Research progress on high-resolution imaging system for optical remote sensing in aerospace
-
摘要:
随着光学成像技术的不断发展和遥感应用需求的日益增长,跨尺度高分辨率光学技术在遥感领域得到广泛应用。为了获得更多的目标细节信息,国内外研究学者在不同技术方向开展了相关研究。本文对遥感成像技术进行了总结分类,介绍了具有代表性的航天高分辨率对地光学遥感载荷技术,重点关注单体结构主镜、可展开分块拼接主镜、光学干涉主镜、光栅衍射主镜、虚拟合成孔径、光子型综合孔径成像、计算超分辨成像、编队合成孔径等成像模式,为高分辨率对地光学遥感载荷发展提供新的发展思路。
Abstract:With the continuous development of optical imaging technology and the growing demand for remote sensing applications, cross-scale high-resolution optical technology has been widely used in the field of remote sensing. In order to obtain more detailed information on the target, domestic and foreign researchers have carried out relevant research in different technical directions. In this paper, through the technical classification of remote sensing imaging, we introduce a representative aerospace optical remote sensing high-resolution imaging system. It focuses on monomer structure, block expandable imaging, optical interference synthesis aperture imaging, diffraction main mirror imaging, optical synthetic aperture and other technologies. It provides a new idea for the development of high-resolution optical remote sensing loads on the ground.
-
Key words:
- high-resolution /
- optical remote sensing /
- cross-scale
-
表 1 高分辨率光学遥感卫星光学参数
Table 1. Optical parameters of high-resolution optical remote sensing satellites
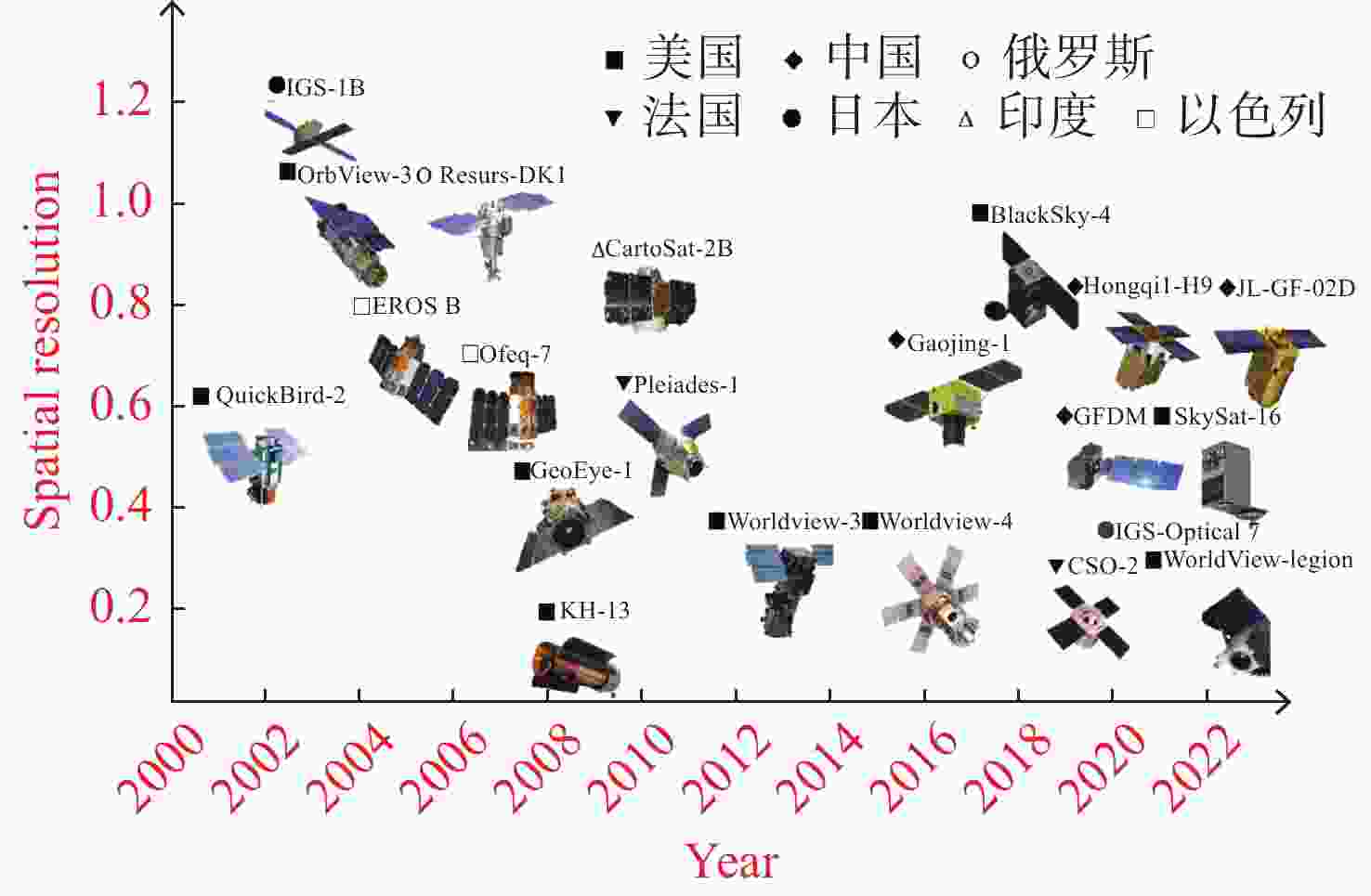
序号 名称 国家 年份 分辨率/m 轨道/km 1 QuickBird-2 美国 2001 0.61 450 2 IGS-1A 日本 2003 1 500 3 OrbView-3 美国 2003 1 470 4 Resurs-DK1 俄罗斯 2006 1 360~610 5 EROS B 以色列 2006 0.7 500 6 Ofeq-7 以色列 2007 0.5 300~600 7 GeoEye-1 美国 2008 0.41 681 8 KH-13 美国 2008 0.07 − 9 CartoSat-2 印度 2010 0.8 635 10 Pleiades-4 法国 2011 0.5 694 11 Worldview-3 美国 2014 0.3 617 12 Gaojing-1 中国 2016 0.5 530 13 Worldview-4 美国 2016 0.25 617 14 BlackSky-4 美国 2018 0.85 450 15 Hongqi1-H9 中国 2020 0.75 481.6 16 GFDM 中国 2020 0.5 643.8 17 IGS-Optical 7 日本 2020 0.3 485 18 SkySat-16 美国 2020 0.5 456 19 JL-GF-02D 中国 2021 0.75 650 20 WorldView –Legion 美国 预计2022 0.3 − 表 2 JEM-EUSO指标参数
Table 2. Index parameters of JEM-EUSO
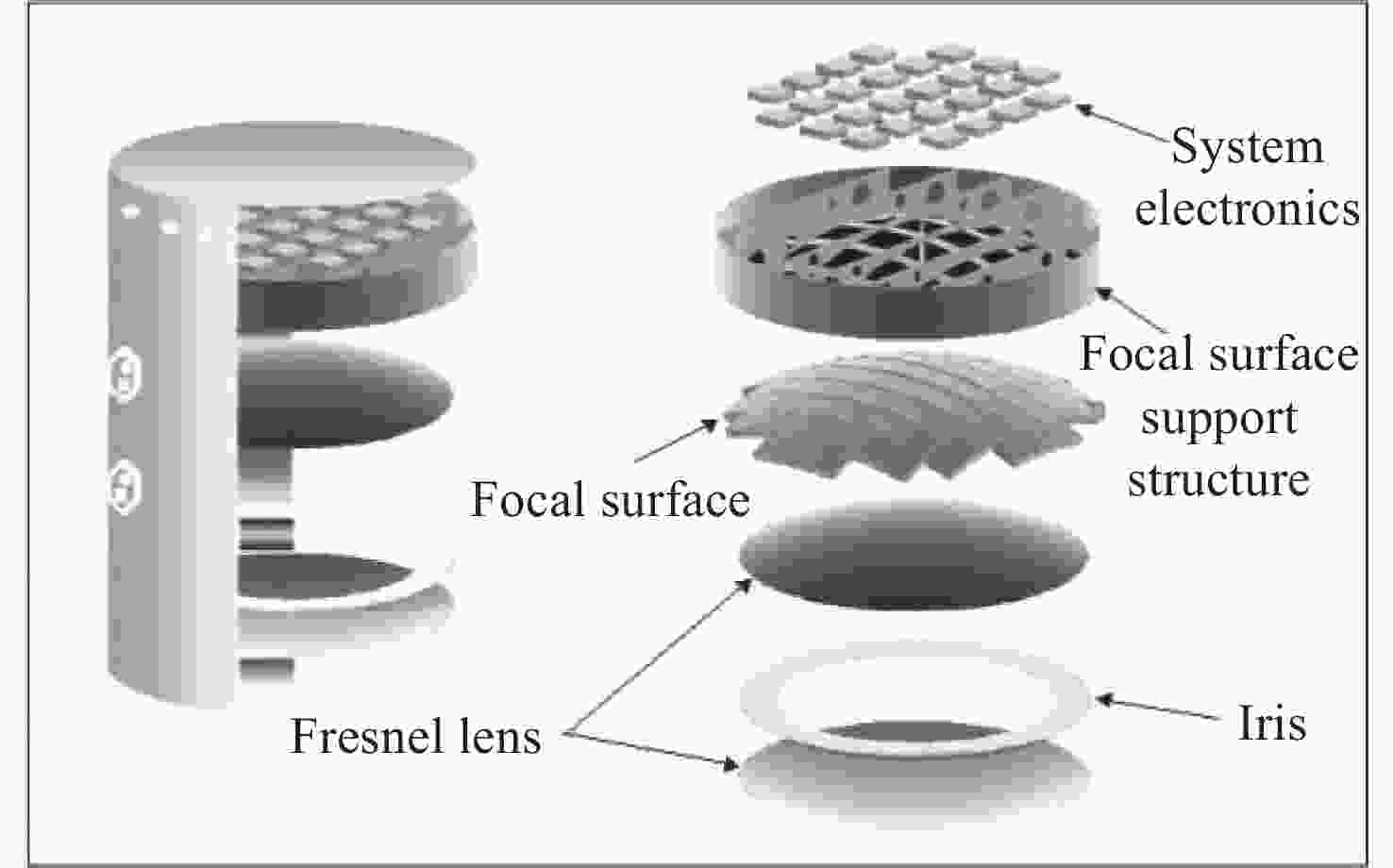
探测谱段/nm 330~400 口径/m 2.5 视场角/(°) ±30 可观测区域/km2 >1.9×105 焦面面积/m2 4.5 像元数 2.0×105 像元尺寸/mm 4.5 角分辨率/(°) 0.1 时间分辨率/μs ≤2.5 表 3 成像观测航天器口径参数
Table 3. Comparison of large aperture imaging observation spacecraft
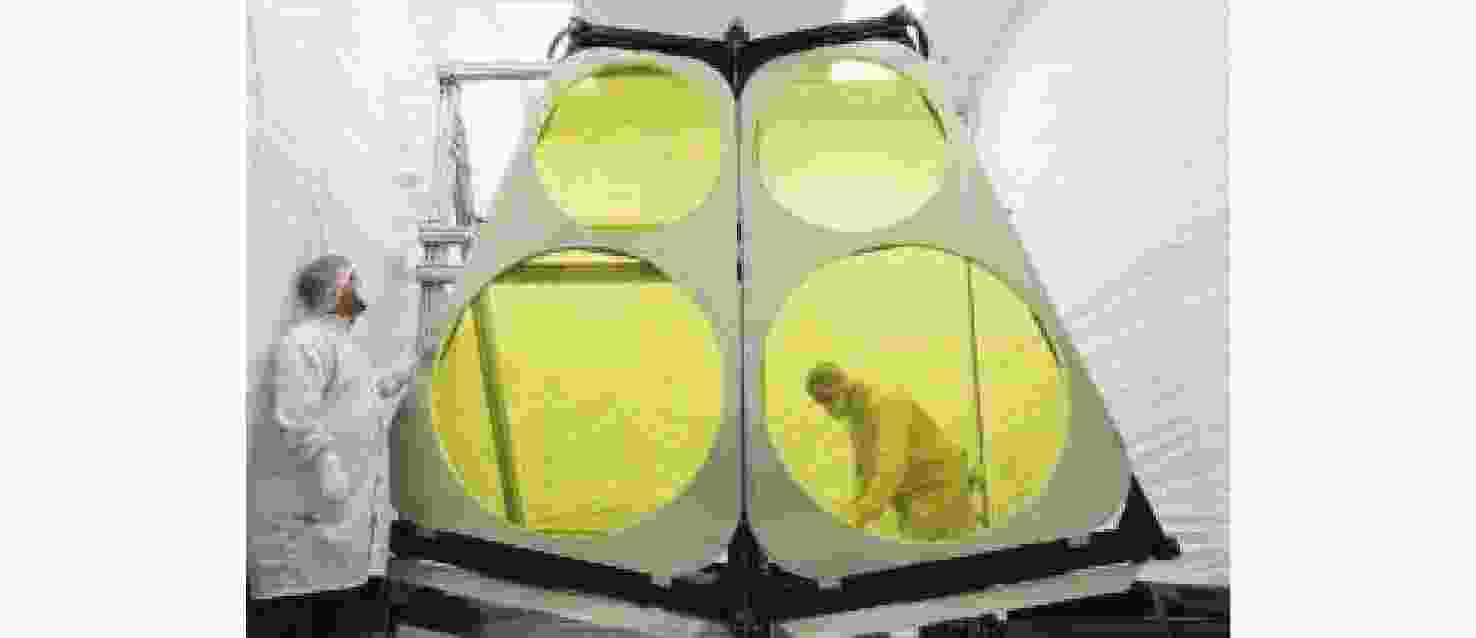
参数 口径/m 主镜 面密度/(kg·m−2) 运行温度/K JWST 6.5 分块 20 50 HST 2.4 单体 180 300 “赫歇尔空间望远镜” 3.5 单体 21.8 90 KH-11 侦察卫星 2.4 单体 不详 常温 KH-12侦察卫星 约3.3 单体 不详 常温 表 4 JWST 航天器基本情况
Table 4. Basic parameters of JWST
参数 基本情况 质量 总质量约6500 kg,主镜质量约705 kg 功率/W 2000 最大数据速率/(Mbit·s−1) 28 主镜 直径6.5 m,由 18 块镀金六边形铍镜组成,
每个镜块的直径为1.32 m,焦距为131.4 m遮阳板 5层可展开遮阳板,展开约21.2 m×14.2 m 观测波长 可见光、近红外、中红外(0.6~28.5 μm) 光学分辨率 大约0.1 仪器 近红外相机、近红外光谱仪、中红外仪器、带
有精巧导航系统的近红外成像仪与无缝光谱仪轨道 日地拉格朗日L2点晕轨道 工作温度/°C −235 任务寿命 5年,目标10年以上 表 5 不同类型遥感成像技术总结
Table 5. Summary of different types of remote sensing imaging technology
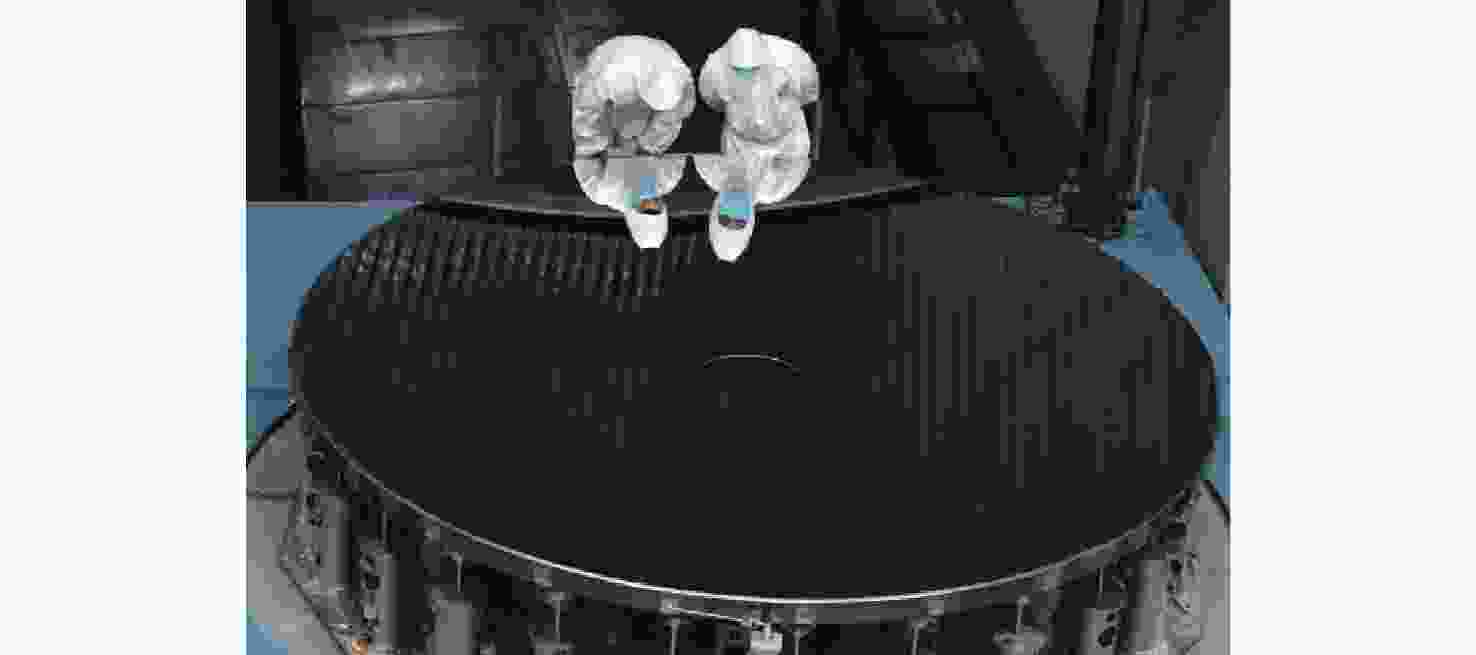
序号 技术名称 优点 缺点 1 大口径单体光学遥感成像技术 技术成熟度高、
成像分辨率高口径受限、系统精密、加工、装调
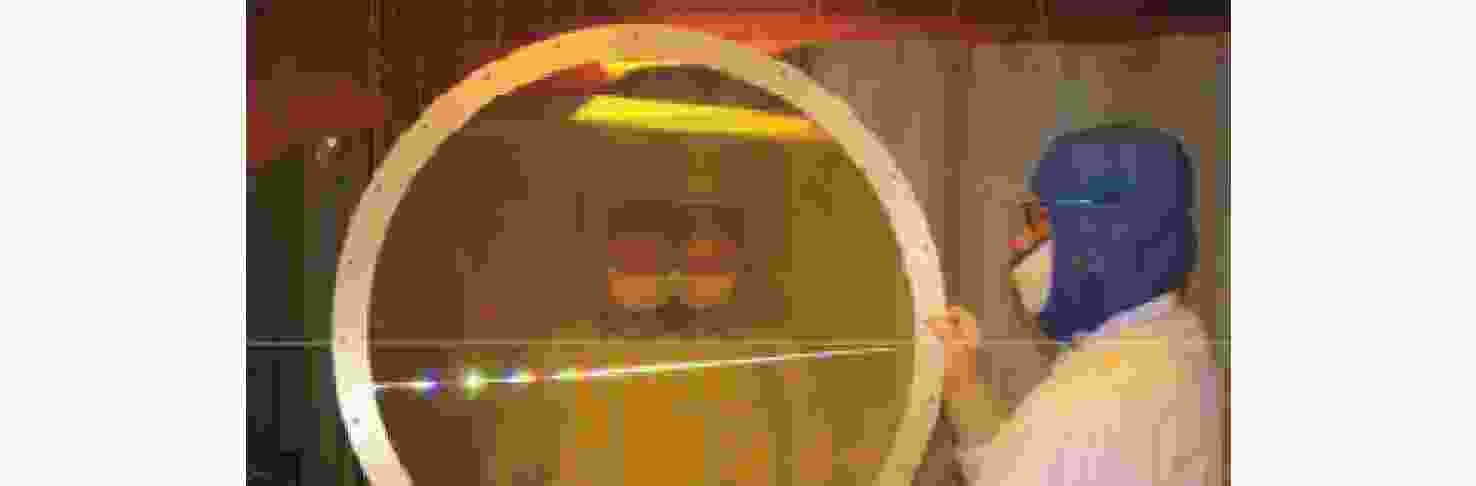
难度大2 单体衍射元件成像系统 系统衍射效率高 成像质量低、衍射元件复杂 3 空间展开式分块镜拼接主镜技术 易满足发射要求、可实现分辨率高 设计难度大、镜面调整难度大 4 光学综合孔径成像系统 可实现大口径成像、
系统结构分布
式灵活布置子孔径共相位调整难度大 5 分块式平板光电成像探测系统 系统集成度高、可实现轻小型化 成像分辨率较低、加工工艺复杂 6 器件亚像素
拼接技术可实现超分辨率成像、可行性高 分辨率提升有限 7 多帧超分辨率成像技术 可实现超分辨率成像、技术成熟 分辨率提升有限、时间分辨率低 8 计算超分主动探测 可实现超分辨率
成像、系统可灵活
分布式构型远距离对主动光源功率要求过高、易受噪声影响 -
[1] 何国金, 李克鲁, 胡德永, 等. 多卫星遥感数据的信息融合: 理论、方法与实践[J]. 中国图象图形学报,1999,4(9):744-750.HE G J, LI K L, HU D Y, et al. Information fusion of multisensor satellite remote sensing data: theory, methodology and experiment[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 1999, 4(9): 744-750. (in Chinese) [2] HUANG J P, YU H P, GUAN X D, et al. Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2016, 6(2): 166-171. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2837 [3] FAN Y D, WEN Q, CHEN SH R. Engineering survey of the environment and disaster monitoring and forecasting small satellite constellation[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2012, 5(3): 217-227. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2011.648540 [4] ZHANG P, HU X P, LU Q F, et al. FY-3E: the first operational meteorological satellite mission in an early morning orbit[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2022, 39(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1007/s00376-021-1304-7 [5] MARTIN S. An Introduction to Ocean Remote Sensing[J]. Oceanography, 2005, 18(3): 86-89. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2005.36 [6] 裴照宇, 侯军, 王琼. 光学技术在中国月球和深空探测中的应用(特约)[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2020,49(5):20201002. doi: 10.3788/irla.2_invited-peizhaoyuPEI ZH Y, HOU J, WANG Q. Applications of optical technology in lunar and deep space exploration in China (Invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(5): 20201002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/irla.2_invited-peizhaoyu [7] 曲宏松, 金光, 张叶. “Next View计划”与光学遥感卫星的发展趋势[J]. 中国光学与应用光学,2009,2(6):467-476.QU H S, JIN G, ZHANG Y. NextView program and progress in optical remote sensing satellites[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics and Applied Optics, 2009, 2(6): 467-476. (in Chinese) [8] BRANDTBERG T, WARNER T. High-spatial-resolution remote sensing[M]//SHAO G F, REYNOLDS K M. Computer Applications in Sustainable Forest Management. Netherlands: Springer, 2006: 19-41. [9] BENEDIKTSSON J A, CHANUSSOT J, MOON W M. Very high-resolution remote sensing: challenges and opportunities [Point of View][J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(6): 1907-1910. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2190811 [10] AKUMU C E, AMADI E O, DENNIS S. Application of drone and WorldView-4 satellite data in mapping and monitoring grazing land cover and pasture quality: pre- and post-flooding[J]. Land, 2021, 10(3): 321. doi: 10.3390/land10030321 [11] TU T M, HUANG P S, HUNG C L, et al. A fast intensity–hue–saturation fusion technique with spectral adjustment for IKONOS imagery[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(4): 309-312. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.834804 [12] AGUILAR M A, DEL MAR SALDAÑA M, AGUILAR F J, et al. Assessing geometric accuracy of the orthorectification process from GeoEye-1 and WorldView-2 panchromatic images[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2013, 21: 427-435. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2012.06.004 [13] ASADZADEH S, DE SOUZA FILHO C R. Investigating the capability of WorldView-3 superspectral data for direct hydrocarbon detection[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 173: 162-173. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.11.030 [14] NGUYEN T T H, PHAM T A, LUONG T P. Estimate tropical forest stand volume using SPOT 5 satellite image[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 652(1): 012016. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/652/1/012016 [15] 曹福成. 高分系列遥感卫星布设中国太空“慧眼”——我国高分专项建设回眸[J]. 中国军转民,2015(1):28-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5874.2015.01.006CAO F CH. The high-score series of remote sensing satellites is deployed in China’s Space “Wise Eye” - a review of China's high-score special construction[J]. Defense Industry Conversion in China, 2015(1): 28-33. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5874.2015.01.006 [16] 曾文, 林辉, 李新宇, 等. 基于高景一号遥感影像的林地信息提取[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报,2020,40(7):32-40. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2020.07.005ZENG W, LIN H, LI X Y, et al. Study on extracting forest information based on SV-1 image[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry &Technology, 2020, 40(7): 32-40. (in Chinese) doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2020.07.005 [17] 张召才. 吉林一号卫星组星[J]. 卫星应用,2015(11):1.ZHANG ZH C. Jilin No. 1 satellite group[J]. Satellite Application, 2015(11): 1. (in Chinese) [18] CASOLINO M, PICOZZA P. Launch and commissioning of the PAMELA experiment on board the resurs-DK1 satellite[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2008, 41(12): 2064-2070. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2007.06.062 [19] KRISHNA B G, SRINIVASAN T P, SRIVASTAVA P K. An integrated approach for topographical mapping from space using Cartosat-1 and Cartosat-2 imagery[C]//ISPRS Congress 2008. 2008. [20] TU T M, HSU C L, TU P Y, et al. An adjustable pan-sharpening approach for IKONOS/QuickBird/GeoEye-1/WorldView-2 imagery[J]. IEEE Journal Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2012, 5(1): 125-134. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2011.2181827 [21] MURTHY K, SHEARN M, SMILEY B D, et al. SkySat-1: Very high-resolution imagery from a small satellite[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9241: 92411e. [22] LEVIN N, JOHANSEN K, HACKER J M, et al. A New source for high spatial resolution night time images —— the EROS-B Commercial Satellite[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 149: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.03.019 [23] BEN-DAVID A. Ofeq-7 bolsters Israel's intelligence coverage[J]. Jane's Defence Weekly, 2007, 44(25): 17. [24] LIU J F, WANG H J, SUN D W, et al. On-orbit adjustment and compensation for large aperture optical system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica,34(3):, 0322, 005: 2014. [25] PANG ZH H, FAN X W, CHEN Q F, et al. Influence of surface-profile error of larger mirror on aberrations characteristics of optical system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2013, 33(4): 0422002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.0422002 [26] LIU SH T, HU R, LI Q H, et al. Topology optimization-based lightweight primary mirror design of a large-aperture space telescope[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(35): 8318-8325. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.008318 [27] HU R, LIU SH T, LI Q H. Topology-optimization-based design method of flexures for mounting the primary mirror of a large-aperture space telescope[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(15): 4551-4560. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.004551 [28] YI K, MA P, QIU H, et al. Progress on large aperture transport mirrors[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(12): 2902-2907. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162412.2902 [29] 常君磊, 李庆林, 李富强, 等. 航天光学遥感探测器滤光片环境考核方法[J]. 航天器环境工程,2018,35(1):87-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2018.01.016CHANG J L, LI Q L, LI F Q, et al. Environmental adaptability assessment of the filter of space optical remote sensor detector[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2018, 35(1): 87-91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2018.01.016 [30] ZHENG D H, CHEN L, ZHU W H. Research on adjusting and testing of off-axis paraboloid mirror with large aperture[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9684: 968406. [31] MATHEW L M, DEEPAK B P, SABU B. Design and analysis of a metallic Ogive payload fairing for a new generation launch vehicle[J]. IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering, 2016, 13(5): 99-103. [32] GUO J, GONG D P, ZHU L, et al. Calculation of overlapping pixels in interleaving assembly of CCD focal plane of mapping camera[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2013, 21(5): 1251-1257. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20132105.1251 [33] ZHANG Y L, LU B, ZHANG W T, et al. A new method for detecting moving objects in video[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019, 48(1): 46-52. [34] LIN H B, BO Y CH, WANG J D, et al. Research progress in super-resolution mapping from remotely sensed imagery[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2011, 16(4): 495-502. [35] SICA L. Effects of nonredundance on a synthetic-aperture imaging system[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1993, 10(4): 567-572. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.10.000567 [36] MACKENZIE C, SWEETMAN B. Snakes and lasers[J]. Aviation Week & Space Technology, 2012. [37] MATTHEW F, MATTHEW R, DOUGLAS E, et al. The future of Earth observation in hydrology[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2017, 21(7): 3879-3914. [38] 吴同舟, 王浩, 周峰, 等. 基于月球观测的“高分四号”卫星相机在轨MTF测试[J]. 航天返回与遥感,2019,40(1):41-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2019.01.005WU T ZH, WANG H, ZHOU F, et al. The Lunar trail of GF-4 satellite and on-orbit knife-edge measurements of MTF[J]. Spacecraft Recovery &Remote Sensing, 2019, 40(1): 41-49. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2019.01.005 [39] 童旭东. 中国高分辨率对地观测系统重大专项建设进展[J]. 遥感学报,2016,5:775-780.TONG X D. Progress in the construction of chinese major special project on high-resolution earth observation system[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 5: 775-780. (in Chinese) [40] 郭疆. 碳化硅大口径空间反射镜设计与制造研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019.GUO J. Research on design and manufacturing of large aperture space mirror of silicon carbide[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019. [41] 邵梦旗. 空间相机光机结构集成优化设计方法研究[D]. 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2021. DOI: 10.27522/d.cnki.gkcgs.2021.000079.SHAO M Q, Space camera optical structure integration optimization design method research[D]. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2021. DOI: 10.27522/d.cnki.gkcgs.2021.000079. [42] 汪逸群, 王龙, 郭万存, 等. 空间多用途双面反射镜的设计与制备[J]. 光学学报,2015,35(4):0428001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.0428001WANG Y Q, WANG L, GUO W C, et al. Design and manufacture of space all-purpose double-faced reflective mirror[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(4): 0428001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.0428001 [43] JAHNS J J. TURUNEN, F. W (eds. ), Diffractive Optics for Industrial and Commercial Applications[M], Berlin: Akademie Verlag, , Germany, 1997: 426 [44] MADSEN C K. Linking diffractive and geometrical optics surface scattering at a fundamental level[J]. Optics and Photonics Journal, 2022, 12(1): 1-17. doi: 10.4236/opj.2022.121001 [45] DUFRESNE E R, GRIER D G. Optical tweezer arrays and optical substrates created with diffractive optics[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1998, 69(5): 1974-1977. doi: 10.1063/1.1148883 [46] ATCHESON P D, STEWART C, DOMBER J, et al. MOIRE: Initial demonstration of a transmissive diffractive membrane optic for large lightweight optical telescopes[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8442: 844221. doi: 10.1117/12.925413 [47] ATCHESON P, DOMBER J, WHITEAKER K, et al. MOIRE: Ground demonstration of a large aperture diffractive transmissive telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9143: 91431W. [48] 赵新龙, 成志铎, 刘君. 复杂战场环境导弹发射装置隐身防护技术研究[J]. 现代防御技术,2016(1):146-150,160.ZHAO X L, CHENG Z D, LIU J. Research on stealth protection technology for missile launchers in complex battlefield environments[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2016(1): 146-150,160. (in Chinese) [49] ATCHESON PAUL D. MOIRE: initial demonstration of a transmissive diffractive membrane optic for large lightweight optical telescopes[J]. 2012, 8442 : 844221-844221-14. [50] DOMBER J L, PAUL D A, JEFF K. MOIRE: ground test bed results for a large membrane telescope[C]. Spacecraft Structures Conference. 2014. [51] 王若秋.基于衍射成像系统的薄膜元件关键技术研究[D]. 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2017.WANG R Q. Key Technology research on thin film components based on diffraction imaging system[D]. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2017. [52] DOMBER J L, ATCHESON P D, KOMMERS J. MOIRE: Ground test bed results for a large membrane telescope[C]//Spacecraft Structures Conference. 2014. [53] TANDY W D, COPP T, CAMPBELL L, et al.. MOIRE gossamer space telescope-membrane analysis[C]//Spacecraft Structures Conference. 2014. [54] STAGUHN J G, BENFORD D J, ALLEN C A, et al. Instrument performance of GISMO, a 2 millimeter tes bolometer camera used at the IRAM 30 m telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7020: 702004. doi: 10.1117/12.789764 [55] 郑耀辉. 空间薄膜衍射望远镜主镜展开技术研究[D]. 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2016.ZHENG Y H. Space thin-film diffraction telescope primary mirror unfolding technique study[D]. Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016. [56] CATALANO O. Extreme Universe Space Observatory-EUSO: An innovative project for the detection of extreme energy cosmic rays and neutrinos[J]. Il Nuovo Cimento C, 2001, 24(3): 445-469. [57] SANTANGELO A, PETROLINI A. Observing ultra-high-energy cosmic particles from space: s-EUSO, super-extreme universe space observatory mission[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2009, 11(6): 065010. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/11/6/065010 [58] PETROLINI A. The extreme universe space observatory (EUSO) instrument[J]. Nuclear Physics B - Proceedings Supplements, 2002, 113(1-3): 329-336. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5632(02)01860-1 [59] TAKIZAWA Y, EBISUZAKI T, KAWASAKI Y, et al. JEM-EUSO: Extreme universe space observatory on JEM/ISS[J]. Nuclear Physics B-Proceedings Supplements, 2007, 166: 72-76. doi: 10.1016/j.nuclphysbps.2006.12.007 [60] ANDERSEN G, ASMOLOV O, DEARBORN M E, et al. FalconSAT-7: a membrane photon sieve CubeSat solar telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8442: 84421C. [61] ANDERSEN G P, ASMOLOVA O. FalconSAT-7: a membrane space telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9143: 91431X. [62] ANDERSEN G, ASMOLOVA O, MCHARG M G, et al. FalconSAT-7: a membrane space solar telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9904: 99041P. [63] DEARBORN M, ANDERSEN G, MCHARG M G, et al.. FALCONSAT-7: A Deploy Able Solar Telescope Mission[C]//28th Annual AIAA/USU Conference of Small Satellites, 2012. [64] 郭明. 卫星大尺度展开机构地面测控系统的设计与实现[D]. 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.GUO M. Design and implementation of a ground-based measurement and control system for large scale satellite deployment mechanism[D]. Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. [65] HYDE R A. Eyeglass. 1. Very large aperture diffractive telescopes[J]. Applied Optics, 1999, 38(19): 4198-4212. doi: 10.1364/AO.38.004198 [66] HYDE R A, DIXIT S N, WEISBERG A H, et al. Eyeglass: a very large aperture diffractive space telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2002, 4849: 28-39. doi: 10.1117/12.460420 [67] HYDE R A, DIXIT S N, WEISBERG A H, et al. . Large aperture diffractive space telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, 2001. [68] HYDE R. Eyeglass large aperture, lightweight space optics FY2000 - FY2002 LDRD strategic initiative[R]. Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Lab. , 2003. [69] 王昊, 康福增, 赵卫, 谢永军. 一种红外衍射望远镜的光学设计[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2016,35(4):425-429.WANG H, KANG F Z, ZHAO W, XIE Y J. Optical design of an infrared diffraction telescope[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2016, 35(4): 425-429. (in Chinese) [70] 陈晓丽, 傅丹鹰. 大口径甚高分辨率空间光学遥感器技术途径探讨[J]. 航天返回与遥感,2003,24(4):19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2003.04.005CHEN X L, FU D Y. Solutions for space optical remote sensor with large aperture and ultrahigh resolution[J]. Spacecraft Recovery &Remote Sensing, 2003, 24(4): 19-24. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2003.04.005 [71] WANG R Q, ZHANG ZH Y, GUO CH L, et al. Effects of fabrication errors on diffraction efficiency for a diffractive membrane[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14(12): 120501. doi: 10.3788/COL201614.120501 [72] XUE CH X, CUI Q F. Design of multilayer diffractive optical elements with polychromatic integral diffraction efficiency[J] Optics Letters, 2010, 35(7): 986-988. [73] 刘民哲, 刘华, 许文斌, 等. 用于空间望远镜的膜光子筛[J]. 光学 精密工程,2014,22(8):2127-2134. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20142208.2127LIU M ZH, LIU H, XU W B, et al. Membrane photon sieve for space telescope[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2014, 22(8): 2127-2134. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20142208.2127 [74] 张健, 栗孟娟, 阴刚华, 等. 用于太空望远镜的大口径薄膜菲涅尔衍射元件[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(6):1289-1296. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162406.1289ZHANG J, SU M Y, YIN G H, et al. Large-diameter membrane fresnel diffraction elements for space telescope[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(6): 1289-1296. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162406.1289 [75] DANIEL J. SCHROEDER. Reflecting Telescopes in Astronomical Optics (Second Edition) [M]. Elsevier Inc, 2000, 112-163. [76] NICHOLAS G, KEDAR K. Digital Binary MEMS Wavefront Control, US, 8379292-B2[P]. 2013-02-19. [77] LIESENER J, HUPFER W J, GEHNER R, et al. Tests on micromirror arrays for adaptive optics[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5553: 319-329. doi: 10.1117/12.558679 [78] DEKANY R G, MACMARTIN D G, CHANAN G A, et al. Advanced segmented silicon space telescope (ASSIST)[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2002, 4849: 103-111. doi: 10.1117/12.460563 [79] AGRAWAL B, KUBBY J. Applications of MEMS in segmented mirror space telescopes[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 7931: 793102. [80] MARK C. The James Webb Space Telescope[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2008, 41(12): 1983-1991. [81] DEAN B H, ARONSTEIN D L, SMITH J S, et al. Phase retrieval algorithm for JWST flight and testbed telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6265: 626511. doi: 10.1117/12.673569 [82] WRIGHT G S, RIEKE G H, COLINA L, et al. The JWST MIRI instrument concept[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5487: 653-663. doi: 10.1117/12.551717 [83] FREESE K, ILIE C, SPOLYAR D, et al. Supermassive dark stars: detectable in JWST[J]. The Astrophysical Journal, 2010, 716(2): 1397-1407. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/716/2/1397 [84] THOMAS E. Towards 1 m Resolution from GEO Executive Summary Report[B]. Thales Alenia Space, Italy, 2010: 1-13. [85] BOLCAR M R, FEINBERG L, FRANCE K, et al. Initial Technology Assessment for the Large-Aperture UV-Optical-Infrared (LUVOIR) Mission Concept Study[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9904: 99040J. [86] STAHL H P, HOPKINS R C. SLS Launched missions concept studies for LUVOIR mission[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9602: 960206. [87] FRANCE K, FLEMING B, WEST G, et al. The LUVOIR ultraviolet multi-object spectrograph (LUMOS): instrument definition and design[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10397: 1039713. [88] MENNESSON B, GAUDI S, SEAGER S, et al. The Habitable Exoplanet (HabEx) imaging mission: preliminary science drivers and technical requirements[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9904: 99040L. [89] 陈晓丽, 杨秉新, 王永辉, 等. 空间可展开光学系统主镜分块方案研究[J]. 航天返回与遥感,2008,29(1):28-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2008.01.006CHEN X L, YANG B X, WANG Y H, et al. Segmentation of primary mirror for the space deployable optical system[J]. Spacecraft Recovery &Remote Sensing, 2008, 29(1): 28-33. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2008.01.006 [90] 郭崇岭, 陈传志, 陈金宝, 等. 空间光学望远镜在轨建造中的结构机构技术[J]. 宇航学报,2022,43(2):158-166. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2022.02.003GUO CH L, CHEN CH ZH, CHEN J B, et al. Structure and mechanism technology of in-space manufacturing space optical telescope[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2022, 43(2): 158-166. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2022.02.003 [91] 金建高, 阮宁娟, 苏云, 等. 空间大型光学遥感器主镜问题解决方法探讨[J]. 空间电子技术,2016,13(2):20-25,43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2016.02.005JIN J G, RUAN N J, SU Y, et al. Discussion for solution of huge space remote sensor primary mirror issue[J]. Space Electronic Technology, 2016, 13(2): 20-25,43. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2016.02.005 [92] 乔彦峰, 刘坤, 段相永. 光学合成孔径成像技术及发展现状[J]. 中国光学与应用光学,2009,2(3):175-183.QIAO Y F, LIU S, DUAN X Y. Optical synthetic aperture imaging techniques and development[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics and Applied Optics, 2009, 2(3): 175-183. (in Chinese) [93] 范伟军, 周必方, 王海涛. 光学综合孔径成像中的傅里叶相位研究[J]. 光学学报,2004,24(3):408-412.FAN W J, ZHOU B F, WANG H T. Research of Fourier phase in optical synthetic-aperture imaging technique[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2004, 24(3): 408-412. (in Chinese) [94] LUCKE R L, RICKARD L J. Photon-limited synthetic-aperture imaging for planet surface studies[J]. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(24): 5084-5095. doi: 10.1364/AO.41.005084 [95] LIU ZH, WANG SH Q, RAO CH H. The Co-phasing detection method for sparse optical synthetic aperture systems[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2012, 21(6): 069501. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/21/6/069501 [96] RHODES W T. Digital processing of synthetic aperture optical imagery[J]. Optical Engineering, 1974, 13(3): 267-274. [97] WU Y, HUI M, LI W Q, et al. MTF improvement for optical synthetic aperture system via mid-frequency compensation[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(7): 10249-10264. doi: 10.1364/OE.420512 [98] CHUNG S J, MILLER D W, DE WECK O L. ARGOS testbed: study of multidisciplinary challenges of future spaceborne interferometric arrays[J]. Optical Engineering, 2004, 43(9): 2156-2167. doi: 10.1117/1.1779232 [99] WONG M H. A dedicated space observatory for time-domain solar system science[Z]. AAS/Division for Planetary Sciences Meeting Abstracts. 2009. [100] CHUNG S J, LO B D M, MILLER D W, et al. . Multidisciplinary Control of a Sparse Interferometric Array Satellite Testbed[C]//AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit, AIAA, 2013. [101] LAWSON P R, LAY O P, MARTIN S R, et al. Terrestrial planet finder interferometer 2007—2008 progress and plans[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7013: 70132N. [102] LAWSON P R, LAY O P, MARTIN S R, et al. Terrestrial planet finder interferometer: 2006—2007 progress and plans[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6693: 669308. doi: 10.1117/12.734914 [103] BEICHMAN C, LAWSON P, LAY O, et al. Status of the terrestrial planet finder interferometer (TPF-I)[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6268: 62680S. doi: 10.1117/12.673583 [104] LAWSON P R, AHMED A, GAPPINGER R O, et al. Terrestrial planet finder interferometer technology status and plans[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6268: 626828. doi: 10.1117/12.670318 [105] GUARNIERI A M, BOMBACI O, CATALANO T F, et al. ARGOS: A fractioned geosynchronous SAR[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2019, 164: 444-457. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.11.022 [106] QIAN J H, WU X Y, LIU H W, et al. The structure research and design for beam steering and adjustment in Golay3 sparse-aperture imaging system[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(8): 4003. [107] STUBBS D, DUNCAN A, PITMAN J T, et al. Multiple instrument distributed aperture sensor (MIDAS) evolved design concept[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5550: 391-398. doi: 10.1117/12.560319 [108] PITMAN J, DUNCAN A, STUBBS D, et al. Multiple instrument distributed aperture sensor (MIDAS) for remote sensing[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5570: 168-180. [109] SCUDERI S, GIULIANI A, PARESCHI G, et al. The ASTRI Mini-Array of Cherenkov telescopes at the Observatorio del Teide[J]. Journal of High Energy Astrophysics, 2022, 35: 52-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jheap.2022.05.001 [110] SUZUMOTO R, IKARI S, MIYAMURA N, et al.. Experimental study for synthetic aperture telescope using formation flying micro-satellites for high-frequency and high-resolution GEO remote sensing[C]. 34th Annual Small Satellite Conference, 2020. [111] WANG D Y. Experimental study on imaging and image restoration of optical sparse aperture systems[J]. Optical Engineering, 2007, 46(10): 103201. doi: 10.1117/1.2799512 [112] 马佳. 欧洲启动达尔文计划搜捕地外生命[J]. 今日科苑,2007(15):12-14.MA J. Europe launched the darwin plan to hunt for extraterrestrial life[J]. Modern Science, 2007(15): 12-14. (in Chinese) [113] 周程灏, 王治乐, 朱峰. 大口径光学合成孔径成像技术发展现状[J]. 中国光学,2017,10(1):25-38.ZHOU CH H, WANG ZH Y, ZHU F. Status of development of large-aperture optical synthetic aperture imaging technology[J]. China Optics, 2017, 10(1): 25-38. (in Chinese) [114] SUZUMOTO R, IKARI S, MIYAMURA N, et al.. Experimental study for synthetic aperture telescope using formation flying micro-satellites for high-frequency and high-resolution GEO remote sensing[C]. 34th Annual Small Satellite Conference. 2020. [115] 徐伟, 金光, 王家骐. 吉林一号轻型高分辨率遥感卫星光学成像技术[J]. 光学 精密工程,2017,25(8):1969-1978. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172508.1969XU W, JIN G, WANG J Q. Optical imaging technology of JL-1 lightweight high resolution multispectral remote sensing satellite[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(8): 1969-1978. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172508.1969 [116] DUNCAN A L, KENDRICK R L. Segmented planar imaging detector for electro-optic reconnaissance: US, 8913859[P]. 2014-12-16. [117] DUNCAN A L, KENDRICK R L. Segmented planar imaging detector for electro-optic reconnaissance (SPIDER) Zoom: US, 10012827[P]. 2018-07-03. [118] LV G M, LI Q, CHEN Y T, et al. An improved scheme and numerical simulation of segmented planar imaging detector for electro-optical reconnaissance[J]. Optical Review, 2019, 26(6): 664-675. doi: 10.1007/s10043-019-00548-w [119] CHU Q H, SHEN Y J, YUAN M, et al. Numerical simulation and optimal design of segmented planar imaging detector for electro-optical reconnaissance[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 405: 288-296. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.08.021 [120] 余恭敏, 晋利兵, 周峰, 等. 分块式平面光电侦察成像系统发展概述[J]. 航天返回与遥感,2018,39(5):1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2018.05.001YU G M, JIN L B, ZHOU F, et al. A review on development of segmented planar imaging detector for electro-optical reconnaissance system[J]. Spacecraft Recovery &Remote Sensing, 2018, 39(5): 1-9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2018.05.001 [121] BADHAM K, KENDRICK R, WUCHENICH D, et al.. Photonic integrated circuit-based imaging system for SPIDER[C]. 2017 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Pacific Rim (CLEO-PR), IEEE, 2017. [122] DESEILLIGNY M P, PAPARODITIS N. A multiresolution and optimization-based image matching approach: an application to surface reconstruction from Spot5-hrs stereo imagery[C]//Proc of the ISPRS Conference Topographic Mapping from Space. US, 2006. [123] MURTHY K, SHEARN M, SMILEY B D, et al. SkySat-1: very high-resolution imagery from a small satellite[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9241: 92411E. [124] DINARDJ A, ANFLO K, FRIEDHOFF P. On-orbit commissioning of high performance green propulsion (HPGP) in the SkySat constellation[C]. Small Satellite Conference, 2017. [125] 周宇, 王鹏, 傅丹膺. SkySat卫星的系统创新设计及启示[J]. 航天器工程,2015,24(5):91-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2015.05.014ZHOU Y, WANG P, FU D Y, et al. System innovation and enlightenment of SkySat[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2015, 24(5): 91-98. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2015.05.014 [126] JOHANSEN K, DUNNE A F, TU Y H, et al. Monitoring coastal water flow dynamics using sub-daily high-resolution SkySat satellite and UAV-based imagery[J]. Water Research, 2022, 219: 118531. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118531 [127] 李峰, 杨雪, 鲁啸天, 等. 面向星载CMOS相机的超时相工作方式研究[J]. 遥感学报,2021,25(1):514-525.LI F, YANG X, LU X T, et al. A new hyper-temporal imaging mode for spaceborne CMOS cameras[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2021, 25(1): 514-525. (in Chinese) [128] 谢伟, 陈皓, 秦前清. 基于多帧视频序列的盲超分辨率影像重建[J]. 数据采集与处理,2011,26(1):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2011.01.001XIE W, CHEN H, QIN Q Q. Blind super-resolution image reconstruction based on multiframe video sequence[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition &Processing, 2011, 26(1): 1-7. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2011.01.001 [129] ZHENG G A, HORSTMEYER R, YANG C H E. Wide-field, high-resolution Fourier ptychographic microscopy[J]. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(9): 739-745. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.187 [130] HOLLOWAY J, WU Y, SHARMA M K, et al. SAVI: Synthetic apertures for long-range, subdiffraction-limited visible imaging using fourier ptychography[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(4): e1602564. [131] DONG S Y, HORSTMEYER R, SHIRADKAR R, et al. Aperture-scanning Fourier ptychography for 3D refocusing and super-resolution macroscopic imaging[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(11): 13586-13599. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.013586 [132] HOLLOWAY J, ASIF M S, SHARMA M K, et al. Toward long-distance subdiffraction imaging using coherent camera arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2017, 2(3): 251-265. [133] WANG C Y, HU M, TAKASHIMA Y, et al. Snapshot Ptychography on Array cameras[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(2): 2585-2598. doi: 10.1364/OE.447499 [134] WU J CH, YANG F, CAO L C. Resolution enhancement of long-range imaging with sparse apertures[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2022, 155: 107068. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2022.107068 [135] 赵明, 王希明, 张晓慧, 等. 宏观傅里叶叠层超分辨率成像实验研究[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与光电子学进展,2019,56(12):101-107.ZHAO M, WANG X M, ZHANG X H, et al. Experimental research on macroscopic Fourier ptychography super-resolution imaging[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(12): 101-107. (in Chinese) [136] 相萌. 宏观傅里叶叠层成像的关键问题研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学, 2021.XIANG M. Study on key problems of macroscopic Fourier ptychography imaging[D]. Xi’an: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese) -





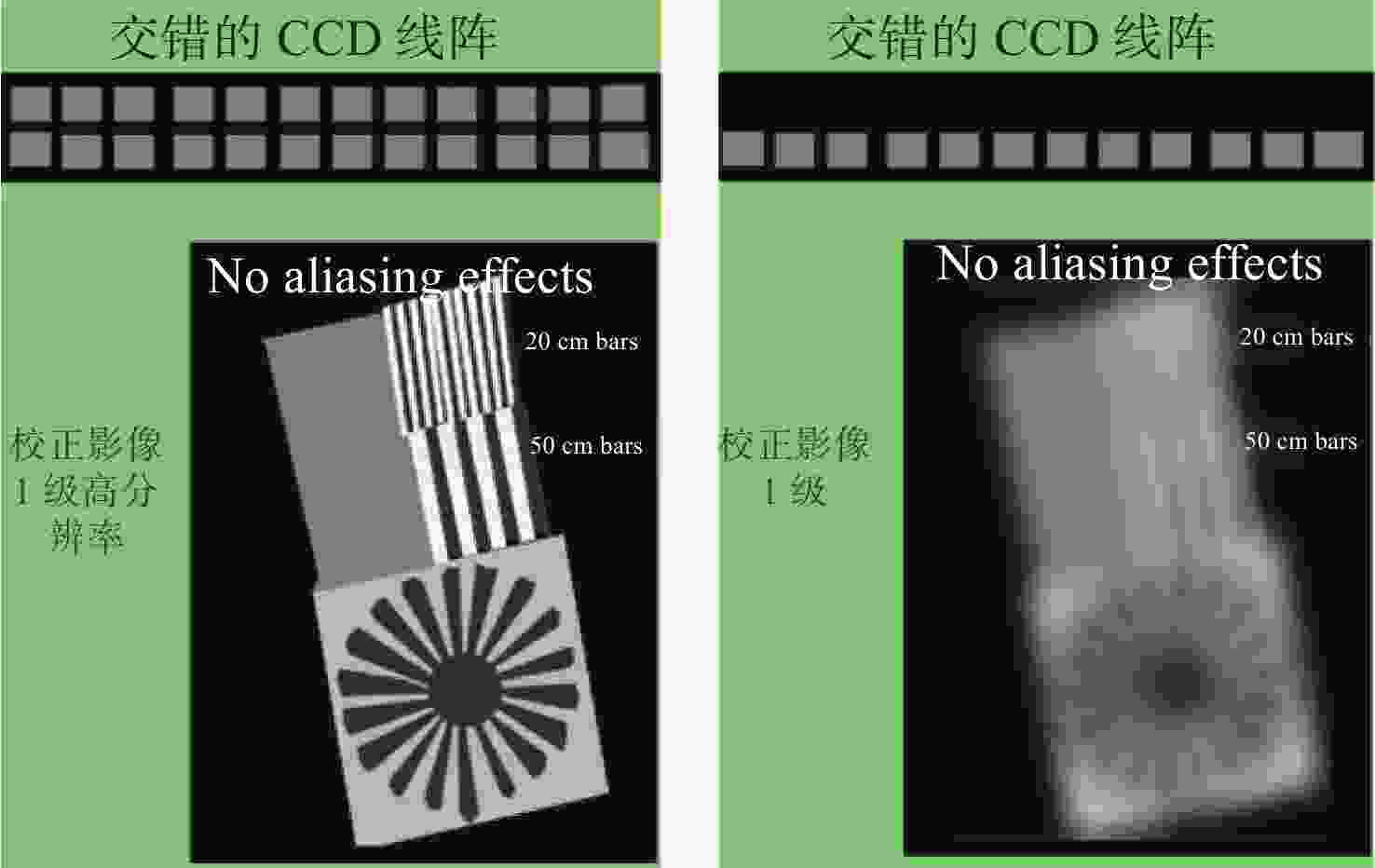
 下载:
下载: