-
摘要:
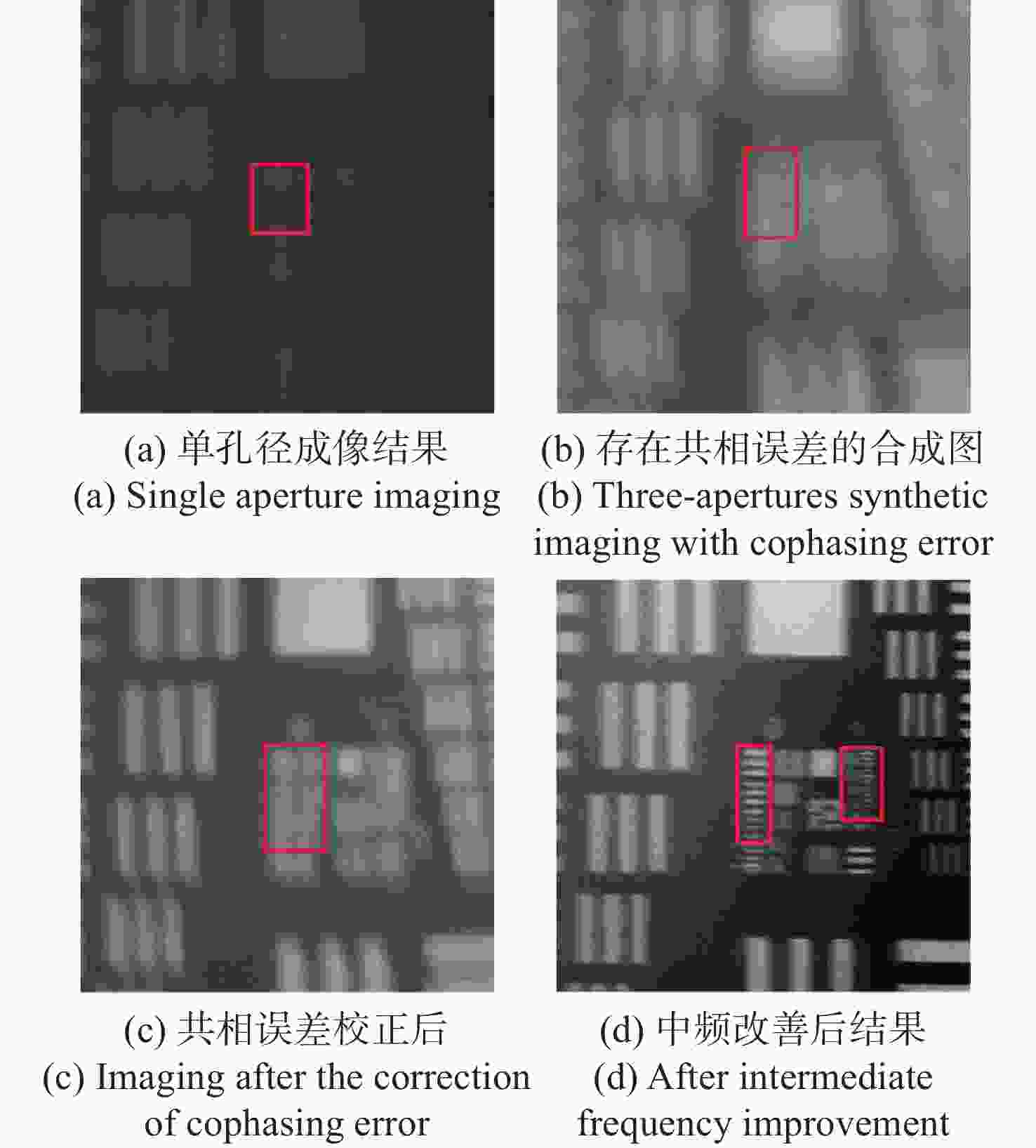
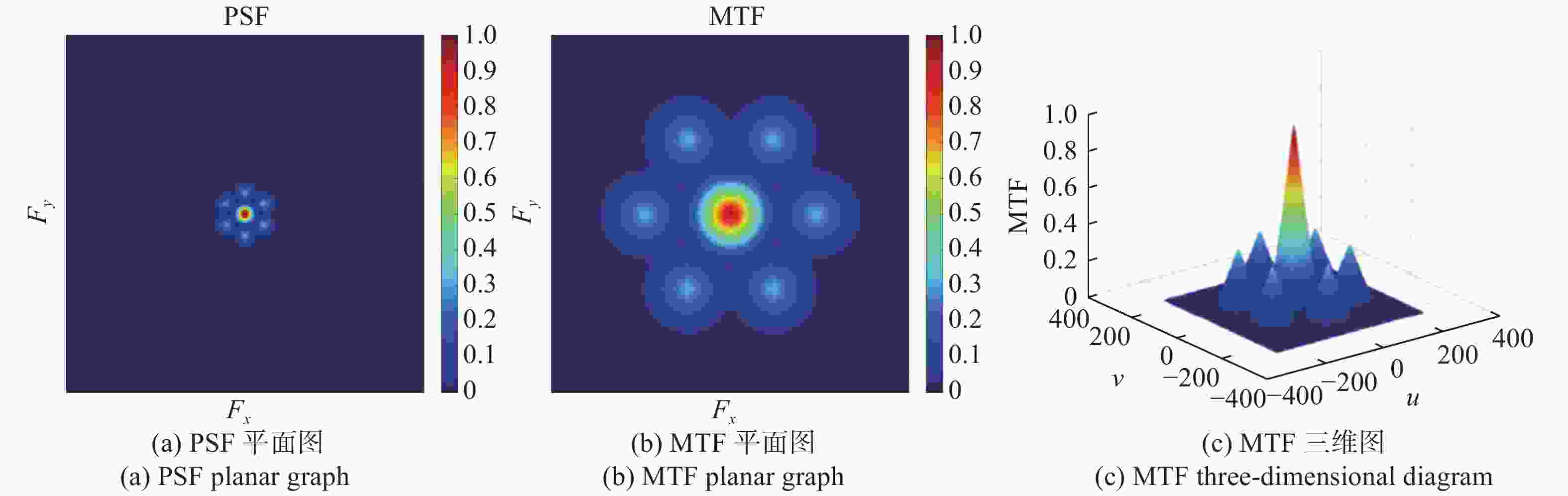
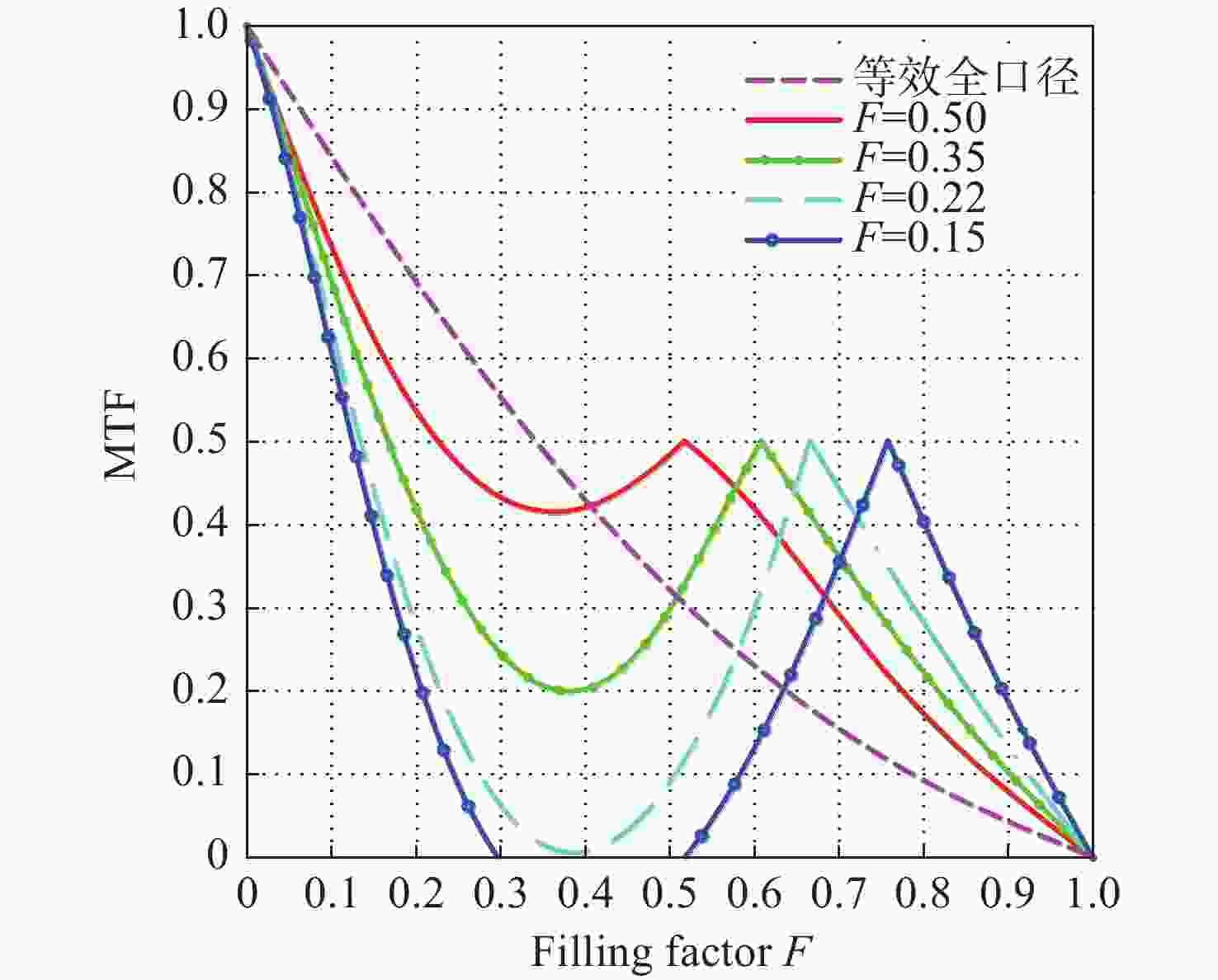
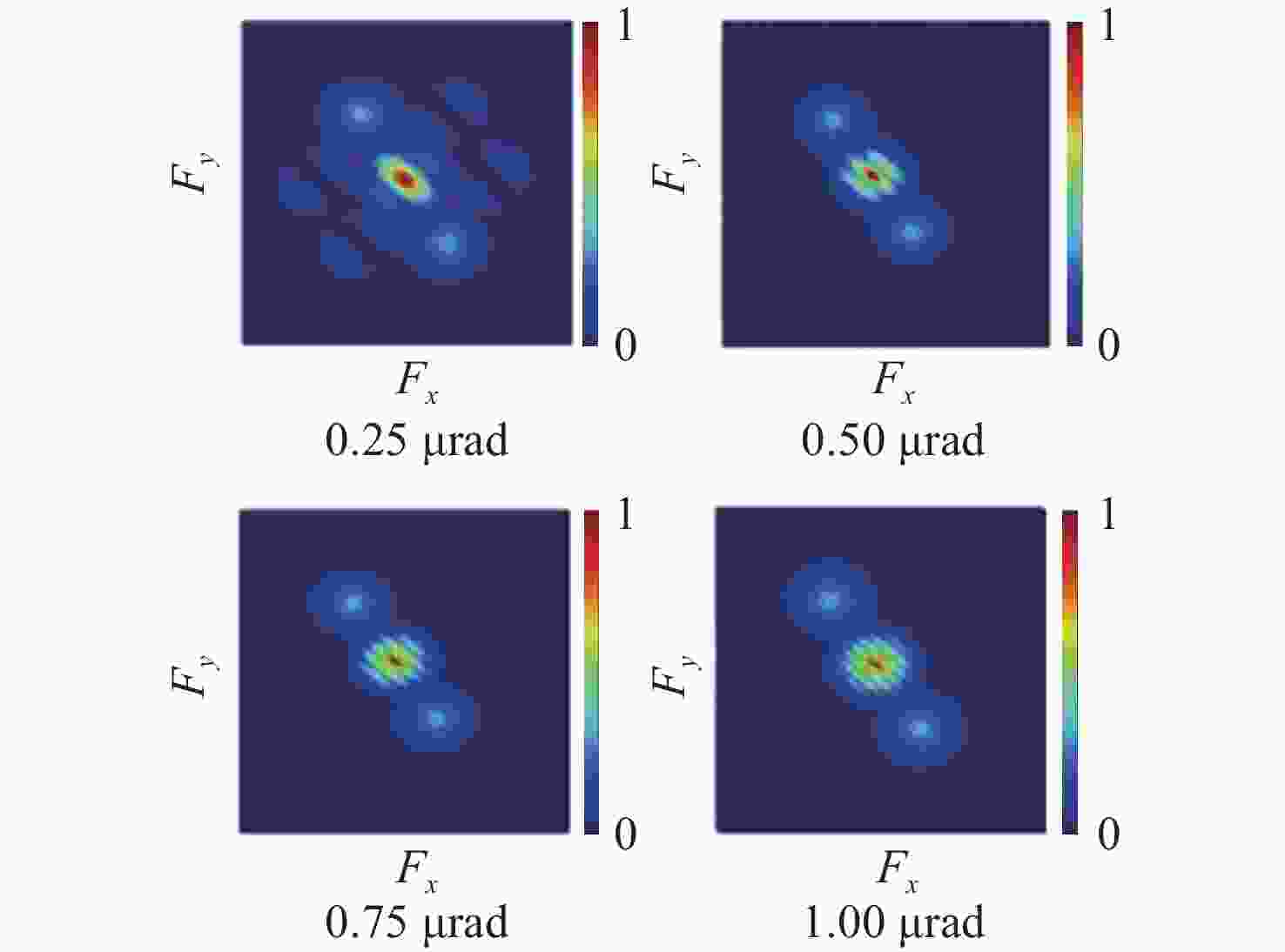
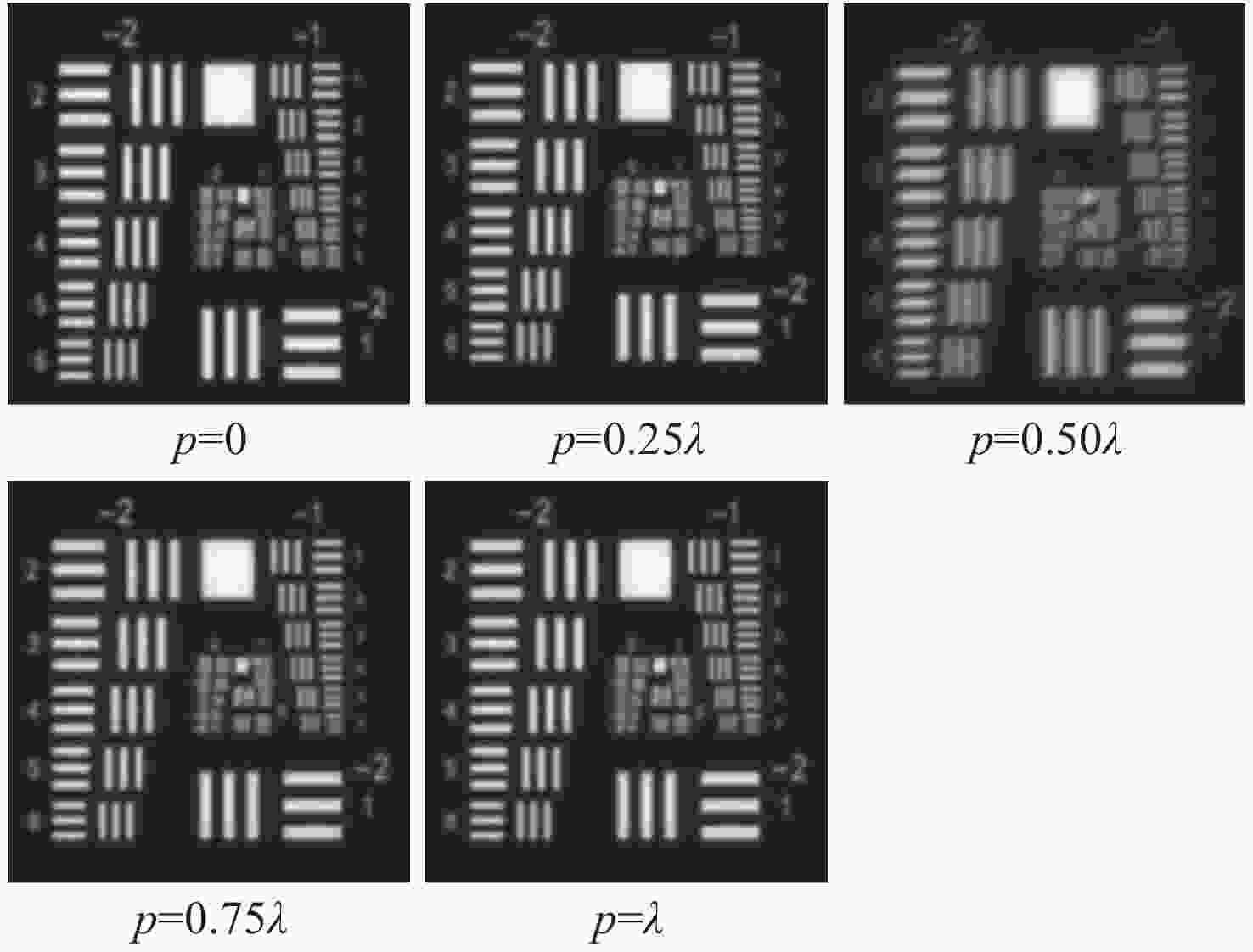
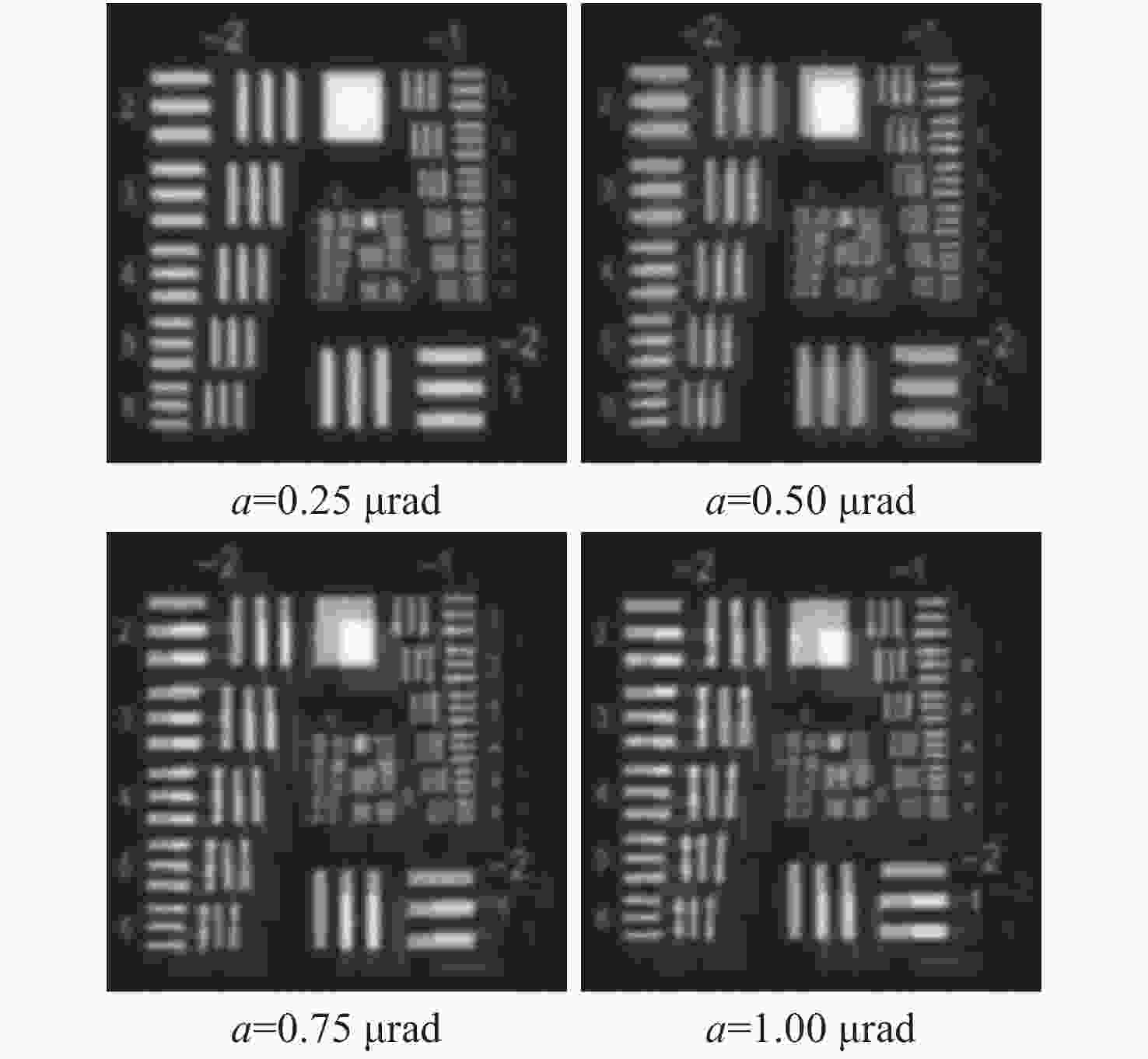
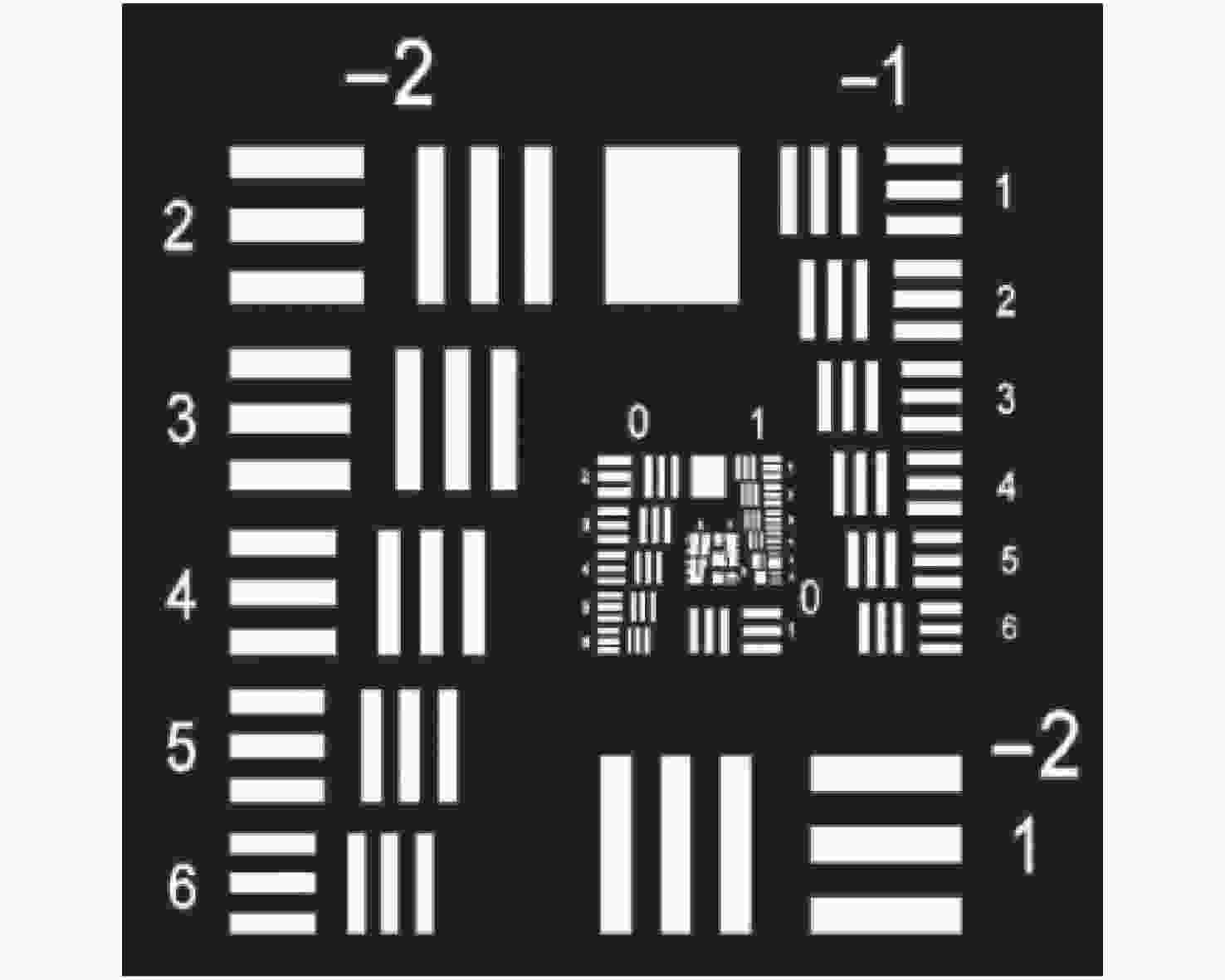
稀疏孔径成像系统在校正共相误差后可实现多个子孔径干涉成像,达到提高成像分辨率的目的。本文以Golay3稀疏孔径成像系统为研究对象,分析了子孔径间存在不同活塞误差和倾斜误差时,系统的MTF和面目标成像情况。研制了一套Golay3稀疏孔径成像系统,以USAF1951分辨率板为面目标进行了成像实验。通过调整光束折转调整模块中的平面反射镜位置,校正了子孔径的活塞误差和倾斜误差,实现了三孔径合成成像,并对理论分析结果进行了验证。实验结果表明:所研制系统的角分辨率为1.77 μrad,接近于等效单口径成像系统的理论极限分辨率1.18 μrad。所研制的Golay3稀疏孔径成像系统能有效校正共相误差,提高成像分辨率。
Abstract:Multiple sub-aperture interference imaging enables the images formed by the sparse aperture imaging system to have a higher resolution after the cophasing error is corrected. In this paper, the MTF and surface target imaging of the system are analyzed with a Golay3 sparse aperture imaging system as the research object when there are different piston and tilt errors among the sub-apertures. A Golay3 sparse aperture imaging system was developed to carry out an imaging experiment with the USAF1951 resolving power test target as the area target. Three-aperture synthetic imaging is achieved by adjusting the position of the plane mirror in the light beam deflection and the adjustment module to correct the piston and tilt errors of the sub-apertures. The results of a theoretical analysis are then verified. According to calculations, the developed system’s angular resolution of 1.38 μrad is close to the equivalent single-aperture imaging system’s theoretical resolution of 1.18 μrad. The developed Golay3 sparse aperture imaging system can correct the cophasing errors and improve the imaging resolution.
-
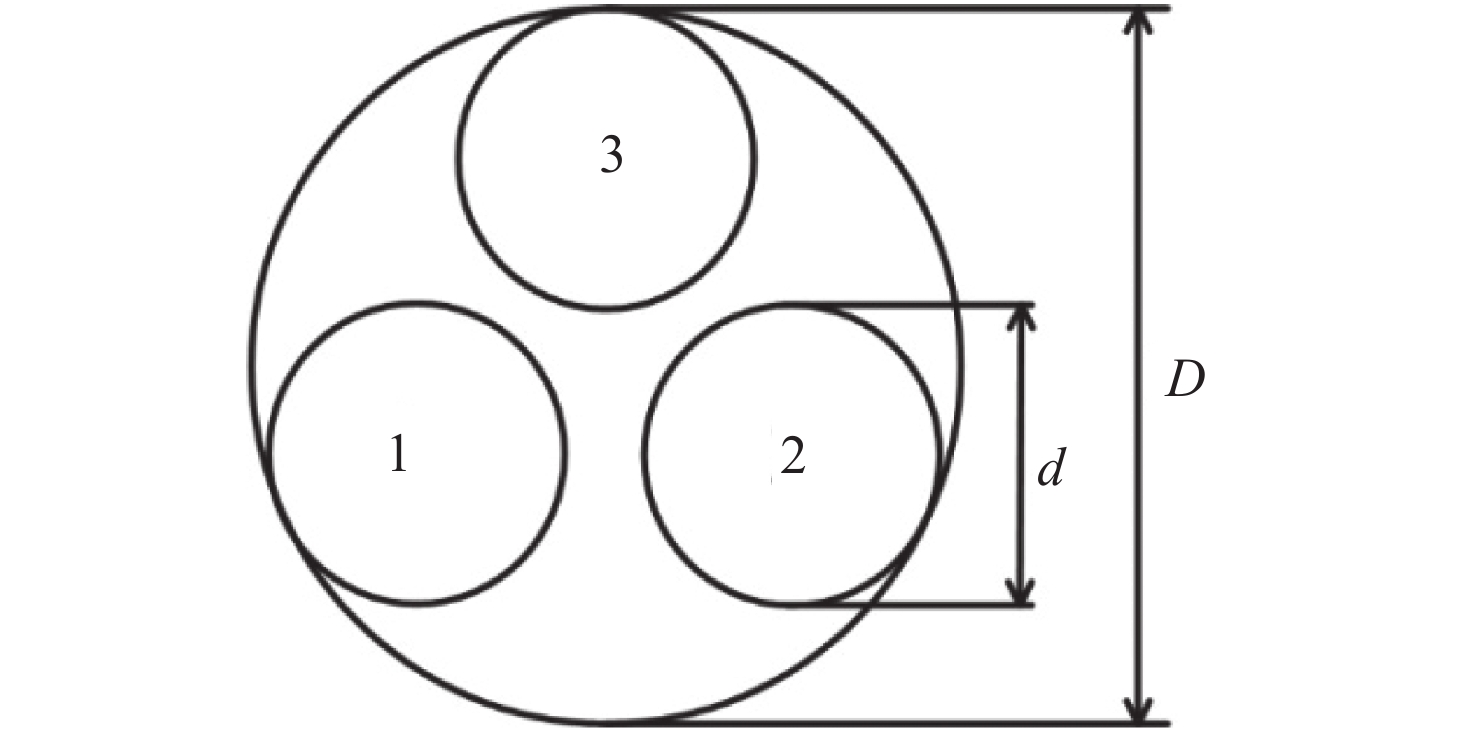
表 1 所设计Golay3稀疏孔径成像系统设计参数
Table 1. Design specifications of the Golay3 sparse aperture imaging system
序号 参数 设计值 1 子孔径口径d 200 mm 2 等效口径D 570 mm 3 系统焦距f 6000 mm 4 全视场角h 0.2° 5 工作波段 0.48~0.65 μm 表 2 理论结果和实测结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of theoretical and measured results
参数名称 单孔径 三孔径 提高倍数 极限角分辨率 3.36 μrad 1.18 μrad 2.85 实测角分辨率 4.47 μrad 1.77 μrad 2.53 -
[1] FAN J L, WU Q Y, CHEN B H, et al. Optical design of the Goaly3 multi-mirror telescope system with a wide field of view[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(3): 1200. doi: 10.3390/app11031200 [2] LIU T CH, HU J P, ZHU L L, et al. Large effective aperture metalens based on optical sparse aperture system[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2020, 18(10): 100001. doi: 10.3788/COL202018.100001 [3] MEINEL A B. Aperture synthesis using independent telescopes[J]. Applied Optics, 1970, 9(11): 2501-2504. doi: 10.1364/AO.9.002501 [4] ZHANG L T, LIU M, ZHAO Y J, et al. The optimal design of a binaural sparse-aperture system[J]. Results in Physics, 2020, 16: 102970. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2020.102970 [5] 张超. 稀疏孔径成像系统相位补偿装置结构研究[D]. 西安: 西安工业大学, 2019.ZHANG CH. Study of phase compensation device structure for optical sparse-aperture imaging system[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Technological University, 2019. (in Chinese) [6] 刘何伟, 钱俊宏, 马秀刚, 等. 稀疏孔径望远系统的装调检测与模拟分析[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 杂志,2021,42(10):31-36. doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2021.10.031LIU H W, QIAN J H, MA X G, et al. Adjustment test and simulation analysis on sparse aperture telescopic system[J]. Laser Journal, 2021, 42(10): 31-36. (in Chinese) doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2021.10.031 [7] TRAUB W A. Combining beams from separated telescopes[J]. Applied Optics, 1986, 25(4): 528-532. doi: 10.1364/AO.25.000528 [8] MILLER N J, DIERKING M P, DUNCAN B D. Optical sparse aperture imaging[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(23): 5933-5943. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.005933 [9] HE X J, MA H T, LUO CH X. Simulation of co-phase error correction of optical multi-aperture imaging system based on stochastic parallel gradient decent algorithm[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9682: 96820V. [10] 何小君. 基于随机并行优化算法的光学多孔径成像共相误差校正技术研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院光电技术研究所), 2017.HE X J. Study on Co-phase error correction of optical multi-aperture imaging system based on stochastic parallel gradient decent algorithm[D]. Chengdu: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2017. (in Chinese) [11] XIE Z H, MA H T, Qi B, et al. Experimental demonstration of enhanced resolution of a Golay3 sparse-aperture telescope[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15(4): 041101. doi: 10.3788/COL201715.041101 [12] 谢宗良. 相控望远镜阵列成像关键技术研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 2018.XIE Z L. Study on key technology of phased telescope array imaging[D]. Chengdu: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018. (in Chinese) [13] JIANG A M, WANG S, DONG ZH CH, et al. Wide-band white light sparse-aperture Fizeau imaging interferometer testbed for a distributed small-satellites constellation[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(11): 2736-2746. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.002736 [14] JIANG A M, DONG ZH CH, XUE J W, et al. Detection and closed-loop control of piston errors for a Fizeau imaging interferometer[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(13): 3892-3900. doi: 10.1364/AO.387895 [15] GOLAY M J E. Point arrays having compact, nonredundant autocorrelations[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1971, 61(2): 272-273. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.61.000272 [16] QIAN J H, LIU H W, LIU T, et al. Piston error evaluation and correction for multi-aperture imaging system[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2020, 1775(1): 012006. [17] MA X F, XIE Z L, MA H T, et al. Piston sensing of sparse aperture systems with a single broadband image via deep learning[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(11): 16058-16070. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.016058 [18] WU Q Y, FAN J L, WU F, et al. Error analysis of the Golay3 optical imaging system[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(13): 2966-2973. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.002966 [19] CHEN B, WU Q Y, FAN J L. A Golay3 sparse aperture optical system of primary mirror with free-form surface[J]. Optical Review, 2021, 28(1): 113-118. doi: 10.1007/s10043-021-00641-z -





 下载:
下载: