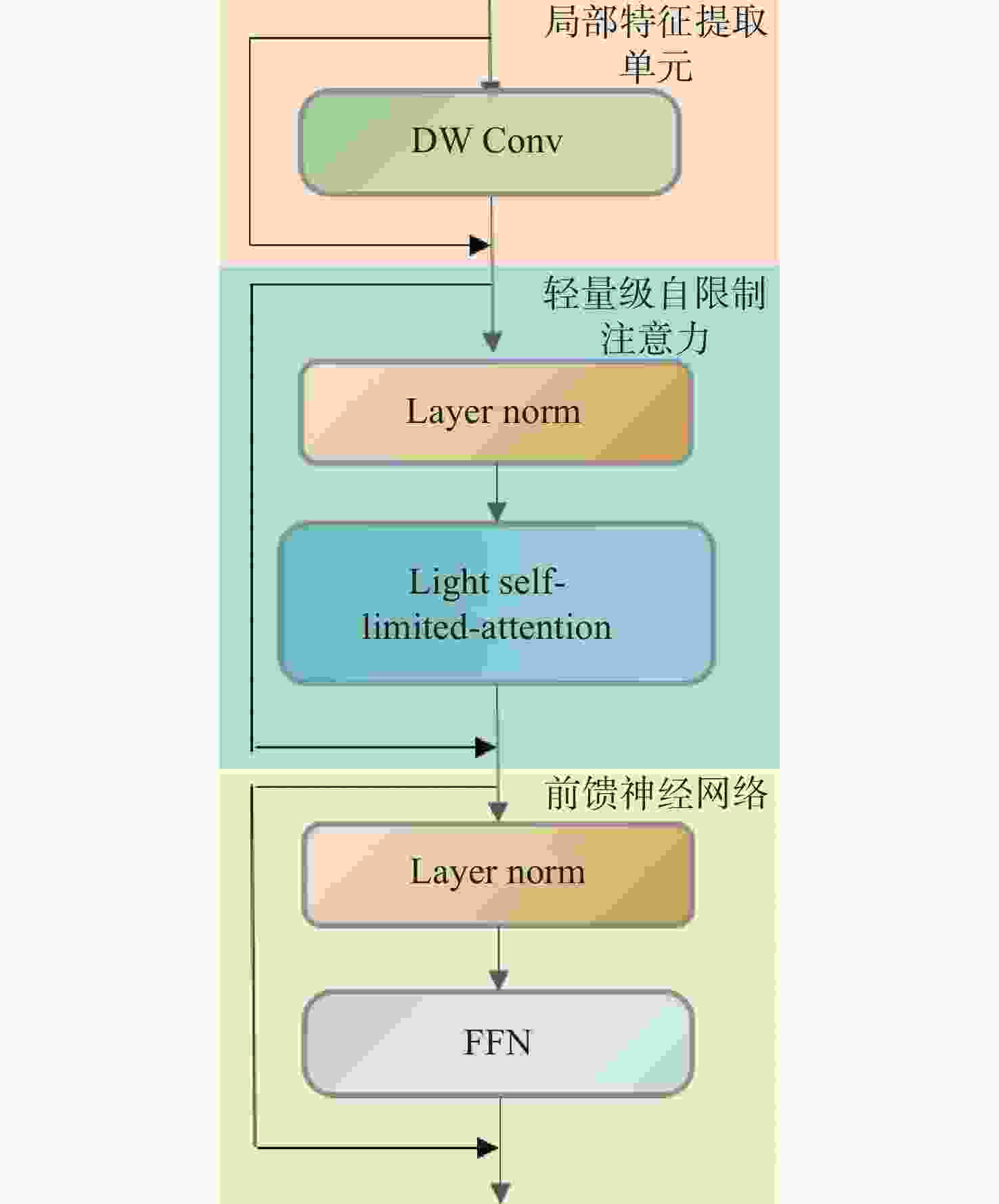
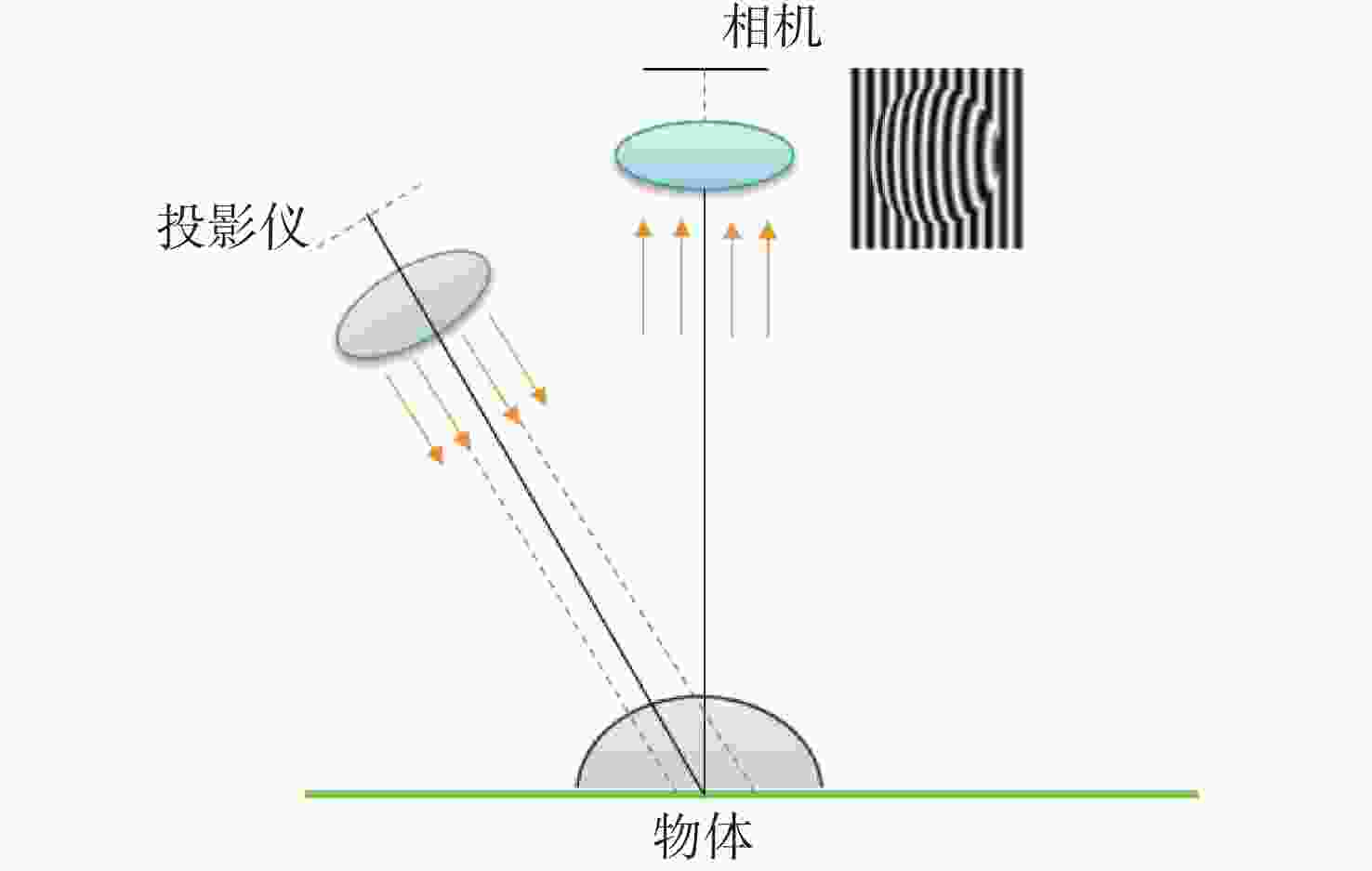
A hybrid network based on light self-limited attention for structured light phase and depth estimation
-
摘要:
相位提取与深度估计是结构光三维测量中的重点环节,目前传统方法在结构光相位提取与深度估计方面存在效率不高、结果不够鲁棒等问题。为了提高深度学习结构光的重建效果,本文提出了一种基于轻型自限制注意力(Light Self-Limited-Attention,LSLA)的结构光相位及深度估计混合网络,即构建一种CNN-Transformer的混合模块,并将构建的混合模块放入U型架构中,实现CNN与Transformer的优势互补。将所提出的网络在结构光相位估计和结构光深度估计两个任务上进行实验,并和其他网络进行对比。实验结果表明:相比其他网络,本文所提出的网络在相位估计和深度估计的细节处理上更加精细,在结构光相位估计实验中,精度最高提升31%;在结构光深度估计实验中,精度最高提升26%。该方法提高了深度神经网络在结构光相位估计及深度估计的准确性。
Abstract:Phase retrieval and depth estimation are vital to three-dimensional measurement using structured light. Currently, conventional methods for structured light phase retrieval and depth estimation have limited efficiency and are lack of robustness in their results and so on. To improve the reconstruction effect of structured light by deep learning, we propose a hybrid network for structured light phase and depth estimation based on Light Self-Limited Attention (LSLA). Specifically, a CNN-Transformer hybrid module is constructed and integrated into a U-shaped structure to realize the advantages complementary of CNN and Transformer. The proposed network is experimentally compared with other networks in structured light phase estimation and structured light depth estimation. The experimental results indicate that the proposed network achieves finer detail processing in phase and depth estimation compared to other networks. Specifically, for structured light phase and depth estimation, its accuracy improves by 31% and 26%, respectively. Therefore, the proposed network improves the accuracy of deep neural networks in the structured light phase and depth estimation areas.
-
Key words:
- structured light /
- deep learning /
- self-limited attention /
- phase estimation /
- depth estimation
-
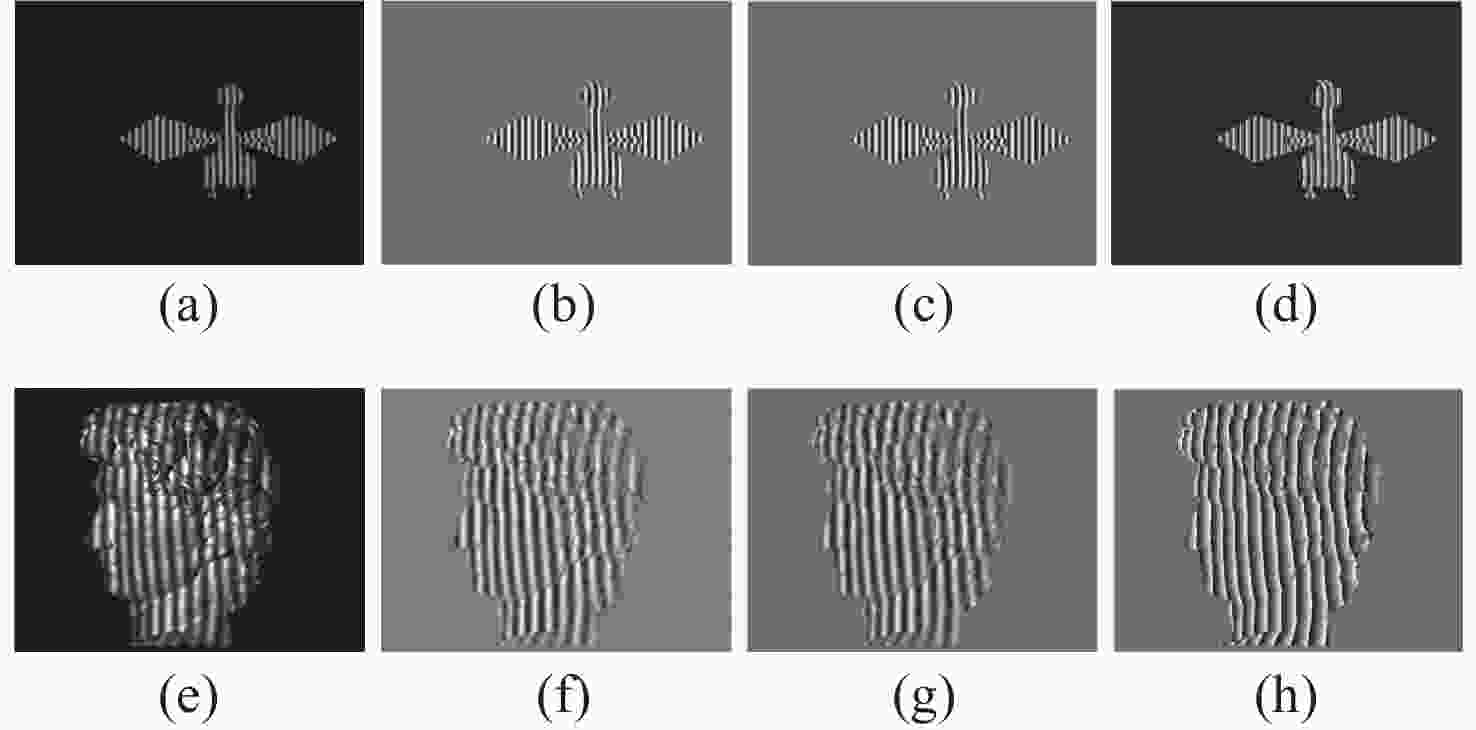
图 4 部分数据示例图。第一行为仿真数据,第二行为真实数据。(a)仿真条纹图;(b)仿真条纹图D;(c)仿真条纹图M;(d)仿真条纹图包裹相位;(e)真实条纹图;(f)真实条纹图D;(g)真实条纹图M;(h)真实条纹图包裹相位
Figure 4. Sample maps in some datasets. The first lines are simulation data, the second lines are real data. (a) Simulation fringe map; (b) simulation fringe map D; (c) simulation fringe map M; (d) simulation fringe wrapped phase; (e) real fringe map; (f) real fringe map D; (g) real fringe map M; (h) real fringe wrapped phase
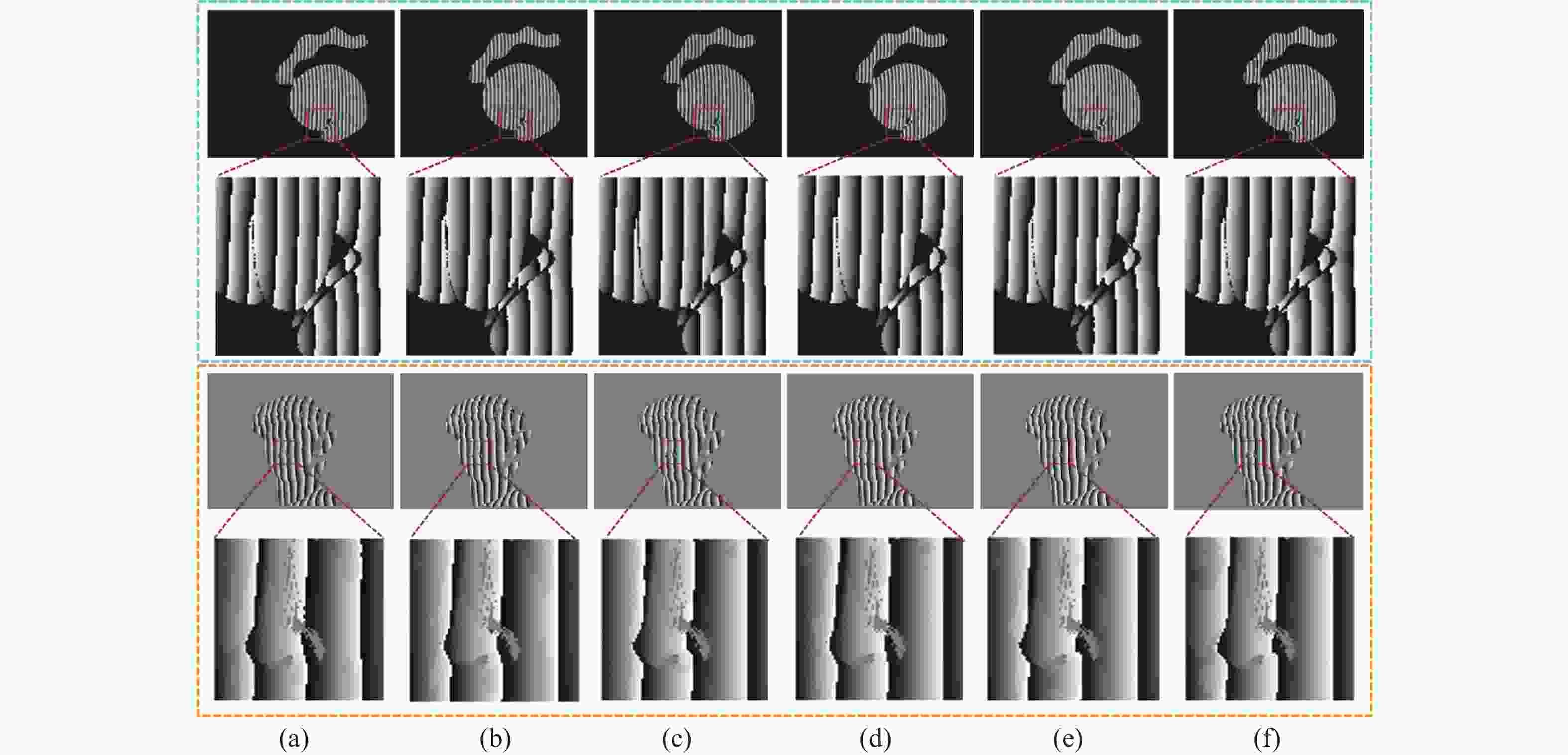
图 5 不同网络仿真和真实数据包裹相位对比。蓝色框为仿真数据,橙色框为真实数据。(a)UNet;(b)DPH;(c)R2UNet;(d)SUNet;(e)Ours;(f)标签
Figure 5. Comparison of different network simulation and real data wrapped phases. The blue boxes are the simulation data, and the orange boxes are the real data. (a) UNet; (b) DPH; (c) R2UNet; (d) SUNet; (e) Ours; (f) Label
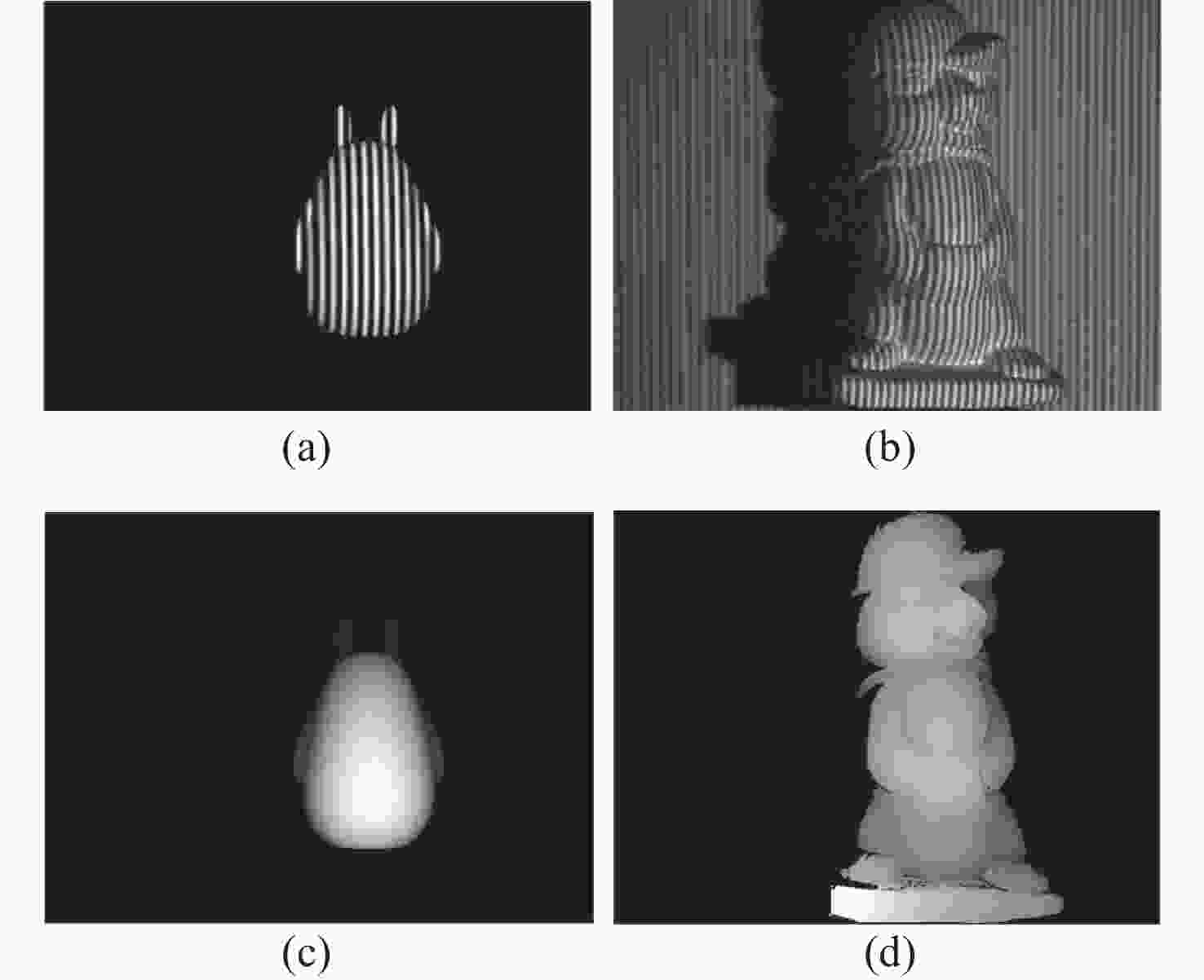
图 9 不同方法深度估计视觉结果比较。蓝色框为仿真数据,橙色框为真实数据。(a) 输入数据; (b) UNet;(c) DPH;(d) R2UNet;(e) Ours;(f)标签
Figure 9. Comparison of the visual results of depth estimation by different methods. The blue boxes are the simulation data, and the orange boxes are the real data. (a) Input data; (b) UNet; (c) DPH; (d) R2UNet; (e) Ours; (f) Label
表 1 不同包裹相位计算方法比较
Table 1. Comparison of the different wrapped phase calculation methods
MSE 时间t/s 直接预测包裹相位 0.2833 5.89 分别预测DM 0.1739 11.7 同时预测 DM 0.16806 7.54 表 2 包裹相位预测方法比较
Table 2. Comparison of the wrapped phase prediction methods
仿真数据 真实数据 MSE 时间t/s MSE 时间t/s UNet 0.02658 6.67 0.16806 7.54 DPH 0.02710 11.65 0.12974 11.78 R2UNet 0.02734 13.69 0.12905 14.30 SUNet 0.02717 7.95 0.14350 8.29 Ours 0.02395 11.06 0.11622 11.67 表 3 消融实验结果比较
Table 3. Comparison of ablation experiment results
MSE 时间t/s CMT 11.32 6.89 CMT替换LSLA 9.17 6.45 CMT替换FFN 11.34 5.54 CMT+U形结构 8.94 9.68 表 4 不同方法深度估计结果比较
Table 4. Comparison of the depth estimation results by different methods
仿真数据 真实数据 MSE 时间t/s MSE 时间t/s Unet 8.78 5.98 9.97 6.44 DPH 8.03 8.66 9.86 10.59 R2UNet 7.57 8.73 8.72 10.92 Ours 6.43 8.09 7.64 8.44 -
[1] 左超, 张晓磊, 胡岩, 等. 3D真的来了吗?—三维结构光传感器漫谈[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2020,49(3):0303001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA202049.0303001ZUO CH, ZHANG X L, HU Y, et al. Has 3D finally come of age?——An introduction to 3D structured-light sensor[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(3): 0303001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA202049.0303001 [2] 王永红, 张倩, 胡寅, 等. 显微条纹投影小视场三维表面成像技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(3):447-457. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0199WANG Y H, ZHANG Q, HU Y, et al. 3D small-field surface imaging based on microscopic fringe projection profilometry: a review[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(3): 447-457. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0199 [3] 冯世杰, 左超, 尹维, 等. 深度学习技术在条纹投影三维成像中的应用[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2020,49(3):0303018. doi: 10.3788/IRLA202049.0303018FENG SH J, ZUO CH, YIN W, et al. Application of deep learning technology to fringe projection 3D imaging[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(3): 0303018. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA202049.0303018 [4] SU X Y, CHEN W J. Fourier transform profilometry: a review[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2001, 35(5): 263-284. doi: 10.1016/S0143-8166(01)00023-9 [5] ZHENG D L, DA F P, KEMAO Q, et al. Phase-shifting profilometry combined with Gray-code patterns projection: unwrapping error removal by an adaptive median filter[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(5): 4700-4713. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.004700 [6] AN Y T, HYUN J S, ZHANG S. Pixel-wise absolute phase unwrapping using geometric constraints of structured light system[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(16): 18445-18459. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.018445 [7] GHIGLIA D C, ROMERO L A. Robust two-dimensional weighted and unweighted phase unwrapping that uses fast transforms and iterative methods[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1994, 11(1): 107-117. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.11.000107 [8] FENG SH J, CHEN Q, GU G H, et al. Fringe pattern analysis using deep learning[J]. Advanced Photonics, 2019, 1(2): 025001. [9] NGUYEN H, WANG Y Z, WANG ZH Y. Single-shot 3D shape reconstruction using structured light and deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(13): 3718. doi: 10.3390/s20133718 [10] VAN D J S, DIRCKX J J J. Deep neural networks for single shot structured light profilometry[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(12): 17091-17101. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.017091 [11] 张钊, 韩博文, 于浩天, 等. 多阶段深度学习单帧条纹投影三维测量方法[J]. 红外与金宝搏188软件怎么用 工程,2020,49(6):20200023. doi: 10.3788/irla.12_2020-0023ZHANG ZH, HAN B W, YU H T, et al. Multi-stage deep learning based single-frame fringe projection 3D measurement method[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(6): 20200023. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/irla.12_2020-0023 [12] RANFTL R, BOCHKOVSKIY A, KOLTUN V. Vision transformers for dense prediction[C]. Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2021. [13] YANG G L, TANG H, DING M L, et al. Transformer-based attention networks for continuous pixel-wise prediction[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2021. [14] QI F, ZHAI J Z, DANG G H. Building height estimation using Google Earth[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2016, 118: 123-132. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.02.044 [15] ZHU X J, HAN ZH Q, YUAN M K, et al. Hformer: hybrid CNN-transformer for fringe order prediction in phase unwrapping of fringe projection[J]. Optical Engineering, 2022, 61(9): 093107. [16] GENG J. Structured-light 3D surface imaging: a tutorial[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2011, 3(2): 128-160. doi: 10.1364/AOP.3.000128 [17] GUO J Y, HAN K, WU H, et al. CMT: convolutional neural networks meet vision transformers[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2022. [18] CHEN ZH ZH, HANG W, ZHAO Y X. ViT-LSLA: Vision Transformer with Light Self-Limited-Attention[J]. arXiv:2210.17115. [19] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Springer, 2015. [20] WANG L, LU D Q, QIU R W, et al. 3D reconstruction from structured-light profilometry with dual-path hybrid network[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2022, 2022(1): 14. doi: 10.1186/s13634-022-00848-5 [21] 袁梦凯, 朱新军, 侯林鹏. 基于R2U-Net的单帧投影条纹图深度估计[J]. 金宝搏188软件怎么用 与光电子学进展,2022,59(16):1610001.YUAN M K, ZHU X J, HOU L P. Depth estimation from single-frame fringe projection patterns based on R2U-Net[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(16): 1610001. (in Chinese) [22] FAN CH M, LIU T J, LIU K H. SUNet: swin transformer UNet for image denoising[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, IEEE, 2022. [23] ZHU X J, ZHANG ZH ZH, HOU L P, et al. Light field structured light projection data generation with Blender[C]. Proceedings of 2022 3rd International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning & International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications, IEEE, 2022. -





 下载:
下载: