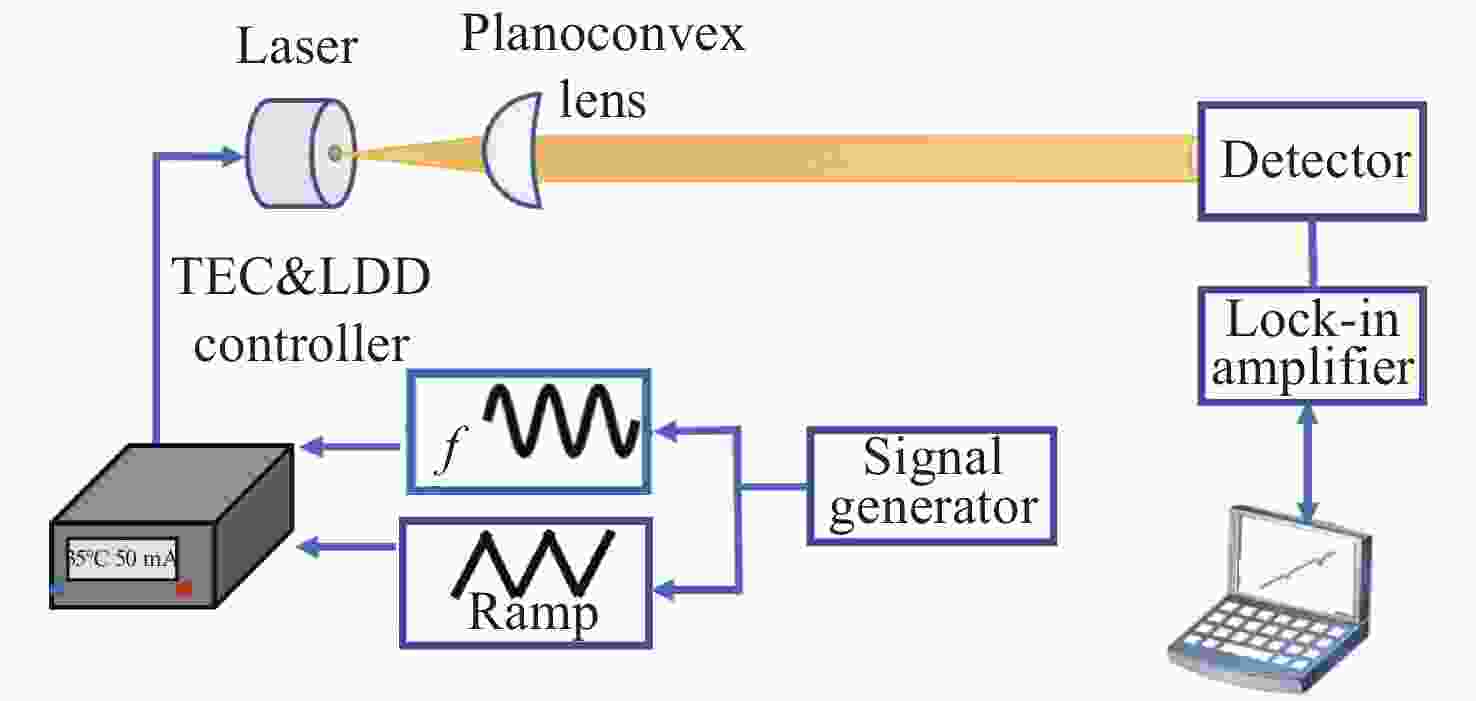
 下载:
下载: