Recent progress of non-line-of-sight imaging reconstruction algorithms in typical imaging modalities
-
摘要:
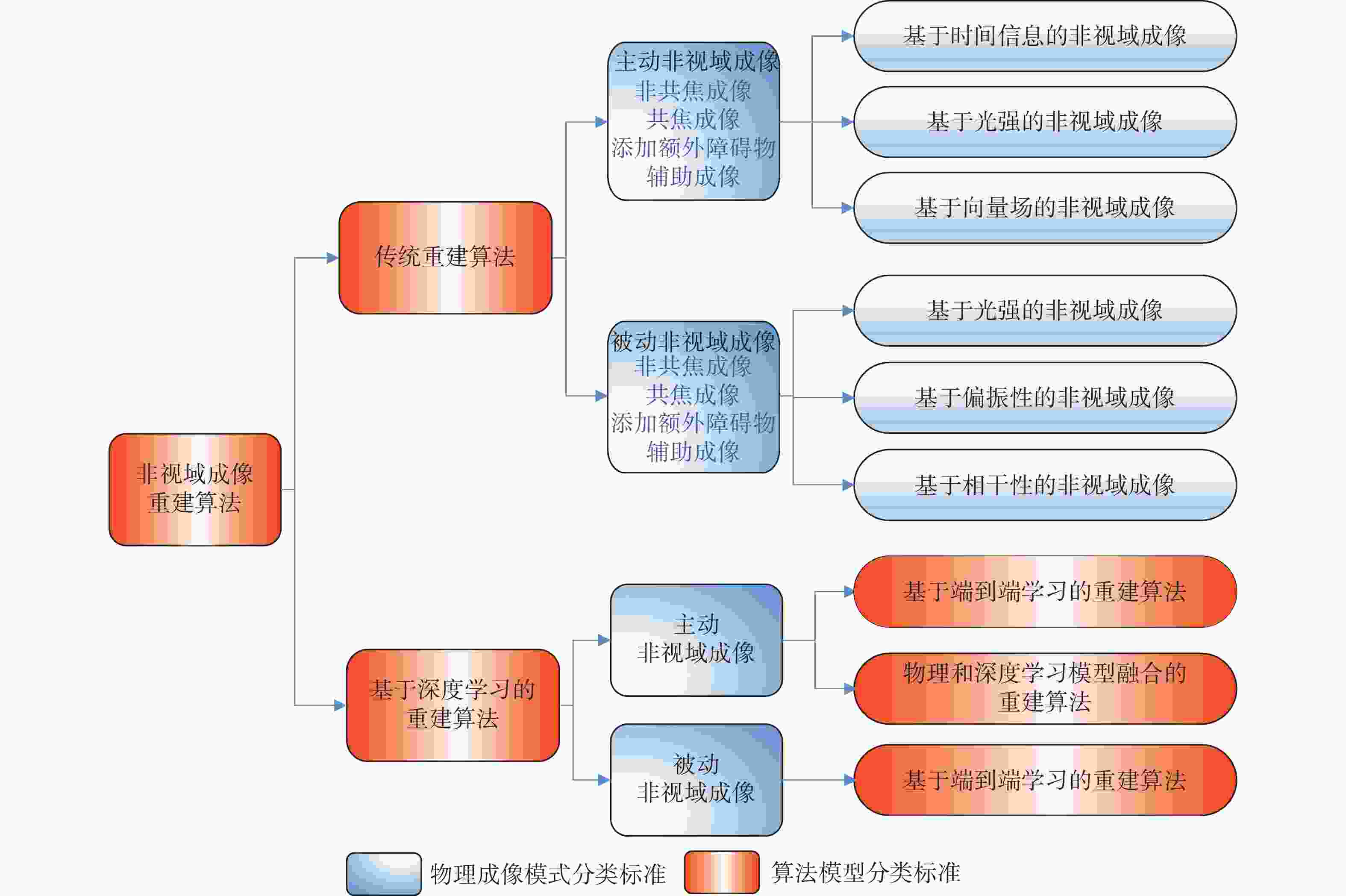
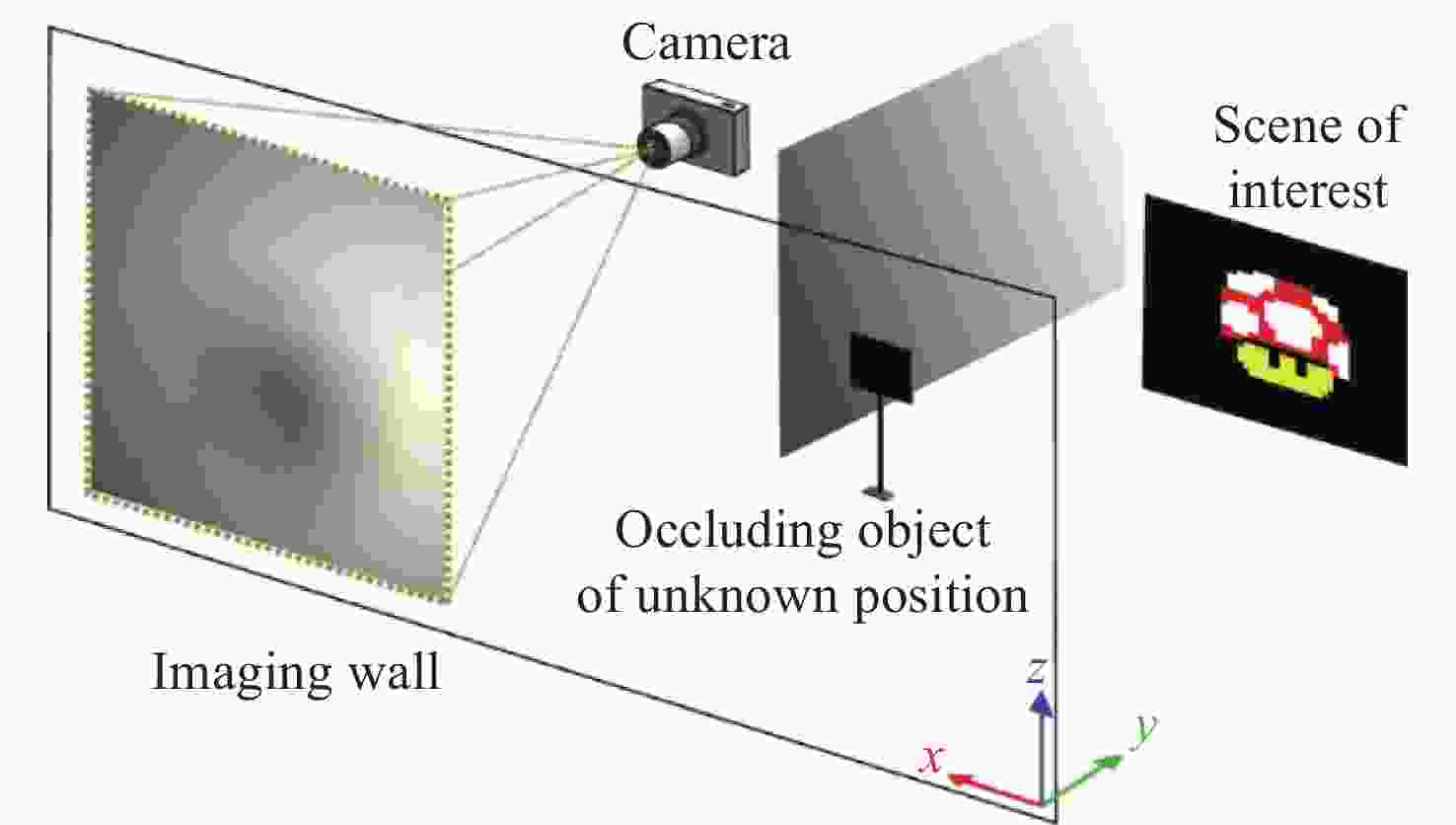
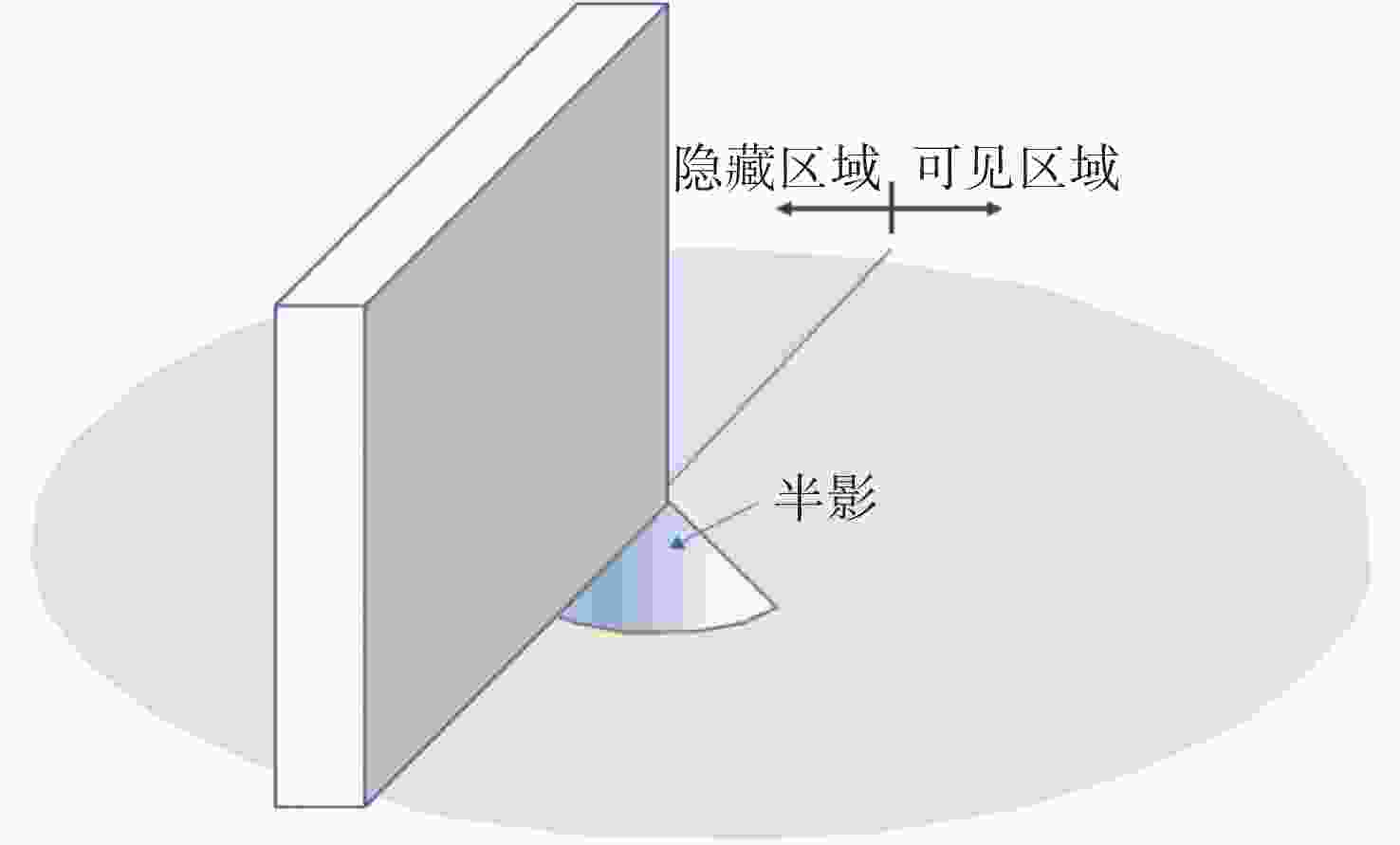
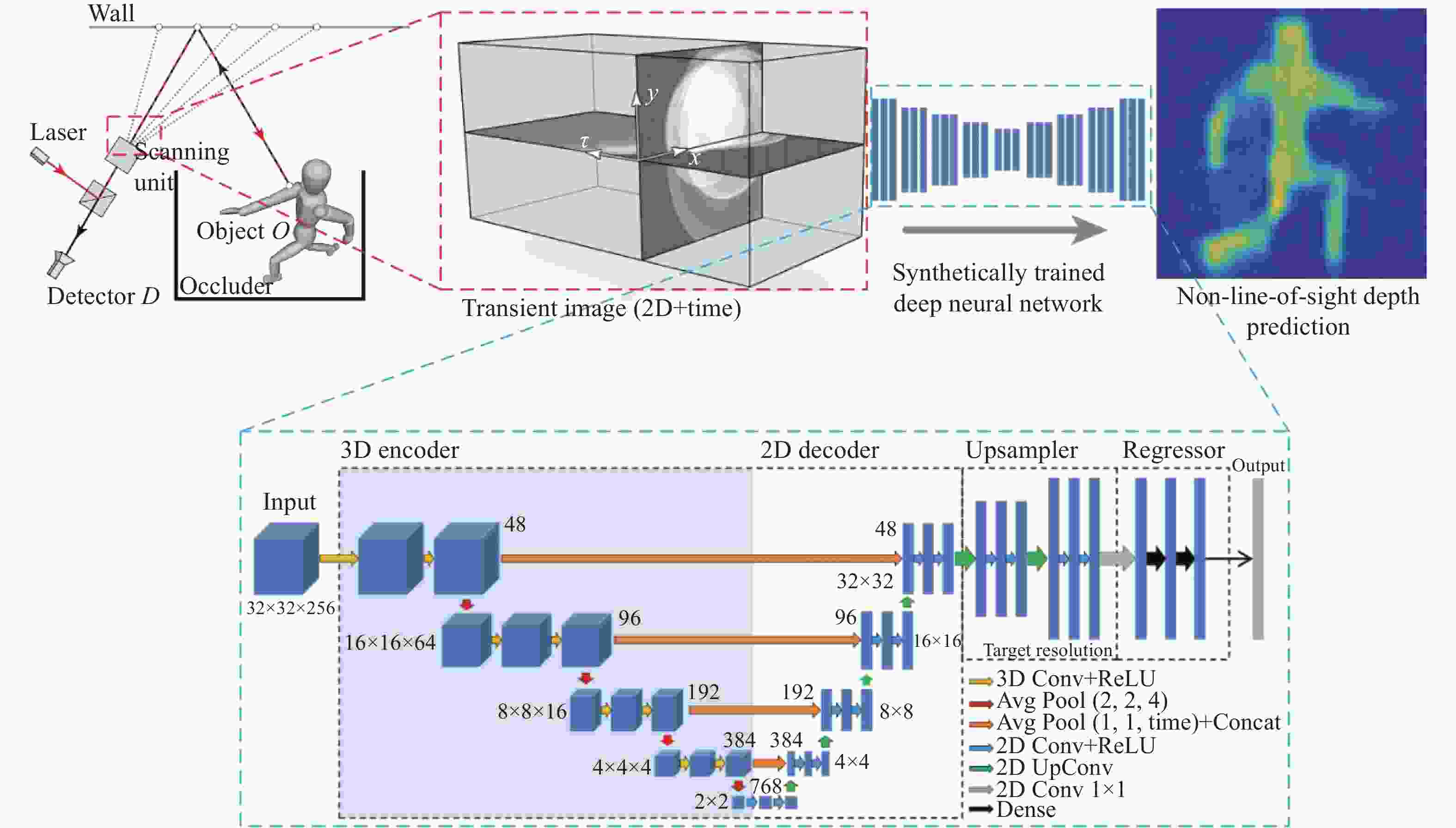
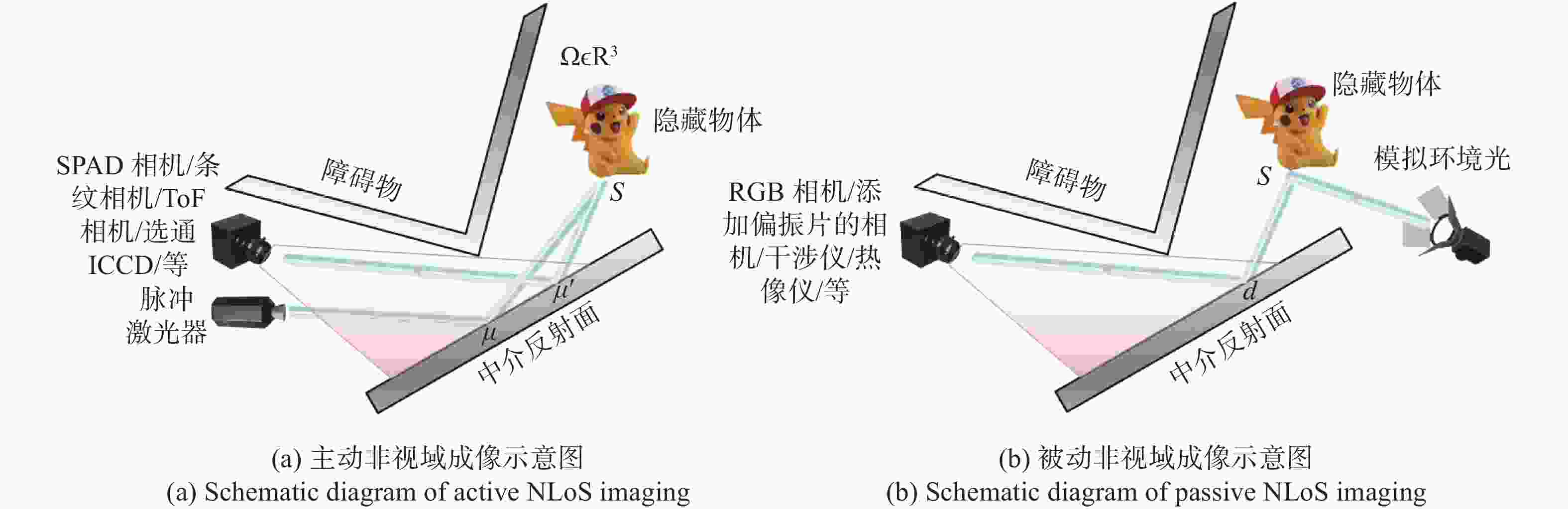
非视域(Non-Line-of-Sight, NLoS)成像是近年来发展起来的一项新兴技术,其通过分析成像场景中的中介面信息来重建隐藏场景,实现了“拐弯成像”的效果,在多个领域有巨大的应用价值。本文主要针对NLoS成像重建算法进行综述性研究。考虑到目前NLoS成像分类存在交叉和非独立现象,本文基于物理成像模式和算法模型的不同特点,对其进行了独立的重新分类。根据提出的分类标准分别对传统和基于深度学习的NLoS成像重建算法进行了归纳总结,对代表性算法的发展现状进行了概述,推导了典型方法的实现原理,并对比了传统重建方法和基于深度学习的NLoS成像重建算法的重建应用结果。总结了NLoS成像目前存在的挑战和未来的发展方向。该研究对不同类型的NLoS成像进行了较为全面的梳理,对NLoS成像重建算法在内的一系列研究的进一步发展有着一定的支撑和推动作用。
Abstract:Non-line-of-sight (NLoS) imaging is a promising technique developed in recent years, which can reconstruct hidden scenes by analyzing the information in the intermediate surface, and "see around the corner", and has strong application value in many fields. In this paper, we review the reconstruction algorithm for NLoS imaging tasks. Firstly, considering the crossover and non-independent phenomena existing in the NLoS imaging classification, we use the different features of physical imaging models and algorithm models to reclassify them. Secondly, according to the proposed classification criteria, we respectively review the traditional and deep learning-based NLoS imaging reconstruction algorithms, summarize the state-of-the-art algorithms, and derive the implement principle. We also compare the results of deep learning-based and traditional NLoS imaging reconstruction algorithms for reconstruction tasks. Finally, the current challenges and the future development of NLoS imaging are summarized. Different types of NLoS imaging reconstruction algorithms are comprehensively analyzed in this review, which provides important support for the further development of NLoS imaging reconstruction algorithms.
-
Key words:
- non-line-of-sight imaging /
- reconstruction algorithm /
- imaging mode /
- deep learning
-
表 1 不同种类的NLoS重建SOTA算法的多角度总结和对比分析
Table 1. A multi-perspective summary and comparative analysis of different kinds of NLoS reconstruction SOTA algorithms
算法分类 SOTA NLoS场景中的硬件 任务 重建质量 重建速度 实际应用
的差距传统
重建
算法主动
NLoS
成像基于时间信息 ①空间多路复用感知+
压缩感知[19]
②空间点扩散函数的优化[20]①数字微反射镜+SPAD
②SPAD阵列2D重建 ①好
②较好较快 较大 基于光强 逆优化[39] 传统相机 2D重建/跟踪/定位 一般 较快 大 基于向量场 衍射积分法[41] SPAD 3D重建 较好 快 小 被动
NLoS
成像基于光强 ①添加遮挡的优化[48]
②优化墙角阴影[52]传统相机 ①2D重建
②2D重建/定位①较好
②好一般 大 基于偏振性 逆优化[56] 偏光器+传统相机 2D重建 一般 快 大 基于相干性 双谱+相位检索[58] 遮挡板+阵列相机 2D重建 一般 快 大 基于深度
学习的
重建算法主动
NLoS
成像基于端到端学习 快速光场断层扫描+
深度神经网络[64]条纹相机 3D重建 较好 很快 小 物理和深度学习
模型融合①神经瞬态场[75]
②逆矩阵生成+
深度神经网络[74]①SPAD
②传统相机①3D重建
②2D重建好 一般 较大 被动NLoS
成像基于端到端学习 最有传输理论+
深度神经网络[80]传统相机 2D重建 很好 快 小 -
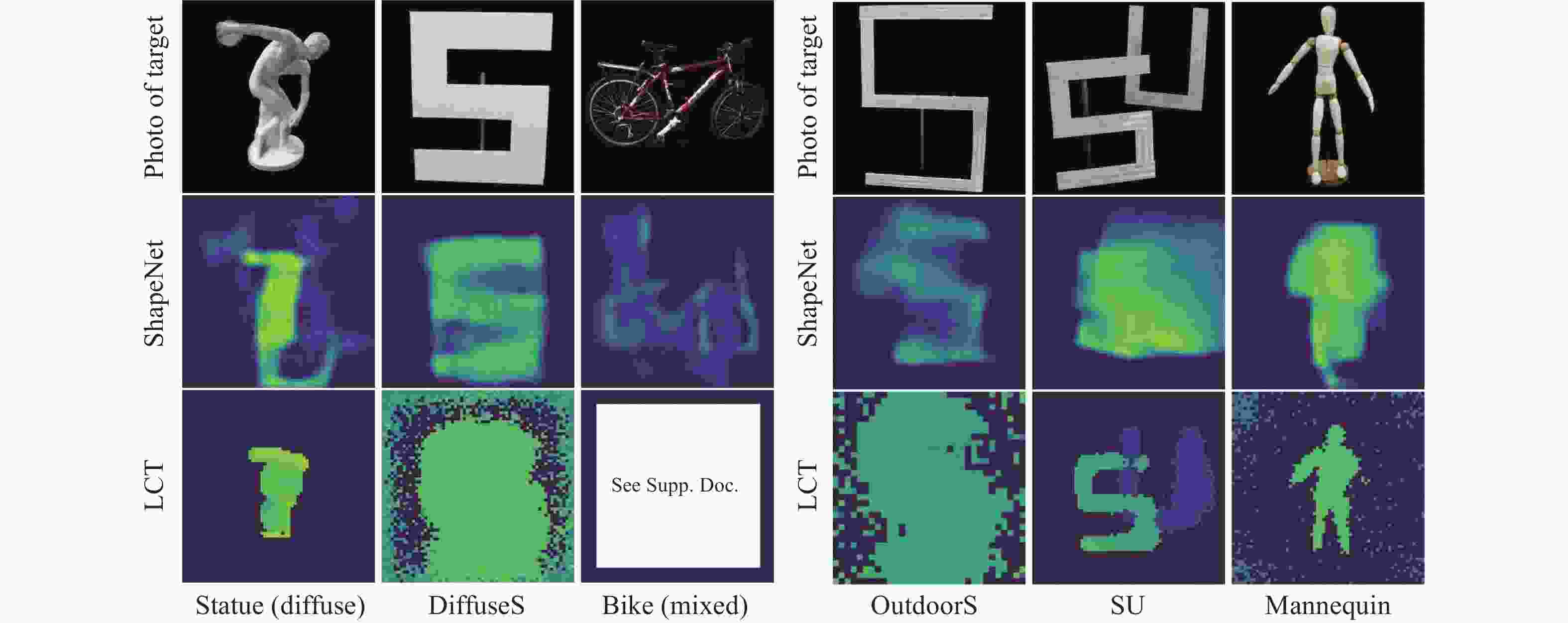
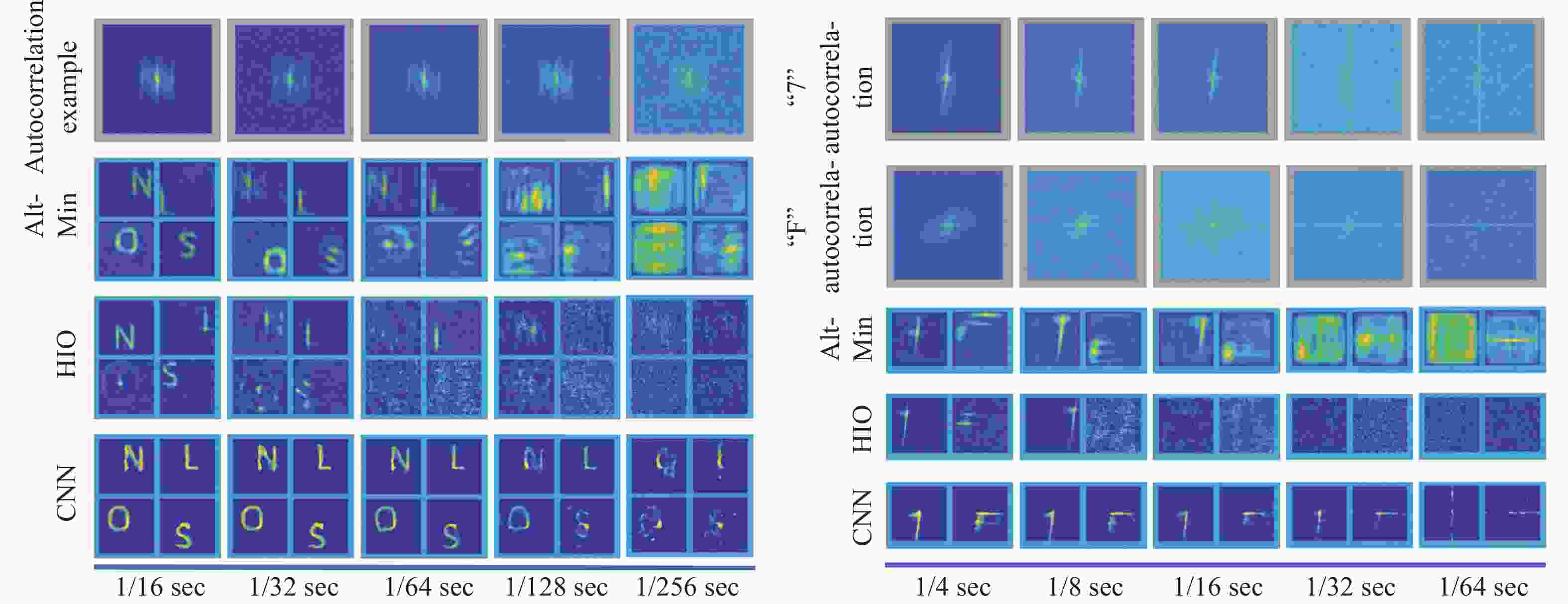
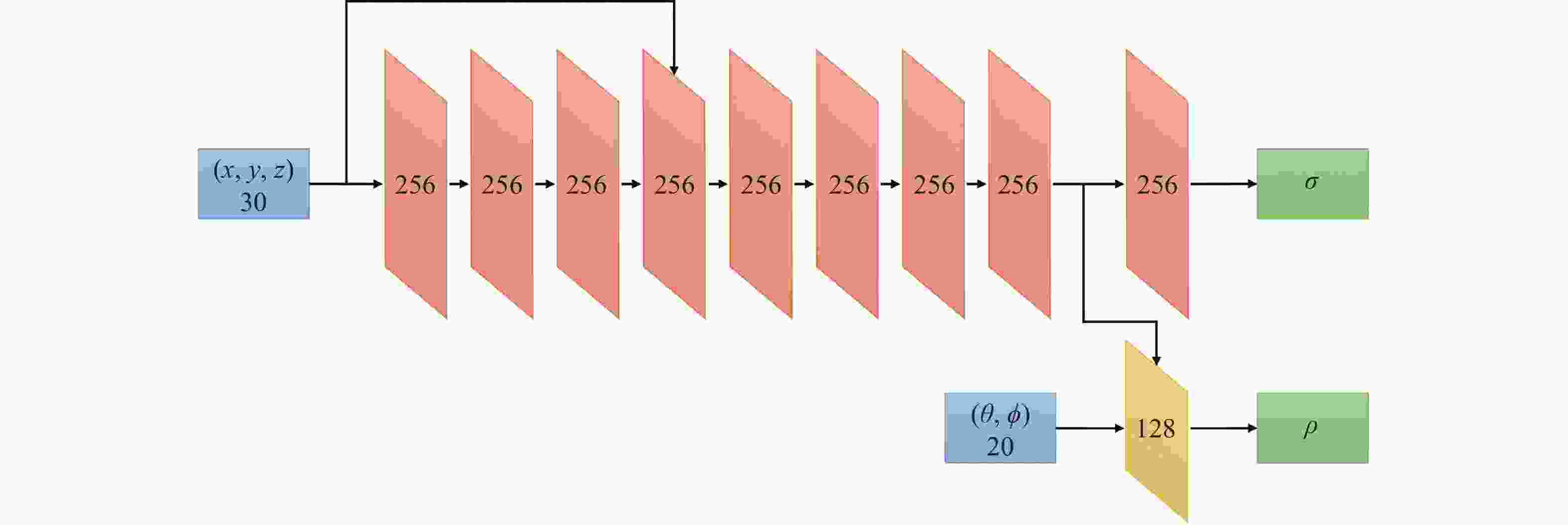
[1] RAMESH R, DAVIS J. 5d time-light transport matrix: What can we reason about scene properties?[EB/OL]. [2008-03-01] [2008-03-01]. http://dspace.mt.edu/handle/1721.1/67888. [2] KIRMANI A, HUTCHISON T, DAVIS J, et al.. Looking around the corner using transient imaging[C]. 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2009: 159-166. [3] VELTEN A, WILLWACHER T, GUPTA O, et al. Recovering three-dimensional shape around a corner using ultrafast time-of-flight imaging[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3(1): 745. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1747 [4] MAEDA T, SATAT G, SWEDISH T, et al. Recent advances in imaging around corners[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 1910, 05613: 2019. [5] GENG R X, HU Y, CHEN Y. Recent advances on non-line-of-sight imaging: Conventional physical models, deep learning, and new scenes[J]. APSIPA Transactions on Signal and Information Processing, 2021, 11(1): e1. [6] FACCIO D, VELTEN A, WETZSTEIN G. Non-line-of-sight imaging[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2020, 2(6): 318-327. doi: 10.1038/s42254-020-0174-8 [7] 吴术孔, 张宇宁. 被动非视域成像方法的研究进展[J]. 光电子技术,2021,41(2):87-93.WU SH K, ZHANG Y N. Research progress of passive non-line-of-sight imaging methods[J]. Optoelectronic Technology, 2021, 41(2): 87-93. (in Chinese) [8] YE J T, HUANG X, LI ZH P, et al. Compressed sensing for active non-line-of-sight imaging[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(2): 1749-1763. doi: 10.1364/OE.413774 [9] GUPTA O, WILLWACHER T, VELTEN A, et al. Reconstruction of hidden 3D shapes using diffuse reflections[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(17): 19096-19108. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.019096 [10] LAURENZIS M, KLEIN J, BACHER E, et al. Multiple-return single-photon counting of light in flight and sensing of non-line-of-sight objects at shortwave infrared wavelengths[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(20): 4815-4818. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.004815 [11] ARELLANO V, GUTIERREZ D, JARABO A. Fast back-projection for non-line of sight reconstruction[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(10): 11574-11583. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.011574 [12] NAIK N, ZHAO SH, VELTEN A, et al.. Single view reflectance capture using multiplexed scattering and time-of-flight imaging[C]. Proceedings of the 2011 SIGGRAPH Asia Conference, Association for Computing Machinery, 2011: 171. [13] BUTTAFAVA M, ZEMAN J, TOSI A, et al. Non-line-of-sight imaging using a time-gated single photon avalanche diode[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(16): 20997-21011. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.020997 [14] LA MANNA M, KINE F, BREITBACH E, et al. Error backprojection algorithms for non-line-of-sight imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(7): 1615-1626. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2843363 [15] JIN CH F, XIE J H, ZHANG S Q, et al. Reconstruction of multiple non-line-of-sight objects using back projection based on ellipsoid mode decomposition[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(16): 20089-20101. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.020089 [16] CHAN S, WARBURTON R E, GARIEPY G, et al. Non-line-of-sight tracking of people at long range[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(9): 10109-10117. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.010109 [17] MUSARRA G, LYONS A, CONCA E, et al. Non-line-of-sight three-dimensional imaging with a single-pixel camera[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2019, 12(1): 011002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.12.011002 [18] YANG W Q, ZHANG CH, JIANG W J, et al. None-line-of-sight imaging enhanced with spatial multiplexing[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(4): 5855-5867. doi: 10.1364/OE.450238 [19] HEIDE F, O’TOOLE M, ZANG K, et al. Non-line-of-sight imaging with partial occluders and surface normals[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, 38(3): 22. [20] PEI CH Q, ZHANG A K, DENG Y, et al. Dynamic non-line-of-sight imaging system based on the optimization of point spread functions[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(20): 32349-32364. doi: 10.1364/OE.439372 [21] PANDHARKAR R, VELTEN A, BARDAGJY A, et al.. Estimating motion and size of moving non-line-of-sight objects in cluttered environments[C]. CVPR 2011, IEEE, 2011: 265-272. [22] HEIDE F, XIAO L, HEIDRICH W, et al.. Diffuse mirrors: 3D reconstruction from diffuse indirect illumination using inexpensive time-of-flight sensors[C]. Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2014: 3222-3229. [23] TSAI C Y, KUTULAKOS K N, NARASIMHAN S G, et al.. The geometry of first-returning photons for non-line-of-sight imaging[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2017: 2336-2344. [24] KADAMBI A, ZHAO H, SHI B X, et al. Occluded imaging with time-of-flight sensors[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2016, 35(2): 15. [25] TSAI C Y, SANKARANARAYANAN A C, GKIOULEKAS I. Beyond volumetric albedo-a surface optimization framework for non-line-of-sight imaging[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2019: 1545-1555. [26] ISERINGHAUSEN J, HULLIN M B. Non-line-of-sight reconstruction using efficient transient rendering[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2020, 39(1): 8. [27] AHN B, DAVE A, VEERARAGHAVAN A, et al.. Convolutional approximations to the general non-line-of-sight imaging operator[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2019: 7888-7898. [28] CHEN J H, ZHANG Y, GUO SH SH, et al. Joint estimation of NLOS building layout and targets via sparsity-driven approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5114513. [29] LIU X CH, BAUER S, VELTEN A. Analysis of feature visibility in non-line-of-sight measurements[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2019: 10132-10140. [30] LINDELL D B, WETZSTEIN G, O'TOOLE M. Wave-based non-line-of-sight imaging using fast f-k migration[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, 38(4): 116. [31] YOUNG S I, LINDELL D B, GIROD B, et al.. Non-line-of-sight surface reconstruction using the directional light-cone transform[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2020: 1404-1413. [32] O’TOOLE M, LINDELL D B, WETZSTEIN G. Confocal non-line-of-sight imaging based on the light-cone transform[J]. Nature, 2018, 555(7696): 338-341. doi: 10.1038/nature25489 [33] ISOGAWA M, CHAN D, YUAN Y, et al.. Efficient non-line-of-sight imaging from transient sinograms[C]. Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2020: 193-208. [34] WU CH, LIU J J, HUANG X, et al. Non–line-of-sight imaging over 1.43 km[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2021, 118(10): e2024468118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2024468118 [35] WANG B, ZHENG M Y, HAN J J, et al. Non-line-of-sight imaging with picosecond temporal resolution[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2021, 127(5): 053602. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.053602 [36] THRAMPOULIDIS C, SHULKIND G, XU F H, et al. Exploiting occlusion in non-line-of-sight active imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2018, 4(3): 419-431. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2018.2829599 [37] RAPP J, SAUNDERS C, TACHELLA J, et al. Seeing around corners with edge-resolved transient imaging[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5929. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19727-4 [38] GARIEPY G, TONOLINI F, HENDERSON R, et al. Detection and tracking of moving objects hidden from view[J]. Nature Photonics, 2016, 10(1): 23-26. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2015.234 [39] KLEIN J, PETERS C, MARTÍN J, et al. Tracking objects outside the line of sight using 2D intensity images[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 32491. doi: 10.1038/srep32491 [40] LIU X CH, VELTEN A. The role of wigner distribution function in non-line-of-sight imaging[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), IEEE, 2020: 1-12. [41] LIU X CH, GUILLÉN I, LA MANNA M, et al. Non-line-of-sight imaging using phasor-field virtual wave optics[J]. Nature, 2019, 572(7771): 620-623. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1461-3 [42] REZA S A, LA MANNA M, BAUER S, et al. Phasor field waves: A Huygens-like light transport model for non-line-of-sight imaging applications[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(20): 29380-29400. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.029380 [43] LA MANNA M, NAM J H, REZA S A, et al. Non-line-of-sight-imaging using dynamic relay surfaces[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(4): 5331-5339. doi: 10.1364/OE.383586 [44] LIU X CH, BAUER S, VELTEN A. Phasor field diffraction based reconstruction for fast non-line-of-sight imaging systems[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1645. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15157-4 [45] XIN SH M, NOUSIAS S, KUTULAKOS K N, et al.. A theory of fermat paths for non-line-of-sight shape reconstruction[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2019: 6793-6802. [46] SMITH B M, O'TOOLE M, GUPTA M. Tracking multiple objects outside the line of sight using speckle imaging[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 6258-6266. [47] SASAKI T, LEGER J R. Light-field reconstruction from scattered light using plenoptic data[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10772: 1077203. [48] SAUNDERS C, MURRAY-BRUCE J, GOYAL V K. Computational periscopy with an ordinary digital camera[J]. Nature, 2019, 565(7740): 472-475. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0868-6 [49] SAUNDERS C, BOSE R, MURRAY-BRUCE J, et al.. Multi-depth computational periscopy with an ordinary camera[C]. ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), IEEE, 2020: 9299-9305. [50] BARADAD M, YE V, YEDIDIA A B, et al.. Inferring light fields from shadows[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 6267-6275. [51] BOUMAN K L, YE V, YEDIDIA A B, et al.. Turning corners into cameras: Principles and methods[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2017: 2289-2297. [52] SEIDEL S W, MURRAY-BRUCE J, MA Y T, et al. Two-dimensional non-line-of-sight scene estimation from a single edge occluder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020, 7: 58-72. [53] SEIDEL S W, MA Y T, MURRAY-BRUCE J, et al.. Corner occluder computational periscopy: estimating a hidden scene from a single photograph[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), IEEE, 2019: 1-9. [54] YEDIDIA A B, BARADAD M, THRAMPOULIDIS C, et al.. Using unknown occluders to recover hidden scenes[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2019: 12223-12231. [55] MAEDA T, WANG Y Q, RASKAR R, et al.. Thermal non-line-of-sight imaging[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), IEEE, 2019: 1-11. [56] TANAKA K, MUKAIGAWA Y, KADAMBI A. Polarized non-line-of-sight imaging[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2020: 2133-2142. [57] KATZ O, HEIDMANN P, FINK M, et al. Non-invasive single-shot imaging through scattering layers and around corners via speckle correlations[J]. Nature Photonics, 2014, 8(10): 784-790. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.189 [58] DIVITT S, GARDNER D F, WATNIK A T. Imaging around corners in the mid-infrared using speckle correlations[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(8): 11051-11064. doi: 10.1364/OE.388260 [59] BOGER-LOMBARD J, KATZ O. Passive optical time-of-flight for non line-of-sight localization[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 3343. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11279-6 [60] BATARSEH M, SUKHOV S, SHEN Z, et al. Passive sensing around the corner using spatial coherence[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 3629. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05985-w [61] BECKUS A, TAMASAN A, ATIA G K. Multi-modal non-line-of-sight passive imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(7): 3372-3382. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2896517 [62] CHOPITE J G, HULLIN M B, WAND M, et al.. Deep non-line-of-sight reconstruction[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2020: 957-966. [63] SATAT G, TANCIK M, GUPTA O, et al. Object classification through scattering media with deep learning on time resolved measurement[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(15): 17466-17479. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.017466 [64] FENG X H, GAO L. Ultrafast light field tomography for snapshot transient and non-line-of-sight imaging[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 2179. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22461-0 [65] CHEN W ZH, DANEAU S, BROSSEAU C, et al.. Steady-state non-line-of-sight imaging[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2019: 6783-6792. [66] CHANDRAN S, JAYASURIYA S. Adaptive lighting for data-driven non-line-of-sight 3d localization and object identification[C]. Proceedings of the 30th British Machine Vision Conference 2019, BMVC, 2019. [67] CAO Y P, LIANG R, YANG J X, et al. Computational framework for steady-state NLOS localization under changing ambient illumination conditions[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(2): 2438-2452. doi: 10.1364/OE.444080 [68] CARAMAZZA P, BOCCOLINI A, BUSCHEK D, et al. Neural network identification of people hidden from view with a single-pixel, single-photon detector[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 11945. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30390-0 [69] MUSARRA G, CARAMAZZA P, TURPIN A, et al. Detection, identification, and tracking of objects hidden from view with neural networks[J]. Proceedings of the SPIE, 2019, 10978: 1097803. [70] SU SH CH, HEIDE F, WETZSTEIN G, et al.. Deep end-to-end time-of-flight imaging[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 6383-6392. [71] CHEN Y, QU B, LU X Q. Robust speckle-autocorrelation non-line-of-sight imaging with generative adversarial networks[J]. Proceedings of the SPIE, 2022, 12083: 120830B. [72] METZLER C A, HEIDE F, RANGARAJAN P, et al. Deep-inverse correlography: towards real-time high-resolution non-line-of-sight imaging[J]. Optica, 2020, 7(1): 63-71. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.374026 [73] LEI X, HE L Y, TAN Y X, et al.. Direct object recognition without line-of-sight using optical coherence[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2019: 11729-11738. [74] AITTALA M, SHARMA P, MURMANN L, et al. Computational mirrors: blind inverse light transport by deep matrix factorization[J]. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems,Curran Associates Inc., 2019: 1283. [75] SHEN S Y, WANG Z, LIU P, et al. Non-line-of-sight imaging via neural transient fields[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(7): 2257-2268. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3076062 [76] CHEN W ZH, WEI F Y, KUTULAKOS K N, et al. Learned feature embeddings for non-line-of-sight imaging and recognition[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2020, 39(6): 230. [77] MU F ZH, MO S CH, PENG J Y, et al.. Physics to the rescue: deep non-line-of-sight reconstruction for high-speed imaging[J/OL]. IEEE Transaction on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022: 1-12. [78] GRAU J, PLACK M, HAEHN P, et al.. Occlusion fields: an implicit representation for non-line-of-sight surface reconstruction[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2203.08657, 2022. [79] TANCIK M, SATAT G, RASKAR R. Flash photography for data-driven hidden scene recovery[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1810.11710, 2018. [80] GENG R X, HU Y, LU ZH, et al. Passive non-line-of-sight imaging using optimal transport[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 31: 110-124. [81] HE J H, WU SH K, WEI R, et al. Non-line-of-sight imaging and tracking of moving objects based on deep learning[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(10): 16758-16772. doi: 10.1364/OE.455803 [82] ISOGAWA M, YUAN Y, O'TOOLE M, et al.. Optical non-line-of-sight physics-based 3D human pose estimation[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2020: 7011-7020. [83] HE Y, ZHANG D H, HU Y, et al. . Non-line-of-sight imaging with radio signals[C]. 2020 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), IEEE, 2020: 11-16. [84] GALINDO M, MARCO J, O'TOOLE M, et al.. A dataset for benchmarking time-resolved non-line-of-sight imaging[C]. ACM SIGGRAPH 2019 Posters, Association for Computing Machinery, 2019: 73. [85] FIENUP J R. Phase retrieval algorithms: a comparison[J]. Applied Optics, 1982, 21(15): 2758-2769. doi: 10.1364/AO.21.002758 [86] NETRAPALLI P, JAIN P, SANGHAVI S. Phase retrieval using alternating minimization[J]. Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems,Curran Associates Inc., 2013: 2796-2804. [87] KUPYN O, BUDZAN V, MYKHAILYCH M, et al.. DeblurGAN: blind motion deblurring using conditional adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 8183-8192. [88] OU Z, WU J M, YANG Y H, et al. Computational adaptive optics for high-resolution non-line-of-sight imaging[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(3): 4583-4591. doi: 10.1364/OE.447174 [89] GROSSMAN E N, SASAKI T, LEGER J R. Passive terahertz non-line-of-sight imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2022, 12(5): 489-498. doi: 10.1109/TTHZ.2022.3173168 [90] 曹丙花, 张宇盟, 范孟豹, 等. 太赫兹超分辨率成像研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(3):405-417. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0198CAO B H, ZHANG Y M, FAN M B, et al. Research progress of terahertz super-resolution imaging[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(3): 405-417. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0198 [91] 陆冬筱, 房文汇, 李玉瑶, 等. 光学相干层析成像技术原理及研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(5):919-935. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0037LU D X, FANG W H, LI Y Y, et al. Optical coherence tomography: principles and recent developments[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(5): 919-935. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0037 -





 下载:
下载: