Real-time semantic segmentation of microvascular decompression images based on encoder-decoder structure
-
摘要:
针对真彩色微血管减压图像实时语义分割网络参数量大、语义分割精度低的问题,本文提出了一种适用于微血管减压场景的U型轻量级快速语义分割网络U-MVDNet (U-Shaped Microvascular Decompression Network),该网络由编码解码结构构成。在编码器中设计了轻型非对称瓶颈模块(LABM)对上下文特征进行编码,解码器中引入了特征融合模块(FFM),有效组合高级语义特征和低级空间细节。实验结果表明:对于微血管减压测试集,U-MVDNet在单NVIDIA GTX 2080Ti上的参数量只有0.66 M,平均交并比(mIoU)达到了76.29%,速度达到140 frame/s,且当输入图像尺寸为
$640 \times 480$ 时,U-MVDNet在嵌入式平台 NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier上实现了实时(24 frame/s)语义分割。本文方法未使用任何的预训练模型,参数量少且推理速度快,语义分割性能优于其他对比方法,在分割精度和速度上做到了良好的平衡。同时,还可以方便地在嵌入式平台上开发和应用,性能优越,易于部署。Abstract:Aiming at the problems of large parameters and low semantic segmentation accuracy of real-time semantic segmentation networks for true-color microvascular decompression (MVD) images. This paper proposes a U-shaped lightweight fast semantic segmentation network U-MVDNet (U-Shaped Microvascular Decompression Network) for MVD scenarios, which consists of encoder-decoder structure. A Light Asymmetric Bottleneck Module (LABM) is designed in the encoder to encode context features. Feature Fusion Module (FFM) is introduced in the decoder to effectively combine high-level semantic features and underlying spatial details. Experimental results show that for the MVD test set, U-MVDNet achieves 0.66 M parameters, 76.29% mIoU (mean Intersection-over-Union), and 140 frame/s speed on NVIDIA GTX 2080Ti. And when input image size is 640 × 480, the real-time (24 frame/s) semantic segmentation is realized on NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier embedded development board. The proposed network has no pretrained model, fewer parameters, and fast inference speed. The semantic segmentation performance is superior to other comparison methods, and a good trade-off between segmentation accuracy and speed is achieved. Furthermore, U-MVDNet can also be easily developed and applied on embedded platform with superior performance and easy deployment.
-
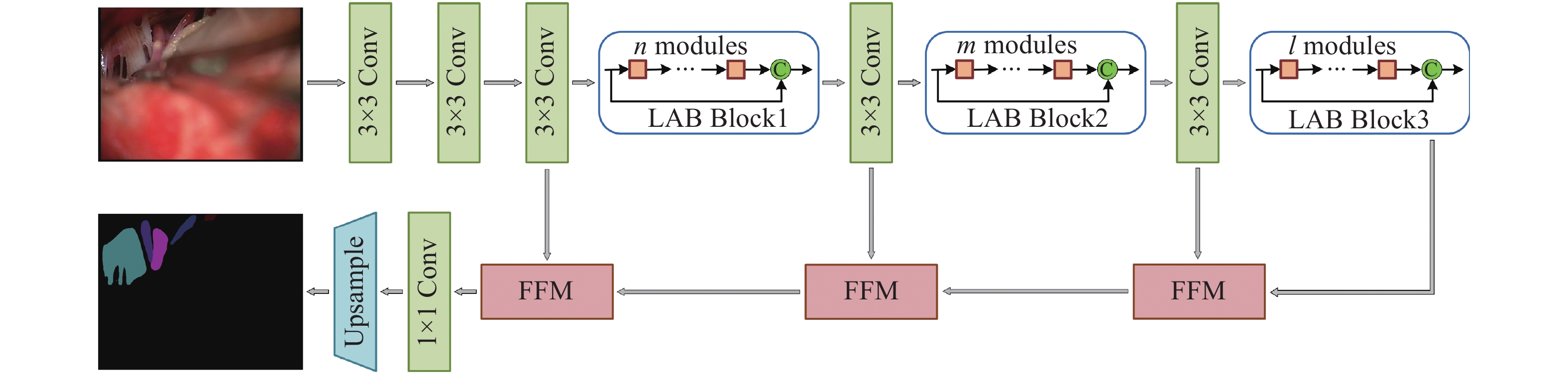
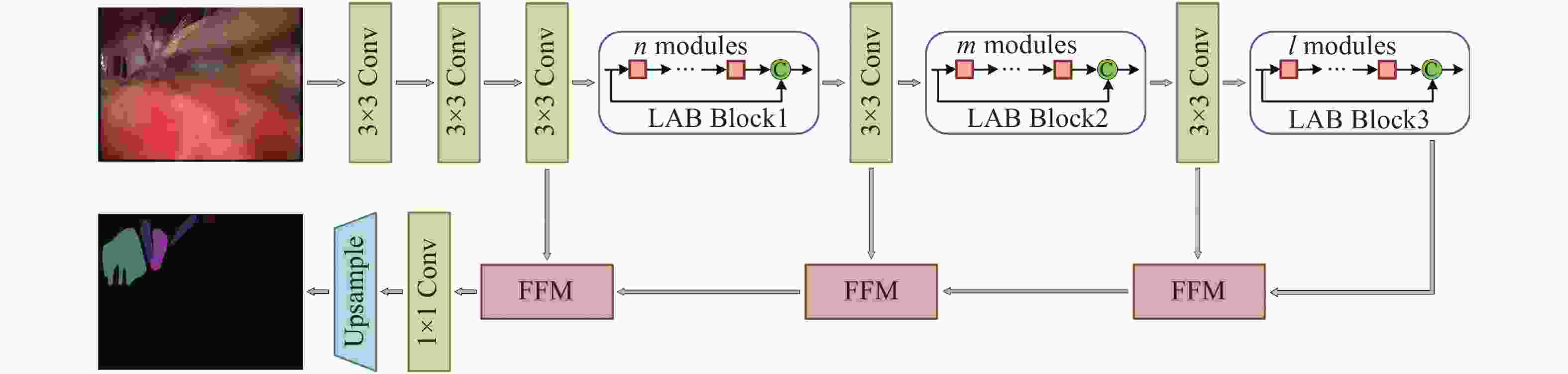
表 1 U-MVDNet架构细节
Table 1. Architecture details of proposed U-MVDNet
Layer Operator Mode Channel Output size 1 $3 \times 3$ Conv stride 2 32 $256 \times 256$ 2 $3 \times 3$ Conv stride 1 32 $256 \times 256$ 3 $3 \times 3$ Conv stride 1 32 $256 \times 256$ 4-5 $n \times $LABM dilated 2 32 $256 \times 256$ 6 $3 \times 3$ Conv stride 2 64 $128 \times 128$ 7-8 $m \times $LABM dilated 4 64 $128 \times 128$ 9 $3 \times 3$ Conv stride 2 128 $64 \times 64$ 10-12 $l \times $LABM dilated 8 128 $64 \times 64$ 13 1×FFM − 128 $64 \times 64$ 14 1×FFM − 64 $128 \times 128$ 15 1×FFM − 32 $256 \times 256$ 16 1×1 Conv stride 1 10 $256 \times 256$ 17 Bilinear interpolation $ \times 2$ 10 $512 \times 512$ 表 2 医学术语缩写及对应颜色
Table 2. Abbreviations of medical terms and corresponding color
简称 全称 对应颜色 cn5 三叉神经 
cn7 面神经 
cn9 舌咽神经 
cn10 迷走神经 
aica+cn7 小脑前下动脉及面神经 
pica+cn7 小脑后下动脉及面神经 
pica 小脑后下动脉 
aica 小脑前下动脉 
pv 岩静脉 
表 3 训练参数
Table 3. Training parameters
Parameter name Parameter selection Learning rate Policy Initialization Power poly 0.16 0.9 Optimizer Policy Momentum Weight decay SGD 0.9 $1\times10 ^{- 4}$ Enter picture size $768 \times 576$ Batch size 8 表 4 不同扩张率组合的LABM编码器结果
Table 4. Results of LABM encoder with different combinations of dilation rates
Name Dilation rates mIoU(%) LABM_N2M2L4 2,4,8 72.35 LABM_N2M2L4 4,8,16 72.08 表 5 不同设置下的LABM编码器结果
Table 5. Results of LABM encoder with different settings
Concatenation Params(M) FLOPs(G) mIoU(%) 0.30 2.81 72.35 √ 0.54 4.03 73.08 表 6 输入尺寸为512 × 512时,不同深度的编码器结果
Table 6. Results of encoder with different depths when the input size is 512 × 512
n m l Params(M) FLOPs(G) mIoU(%) 2 2 2 0.52 3.95 72.35 2 2 4 0.54 4.03 73.08 2 4 4 0.55 4.11 73.84 4 4 4 0.55 4.20 73.37 表 7 不同构成要素的FFM解码器结果
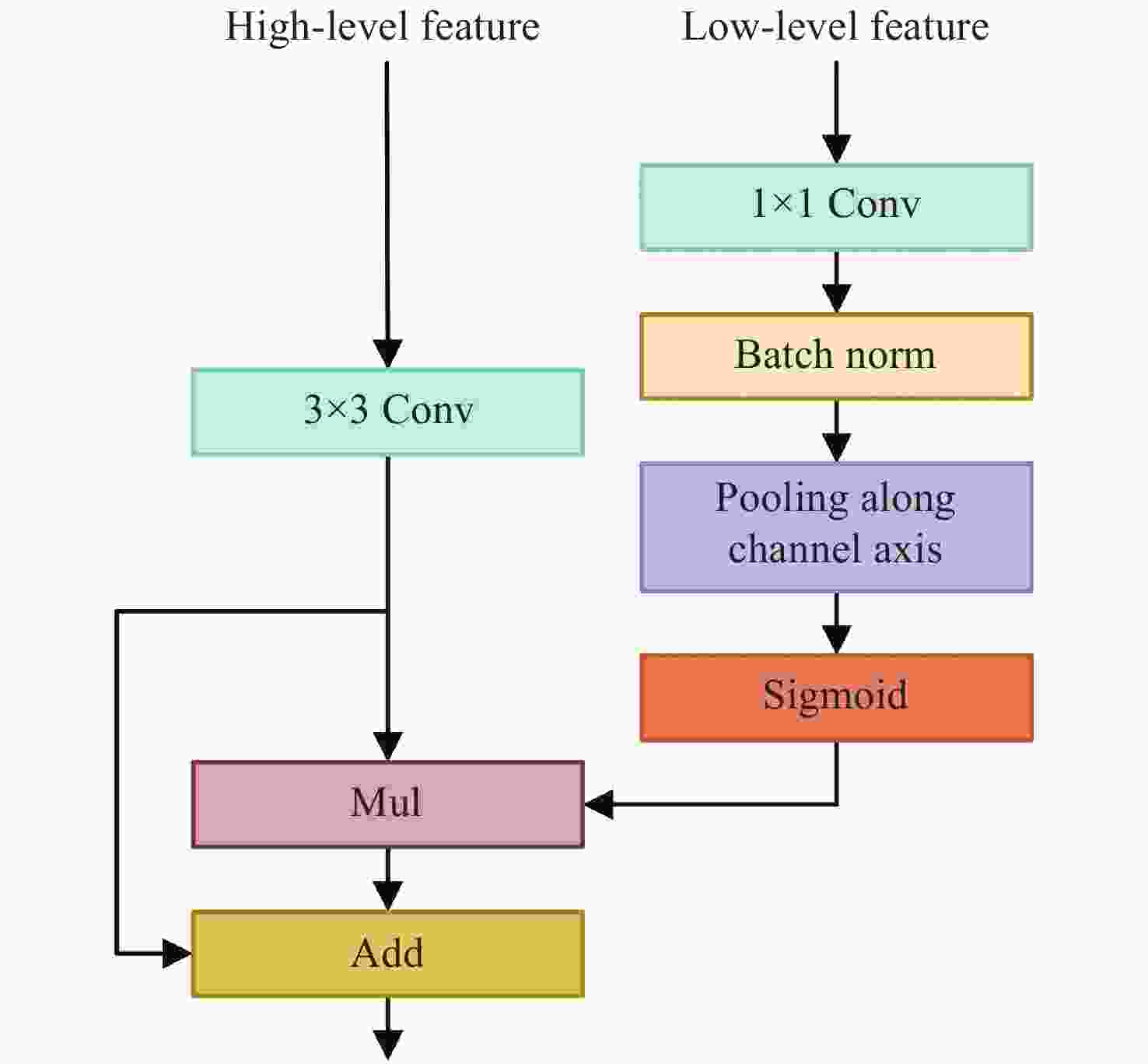
Table 7. Results of FFM decoder with different components
FFM Pooling mIoU(%) w/o − 73.84 w 77.11 w √ 77.34 表 8 U-MVDNet的扩张率对mIoU的影响
Table 8. Effect of dilation of U-MVDNet on mIoU
Concatenation mIoU(%) Params(M) U-MVDNet 77.34 0.66 U-MVDNet_w/o dilation 75.61 0.66 U-MVDNet_First $3 \times 3$ conv ($r = 2$) 76.81 0.66 表 9 MVD测试集实验结果
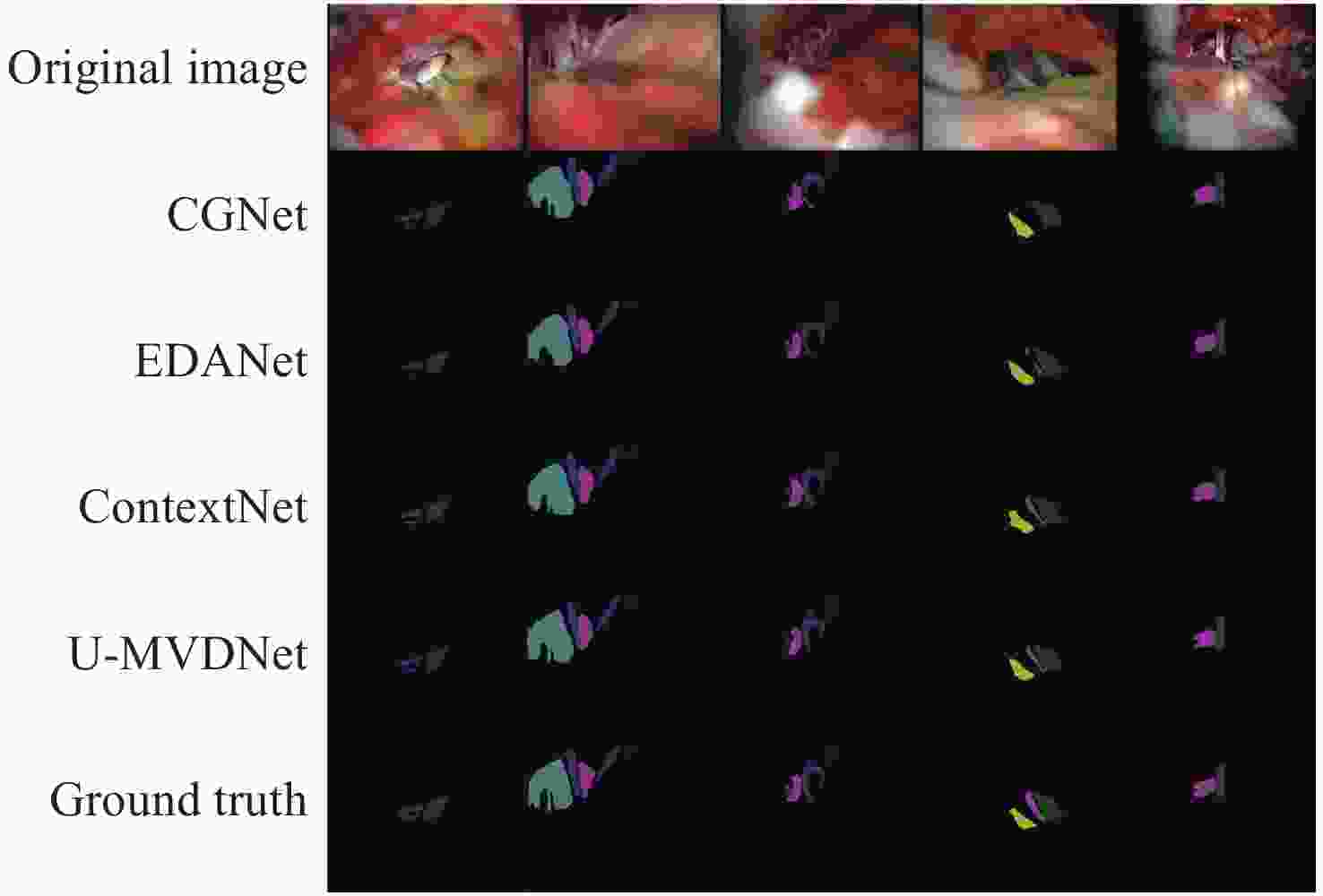
Table 9. Experimental results on MVD test set
Method Params(M) Speed(frame·s−1) mIoU(%) cn5 cn7 cn9 cn10 aica+cn7 pica+cn7 pica aica pv CGNet[28] 0.94 87.4 71.95 81.26 82.9 71.29 69.85 71.64 87.16 67.37 65.66 50.42 EDANet[29] 0.69 125 74.51 83.03 84.02 70.31 77.25 75.09 87.98 70.37 68.18 54.34 ContextNet[30] 0.88 163.3 75.81 82.14 84.15 74.91 78.08 76.67 87.84 72.08 69.77 56.65 U-MVDNet 0.66 140.8 76.29 82.25 85.45 74.8 76.91 76.32 87.85 74.08 69.83 59.12 表 10 ISIC 2016 + PH2测试集实验结果
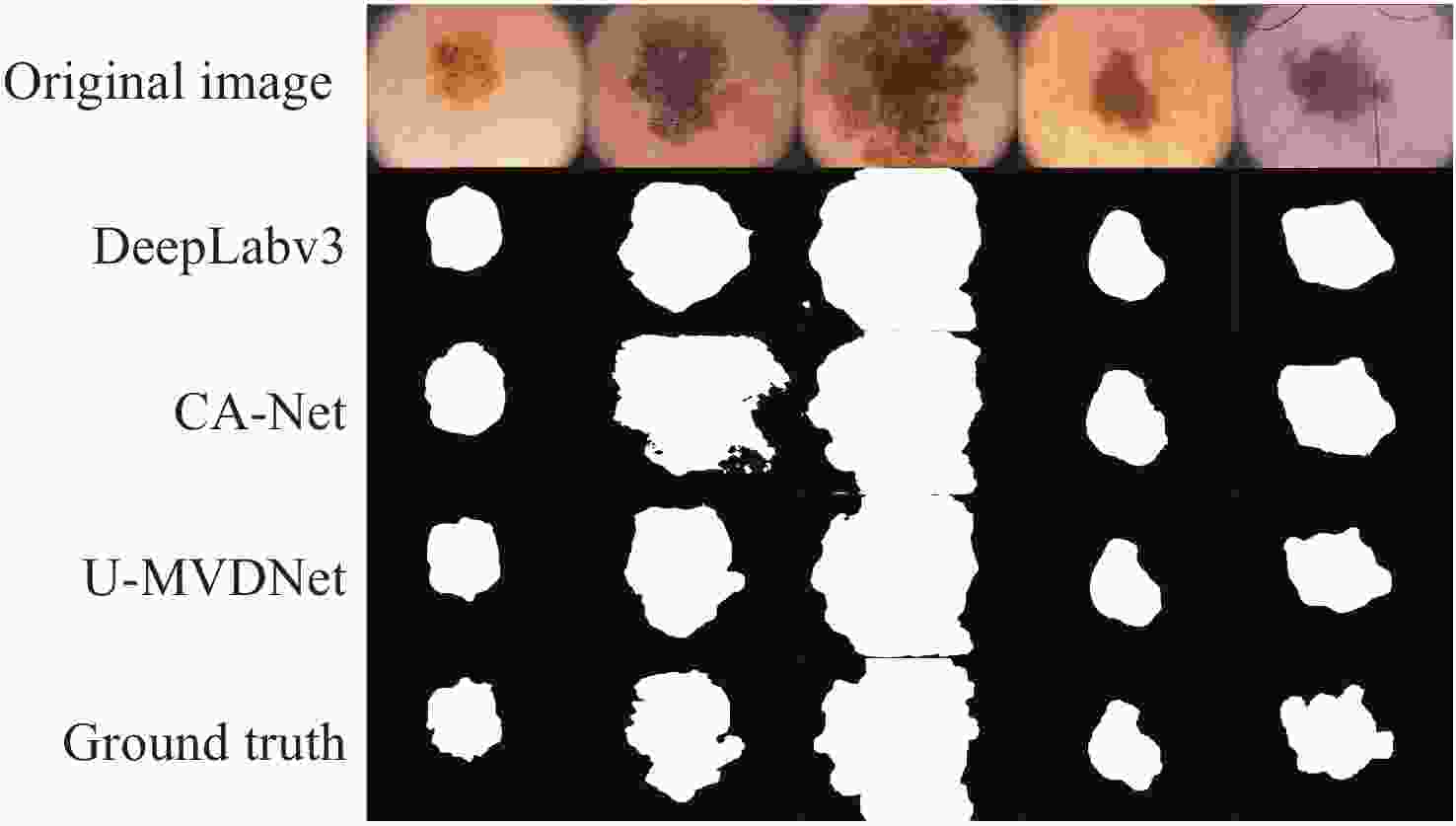
Table 10. Experimental results on ISIC 2016 + PH2 test set
表 11 两种不同的硬件环境
Table 11. Two different hardware environments
Jetson Xavier 服务器 GPU Volta GTX 2080Ti CPU 8核Carmel ARM 8核i7-9700K 显存 32GB LPDDR4x 11GB GDDR6 显存带宽 136.5 GB/s 616 GB/s CUDA核心 512 4352 表 12 不同分辨率下的测试结果
Table 12. Test results by different methods with different resolutions
Method Size Times/ms Speed/frame·s−1 mIoU/% CGNet[28] $640 \times 480$ 65.7 15.2 70.31 $768 \times 576$ 69.2 14.4 71.95 EDANet[29] $640 \times 480$ 42.3 23.6 73.2 $768 \times 576$ 45.2 22.1 74.18 ContextNet[30] $640 \times 480$ 34.5 28.9 74.81 $768 \times 576$ 36.1 27.7 75.81 U-MVDNet $640 \times 480$ 41.5 24.2 75.76 $768 \times 576$ 43.6 22.9 76.29 -
[1] BENNETTO L, PATEL N K, FULLER G. Trigeminal neuralgia and its management[J]. BMJ, 2007, 334(7586): 201-205. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39085.614792.BE [2] KIZILTAN M E, GUNDUZ A. Reorganization of sensory input at brainstem in hemifacial spasm and postparalytic facial syndrome[J]. Neurological Sciences, 2018, 39(2): 313-319. doi: 10.1007/s10072-017-3185-1 [3] NAZIR A, CHEEMA M N, SHENG B, et al. OFF-eNET: an optimally fused fully end-to-end network for automatic dense volumetric 3D intracranial blood vessels segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7192-7202. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2999854 [4] 吴红宇, 郑波. 脑动静脉畸形CTA、DSA的影像学表现及诊断的对照性研究[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志,2021,19(1):36-37,52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2021.01.012WU H Y, ZHENG B. Analysis on imaging manifestations and diagnostic contrast of cerebral arteriovenous malformations in CTA and DSA[J]. Chinese Journal of CT and MRI, 2021, 19(1): 36-37,52. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2021.01.012 [5] PATEL T R, PALIWAL N, JAISWAL P, et al. Multi-resolution CNN for brain vessel segmentation from cerebrovascular images of intracranial aneurysm: a comparison of U-Net and DeepMedic[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2020, 11314: 113142W. [6] 王华. 磁共振血管成像与三维动脉自旋标记脑灌注成像技术诊断缺血性脑血管疾病一致性比较[J]. 实用医院临床杂志,2020,17(1):36-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2020.01.011WANG H. Comparison of consistency of MRA and 3D-ASL cerebral perfusion imaging in the diagnosisof ischemic cerebrovascular diseases[J]. Practical Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2020, 17(1): 36-39. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2020.01.011 [7] 徐冰洁. 电子计算机断层扫描联合核磁共振血管成像对脑血管疾病的诊断价值[J]. 临床合理用药杂志,2021,14(32):177-178. doi: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2021.32.071XU B J. Diagnostic value of computed tomography combined with nuclear magnetic resonance angiography in cerebrovascular diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rational Drug Use, 2021, 14(32): 177-178. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2021.32.071 [8] ZHANG H, XIA L K, SONG R, et al. . Cerebrovascular segmentation in mra via reverse edge attention network[C]. Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Springer, 2020: 66-75. [9] GUO X Y, XIAO R X, LU Y Y, et al. Cerebrovascular segmentation from TOF-MRA based on multiple-U-net with focal loss function[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2021, 202: 105998. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.105998 [10] HILBERT A, MADAI V I, AKAY E M, et al. BRAVE-NET: fully automated arterial brain vessel segmentation in patients with cerebrovascular disease[J]. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 3: 552258. doi: 10.3389/frai.2020.552258 [11] 陈星, 宋智洋, 周明全, 等. 面向脑血管分割的改进型非局部均值滤波算法研究[J]. 中国光学,2014,7(4):572-580.CHEN X, SONG ZH Y, ZHOU M Q, et al. An improved non-local mean filter algorithm facing the cerebrovascular segmentation[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(4): 572-580. (in Chinese) [12] WANG R, LI CH, WANG J, et al. Threshold segmentation algorithm for automatic extraction of cerebral vessels from brain magnetic resonance angiography images[J]. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2015, 241: 30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.12.003 [13] BHUIYAN A, NATH B, CHUA J. An adaptive region growing segmentation for blood vessel detection from retinal images[C]. Visapp: Second International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, 2007: 404-409. [14] 王醒策, 张美霞, 武仲科, 等. 基于全局LBF水平集模型的脑血管层次粗分割[J]. 光学 精密工程,2013,21(12):3283-3297. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20132112.3283WANG X C, ZHANG M X, WU ZH K, et al. Level coarse brain vessel segmentation based on global LBF model[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2013, 21(12): 3283-3297. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20132112.3283 [15] WANG J X, ZHAO SH F, LIU Z F, et al. An active contour model based on adaptive threshold for extraction of cerebral vascular structures[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2016, 2016: 6472397. [16] 陈晓冬, 艾大航, 张佳琛, 等. Gabor滤波融合卷积神经网络的路面裂缝检测方法[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1293-1301. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0041CHEN X D, AI D H, ZHANG J CH, et al. Gabor filter fusion network for pavement crack detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1293-1301. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0041 [17] 王春哲, 安军社, 姜秀杰, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的候选区域优化算法[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(6):1348-1361. doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1348WANG CH ZH, AN J SH, JIANG X J, et al. Region proposal optimization algorithm based on convolutional neural networks[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(6): 1348-1361. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1348 [18] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2015: 3431-3440. [19] SHVETS A A, IGLOVIKOV V I, RAKHLIN A, et al. . Angiodysplasia detection and localization using deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), IEEE, 2018: 612-617. [20] ZHANG M, ZHANG CH, WU X, et al. A neural network approach to segment brain blood vessels in digital subtraction angiography[J]. Computer Methods Programs in Biomedicine, 2020, 185: 105159. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105159 [21] XIA L K, XIE Y X, WANG Q W, et al. A nested parallel multiscale convolution for cerebrovascular segmentation[J]. Medical Physics, 2021, 48(12): 7971-7983. doi: 10.1002/mp.15280 [22] MENG C, SUN K, GUAN SH Y, et al. Multiscale dense convolutional neural network for DSA cerebrovascular segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 373: 123-134. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.035 [23] HUANG G, LIU ZH, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. . Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2017: 2261-2269. [24] ALVAREZ J, PETERSSON L. DecomposeMe: simplifying convnets for end-to-end learning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: , 1606, 05426: 2016. [25] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN SH Q, et al. . Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2015: 1026-1034. [26] CODELLA N C F, GUTMAN D, CELEBI M E, et al. . Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: a challenge at the 2017 international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI), hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC)[C]. Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, IEEE, 2016. [27] MENDONÇA T, FERREIRA P M, MARQUES J S, et al. . PH2-A dermoscopic image database for research and benchmarking[C]. Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), IEEE, 2013: 5437-5440. [28] WU T Y, TANG SH, ZHANG R, et al. CGNet: a light-weight context guided network for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 30: 1169-1179. [29] LO S Y, HANG H M, CHAN SH W, et al. . Efficient dense modules of asymmetric convolution for real-time semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the ACM Multimedia Asia, ACM, 2019: 1. [30] POUDEL R P K, BONDE U, LIWICKI S, et al. ContextNet: exploring context and detail for semantic segmentation in real-time[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: , 0455, 4: 2018. [31] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: , 1706, 05587: 2017. [32] GU R, WANG G T, SONG T, et al. CA-Net: comprehensive attention convolutional neural networks for explainable medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2021, 40(2): 699-711. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.3035253 -






 下载:
下载: