Overview of key technologies for segmented mirrors of large-aperture optical telescopes
-
摘要:
随着天文探测的不断发展,望远镜的口径越来越大,拼接镜面技术为大口径望远镜主镜的设计提供了一种比单镜面形式更简单可行的替代方案,现已成为大口径望远镜主镜设计的重要途径。本文以詹姆斯·韦伯空间望远镜(JWST)和三十米望远镜(TMT)等典型拼接式望远镜的主镜设计为参考,总结了当前拼接镜面技术的发展现状;并阐述了在大规模子镜背景下,不同子镜拼接方案的性能差异,以及镜面支撑技术和共相检测技术的未来发展趋势,希望可以为我国下一代极大口径光学望远镜的自主研制提供参考。
Abstract:With the continuous development of astronomical exploration, the aperture of telescopes is getting larger and larger. Segmented mirror technology offers a viable and much simpler alternative to a large single monolithic primary mirrors, and has become an important way of designing the primary mirror of large-aperture telescopes. This paper summarizes the current development status of various technologies with reference to the primary mirror design of typical segmented telescopes such as the JWST and TMT, and elaborates on the performance differences and mirror supports of different segmented primary mirror schemes under the background of large-scale sub-mirrors. Potential future development trends of this technology and co-phasing detection technology are provided. This research acts as a reference for the independent development of the next generation of very large aperture optical infrared telescopes in China.
-
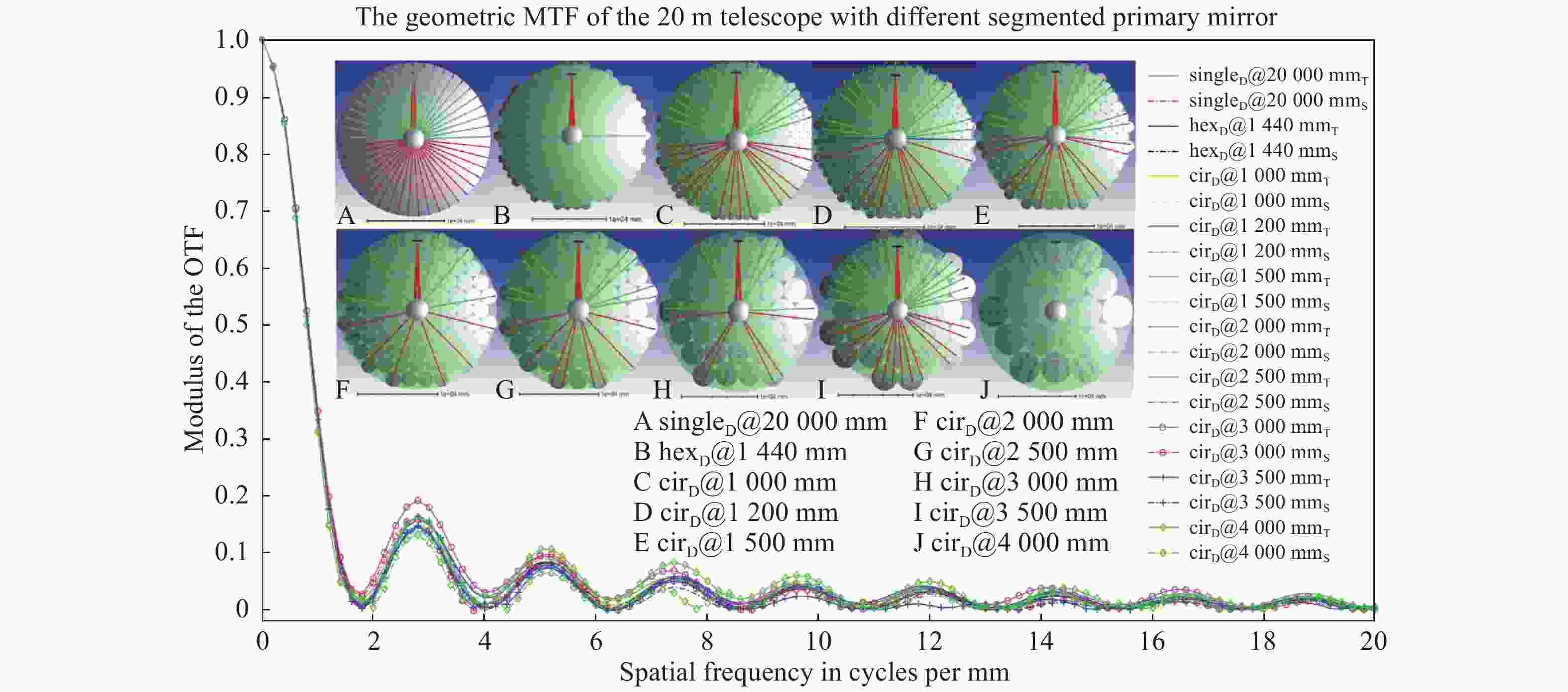
表 1 不同子镜形状差异
Table 1. Comparison of different sub-mirror shapes
子镜形状 拼接间隙 对称性 子镜种类 制造难度 六边形 较小 六重 多 较大 扇形 小 一般 较少 大 圆形 大 好 少 小 表 2 大型拼接镜面望远镜基本参数
Table 2. Basic parameters of large segmented mirror telescopes
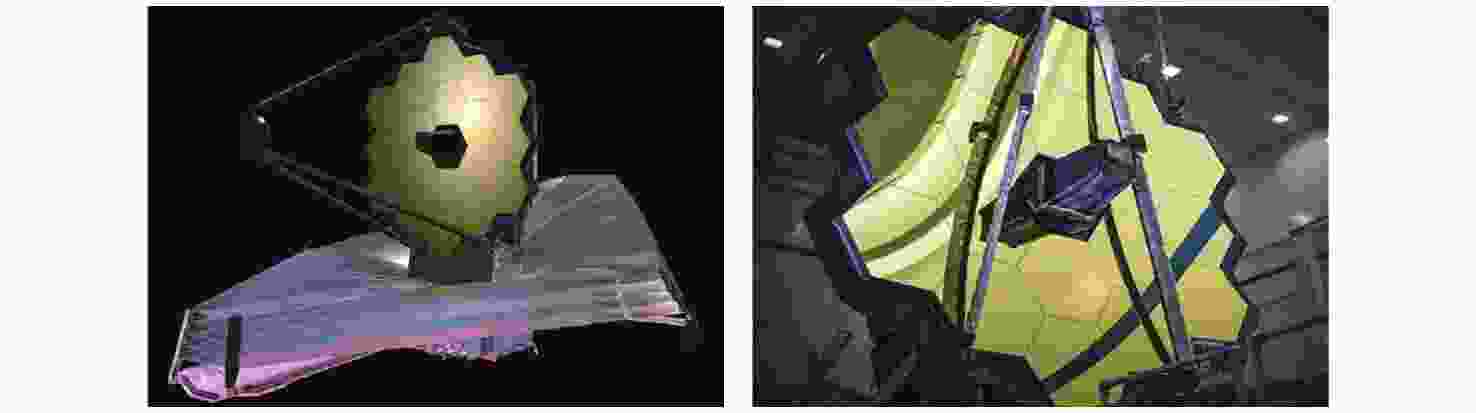
时间选址 名称 主镜 拼接子镜 等效口径/m 材料 形状 数量 尺寸/m 1993 American Keck Ⅰ 10 Zerodur Hexagon 36 1.8 1996 American Keck Ⅱ 10 Zerodur Hexagon 36 1.8 1997 American HET 9.2 Zerodur Hexagon 91 1.15 2005 South Africa SALT 9.5 Glass-ceramic Hexagon 91 1.16 2008 Spain GTC 10.4 Glass-ceramic Hexagon 36 1.9 2008 China LAMOST 4 Zerodur Hexagon 61 1.1 2019 Japan Seimei 3.8 Zerodur Petals 18 1.2 2021 American JWST 6.5 Be Hexagon 18 1.5 — American GMT 21 E6 Circular 7 8.4 — American TMT 30 Zerodur Hexagon 492 1.44 — Europe E-ELT 39.3 Zerodur Hexagon 798 1.4 — China LOT 12 Zerodur Hexagon 84 1.44 表 3 大型拼接望远镜支撑结构
Table 3. Large segmented mirror telescope support structures
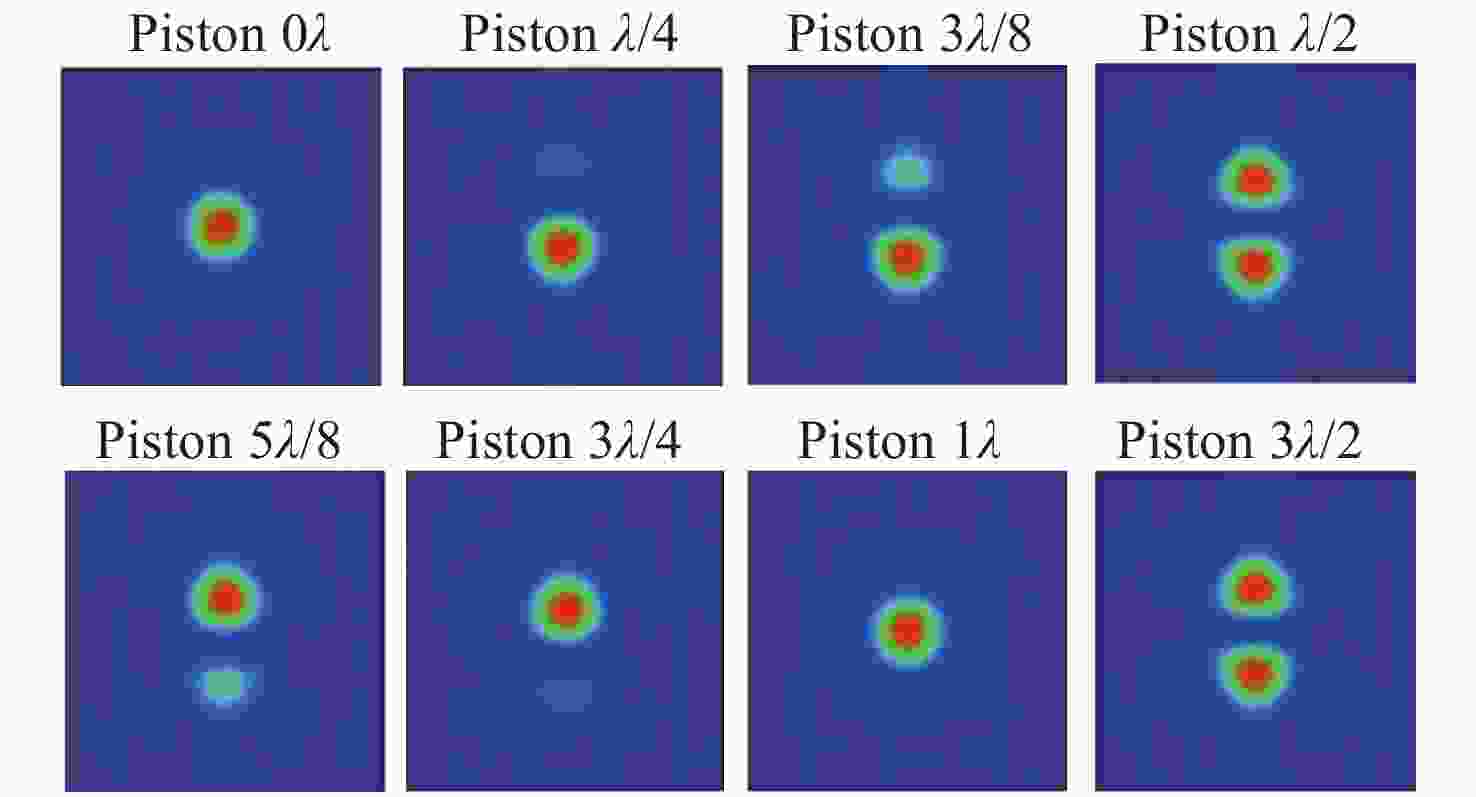
Keck HET SALT GTC LAMOST TMT E-ELT 支撑点数 36-pt 9-pt 9-pt 36-pt 18-pt 27-pt 27-pt 轴向支撑 Whiffletree Whiffletree Whiffletree Whiffletree Whiffletree Whiffletree Whiffletree 径向支撑 中心膜片 中心膜片 中心膜片 中心膜片 中心膜片 中心膜片 中心膜片 Warping Harness 手动 无 无 自动 无 自动 自动 促动方式 直接促动 直接促动 移动架 直接促动 直接促动 移动架 移动架 表 4 共相检测技术的性能对比
Table 4. Performance comparison of co-phasing detection technologies
技术分类 Piston
检测Tip/Tlit
检测光瞳
对准粗/精
共相2π
模糊量程
(λ)非共光
路误差像平面 PD Y Y N 精 Y ±λ/2 N PR Y Y N 精 Y ±λ/2 N 光瞳面 SHAPS Y Y Y 粗/精 Y ±λ/2 Y PY Y Y Y 精 Y ±λ/4 Y ZELDA Y Y N 粗/精 Y ±λ/2 Y DHS/DFS Y N Y 粗/精 N ±λ/2 Y PISTIL Y Y N 精 Y 3λ Y 中间面 DIPSI Y Y N 粗/精 Y ±λ/2 N CS Y Y N 精 Y ±λ/8 N -
[1] 张景旭. 地基大口径望远镜系统结构技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2012,5(4):327-336. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2012.04.004ZHANG J X. Overview of structure technologies of large aperture ground-based telescopes[J]. Chinese Optics, 2012, 5(4): 327-336. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2012.04.004 [2] KIM D, CHOI H, BRENDEL T, et al. Advances in optical engineering for future telescopes[J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2021, 4(6): 210040. doi: 10.29026/oea.2021.210040 [3] 罗群. 相位差波前探测技术及其在拼接镜共相检测中的应用研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2012.LUO Q. Studies on the phase diversity wavefront sensor and Co-phasing measurement for segmented mirrors[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2012. (in Chinese) [4] 曹海峰. 大型光学红外望远镜拼接镜面主动光学技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2020.CAO H F. Research on the technologies of active optics for large aperture segmented optical/infrared telescope[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese) [5] 范文强, 王志臣, 陈宝刚, 等. 地基大口径拼接镜面主动控制技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1194-1208. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0032FAN W Q, WANG ZH CH, CHEN B G, et al. Review of the active control technology of large aperture ground telescopes with segmented mirrors[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1194-1208. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0032 [6] 安其昌. 三十米望远镜三镜集成检测关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2018.AN Q CH. Thirty meter telescope tertiary mirror alignment and metrology[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018. (in Chinese) [7] 蔡峥, 张超, 樊凡. 天文望远镜的历史与展望——兼论清华宽视场巡天望远镜(MUST)[J]. 实验技术与管理,2021,38(5):1-9,37.CAI ZH, ZHANG CH, FAN F. History and prospect of astronomical telescopes: introducing Tsinghua multiplexed survey telescope (MUST)[J]. Experimental Technology and Management, 2021, 38(5): 1-9,37. (in Chinese) [8] 宋家宝, 李国平. 大型光学望远镜扇形子镜拼接设计及仿真分析[J]. 天文研究与技术,2010,7(4):355-361.SONG J B, LI G P. Design and simulation of splicing of sector-shaped segments of a large optical telescope[J]. Astronomical Research &Technology, 2010, 7(4): 355-361. (in Chinese) [9] 雷存栋. 大口径合成孔径望远镜拼接误差分析与控制技术研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2016.LEI C D. Research on stitching errors analysis and control technology for large synthetic aperture telescope[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2016. (in Chinese) [10] KENDRICK S E. Monolithic versus segmented primary mirror concepts for space telescopes[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2009, 7426: 74260O. [11] 李斌. 拼接镜共相检测技术研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 2017.LI B. The co-phasing detection of segmented mirror[D]. Chengdu: Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese) [12] Mirrors Webb_NASA[EB/OL]. https://jwst.nasa.gov/content/observatory/ote/mirrors/index.html. [13] EGRON S, SOUMMER R, LAJOIE C P, et al. James Webb Space Telescope optical simulation testbed Ⅳ: linear control alignment of the primary segmented mirror[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10398: 1039811. [14] 邵亮, 杨飞, 王富国, 等. 1.2 m轻量化SiC主镜支撑系统优化设计[J]. 中国光学,2012,5(3):229-234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2012.03.006SHAO L, YANG F, WANG F G, et al. Design and optimization of supporting system for 1.2 m lightweight SiC primary mirror[J]. Chinese Optics, 2012, 5(3): 229-234. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2012.03.006 [15] 赵宇, 苏成志, 赵贵军, 等. Φ500 mm超轻量化SiC反射镜结构优化设计[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1352-1361. doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0201ZHAO Y, SU CH ZH, ZHAO G J, et al. Structural optimization for the design of an ultra-lightweight SiC mirror with a diameter of 500 mm[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1352-1361. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0201 [16] 赵汝成, 包建勋. 大口径轻质SiC反射镜的研究与应用[J]. 中国光学,2014,7(4):552-558.ZHAO R CH, BAO J X. Investigation and application of large scale lightweight SiC mirror[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(4): 552-558. (in Chinese) [17] 郭疆. 碳化硅大口径空间反射镜设计与制造研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019.GUO J. Research on design and manufacturing of large aperture space mirror of silicon carbide[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019. (in Chinese) [18] 魏祥通. TMT三镜Whiffletree底支撑系统设计与测试方法研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2017.WEI X T. Design and test method study of TMT tertiary mirror whiffletree axial support system[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, 2017. (in Chinese) [19] GUO P, ZHANG J, YANG F, et al. Geometric layout optimization of a large aperture thin elliptical mirror’s axial and lateral support[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(10): 2861-2869. doi: 10.1364/AO.405638 [20] 宋永锋. 12米红外光学望远镜子镜轴向及侧向支撑技术研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019.SONG Y F. Research on techniques of axial and lateral supporting of 12-meter large optical-infrared telescope (LOT) segments[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese) [21] YANG F, ZHANG X J, ZHAO H CH, et al. Relay optical function and pre-construction results of a Giant Steerable Science Mirror for a thirty meter telescope[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(10): 13991-14008. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.013991 [22] BAFFES C, MAST T, NELSON J, et al. Primary mirror segmentation studies for the thirty meter telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7018: 70180S. doi: 10.1117/12.790206 [23] WILLIAMS E C, BAFFES C, MAST T, et al. Advancement of the segment support system for the thirty meter telescope primary mirror[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7018: 701810. doi: 10.1117/12.790176 [24] 张龙, 王孝坤, 程强, 等. 拼接式望远镜主镜衍射效应研究[J]. 应用光学,2020,41(3):447-454. doi: 10.5768/JAO202041.0301003ZHANG L, WANG X K, CHENG Q, et al. Research on diffraction effect of primary mirror in segmented telescope[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2020, 41(3): 447-454. (in Chinese) doi: 10.5768/JAO202041.0301003 [25] 廖周. 大口径分块望远镜主镜的误差分析与共相探测方法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2015.LIAO ZH. Error analysis of segmented primary mirror and research on co-phasing measurement[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015. (in Chinese) [26] WANG Y R, JIANG F Y, JU G H, et al. Deep learning wavefront sensing for fine phasing of segmented mirrors[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(16): 25960-25978. doi: 10.1364/OE.434024 [27] QIN SH, CHAN W K. A tip–tilt and piston detection approach for segmented telescopes[J]. Photonics, 2020, 8(1): 3. doi: 10.3390/photonics8010003 [28] 林旭东, 陈涛, 王建立, 等. 拼接镜主动光学共焦实验[J]. 光学 精密工程,2010,18(3):563-569.LIN X D, CHEN T, WANG J L, et al. Co-focus experiment of segmented-mirror active optics[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2010, 18(3): 563-569. (in Chinese) [29] ZHAO W R, ZHANG L, ZHAO Y J, et al. High-accuracy piston error measurement with a large capture range based on coherent diffraction[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11056: 110563B. [30] SHEN SH D, CUI X Q, ZHANG Y. Simulation and analysis of co-phasing errors of the segmented primary mirror tiled by hexagonal segments in LOT[J]. Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2021, 21(10): 245. doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/21/10/245 [31] JIANG J L, ZHAO W R. Phasing piston error in segmented telescopes[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(17): 19123-19137. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.019123 [32] YANG L L, YANG D, YANG ZH M, et al. Co-phase state detection for segmented mirrors by dual-wavelength optical vortex phase-shifting interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(9): 14088-14102. doi: 10.1364/OE.455890 [33] WANG P F, ZHAO H, XIE X P, et al. Multichannel left-subtract-right feature vector piston error detection method based on a convolutional neural network[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(14): 21320-21335. doi: 10.1364/OE.428690 [34] JIN K H, MCCANN M T, FROUSTEY E, et al. Deep convolutional neural network for inverse problems in imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4509-4522. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2713099 [35] RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG J, SU H, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [36] MA X F, XIE Z L, MA H T, et al. Piston sensing of sparse aperture systems with a single broadband image via deep learning[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(11): 16058-16070. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.016058 [37] LI D Q, XU SH Y, WANG D, et al. Large-scale piston error detection technology for segmented optical mirrors via convolutional neural networks[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(5): 1170-1173. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.001170 [38] CAO H F, ZHANG J X, YANG F, et al. Extending capture range for piston error in segmented primary mirror telescopes based on wavelet support vector machine with improved particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 111585-111597. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3002901 -






 下载:
下载: